Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Computational evidence that hyperconjugative interactions are not responsible for the anomeric effect
Computational evidence that hyperconjugative interactions are not responsible for the anomeric effect
The anomeric effect, which influences the position of polar substituents in the chair conformation of various heterocycles, is commonly rationalized using hyperconjugation. Now, by theoretically studying molecules that display the anomeric effect, strong evidence is provided that hyperconjugation is not responsible and it is better interpreted in terms of electrostatics.
- Yirong Mo
-
News & Views |
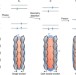 Two electrons from one photon
Two electrons from one photon
The absorption of a single photon can cause the excitation of more than one electron, but the mechanism of this 'multi-exciton generation' process is elusive. Now, calculations on pentacene show that geometrical distortions and intermediate excited states assist in producing two excited electrons from one photon.
- Laurens D. A. Siebbeles
-
Article |
 Singlet fission in pentacene through multi-exciton quantum states
Singlet fission in pentacene through multi-exciton quantum states
A fundamental mechanism for singlet fission, a process that may govern instances of multi-exciton generation, has yet to be described. Sophisticated calculations now show that singlet fission in pentacene proceeds through the conversion of a photoexcited state into a dark state of multi-exciton character that subsequently splits into two triplets.
- Paul M. Zimmerman
- , Zhiyong Zhang
- & Charles B. Musgrave
-
Article |
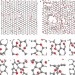 Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide
Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide
Thermal reduction of graphene oxide is an attractive route towards the preparation of graphene, but complete removal of residual oxygen is problematic. Now, molecular dynamics simulations elucidate the chemical changes involved in this process.
- Akbar Bagri
- , Cecilia Mattevi
- & Vivek B. Shenoy
-
News & Views |
 Catalysis without a catalyst
Catalysis without a catalyst
Can two identical reactors with the same concentrations, under identical physical conditions, have reaction rates that differ by a factor of a thousand? A study now shows that, although not true in uncrowded environments, a reactant's starting point makes a large difference to reaction kinetics in identically crowded systems, such as cellular nuclei.
- Raoul Kopelman
-
Research Highlights |
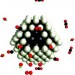 Poison control
Poison control
A combined theoretical and experimental approach has been used to improve catalysts for the selective oxidation of carbon monoxide in hydrogen feedstocks.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Experimental evidence for the functional relevance of anion–π interactions
Experimental evidence for the functional relevance of anion–π interactions
For quadrupole moments up to +39 Buckinghams, increasing π-acidity of aromatic surfaces is shown to cause tighter anion binding in tandem mass spectrometry experiments, higher binding energies in molecular models, stronger charge-transfer absorption bands, and increasingly effective and selective anion transport across lipid-bilayer membranes.
- Ryan E. Dawson
- , Andreas Hennig
- & Stefan Matile
-
Research Highlights |
 Environmental issues
Environmental issues
A computational investigation into how environmental factors influence phosphoester hydrolysis reveals differences between the mechanisms observed in aqueous solution and within an enzyme active site.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
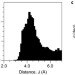 Direct detection of CH/π interactions in proteins
Direct detection of CH/π interactions in proteins
Weakly polar XH/π interactions are thought to be capable of influencing both the structure and function of proteins, but such interactions are usually identified from three-dimensional structural models. Now, using NMR spectroscopy and isotopic labelling, it has been shown that individual methyl/π interactions can be detected directly in proteins by measuring weak scalar couplings between the nuclei involved.
- Michael J. Plevin
- , David L. Bryce
- & Jérôme Boisbouvier
-
-
Article |
 Using first principles to predict bimetallic catalysts for the ammonia decomposition reaction
Using first principles to predict bimetallic catalysts for the ammonia decomposition reaction
The decomposition of ammonia is an important process if ammonia is to be used as a hydrogen storage medium. The most active catalyst for this is ruthenium, but its expense has provoked the search for alternatives. Now, using theory to guide the investigation, researchers have identified a bimetallic nickel–platinum surface as an active catalyst for this process.
- Danielle A. Hansgen
- , Dionisios G. Vlachos
- & Jingguang G. Chen
-
Article |
 Geometry-controlled kinetics
Geometry-controlled kinetics
The time taken for a reactant to reach a target is best represented theoretically by a distribution of times. This distribution has now been calculated analytically and shows quantitatively that in the case of uncrowded environments, a reactant's starting point — in relation to the target — does not influence the search time. It does, however, have an effect in the case of crowded systems — leading to ‘geometry-controlled kinetics’.
- O. Bénichou
- , C. Chevalier
- & R. Voituriez
-
Article |
 The rational design of helium bonds
The rational design of helium bonds
Helium is a reluctant participant when it comes to chemical reactions and bonding and it is one of only two stable elements for which there are currently no known crystalline derivatives. Now, based on a computational investigation, compounds containing helium atoms that form charge-shift, rather than covalent bonds have been proposed.
- Henry S. Rzepa
-
Research Highlights |
 Carbamate tunnel syndrome
Carbamate tunnel syndrome
Molecular dynamics simulations have revealed important mechanistic details about how carbamate is transported from one active site to another within in an enzyme.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Stereoinduction by distortional asymmetry
Stereoinduction by distortional asymmetry
Steric, torsion, stereoelectronic and polar effects are widely used to explain and predict the stereochemical outcome of synthetic organic reactions. Here, the asymmetric distortion of the reactant is considered and used to explain the observed stereoselectivity where these accepted models are unable to provide a clear prediction.
- Robert V. Kolakowski
- & Lawrence J. Williams
-
Article |
 Quantum-induced symmetry breaking explains infrared spectra of CH5+ isotopologues
Quantum-induced symmetry breaking explains infrared spectra of CH5+ isotopologues
Stepwise deuteration of protonated methane CH5+ — a fluxional structure that undergoes ‘hydrogen scrambling’ — leads to dramatic changes in the infrared spectra of the isotopologues. The spectra can be assigned using ab initio quantum simulations that account for the non-classical occupation — by H and D atoms — of topologically different sites within the molecule.
- Sergei D. Ivanov
- , Oskar Asvany
- & Stephan Schlemmer
-
Research Highlights |
 Hot to trot
Hot to trot
The motion of a molecule on a hot surface is investigated using molecular dynamics, revealing a regime of fast rolling and vibrational excitation.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Exploring local currents in molecular junctions
Exploring local currents in molecular junctions
A methodology for describing local electronic transmission through bridging molecules between metallic electrodes is presented. Its application to simple alkane, phenyl and cross-conjugated systems highlights an unexpected number of cases whereby ‘through space’, rather than ‘through bond’ terms dominate and that interference effects coincide with the reversal of ring currents.
- Gemma C. Solomon
- , Carmen Herrmann
- & Mark A. Ratner
-
News & Views |
 Chemistry from photons
Chemistry from photons
The use of conventional computers to calculate molecular properties is hindered by the exponential increase in computational cost on increasing the size of the molecules studied. Using quantum computers could be the solution and the initial steps are now being taken.
- Kenneth R. Brown
-
News & Views |
 Unearthing the unconventional
Unearthing the unconventional
Quantum tunnelling can at times be the cause of kinetic isotope effects, and in these cases conventional wisdom has been that molecules with isotopes of larger mass will react more slowly. New calculations, however, predict that sometimes the reverse should be true.
- Barry K. Carpenter
-
Article |
 A concentric planar doubly π-aromatic B19− cluster
A concentric planar doubly π-aromatic B19− cluster
A combined theoretical and experimental approach has been used to investigate the structure and bonding of an all-boron cluster (B19−). Calculations suggest that the minimum energy structure is a near-planar one — in which a pentagonal B6 unit is encircled by a larger B13 ring — possessing two concentric aromatic π systems.
- Wei Huang
- , Alina P. Sergeeva
- & Alexander I. Boldyrev
-
Article |
 Towards quantum chemistry on a quantum computer
Towards quantum chemistry on a quantum computer
Precise calculations of molecular properties from first-principles set great problems for large systems because their conventional computational cost increases exponentially with size. Quantum computing offers an alternative, and here the H2 potential energy curve is calculated using the latest photonic quantum computer technology.
- B. P. Lanyon
- , J. D. Whitfield
- & A. G. White

 Defying cavity
Defying cavity Carbamate tunnel syndrome
Carbamate tunnel syndrome