
The present and future of bispecific antibodies for cancer therapy
More than 200 bispecific antibodies are now in clinical development for cancer. Read about progress with them and the future of the field in this Review in the April issue

More than 200 bispecific antibodies are now in clinical development for cancer. Read about progress with them and the future of the field in this Review in the April issue

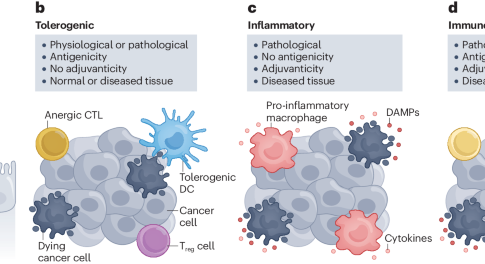
Immunogenic cell death (ICD) is crucial for the elicitation of anticancer immune responses by therapy, but the successful development of ICD-inducing treatments is hindered by various obstacles. This Review provides an overview of the core mechanisms of ICD, discusses obstacles to the development of novel ICD modulators and assesses established and innovative therapeutic approaches for ICD induction.
