Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Lung cancer in patients who have never smoked — an emerging disease
Lung cancer in patients who have never smoked — an emerging disease
Lung cancer is a disease typically associated with tobacco smoking; however, lung cancer in individuals who have never smoked (LCINS) is estimated to be the fifth most common cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Moreover, smoking rates are declining around the world and therefore LCINS is likely to increase as a proportion of all lung cancers over time. Thus, understanding the aetiology and features of LCINS is increasingly important. Herein, the authors review the emerging data on the epidemiology, clinical characteristics and molecular features of LCINS as well as the genetic and environmental risk factors for this disease. They also summarize the unique diagnostic and management paradigms of LCINS.
- Jaclyn LoPiccolo
- , Alexander Gusev
- & Pasi A. Jänne
-
Review Article |
 Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: implications for screening, prevention and therapy
Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: implications for screening, prevention and therapy
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the most common causes of cancer-related death globally, and despite improvements in prevention and treatment strategies, continued increases in HCC incidence and mortality are predicted. Cirrhosis remains the major risk factor for HCC, although the underlying aetiology is shifting from virus-related to non-viral liver diseases. In this Review, the authors discuss the changing trends in HCC epidemiology and their implications for screening, prevention and therapy, including opportunities to further improve the management of patients with, or at high risk of, HCC.
- Amit G. Singal
- , Fasiha Kanwal
- & Josep M. Llovet
-
Review Article |
 Improving quality and quantity of life for childhood cancer survivors globally in the twenty-first century
Improving quality and quantity of life for childhood cancer survivors globally in the twenty-first century
Advances in the treatment of childhood cancers have substantially improved cure rates, although the gains in survival are offset by an elevated burden of morbidities and an excess risk of early death owing predominantly to the adverse effects of therapy. In this Review, the authors summarize the evolution of paediatric cancer therapies over the past five decades as well as the associated landscape of treatment-related late and/or long-term health conditions experienced by childhood cancer survivors. In addition, they discuss strategies that are being explored to reduce the overall burden and consequences of these morbidities with the ultimate aim of improving not only the quantity but also the quality of life-years gained for this large, medically vulnerable population.
- Matthew J. Ehrhardt
- , Kevin R. Krull
- & Melissa M. Hudson
-
Review Article |
 The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends
The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends
Lung cancer is the commonest cancer globally. Reflecting patterns of smoking and other risk factor exposures, both the incidence of and mortality from lung cancer are highest in economically developed countries. Nonetheless, developing and less economically developed countries are likely to have the biggest increases in lung cancer in the coming years. In this Review, the authors describe the global epidemiology of lung cancer, and how changes in exposures, socioeconomic status, public health interventions and better treatment strategies are influencing both the incidence of and mortality from lung cancer.
- Amanda Leiter
- , Rajwanth R. Veluswamy
- & Juan P. Wisnivesky
-
Review Article |
 Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
The incidence of early-onset forms of many cancers (defined as cancers diagnosed in individuals <50 years of age) has increased in a number of countries over the past several decades. The underlying reasons for this apparent increase probably include greater use of screening programmes, but also changing patterns in early-life exposures. In this Review, the authors describe the emerging global increase in the incidence of early-onset cancers and suggest changes that might address this situation.
- Tomotaka Ugai
- , Naoko Sasamoto
- & Shuji Ogino
-
Correspondence |
HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer — discussion points
- Peter Goon
- & Holger Sudhoff
-
Correspondence |
Reply to ‘HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer — discussion points’
- Matt Lechner
- , Jacklyn Liu
- & Tim R. Fenton
-
Review Article |
 HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management
HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management
The incidence of human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) is increasing rapidly in most developed countries. In this Review, the authors provide an overview of the epidemiology, molecular biology and treatment of HPV-positive OPSCC, including discussions of the role of treatment de-escalation and emerging novel therapies.
- Matt Lechner
- , Jacklyn Liu
- & Tim R. Fenton
-
Perspective |
 Planning for tomorrow: global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070
Planning for tomorrow: global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070
Assuming that the latest incidence trends continue for the major cancer types, the incidence of all cancers combined will double by 2070 relative to 2020, with the greatest increases predicted in lower-resource settings. The authors of this Perspective discuss how population-level approaches with amenable goals should be considered an integral part of cancer control.
- Isabelle Soerjomataram
- & Freddie Bray
-
Review Article |
 Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Chronic inflammation can promote the development of various cancers. In this Review, the current clinical advances in ameliorating inflammation for the prevention or treatment of cancer are highlighted, and the experimental insights into the biological mechanisms supporting current and potential novel anti-inflammatory approaches to the management of cancer are discussed.
- Jiajie Hou
- , Michael Karin
- & Beicheng Sun
-
Perspective |
 Rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer — a call to action
Rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer — a call to action
The incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) is increasing worldwide for reasons that are currently unclear. Herein, the authors review the current epidemiological, clinical, pathological and molecular understanding of early-onset CRC that occurs in patients ≥50 years of age, drawing contrasts with later-onset CRC. They also discuss future research strategies for improved understanding, prevention, early detection and clinical management of early-onset CRC.
- Naohiko Akimoto
- , Tomotaka Ugai
- & Shuji Ogino
-
Perspective |
 The changing landscape of cancer in the USA — opportunities for advancing prevention and treatment
The changing landscape of cancer in the USA — opportunities for advancing prevention and treatment
Monitoring both cancer incidence and death rates is important for guiding health policy and the direction of future research. In this Perspective, the authors describe changes in cancer incidence and death rates in the USA, highlighting the effects of specific policies and research developments, and providing insight into unmet needs that should be addressed by future health policies.
- Farhad Islami
- , Rebecca L. Siegel
- & Ahmedin Jemal
-
Comment |
COVID-19 and cancer: do we really know what we think we know?
Early published data on COVID-19 in patients with cancer are being referenced in clinical guidelines, despite methodological flaws that limit the quality of much of this evidence. In the next phase of research in this area, we argue that the quality of observational evidence should be prioritized over speed of publication.
- Andrew G. Robinson
- , Bishal Gyawali
- & Gerald Evans
-
News & Views |
Palliative care services at cancer centres — room for improvement
Evidence of quality of life improvements in patients with advanced-stage cancer has spurred a move towards early integration of palliative care into the outpatient setting. As discussed herein, meaningful and sustained improvements in timely access to palliative care requires commitments to funding, encouraging integration and routinizing referral across care settings. More palliative medicine training positions as well as broader education of clinicians and the public about the benefits of palliative care throughout the disease course are also needed.
- Jean Mathews
- & Camilla Zimmermann
-
News & Views |
 Health burden in cancer survivors: below the tip of the iceberg
Health burden in cancer survivors: below the tip of the iceberg
In recent decades, cancer survival has improved dramatically, resulting in a growing population of cancer survivors with chronic health needs and disease risks. While large epidemiological studies are useful in tracking broad trends in health outcomes of cancer survivors, they lack the level of detail needed to inform the delivery of appropriate clinical care and optimal allocation of resources.
- Eden R. Brauer
- & Patricia A. Ganz
-
Review Article |
 Active surveillance for prostate and thyroid cancers: evolution in clinical paradigms and lessons learned
Active surveillance for prostate and thyroid cancers: evolution in clinical paradigms and lessons learned
Broad population screening of asymptomatic individuals for cancers of the prostate or thyroid has resulted in overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Herein, the authors describe the epidemiology, pathology, and screening guidelines for the management of patients with those cancers, and discuss existing international active surveillance protocols.
- Lisa M. Lowenstein
- , Spyridon P. Basourakos
- & Jeri Kim
-
News & Views |
 Addressing the health burden of childhood cancer survivors — improvements are needed
Addressing the health burden of childhood cancer survivors — improvements are needed
Recently published data from a large-cohort study confirm the substantial burden of chronic health conditions among childhood cancer survivors, and describe the multiple chronic conditions faced by these individuals. The findings emphasize the need for specialized care in this unique patient population that, as discussed herein, often goes unmet. More must be done to ease the burden on cancer survivors; new models of care are required to improve their long-term health.
- Tara O. Henderson
- & Kevin C. Oeffinger
-
Review Article |
 Cholangiocarcinoma — evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma — evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma, the second most common form of liver cancer after hepatocellular carcinoma, is a heterogeneous disease entity with a near-universal poor prognosis. Our understanding of the epidemiology and biology of cholangiocarcinoma is increasing, and importantly, potentially actionable molecular and immunological targets for novel therapies are increasingly being identified. Herein, the evolving developments in the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management of cholangiocarcinoma are reviewed.
- Sumera I. Ilyas
- , Shahid A. Khan
- & Gregory J. Gores
-
Review Article |
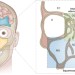 Sinonasal carcinoma: clinical, pathological, genetic and therapeutic advances
Sinonasal carcinoma: clinical, pathological, genetic and therapeutic advances
The sinonasal cavities are affected by a range of tumour types, the most common of which are sinonasal squamous-cell carcinoma (SNSCC) and intestinal-type adenocarcinoma (ITAC). Compared with the main types of head and neck cancer, these sinonasal cancers have distinct epidemiological, clinical, aetiological, pathological and genetic characteristics, and require specialized treatment, bearing in mind their important anatomical location. All these aspects of ITAC and SNSCC are reviewed in this article.
- José Luis Llorente
- , Fernando López
- & Mario A. Hermsen
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Biorepositories for cancer research in developing countries
Biorepositories for cancer research in developing countries
Well-documented biorepositories are essential for cancer research. Currently, major biobanks are located in the developed world, which represents the minority global population; however, countries with low-resource settings contribute more than 50% of the global cancer burden. Therefore, there is an urgent need to establish next-generation biorepositories in developing countries.
- Sandipan Ray
- , Aliasgar Moiyadi
- & Sanjeeva Srivastava
-
-
Review Article |
 Access to cancer medications in low- and middle-income countries
Access to cancer medications in low- and middle-income countries
For patients in low and middle-income countries (LMICs), many of the advances in medical oncology enjoyed in the developed world are nothing but an aspiration for the future. However, as Gilberto Lopes Jr and colleagues describe, LMICS are using generic and biosimilar drugs, expanding participation in clinical trials, implementing universal health-care schemes, using compulsory licensing schemes and increasing public–private partnerships to increase access to cancer medications for their citizens.
- Gilberto de Lima Lopes Jr
- , Jonas A. de Souza
- & Carlos Barrios
-
News & Views |
Excess cancer in men—a call for an increased research focus
A recent report entitled “Excess cancer burden in men” further highlights the stark differences in cancer incidence and mortality rates between sexes, yet the causes of such differences remain largely enigmatic. It is time clinicians, researchers, and funding organizations took notice and necessary action.
- Michael B. Cook
-
-
Review Article |
 Palliative care reduces morbidity and mortality in cancer
Palliative care reduces morbidity and mortality in cancer
Palliative care is a crucial part of the treatment spectrum for patients with cancer because these patients frequently undergo aggressive therapy, sometimes in discordance with their wishes. This Review article outlines the different elements of palliative care, including communication, quality of life, symptom control, patient satisfaction and resource utilization, and shows how it can benefit patients.
- Gabrielle B. Rocque
- & James F. Cleary
-
Science and Society |
 Perspectives of a lifelong cancer survivor—improving survivorship care
Perspectives of a lifelong cancer survivor—improving survivorship care
In this article, Ruth Rechis—a 20-year survivor of Hodgkin lymphoma—describes her personal account of surviving cancer and her experience as a researcher and advocate in the field of survivorship. She provides recommendations for engaging survivors as active participants in their post-treatment, long-term survivorship care and to ensure appropriate care is universally available as part of patient-centred comprehensive care.
- Ruth Rechis
- , Sarah R. Arvey
- & Ellen Burke Beckjord
-
News & Views |
Aspirin and the risk of prostate cancer mortality
The observational registry CaPSURE study reported that men with prostate cancer who were taking aspirin were less likely to die of prostate cancer than nonusers. This favourable effect seems to be stronger than that observed in a pooled analysis of randomized clinical trials of aspirin, and in other observational studies.
- Carlo La Vecchia
- & Cristina Bosetti
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 The European LeukemiaNet AML Working Party consensus statement on allogeneic HSCT for patients with AML in remission: an integrated-risk adapted approach
The European LeukemiaNet AML Working Party consensus statement on allogeneic HSCT for patients with AML in remission: an integrated-risk adapted approach
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is frequently applied as part of treatment in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in their first or subsequent remission. In this Review, the authors propose risk assessment as a dynamic process during treatment, incorporating both disease-related and transplant-related factors for the decision to proceed either to allogeneic HSCT or to apply a nontransplant strategy.
- Jan J. Cornelissen
- , Alois Gratwohl
- & Gert J. Ossenkoppele
-
-
-
News & Views |
BREAKing a path for progress—dabrafenib confirms class effect
Dabrafenib is the second agent in the therapeutic class of selective BRAF inhibitors, and has proven efficacy in a phase III trial (BREAK-3) with impressive improvements in progression-free survival and response rates. Differences in the safety profile exist compared with vemurafenib, but the future lies in combinatorial strategies and improved patient selection.
- Hussein A. Tawbi
- & John M. Kirkwood
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Geriatric oncology research to improve clinical care
Geriatric oncology research to improve clinical care
The needs and treatment requirements of older patients with cancer are different to their younger counterparts. However, few data are available on which to base important clinical decisions for the treatment of this patient population. This Review article outlines the issues and some of the solutions associated with treating cancer in older patients and uses three case studies to illustrate the practical problems that clinicians face.
- Supriya Mohile
- , William Dale
- & Arti Hurria
-
News & Views |
Locally advanced NCSLC in the elderly: which treatment?
Treatment of locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the elderly is challenging, with many available treatment options from radiotherapy alone to sequential chemoradiation. The latest phase III trial comparing radiotherapy alone with concurrent chemoradiation reported a survival improvement for the combination; however, this does not define a new standard treatment.
- Cesare Gridelli
-
Perspectives |
 Tumour molecular profiling for deciding therapy—the French initiative
Tumour molecular profiling for deciding therapy—the French initiative
The use of tumour molecular profiles for therapeutic decision making requires that molecular diagnostics be introduced into routine clinical practice. To this end, the French National Cancer Institute and French Ministry of Health have set up a national network of 28 regional molecular genetics centres. In this Perspectives article, the authors look at the 4-year history of the French initiative and discuss its success in rapidly implementing molecular tests for new tumour biomarkers.
- Frédérique Nowak
- , Jean-Charles Soria
- & Fabien Calvo
-
Review Article |
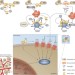 Thrombosis and cancer
Thrombosis and cancer
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a potentially life-threatening condition that can be associated with significant morbidity and is linked to cancer by numerous pathophysiological mechanisms. Here, the risk factors, mechanisms, prevention, and optimal treatment of VTE in patients with cancer are discussed.
- Annie Young
- , Oliver Chapman
- & Ajay K. Kakkar
-
In Brief |
Infertility and ovarian cancer
-
-
News & Views |
 Pazopanib for soft-tissue sarcoma: a PALETTE of data emerges
Pazopanib for soft-tissue sarcoma: a PALETTE of data emerges
The PALETTE randomized phase III trial has reported a statistically significant benefit for the use of pazopanib compared to placebo in terms of progression-free survival for the treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma. However, no benefit in terms of overall survival was observed, the reasons for which might lie in the study design.
- Isabelle Ray-Coquard
- & David Thomas

 Epidemiology of HPV-associated cancers past, present and future: towards prevention and elimination
Epidemiology of HPV-associated cancers past, present and future: towards prevention and elimination Time to ESCAPE the city? Air pollution linked to lung cancer
Time to ESCAPE the city? Air pollution linked to lung cancer Radiation risk in BRCA carriers
Radiation risk in BRCA carriers Risk of death not increased for patients with dense breasts
Risk of death not increased for patients with dense breasts Less is more for paediatric patients—it's ALL in the dosing
Less is more for paediatric patients—it's ALL in the dosing Harmonizing the immune response with a cancer vaccine
Harmonizing the immune response with a cancer vaccine