Featured
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Early promising results with the novel KRASG12C inhibitor divarasib
Early promising results with the novel KRASG12C inhibitor divarasib
- Diana Romero
-
Review Article |
 TAM family kinases as therapeutic targets at the interface of cancer and immunity
TAM family kinases as therapeutic targets at the interface of cancer and immunity
The TAM (TYRO3, AXL and MERTK) family receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) have diverse cancer-promoting functions in malignant cells as well as immune cells and other cell types in the tumour microenvironment, presenting an attractive opportunity for both direct and immune-mediated therapeutic activity manifest through inhibition of a single target. Accordingly, a variety of agents designed to selectively target TAM RTKs are entering clinical testing. This Review provides an essential guide to the TAM RTKs for clinicians. The authors comprehensively review the various roles of TAM RTKs in cancer, the evidence supporting their potential as therapeutic targets, and the translational development of TAM-targeted agents as cancer treatments.
- Deborah DeRyckere
- , Justus M. Huelse
- & Douglas K. Graham
-
News & Views |
Precision oncology for KRASG12C-mutant colorectal cancer
Allele-specific inhibitors of KRASG12C are approved in non-small-cell lung cancer. Herein, we discuss recent results from the phase I/II KRYSTAL-1 trial of adagrasib alone and in combination with cetuximab in patients with KRASG12C-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. The combination had promising efficacy and, if confirmed in later-phase trials, concomitant inhibition of EGFR and KRASG12C will present a new paradigm in precision oncology.
- Federica Di Nicolantonio
- & Alberto Bardelli
-
Review Article |
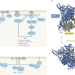 At a crossroads: how to translate the roles of PI3K in oncogenic and metabolic signalling into improvements in cancer therapy
At a crossroads: how to translate the roles of PI3K in oncogenic and metabolic signalling into improvements in cancer therapy
Several PI3K pathway inhibitors are currently approved as cancer treatments; however, finding an acceptable therapeutic window to target this key signalling cascade linking cancer growth with metabolism has proven challenging and the clinical results to date have arguably been disappointing. In this Review, Vasan and Cantley discuss the effects of PI3K pathway alterations on signalling and metabolism in solid tumours as well as past and present efforts to improve the somewhat limited clinical efficacy of PI3K pathway inhibitors, with a particular focus on PI3Kα in breast cancers.
- Neil Vasan
- & Lewis C. Cantley
-
Review Article |
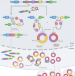 The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology
The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a novel class of primarily non-coding RNAs with increasingly recognized roles in cancer development and progression through diverse mechanisms of action. Herein, the authors review the current understanding of circRNA biogenesis, regulation, physiological functions and pathophysiological roles in cancer. They also discuss the clinical potential of circRNAs as biomarkers, therapeutic agents and drug targets in oncology as well as research controversies, technical issues and biological knowledge gaps that need to be addressed before this promise can be realized.
- Lasse S. Kristensen
- , Theresa Jakobsen
- & Jørgen Kjems
-
Review Article |
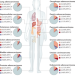 The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC proto-oncogenes are among the most commonly activated proteins in human cancer, yet the clinical efficacy of MYC-targeted agents remains to be demonstrated. The authors of this Review describe how activation of the MYC pathway affects cancer cells as well as the tumour microenvironment and propose strategies for the therapeutic targeting of MYC-driven cancers.
- Renumathy Dhanasekaran
- , Anja Deutzmann
- & Dean W. Felsher
-
Review Article |
 ROS1-dependent cancers — biology, diagnostics and therapeutics
ROS1-dependent cancers — biology, diagnostics and therapeutics
ROS1 fusions can be identified across a range of malignancies and confer a high level of sensitivity to ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Herein, the authors discuss the non-malignant and malignant biology of ROS1, the diagnostic approaches to identifying ROS1 fusions and the current therapeutic concepts relating to ROS1 fusion-positive cancers, including the resistance mechanisms that have emerged with current ROS1 inhibitors.
- Alexander Drilon
- , Chelsea Jenkins
- & Monika A. Davare
-
Review Article |
 MET-dependent solid tumours — molecular diagnosis and targeted therapy
MET-dependent solid tumours — molecular diagnosis and targeted therapy
Therapies targeting MET-overexpressing cancers have limited efficacy. However, owing to advances in detection methods, therapies targeting MET-dependent tumours harbouring MET amplifications, activating mutations or fusions are emerging. In this review, the authors describe emerging data on this new class of targeted therapies.
- Robin Guo
- , Jia Luo
- & Alexander Drilon
-
Review Article |
 Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer — implications for care
Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer — implications for care
Alternative splicing enables the regulated generation of multiple mRNA and protein products from a single gene. This Review outlines the splicing process and its alterations in cancer before highlighting related opportunities for the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
- Sophie C. Bonnal
- , Irene López-Oreja
- & Juan Valcárcel
-
Comment |
The roles of patient groups in fostering cancer research
As more patients with oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer are treated with targeted therapies, they are joining forces online to form groups that provide support, education and advocacy focused on specific oncogenes. Herein, we discuss how the involvement of these groups in patient-partnered research can benefit both patients and lung cancer research.
- Merel Hennink
- , Geert Vandeweyer
- & Janet Freeman-Daily
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Somatic and germline genomics in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Somatic and germline genomics in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Herein, advances in our understanding of the genomic landscape of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), encompassing both somatic and germline alterations, are reviewed. The clinical implications of these alterations, particularly those in the germ line, are discussed with regard to susceptibility to ALL, treatment responses and therapy-related toxicities.
- Ching-Hon Pui
- , Kim E. Nichols
- & Jun J. Yang
-
Research Highlight |
 BCC identity switch breaks restraints of Hedgehog pathway inhibition
BCC identity switch breaks restraints of Hedgehog pathway inhibition
- David Killock
-
Review Article |
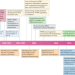 NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
TRK fusion proteins are pathognomonic in certain rare tumour types and present in a small subset of diverse cancer types, including some common cancers; TRK inhibitors have promising efficacy in the treatment of these cancers, in a histology-agnostic manner. In this Review, the biology of TRK signalling and TRK fusions, strategies to target these drivers, the unique safety profile of TRK inhibitors and mechanisms of and strategies to overcome acquired resistance to these agents are discussed.
- Emiliano Cocco
- , Maurizio Scaltriti
- & Alexander Drilon
-
Review Article |
 Therapeutic strategies to target RAS-mutant cancers
Therapeutic strategies to target RAS-mutant cancers
Effective therapeutic strategies to target RAS-mutant cancers have proved elusive, but in the past few years, several promising strategies have been tested in clinical trials. The authors describe historical and ongoing therapeutic approaches based on the direct or indirect targeting of RAS.
- Meagan B. Ryan
- & Ryan B. Corcoran
-
Research Highlight |
Uncovering the clonal basis of response and resistance to IDH2 inhibition in AML
- David Killock
-
Review Article |
 Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
The PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway has key roles in tumorigenesis and is dysregulated in most cancers. Consequently, numerous drugs that target key nodes of this pathway have been developed, although few of these agents have been approved for the treatment of cancer. Herein, the authors review the current experience with anticancer therapies that target the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway, discuss the challenges that have limited the clinical translation of these agents, and provide perspectives for the future development of these drugs.
- Filip Janku
- , Timothy A. Yap
- & Funda Meric-Bernstam
-
-
Review Article |
 Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes
Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes
The receptor-tyrosine kinase RET has been identified as a potentially actionable driver of oncogenesis. Several multikinase inhibitors with activity against RET have been explored in the clinic, but have only modest efficacy in patients with thyroid cancers, mostly in those withRET mutations, or RET-rearranged lung cancers. Herein, the authors outline the aberrations in RET that contribute to tumorigenesis, review the current clinical data for inhibitors of this kinase, and discuss whether the limited clinical success achieved with these agents to date is attributable to the intractability of RET as a drug target or the lack of highly specific RET inhibitors.
- Alexander Drilon
- , Zishuo I. Hu
- & Daniel S. W. Tan
-
Review Article |
 Therapeutic targeting of p53: all mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others
Therapeutic targeting of p53: all mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others
TP53, encoding the tumour-suppressor p53, is the most frequently mutated gene across all human cancers. Similar to other transcription factors, p53 has proved notoriously difficult to target therapeutically; to date, no p53-targeted therapies have entered the clinic. The diversity ofTP53 mutations, which can be categorized across a spectrum of different functional classes, is increasingly recognized as an additional challenge to developing p53-directed treatments. Herein, Kanaga Sabapathy and David Lane review this 'rainbow of p53 mutants', and discuss the implications for anticancer therapies targeting p53 or directed by TP53status.
- Kanaga Sabapathy
- & David P. Lane
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Conditional selection determines the pathways of cancer evolution
Conditional selection determines the pathways of cancer evolution
- David Killock
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Unravelling the biology of SCLC: implications for therapy
Unravelling the biology of SCLC: implications for therapy
For three decades, the treatment of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) has remained essentially unchanged, and patient outcomes remain dismal. In the past 5 years, however, advances in our understanding of the disease, at the molecular level, have resulted in the development of new therapeutic strategies, encompassing immunotherapies and novel molecularly targeted agents. Herein, authors review the breakthroughs that hold the promise to improve SCLC outcomes.
- Joshua K. Sabari
- , Benjamin H. Lok
- & Charles M. Rudin
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
In a paper published recently in Cell, Guarnerio et al. suggest that circular RNAs derived from cancer-associated chromosomal translocations have an oncogenic role; however, the experimental approach that the authors used was inadequate to generate sufficient evidence to prove this role, calling their study into question.
- Carlo M. Croce
-
Opinion |
 A second chance for telomerase reverse transcriptase in anticancer immunotherapy
A second chance for telomerase reverse transcriptase in anticancer immunotherapy
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) is expressed constitutively in tumour cells throughout the evolution of many cancers; therefore, this potential tumour self-antigen has been an important target for anticancer vaccines over the past 10 years, but only modest benefits from this approach have been observed in clinical trials. In this Perspectives, Maurizio Zanetti reviews these studies, and highlights advances in our knowledge that warrant further development and refinement of TERT immunotherapy.
- Maurizio Zanetti
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Time to shift the burden of proof for oncogene-positive cancer?
Rearrangements of the ALK gene have been associated with sensitivity to crizotinib and other kinase inhibitors with activity against ALK. The phase III PROFILE 1007 randomized study of crizotinib versus chemotherapy has demonstrated that crizotinib is superior to standard second-line chemotherapy in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer.
- Robert C. Doebele
-
-
News & Views |
HER2—a good addiction
Recent neoadjuvant studies have examined the effects of adding single or dual agents targeting HER2 to chemotherapy, finding unanimously that dual HER2 targeting markedly improves pathologic response. These findings have significant implications for future trial designs, particularly if the impact on pathologic response is accompanied by improved disease-free survival or overall survival.
- Lisa A. Carey
-
-
-

 BRAF — a tumour-agnostic drug target with lineage-specific dependencies
BRAF — a tumour-agnostic drug target with lineage-specific dependencies Reliable results from several DNA sources
Reliable results from several DNA sources Nice to see you — evolving MHC I–peptide presentation
Nice to see you — evolving MHC I–peptide presentation EGFR inhibition is effective against KRAS-wild-type disease
EGFR inhibition is effective against KRAS-wild-type disease Place your BETs on combination therapy
Place your BETs on combination therapy Truncation to expansion — a new indication for ALK inhibition?
Truncation to expansion — a new indication for ALK inhibition? The Cancer Genome Atlas maps papillary thyroid cancer
The Cancer Genome Atlas maps papillary thyroid cancer Go on, leave me BRCA-less!
Go on, leave me BRCA-less!