Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Multiparametric MRI for characterization of the tumour microenvironment
Multiparametric MRI for characterization of the tumour microenvironment
By combining multiple MRI sequences, each providing different but complementary information about the tumour microenvironment (TME), multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) enables non-invasive assessment of the heterogeneous features of the TME components. The authors of this Review describe the role of mpMRI in the non-invasive characterization of the TME, presenting examples of its utility in cancer detection, staging and assessment of response to therapy, and considering future applications for personalized integrated diagnostics.
- Emily Hoffmann
- , Max Masthoff
- & Moritz Wildgruber
-
News & Views |
Enhancing diagnostic precision in liver lesion analysis using a deep learning-based system: opportunities and challenges
A recent study reported the development and validation of the Liver Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis System (LiAIDS), a fully automated system that integrates deep learning for the diagnosis of liver lesions on the basis of contrast-enhanced CT scans and clinical information. This tool improved diagnostic precision, surpassed the accuracy of junior radiologists (and equalled that of senior radiologists) and streamlined patient triage. These advances underscore the potential of artificial intelligence to enhance hepatology care, although challenges to widespread clinical implementation remain.
- Jeong Min Lee
- & Jae Seok Bae
-
Review Article |
 Quantitative PET-based biomarkers in lymphoma: getting ready for primetime
Quantitative PET-based biomarkers in lymphoma: getting ready for primetime
Despite advances in drug development for patients with lymphoma over the past decades, the identification of biomarkers for treatment selection remains an unmet need. The authors of this Review provide an overview of quantitative PET-based biomarkers in this patient population and discuss the challenges and opportunities in the integration of these biomarkers in clinical trials and the routine management of patients with lymphoma.
- Juan Pablo Alderuccio
- , Russ A. Kuker
- & Craig H. Moskowitz
-
Review Article |
 Integrated MRI-guided radiotherapy — opportunities and challenges
Integrated MRI-guided radiotherapy — opportunities and challenges
In the past decade, treatment devices that combine imaging with targeted irradiation have been developed to deliver MRI-guided radiotherapy (MRIgRT). This treatment modality uses motion management and biological targeting to improve local control rates whilst reducing the radiation delivered to non-malignant tissues. The authors of this Review describe the current state of MRIgRT, and the opportunities and challenges of this radiotherapy approach.
- Paul J. Keall
- , Caterina Brighi
- & Brendan Whelan
-
Review Article |
 The emerging role of photoacoustic imaging in clinical oncology
The emerging role of photoacoustic imaging in clinical oncology
Photoacoustic imaging is a novel imaging technique that provides scalably high levels of spatial resolution at rapid acquisition speed, without the need for radiation or exogenous contrast agents. In this Review, the authors describe the emerging role of this technology in the screening, diagnosis and management of patients with cancer, and provide an overview of the future implementation of this technology.
- Li Lin
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Review Article |
 Tumour burden and efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors
Tumour burden and efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors
A high tumour burden has long been associated with inferior outcomes on traditional cancer therapies and emerging evidence suggests that tumour burden is particularly relevant for patients receiving immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Here, the authors summarize the available clinical and preclinical evidence for the role of tumour burden in determining the outcomes of patients receiving immune-checkpoint inhibitors and highlight areas that are likely to be of future research interest in this emerging area.
- Filippo G. Dall’Olio
- , Aurélien Marabelle
- & Benjamin Besse
-
Review Article |
 Fundamentals and developments in fluorescence-guided cancer surgery
Fundamentals and developments in fluorescence-guided cancer surgery
Fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS) using tumour-targeted imaging agents has emerged over the past decade as a method of intraoperative cancer detection; however, the clinical implementation of tumour-targeted FGS remains in the early stages. The authors of this Review discuss how target selection, imaging agents and detection systems could enable real-time intraoperative visualization to benefit patients with cancer.
- J. Sven D. Mieog
- , Friso B. Achterberg
- & Alexander L. Vahrmeijer
-
-
Perspective |
 Artificial intelligence in radiation oncology
Artificial intelligence in radiation oncology
The possible uses of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiation oncology are diverse and wide ranging. Herein, the authors discuss the potential applications of AI at each step of the radiation oncology workflow, which might improve the efficiency and overall quality of radiation therapy for patients with cancer. The authors also describe the associated challenges and provide their perspective on how AI platforms might change the roles of radiation oncology medical professionals.
- Elizabeth Huynh
- , Ahmed Hosny
- & Raymond H. Mak
-
Review Article |
 Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer
Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer
Photodynamic and photothermal therapies hold promise in the local treatment of cancer although, arguably, their full potential has not yet been achieved. Herein, the authors review the current clinical progress of these phototherapies and discuss the bioengineering approaches that are being explored to overcome challenges and thereby improve such treatments.
- Xingshu Li
- , Jonathan F. Lovell
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Review Article |
 Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology
Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology
Cancer cells, like non-malignant cells, are dependent on folate uptake for growth. However, cancer cells are much more reliant on folate receptors (FRs) and particularly FRα for folate uptake than non-malignant cells. In this Review, the authors describe the available data on the role of FRα as a biomarker and as a target of imaging probes, and of targeted therapies in patients with solid tumours.
- Mariana Scaranti
- , Elena Cojocaru
- & Udai Banerji
-
News & Views |
Intraoperative brain tumour identification with deep learning
Developing novel technologies to discriminate malignant tissue from nonmalignant structures and thereby facilitate safe, complete tumour resection is a major priority for advancing oncological neurosurgery. Herein, we discuss a recently reported innovation involving stimulated Raman spectroscopy of intraoperative tissue samples and data interpretation with artificial intelligence, as well as the implications of this approach for neurosurgical oncology.
- Michael L. Martini
- & Eric K. Oermann
-
Review Article |
 Current approaches to the management of brain metastases
Current approaches to the management of brain metastases
Brain metastases are a frequent manifestation of several common solid tumour types, including lung cancer, breast cancer and melanoma. Although the presence of brain-metastatic disease continues to be associated with poor outcomes, advances in surgery, radiotherapy and systemic therapies that can permeate the blood–brain barrier are beginning to improve patient outcomes. In this Review, the authors provide an overview of contemporary advances in the management of brain metastases over the past decade.
- John H. Suh
- , Rupesh Kotecha
- & Eric L. Chang
-
News & Views |
Google’s lung cancer AI: a promising tool that needs further validation
Researchers from Google AI have presented results obtained using a deep learning model for the detection of lung cancer in screening CT images. The authors report a level of performance similar to, or better than, that of radiologists. However, these claims are currently too strong. The model is promising but needs further validation and could only be implemented if screening guidelines were adjusted to accept recommendations from black-box proprietary AI systems.
- Colin Jacobs
- & Bram van Ginneken
-
-
Review Article |
 The beginning of the end for conventional RECIST — novel therapies require novel imaging approaches
The beginning of the end for conventional RECIST — novel therapies require novel imaging approaches
The development of more-targeted cancer therapies has not been matched by more-targeted imaging methods. This discrepancy has, in some scenarios, resulted in inaccurate assessments of the effects of novel therapies. In this Review, the authors describe potential novel imaging approaches that could be adopted to enable improvements in imaging-based monitoring of treatment responses and resistance.
- Mirjam Gerwing
- , Ken Herrmann
- & Moritz Wildgruber
-
Perspective |
 Integrating molecular nuclear imaging in clinical research to improve anticancer therapy
Integrating molecular nuclear imaging in clinical research to improve anticancer therapy
Integrating molecular nuclear imaging in clinical research has great potential to improve anticancer therapy, particularly through the development of imaging biomarkers. Herein, the multistage process of developing novel molecular imaging biomarkers is discussed, highlighting both the challenges that have restricted the use of molecular imaging in clinical oncology research and future opportunities in this area.
- Elisabeth G. E. de Vries
- , Laura Kist de Ruijter
- & Sjoukje F. Oosting
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Surgical oncology for gliomas: the state of the art
Surgical oncology for gliomas: the state of the art
Surgery remains the mainstay of treatment for patients with gliomas, independent of tumour grade, and maximal resection of the tumour is essential for long-term disease control. Herein, the authors discuss the current evidence on associations between the extent of glioma resection and clinical outcomes. They also describe the state-of-the-art surgical oncology approaches aimed at maximizing the extent of tumour resection while minimizing patient morbidity.
- Nader Sanai
- & Mitchel S. Berger
-
Review Article |
 Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine
Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine
Radiomics is the high-throughput mining of quantitative image features from standard-of-care medical imaging to enable data to be extracted and applied within clinical-decision support systems. The process of radiomics is described and its pitfalls, challenges, opportunities, and capacity to improve clinical decision making. The radiomics field requires standardized evaluation of scientific findings and their clinical relevance. This review provides guidance for investigations to meet this urgent need in the field of radiomics.
- Philippe Lambin
- , Ralph T.H. Leijenaar
- & Sean Walsh
-
News & Views |
Staging and restaging patients with lymphoma — a better approach?
Response criteria for disease assessment have important therapeutic and prognostic implications in clinical trials and in routine clinical practice. The Lugano classification has been used widely for evaluation of the response of patients with lymphoma to treatment, although the alternative Response Evaluation Criteria In Lymphoma 2017 (RECIL 2017) classification was recently proposed; these criteria are compared herein.
- Vijaya R. Bhatt
- & James O. Armitage
-
-
Reply |
Imaging biomarkers exist and they underpin clinical decision-making
- John C. Waterton
- , Lisa M. McShane
- & James P. B. O'Connor
-
Opinion |
 Evolution of lymphoma staging and response evaluation: current limitations and future directions
Evolution of lymphoma staging and response evaluation: current limitations and future directions
Accurate detection and monitoring of treatment responses is an essential element of the management of patients with lymphoma. In this Perspectives, the authors describe the evolution of lymphoma staging criteria and highlight unaddressed questions, which, if answered, will substantially improve the management of patients with lymphoma.
- Joel Cunningham
- , Sunil Iyengar
- & Bhupinder Sharma
-
-
Review Article |
 Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
Intraoperative fluorescence enables highly specific real-time detection of tumours at the time of surgery. In particular, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence is a promising tool currently being tested in clinical settings. Zhang et al. discuss the latest developments in NIR fluorophores, cancer-targeting strategies, and detection instrumentation for intraoperative cancer detection, as well as the challenges associated with their effective application in clinical settings.
- Ray R. Zhang
- , Alexandra B. Schroeder
- & Jamey P. Weichert
-
Review Article |
 Surveillance after curative treatment for colorectal cancer
Surveillance after curative treatment for colorectal cancer
After curative treatment, 30% of patients with stage I–III and up to 65% of patients with stage IV colorectal cancer (CRC) develop recurrent disease. Thus, surveillance for disease recurrence is clearly needed in these patients, but controversy surrounds the optimal follow-up approaches. Herein, the current evidence relating to surveillance strategies for patients with CRC is comprehensively reviewed, and the future development of patient-centred programmes is discussed.
- Eric P. van der Stok
- , Manon C. W. Spaander
- & Ernst J. Kuipers
-
Consensus Statement
| Open Access Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies
Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies
Imaging biomarkers (IBs) are used extensively in drug development and cancer research, but important differences exist between IBs and biospecimen-derived biomarkers. A tailored 'roadmap' is required for the development of new IBs to be used either in clinical research or for decision-making in healthcare. In this Consensus statement, a group of experts assembled by CRUK and the EORTC present 14 key recommendations for accelerating the clinical translation of IBs.
- James P. B. O'Connor
- , Eric O. Aboagye
- & John C. Waterton
-
Review Article |
 Non-invasive metabolic imaging of brain tumours in the era of precision medicine
Non-invasive metabolic imaging of brain tumours in the era of precision medicine
Many of the molecular pathways that are aberrant in brain tumours result in reprogramming of metabolism, which creates opportunities forin vivometabolic imaging to improve diagnosis, patient stratification, and disease monitoring. Herein, the molecular basis and strategies for non-invasive metabolic imaging of brain tumours are reviewed.
- Michelle M. Kim
- , Abhijit Parolia
- & Sriram Venneti
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Evaluation and management of pancreatic lesions in patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease
Evaluation and management of pancreatic lesions in patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease
Patients with von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) disease are susceptible to a range of neoplasms. More than 50% of these patients suffer from a range of pancreatic lesions at some point in their lifetime, and the different types of lesions require different management approaches. In this Review, the authors describe the types of pancreatic lesions that are associated with VHL disease, and discuss the management of patients with different pancreatic manifestations; an overall patient-management algorithm is also presented.
- Xavier M. Keutgen
- , Pascal Hammel
- & Electron Kebebew
-
News & Views |
The importance of overdiagnosis in breast-cancer screening
The results of three recent studies demand that more attention be placed on defining the most-appropriate approach to population-based breast-cancer screening, in particular regarding the potential harms of increasing overdiagnosis. Two of these studies report that more-sensitive detection of breast neoplasms is possible by 3D tomography and by MRI, but the third paper raises the question of whether this increased sensitivity is desirable.
- Steven Narod
-
News & Views |
Doubtful health benefit of screening from 40 years of age
Results of the UK Age trial suggest a significant benefit of annual mammography initiated at 39–41 years of age in preventing breast-cancer deaths occurring before the age of 50 years; however, this approach had no effect on the risk of breast-cancer death occurring before the age of 60 years and leads to prolonged deteriorations in quality of life owing to overdiagnosis.
- Philippe Autier
-
-
Review Article |
 Lung cancer—a fractal viewpoint
Lung cancer—a fractal viewpoint
The use of traditional Euclidean geometry can present challenges for analysis of image characteristics, particular those of extremely complex biological structures, obtained by medical and scientific imaging modalities. Fractal geometry is a potentially complementary mathematical approach that enables efficient estimation of geometrical complexity, and the irregularity of shapes and patterns. This Review introduces the concept of fractals and fractal geometry, and describes how analysis of fractal (non-integer) dimension and associated measurements, such as lacunarity (texture), can be performed and applied to the analysis of cancer. The authors discuss how fractal analysis might provide information on many diverse biological structures relevant to the natural history of lung cancer, which might prove useful for the diagnosis and management of this disease.
- Frances E. Lennon
- , Gianguido C. Cianci
- & Ravi Salgia
-
Review Article |
 PET in the management of locally advanced and metastatic NSCLC
PET in the management of locally advanced and metastatic NSCLC
PET has evolved from a purely diagnostic imaging technique to a multifunctional modality that can provide diverse information of relevance to oncological management. This modality might offer the potential to improve patient care and outcomes by enabling better disease characterization, treatment-response monitoring, and follow-up assessment. Herein, the authors discuss the data supporting the use of PET in personalizing the clinical management of patients with locally advanced and metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.
- Willem Grootjans
- , Lioe-Fee de Geus-Oei
- & Johan Bussink
-
-
Opinion |
 Quantitative multimodality imaging in cancer research and therapy
Quantitative multimodality imaging in cancer research and therapy
Recent advances in multimodality imaging in cancer have involved the integration of multiple quantitative, functional measurements that provide a more-comprehensive characterization of tumours. In this Review, Yankeelov and colleagues discuss how, although some of these approaches still need some adjusting, they can already be applied informatively in clinical trials of cancer therapeutics using existing tools.
- Thomas E. Yankeelov
- , Richard G. Abramson
- & C. Chad Quarles
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence
Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence
Optical imaging that exploits invisible near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent light (700–900 nm) has the potential to improve cancer surgery outcomes, minimize anaesthesia time and lower health-care costs via its improved contrast and depth of tissue penetration relative to visible light. This Review introduces the concept of NIR fluorescence imaging and examines imaging system and contrast agent optimization.
- Alexander L. Vahrmeijer
- , Merlijn Hutteman
- & John V. Frangioni
-
Review Article |
 Validation and clinical utility of prostate cancer biomarkers
Validation and clinical utility of prostate cancer biomarkers
To improve treatments for patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer, new biomarkers and surrogate end points for clinical trials are required. Identifying biomarkers that reflect clinical benefit and that guide personalized treatment plans are of the highest priority. This Review article outlines the framework for developing such biomarkers, including analytical validation, clinical validation and regulatory approval, and describes promising emerging biomarkers.
- Howard I. Scher
- , Michael J. Morris
- & Glenn Heller
-
Review Article |
 Colorectal cancer screening—optimizing current strategies and new directions
Colorectal cancer screening—optimizing current strategies and new directions
Many methods are available for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, ranging from noninvasive stool tests to endoscopy. In this Review, E. J. Kuipers et al. argue that the strength of any single test must be viewed in the context of a range of factors across the screening programme, including test characteristics, uptake, screenee autonomy, cost, endoscopy performance and long-term follow-up.
- Ernst J. Kuipers
- , Thomas Rösch
- & Michael Bretthauer
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Reducing re-operation rates with ultrasound-guided surgery
Reducing re-operation rates with ultrasound-guided surgery
- M. Teresa Villanueva

 NIR-II light in clinical oncology: opportunities and challenges
NIR-II light in clinical oncology: opportunities and challenges Early PET response predicts complete response
Early PET response predicts complete response What’s new under the Sun for ICIs?
What’s new under the Sun for ICIs? Improving diagnosis — can MP-MRI fulfil its PROMIS?
Improving diagnosis — can MP-MRI fulfil its PROMIS? Follow your PET for guidance
Follow your PET for guidance Improving detection of bone metastases in renal cell carcinoma
Improving detection of bone metastases in renal cell carcinoma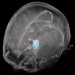 Visualizing secrets of glioma
Visualizing secrets of glioma Reducing ionizing radiation in children and adolescents
Reducing ionizing radiation in children and adolescents Nanotechnology targets cancer cells
Nanotechnology targets cancer cells Radioactive microspheres—see and destroy
Radioactive microspheres—see and destroy