Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer—the stable evidence
Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer—the stable evidence
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a frequent molecular phenomenon of colorectal cancer and is associated with deficient DNA mismatch repair. This Review presents an overview of MSI, including its clinical features and applications. The authors discuss the prognostic and predictive value of MSI and how it can be used to improve our knowledge of other cancer subtypes.
- Eduardo Vilar
- & Stephen B. Gruber
-
Review Article |
 Management of breast cancer with targeted agents: importance of heterogenicity
Management of breast cancer with targeted agents: importance of heterogenicity
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with different molecular drivers regulating its growth, survival and treatment response. Drug development efforts have resulted in agents against new molecular targets that are active against only those tumors with the targeted molecular alteration or phenotype. The authors critically discuss the recently established and investigational strategies for the treatment of the main breast cancer subtypes.
- Serena Di Cosimo
- & José Baselga
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Carcinoembryonic antigen mRNA expression—a marker for early pancreatic cancer recurrence?
Carcinoembryonic antigen mRNA expression—a marker for early pancreatic cancer recurrence?
- Rowan Higgs
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Continued lack of progress in SCLC
Chemotherapy options for patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) are limited. A recent phase III trial assessed the combination of carboplatin and pemetrexed but this regimen produced inferior survival results compared with the standard carboplatin and etoposide regimen. The combination of carboplatin and etoposide remains the standard first-line chemotherapy option for the treatment of patients with extensive-stage SCLC.
- Janakiraman Subramanian
- & Ramaswamy Govindan
-
News & Views |
Optimal first-line therapy for NSCLC with EGFR mutations
Activating mutations in EGFR are characteristic of patients with lung cancer who have high sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as gefitinib and erlotinib. The randomized IPASS study by Mok and colleagues confirmed that patients with EGFR mutations have a higher response rate, longer progression-free survival and improved quality of life when treated with first-line gefinitib instead of chemotherapy.
- Joel W. Neal
- & Lecia V. Sequist
-
News & Views |
Dose-dense treatment for triple-negative breast cancer
Dose-dense chemotherapy has been proposed to improve breast cancer outcome due to its ability to prevent cancer cell repopulation; however, little is known about which patients benefit most from such scheduling. A pooled analysis of studies assessing dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy has shown that most of the therapeutic benefit derived from dose-dense scheduling arises in patients with node-positive, triple-negative disease.
- Eitan Amir
- , Alberto Ocana
- & Bostjan Seruga
-
News & Views |
Tailored treatment for ovarian cancer: are we there yet?
First-line platinum and taxane chemotherapy improves the prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), however, about 80% of patients relapse and long-term survival is poor. The development of drug resistance is the main cause of treatment failure; therefore, the identification of new compounds that interfere with tumor growth and survival is a priority.
- Cristiana Sessa
- & Gianluca Del Conte
-
News & Views |
Cisplatin combinations in cervical cancer—which is best?
We reviewed the results of the Gynecological Oncology Group 204 (GOG-204) randomized phase III trial, which investigated four cisplatin combination chemotherapy regimens for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical carcinoma. As the overall survival was similar between all arms, treatment recommendations need to be tailored based on toxic effects.
- David O. Holtz
- & Charles J. Dunton
-
News & Views |
Treatment and management of malignant gliomas
The considerable progress made in the field of clinical neuro-oncology and the understanding of brain tumor biology is generating cautious optimism. Treatment options for patients with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most common form of malignant gliomas, now include anti-angiogenic therapy after failure of standard multi-modality treatments. Furthermore, scientific advancements are providing new insights into disease pathogenesis and point to novel therapeutic approaches for a disease that traditionally lacked treatment options.
- Deric M. Park
- , Sith Sathornsumetee
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
-
News & Views |
Why biopsying metastatic breast cancer should be routine
Currently, acquisition of tissue from presumed metastatic deposits in breast cancer is not routine. Instead therapeutic decisions in this setting are based on the features of the tumor at initial diagnosis. As biopsies are diagnostic and changes can occur between the primary and the secondary tumors, the routine biopsy of suspected metastatic deposits needs to be considered. Such biopsies will also be key to translational research, which will underpin future therapeutic advances.
- Anand Sharma
- , Tim Crook
- & Carlo Palmieri
-
Case Study |
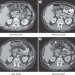 T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder potentially induced by imatinib in a patient with GIST
T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder potentially induced by imatinib in a patient with GIST
A 71-year-old male patient was diagnosed with aKIT-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). The patient received adjuvant imatinib but developed several subcutaneous and intra-abdominal tumor lesions after 4 months of treatment. A T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder was suspected. The authors discuss the potential of imatinib to induce reversible clonal T-cell proliferations in patients with GIST who develop new tumor manifestations that are suspicious for relapse.
- Mareike Verbeek
- , Falko Fend
- & Justus Duyster
-
Review Article |
Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is the most lethal of the solid tumors and most patients present with locally advanced or metastatic disease that precludes curative resection. Considerable efforts have been made during the past decade to identify better systemic treatments. The authors of this Review discuss the current standards of care for patients with locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic carcinoma, and outline future directions for the development of new treatment strategies.
- Anastasios Stathis
- & Malcolm J. Moore
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Sunitinib versus interferon-α in metastatic RCC
Motzer and colleagues present updated results from a multicenter, phase III trial of sunitinib versus interferon-α as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. The observed improvement in overall survival for patients treated with sunitinib further establishes this agent as the reference standard for first-line treatment of good-risk and intermediate-risk patients with metastatic renal cancer.
- Jason E. Faris
- & M. Dror Michaelson
-
News & Views |
Future directions in multimodality therapy for NSCLC
Patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) comprise a heterogeneous population; the role of surgical resection in this setting has been controversial. Albain and colleagues recently demonstrated that trimodality therapy with lobectomy had clinical benefit for patients with pathologic nodal N2 stage III NSCLC. We discuss the trial and its implications for future lung cancer therapy.
- Anne S. Tsao
- , Jack A. Roth
- & Roy S. Herbst
-
News & Views |
ATG and Newton's third law of motion
Patients with hematological malignancies have a risk of developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) following allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. The addition of ATG to prophylaxis regimens decreases the incidence of GVHD without compromising overall survival in these patients.
- Claudio G. Brunstein
-
Opinion |
Explanations for worsening cancer survival
When cancer survival statistics worsen over time a common assumption is that care must have deteriorated. A variety of reasons cause cancer survival to drop, including improved diagnosis of premalignant lesions, deleterious changes in the distribution of prognostic factors, and changes in the distribution of sociodemographic characteristics. In this article, the pitfalls of comparing published population-based survival data from different time periods or populations are discussed.
- Esther de Vries
- , Henrike E. Karim-Kos
- & Jan Willem W. Coebergh
-
Case Study |
 Interaction between capecitabine and brivudin in a patient with breast cancer
Interaction between capecitabine and brivudin in a patient with breast cancer
This Case Study describes a patient with breast cancer who was treated with capecitabine and experienced a severe adverse event when treated with brivudin for a herpes infection. The authors discuss drug–drug interactions and management of the associated toxic effects.
- José M. Baena-Cañada
- , María J. Martínez
- & Pedro Muriel-Cueto
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bone cancer
- Breast cancer
- Cancer epidemiology
- Cancer genetics
- Cancer genomics
- Cancer imaging
- Cancer metabolism
- Cancer microenvironment
- Cancer models
- Cancer of unknown primary
- Cancer prevention
- Cancer screening
- Cancer stem cells
- Cancer therapy
- CNS cancer
- Cysts
- Embryonal neoplasms
- Endocrine cancer
- Eye cancer
- Gastrointestinal cancer
- Germ cell tumours
- Gynaecological cancer
- Haematological cancer
- Hamartoma
- Head and neck cancer
- Lung cancer
- Mesothelioma
- Metastasis
- Oncogenes
- Oral cancer
- Paediatric cancer
- Sarcoma
- Skin cancer
- Testicular cancer
- Tumour angiogenesis
- Tumour biomarkers
- Tumour heterogeneity
- Tumour immunology
- Tumour-suppressor proteins
- Tumour virus infections
- Urological cancer

 Four-gene signature predicts survival in NSCLC
Four-gene signature predicts survival in NSCLC Promising new agent for B-cell lymphoma
Promising new agent for B-cell lymphoma Nilotinib as first-line therapy for Ph+ CML
Nilotinib as first-line therapy for Ph+ CML Farletuzumab—promising new agent in ovarian cancer
Farletuzumab—promising new agent in ovarian cancer EGFRvIII vaccine is safe in GBM
EGFRvIII vaccine is safe in GBM Early disease predictor for ALL relapse
Early disease predictor for ALL relapse IL-12 polymorphism linked to cervical cancer risk
IL-12 polymorphism linked to cervical cancer risk