Featured
-
-
Article |
 Analogies between photochemical reactions and ground-state post-transition-state bifurcations shed light on dynamical origins of selectivity
Analogies between photochemical reactions and ground-state post-transition-state bifurcations shed light on dynamical origins of selectivity
Selectivity of photochemical reactions is notoriously difficult to model. Now it has been shown that by employing an analogy to ground-state reactions with post-transition-state bifurcations, selectivity for a complex photochemical denitrogenation reaction can be captured and rationalized, and its dynamical origins understood.
- Zhitao Feng
- , Wentao Guo
- & Dean J. Tantillo
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoselective umpolung of thiols to episulfoniums for cysteine bioconjugation
Chemoselective umpolung of thiols to episulfoniums for cysteine bioconjugation
Cysteine bioconjugation is an important method to modify biomolecules, but synthetic efforts to diversify reactive warheads and the low reactivity of introducible linchpins often impede application in biological laboratories. Now, a thianthrenium-based reagent permits site-selective installation of episulfonium on biomacromolecules, enabling one-step addition of bioorthogonal nucleophiles and further applications in quantitative proteomics and cross-linking.
- Philipp Hartmann
- , Kostiantyn Bohdan
- & Tobias Ritter
-
Article |
 Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Activation of H2 by a metal–olefin complex is characterized experimentally and computationally using a nickel pincer complex, showing that the reaction proceeds via a direct ligand-to-ligand hydrogen transfer mechanism. An application of this cooperative H2-activation mechanism is demonstrated in the nickel-catalysed semihydrogenation of diphenylacetylene.
- María L. G. Sansores-Paredes
- , Martin Lutz
- & Marc-Etienne Moret
-
Article |
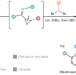 Modular synthesis of 1,2-azaborines via ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation
Modular synthesis of 1,2-azaborines via ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation
Preparation of monocyclic 1,2-azaborines, a unique class of benzene isosteres, has been challenging. Now, an efficient and modular method has been developed to access diverse multi-substituted 1,2-azaborines from readily available cyclopropyl imines/ketones and dibromoboranes. The reaction goes through an unusual ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation mechanism.
- Hairong Lyu
- , Thomas H. Tugwell
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 Iron(III)-based metalloradical catalysis for asymmetric cyclopropanation via a stepwise radical mechanism
Iron(III)-based metalloradical catalysis for asymmetric cyclopropanation via a stepwise radical mechanism
Cobalt(II) complexes of porphyrins have dominated the development of metalloradical catalysts. Now it has been shown that five-coordinate iron(III) complexes of porphyrins with an axial ligand are also potent metalloradical catalysts for olefin cyclopropanation. They are shown to react with different classes of diazo compounds via a stepwise radical mechanism.
- Wan-Chen Cindy Lee
- , Duo-Sheng Wang
- & X. Peter Zhang
-
News & Views |
 How polymers dance to the pulses of ultrasound
How polymers dance to the pulses of ultrasound
Scientists have been studying how polymers break in solutions for decades, but the mechanism by which chains are stretched to the point of covalent bond scission is not trivial. Now, an experiment series provides ample support for a dynamic model in which chains uncoil from end to middle, while concurrently relaxing.
- Charles E. Diesendruck
-
Article
| Open Access Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Pump–probe measurements conventionally achieve femtosecond time resolution for X-ray crystallography of reactive processes, but the measured structural dynamics are complex. Using coherent control techniques, we show that the ultrafast crystallographic differences of a fluorescent protein are dominated by ground-state vibrational processes that are unconnected to the photoisomerization reaction of the chromophore.
- Christopher D. M. Hutchison
- , James M. Baxter
- & Jasper J. van Thor
-
Article |
 Imaging of the charge-transfer reaction of spin–orbit state-selected Ar+(2P3/2) with N2 reveals vibrational-state-specific mechanisms
Imaging of the charge-transfer reaction of spin–orbit state-selected Ar+(2P3/2) with N2 reveals vibrational-state-specific mechanisms
Quantum state-to-state understanding of collisional charge transfer is a long-time goal of chemical dynamics. Now, using high-resolution molecular-beam experiments with spin–orbit state-selected ions and surface-hopping calculations, a vibrational-state-specific mechanism has been observed for the reaction Ar+(2P3/2) + N2 → Ar + N2+(v′, J′). Besides the well-known long-range harpooning mechanism, a hard-collision glory scattering mechanism was also identified.
- Guodong Zhang
- , Dandan Lu
- & Hong Gao
-
News & Views |
 Arene additions
Arene additions
Dipolar cycloadditions are excellent processes for generating heterocyclic systems from simple starting materials, but arenes as dipolarophiles have not been extensively explored. Now, the intramolecular dipolar cycloaddition of aromatic rings has been achieved using in situ generated diazoalkenes to produce bicyclic or tricyclic heterocycles.
- Abraham Ustoyev
- & Mitchell P. Croatt
-
Article
| Open Access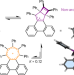 Rupturing aromaticity by periphery overcrowding
Rupturing aromaticity by periphery overcrowding
Stabilization from aromatic electron delocalization is highly favourable so it is typically preserved in even grossly distorted molecules. Now, peripheral overcrowding of an aromatic tropylium has been shown to cause sufficient geometric strain to rupture aromaticity, forming a non-aromatic bicyclic system that is in rapid equilibrium with its aromatic counterpart.
- Promeet K. Saha
- , Abhijit Mallick
- & Paul R. McGonigal
-
Article |
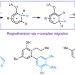 meta-Selective C–H arylation of phenols via regiodiversion of electrophilic aromatic substitution
meta-Selective C–H arylation of phenols via regiodiversion of electrophilic aromatic substitution
The strong regiochemical preferences of electrophilic aromatic substitution have played a key role in defining the diversity of accessible chemical space. Now, it has been shown that the electrophilic arylation of phenols can be achieved at the electronically disfavoured meta-position via a formal 1,2-migration of a key σ-complex intermediate.
- Aaron Senior
- , Katie Ruffell
- & Liam T. Ball
-
News & Views |
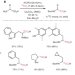 Enriched amino acids
Enriched amino acids
The direct carbon isotope exchange reaction on α-amino acids is highly desirable, as existing labelling methods require several synthetic steps and harsh conditions. Now, an aldehyde-catalysed carboxylate exchange with isotopically labelled *CO2 has enabled the direct formation of 11C, 13C and 14C-labelled α-amino acids.
- Karoline T. Neumann
- & Troels Skrydstrup
-
Article |
 Aldehyde-catalysed carboxylate exchange in α-amino acids with isotopically labelled CO2
Aldehyde-catalysed carboxylate exchange in α-amino acids with isotopically labelled CO2
Carbon-labelled α-amino acids are valuable compounds in drug development and nuclear medicine, but are difficult and time consuming to prepare. Now, an aldehyde-catalysed method has been developed for the direct C1-labelling of α-amino acids using *CO2 (* = 14, 13, 11), providing access to many proteinogenic and non-natural labelled α-amino acids.
- Odey Bsharat
- , Michael G. J. Doyle
- & Rylan J. Lundgren
-
News & Views |
 Isolating intermediates
Isolating intermediates
Noyori-type catalysts and inorganic bases are frequently used together for homogeneous hydrogenation, but key intermediates have not yet been isolated. Now, the structure and reactivity of a long-postulated intermediate — the alkali metal amidate complex — have been reported through experimental and computational studies.
- Pavel A. Dub
-
Article |
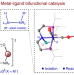 Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Noyori-type hydrogenation catalysts consist of an N–H moiety coordinated to a metal centre. Now, a metal-hydride amidate complex (HMn–NLi) has been isolated and found to have superior reactivity and catalytic performance compared with the corresponding HMn–NH complex, highlighting the superiority of M/NM′ bifunctional catalysis over the classic M/NH bifunctional catalysis for hydrogenation reactions.
- Yujie Wang
- , Shihan Liu
- & Qiang Liu
-
News & Views |
 Back to basics
Back to basics
Amines with free N–H groups have long posed a tremendous challenge in transition metal-catalysed amination reactions. Now, use of a bidentate phosphorus ligand enables the palladium-catalysed oxidative amination of simple olefins with Lewis basic amines, with no prefunctionalization, forming both alkyl and aryl allylamines.
- Logan E. Vine
- & Jennifer M. Schomaker
-
News & Views |
 Radical ring formation
Radical ring formation
N-heterocycles are valuable motifs in pharmaceuticals and materials, but divergent synthetic strategies are lacking. Now, bifunctional sulfilimines have been shown to form nitrogen-centred radicals under photocatalytic conditions, and subsequent coupling with olefins enables the synthesis of diverse N-heterocycles.
- Prabagar Baskaran
- & Wei Li
-
Article |
 Taming phosphorus mononitride
Taming phosphorus mononitride
Precursors for the release of phosphorus mononitride in solution under mild conditions have remained elusive. Now, an explosive anthracene-stabilized azidophosphine has shown PN transfer reactivity in the synthesis of an Fe–NP complex. The PN ligand is N-bonded, as the Fe–N interaction shows significant covalent character and a less unfavourable Pauli repulsion than its Fe–P counterpart.
- André K. Eckhardt
- , Martin-Louis Y. Riu
- & Christopher C. Cummins
-
News & Views |
 Complex networks at life’s origins
Complex networks at life’s origins
Explaining the controlled emergence and growth of molecular complexity at life’s origins is one of prebiotic chemistry’s grand challenges. Now, it has been shown that we can observe how the self-organization of a complex carbohydrate network can be modulated by its environment.
- Quentin Dherbassy
- & Kamila B. Muchowska
-
Article |
 Amino-oxetanes as amide isosteres by an alternative defluorosulfonylative coupling of sulfonyl fluorides
Amino-oxetanes as amide isosteres by an alternative defluorosulfonylative coupling of sulfonyl fluorides
Sulfonyl fluorides typically react with nucleophiles exclusively at sulfur, leading to the substitution of fluoride, as is the case in SuFEx reactions. Now, an alternative defluorosulfonylative reaction has been developed, coupling 3-aryloxetane sulfonyl fluorides with amines to generate amino-oxetanes. The mild conditions and high functional group tolerance enable the preparation of oxetane analogues of benzamide drugs via oxetane carbocation intermediates.
- Juan J. Rojas
- , Rosemary A. Croft
- & James A. Bull
-
Article |
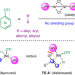 Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Without directing auxiliaries, the addition of carbogenic groups to unactivated alkenes is typically inefficient and suffers from poor regioselectivity. Now, a directing-group-free, nickel catalyst-controlled strategy has been developed, enabling the site-selective dicarbofunctionalization of a broad array of activated and unactivated alkenes.
- Hongyu Wang
- , Chen-Fei Liu
- & Ming Joo Koh
-
Article |
 Asymmetric dearomatization catalysed by chiral Brønsted acids via activation of ynamides
Asymmetric dearomatization catalysed by chiral Brønsted acids via activation of ynamides
Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis is mostly limited to the activation of imine and carbonyl moieties. Now, by direct activation of alkynes, chiral Brønsted acids have been used to enable the catalytic asymmetric dearomatization of naphthol-, phenol- and pyrrole-ynamides for the construction of various spirocyclic enones and 2H-pyrroles bearing a chiral quaternary carbon stereocentre.
- Ying-Qi Zhang
- , Yang-Bo Chen
- & Long-Wu Ye
-
Article |
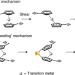 Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Distal conformational locks on ferrocene mechanophores guide reaction pathways for increased mechanochemical reactivity
Metallocenes are attractive mechanophores because they are stable in the absence of force, yet reactive under tension. Now, covalently bridging the two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) ligands of ferrocenes embedded in a polymer has been shown to alter their mechanochemical reactivity, leading to a faster dissociation of the Fe–Cp bond, which occurs through a peeling mechanism rather than a shearing one.
- Yudi Zhang
- , Zi Wang
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article |
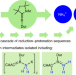 One-pot, room-temperature conversion of dinitrogen to ammonium chloride at a main-group element
One-pot, room-temperature conversion of dinitrogen to ammonium chloride at a main-group element
The vast majority of species capable of converting dinitrogen to ammonia rely on transition metals. Now, a boron compound has been shown to mediate the one-pot binding, cleavage and reduction of N2 to ammonium salts under mild conditions through a complex cascade mechanism involving multiple reduction–protonation sequences.
- Marc-André Légaré
- , Guillaume Bélanger-Chabot
- & Holger Braunschweig
-
Article |
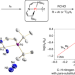 A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
A platinum(ii) metallonitrene with a triplet ground state
Transient metallonitrenes (M–N) have been proposed as key intermediates in nitrogen atom transfer reactions, but well-defined examples have remained elusive. Now, a platinum complex with an atomic nitrogen ligand, best described as a subvalent nitrogen diradical singly bonded to a platinum(ii) ion (Pt–N), has been isolated and shows ambiphilic reactivity.
- Jian Sun
- , Josh Abbenseth
- & Sven Schneider
-
Article |
 Three concomitant C–C dissociation pathways during the mechanical activation of an N-heterocyclic carbene precursor
Three concomitant C–C dissociation pathways during the mechanical activation of an N-heterocyclic carbene precursor
Chemical reactions usually proceed through either a radical, concerted or ionic mechanism; transformations in which all three mechanisms occur are rare. Now, the mechanical dissociation of an N-heterocyclic carbene precursor has been shown to proceed with the rupture of a C–C bond through concomitant heterolytic, concerted and homolytic pathways.
- Robert Nixon
- & Guillaume De Bo
-
Article |
 Demystifying the asymmetry-amplifying, autocatalytic behaviour of the Soai reaction through structural, mechanistic and computational studies
Demystifying the asymmetry-amplifying, autocatalytic behaviour of the Soai reaction through structural, mechanistic and computational studies
The discovery of amplifying autocatalysis in a pyridine-3-carbaldehyde system facilitates a mechanistic deconstruction of the Soai reaction. A tetrameric autocatalyst, assembled by a combination of steric effects and nitrogen–zinc coordination, activates the substrate by two-point binding. This is followed by intra-complex isopropyl group transfer that generates the product alkoxide with high homochiral fidelity.
- Soumitra V. Athavale
- , Adam Simon
- & Scott E. Denmark
-
Article |
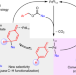 Connecting remote C–H bond functionalization and decarboxylative coupling using simple amines
Connecting remote C–H bond functionalization and decarboxylative coupling using simple amines
A catalytic para-selective alkylation reaction connects C–H functionalization and decarboxylative coupling strategies using simple bases to trap a previously hidden intermediate. This reaction exploits an ‘inverted sequence’ that forms the C–C bond prior to C–H bond cleavage and provides a new entry into C–H functionalization reactions.
- Francisco de Azambuja
- , Ming-Hsiu Yang
- & Ryan A. Altman
-
Article |
 Differentiation and functionalization of remote C–H bonds in adjacent positions
Differentiation and functionalization of remote C–H bonds in adjacent positions
Distinguishing remote C–H bonds on adjacent carbon atoms is a fundamental challenge because of a lack of electronic or steric bias. Now, differentiation of distal C–H bonds that are adjacent to each other has been achieved by combining selective remote C–H activation—based on distance and geometry—with a norbornene-assisted palladium migration.
- Hang Shi
- , Yi Lu
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
News & Views |
 Heavy metal orchestration
Heavy metal orchestration
Many current methods to prepare 2-hydroxybiaryls require the prefunctionalization of phenol groups or show limited substrate scope. Now, use of a pentavalent sulfone-bridged bismacycle, formed in situ by telescoped boron-to-bismuth transmetallation and oxidation, allows the direct and regioselective ortho-arylation of unprotected phenols.
- Adrien Le Roch
- & Alexandre Gagnon
-
News & Views |
 Delving into dynamic effects
Delving into dynamic effects
Although the application of force to induce chemical transformations is an active area of research, detailed understanding of these mechanochemical pathways is still lacking. Now, the mechanochemical activation of [4]-ladderane has been studied and found to exhibit unique non-equilibrium dynamic effects.
- Vincenzo Lordi
-
Article |
 Modular bismacycles for the selective C–H arylation of phenols and naphthols
Modular bismacycles for the selective C–H arylation of phenols and naphthols
Step-economic access to the biologically relevant 2-hydroxybiaryl motif represents a long-standing challenge in synthetic organic chemistry. Now, a bismuth-mediated oxidative arylation of phenols and naphthols with boronic acids has been developed — supported by experimental mechanistic insight — giving a direct and practical route to this valuable molecular architecture.
- Mark Jurrat
- , Lorenzo Maggi
- & Liam T. Ball
-
Article |
 Nickel-catalysed anti-Markovnikov hydroarylation of unactivated alkenes with unactivated arenes facilitated by non-covalent interactions
Nickel-catalysed anti-Markovnikov hydroarylation of unactivated alkenes with unactivated arenes facilitated by non-covalent interactions
The anti-Markovnikov hydroarylation of unactivated alkenes with unactivated arenes has been achieved with high selectivity by using nickel catalysts bearing large N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Energy decomposition analysis indicates that the high activity of the catalysts with large carbene ligands arises from stabilizing non-covalent interactions rather than steric effects.
- Noam I. Saper
- , Akito Ohgi
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
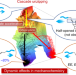 The cascade unzipping of ladderane reveals dynamic effects in mechanochemistry
The cascade unzipping of ladderane reveals dynamic effects in mechanochemistry
The mechanochemical activation of [4]-ladderane/ene has been studied and found to exhibit cascade unzipping and a consistent stereochemical distribution of products under various conditions and in different polymer backbones. Ab initio steered molecular dynamics simulations revealed unique non-equilibrium dynamic effects in the mechanochemistry of ladderane, cascade activation and reaction pathway bifurcation.
- Zhixing Chen
- , Xiaolei Zhu
- & Yan Xia
-
Article |
 Asymmetric redox-neutral radical cyclization catalysed by flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases
Asymmetric redox-neutral radical cyclization catalysed by flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases
Flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases have now been shown to catalyse redox-neutral radical cyclizations of α-haloamides to form enantioenriched oxindoles. Mechanistic studies indicate the reaction proceeds via the flavin semiquinone/quinone redox couple, where a ground state flavin semiquinone provides the electron for substrate reduction and flavin quinone oxidizes the radical formed after cyclization.
- Michael J. Black
- , Kyle F. Biegasiewicz
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Article |
 Energy threshold for chiral symmetry breaking in molecular self-replication
Energy threshold for chiral symmetry breaking in molecular self-replication
Asymmetric autocatalysis—such as that observed experimentally in the Soai reaction—may have been responsible for the origin of biological homochirality. The magnitude of the energy imbalance required to induce directed symmetry breaking and asymmetric amplification in the Soai reaction has now been identified and compared to the parity violation energy difference.
- Neil A. Hawbaker
- & Donna G. Blackmond
-
Article |
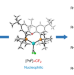 Controllable catalytic difluorocarbene transfer enables access to diversified fluoroalkylated arenes
Controllable catalytic difluorocarbene transfer enables access to diversified fluoroalkylated arenes
Difluorocarbene transfer is mostly limited to reactions that utilize its intrinsic electrophilicity. Now, a controllable palladium-catalysed difluorocarbene transfer reaction is reported that involves nucleophilic and electrophilic palladium difluorocarbene species. The selective reactions between arylboronic acids and the difluorocarbene precursor BrCF2PO(OEt)2 give four different products—difluoromethylated and tetrafluoroethylated arenes and their corresponding fluoroalkylated ketones.
- Xia-Ping Fu
- , Xiao-Song Xue
- & Xingang Zhang
-
News & Views |
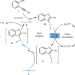 Golden potential
Golden potential
Due to the high oxidation potential of gold, the development of dual gold/photoredox-catalysed processes has been limited by the need for an easily reduced radical source. Now, discovery of an energy transfer photoexcitation process overcomes this limitation, enabling the oxidative addition of iodoalkynes onto organogold intermediates.
- Euan B. McLean
- & Ai-Lan Lee
-
Article |
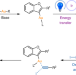 Photosensitized oxidative addition to gold(i) enables alkynylative cyclization of o-alkylnylphenols with iodoalkynes
Photosensitized oxidative addition to gold(i) enables alkynylative cyclization of o-alkylnylphenols with iodoalkynes
Studies into gold-catalysed cross-coupling reactions have expanded over recent decades; however, oxidative addition to gold(i) complexes remains challenging. Now it has been shown that a dual catalytic transformation involving iridium photosensitization to trigger oxidative addition to organogold intermediates enables C(sp2)–C(sp) cross-coupling reactions that are useful for the alkynylation of benzofurans.
- Zhonghua Xia
- , Vincent Corcé
- & Louis Fensterbank
-
Article |
 Structural basis for stereoselective dehydration and hydrogen-bonding catalysis by the SAM-dependent pericyclase LepI
Structural basis for stereoselective dehydration and hydrogen-bonding catalysis by the SAM-dependent pericyclase LepI
LepI is an S-adenosylmethionine-dependent pericyclase that catalyses the dehydration, hetero-Diels–Alder reaction and retro-Claisen rearrangement reactions that occur in the formation of the 2-pyridone natural product leporin C. Now, the mechanistic details that underpin this range of catalytic reactions have been uncovered from the crystal structures of LepI and LepI in complex with ligands.
- Yujuan Cai
- , Yang Hai
- & Yi Tang
-
Article |
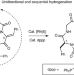 Hydrogenation catalyst generates cyclic peptide stereocentres in sequence
Hydrogenation catalyst generates cyclic peptide stereocentres in sequence
A simple amino acid can be recognized by a synthetic catalyst in a process that initiates the sequential reduction of cyclic dehydropeptides. An experimental and theoretical study provides evidence for a unique mechanism that involves unidirectional reduction to set four stereocentres around a macrocyclic ring.
- Diane N. Le
- , Eric Hansen
- & Vy M. Dong
-
Article |
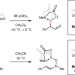 Amine hemilability enables boron to mechanistically resemble either hydride or proton
Amine hemilability enables boron to mechanistically resemble either hydride or proton
Mechanistic studies of the hemilability of MIDA (N-methyliminodiacetic acid) boronates reveal the chameleonic behaviour of the BMIDA group. The superior migratory aptitude of BMIDA compared to hydride and the capacity to resemble a proton when nitrogen decoordinates from boron have now been exploited for the design of new boron transfer reactions.
- C. Frank Lee
- , Diego B. Diaz
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Article |
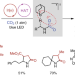 Direct α-alkylation of primary aliphatic amines enabled by CO2 and electrostatics
Direct α-alkylation of primary aliphatic amines enabled by CO2 and electrostatics
CO2 can be used as an activator for the direct transformation of abundant and unprotected primary aliphatic amines into valuable γ-lactams under photoredox and hydrogen-atom-transfer catalysis. Electrostatic interactions between the in situ generated alkylammonium carbamate and the positively charged quinuclidinium radical lead to regioselective hydrogen atom abstraction.
- Juntao Ye
- , Indrek Kalvet
- & Tomislav Rovis
-
Article |
 Concerted nucleophilic aromatic substitutions
Concerted nucleophilic aromatic substitutions
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions have long been thought to occur primarily via stepwise mechanisms. New and sensitive methodology for measuring carbon kinetic isotope effects now shows that most such substitutions actually occur through concerted mechanisms.
- Eugene E. Kwan
- , Yuwen Zeng
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
Article |
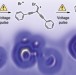 Polyyne formation via skeletal rearrangement induced by atomic manipulation
Polyyne formation via skeletal rearrangement induced by atomic manipulation
Atomic manipulation was used to control the reductive rearrangement of 1,1-dibromo alkenes to acetylenes on a NaCl surface at 5 K, and the stages of the reaction were visualized with atomic resolution using AFM. Polyynes ranging from triyne to octayne were prepared in this way, and STM was used to map their frontier orbitals and determine their transport gaps.
- Niko Pavliček
- , Przemyslaw Gawel
- & Leo Gross
-
Article |
 Catalytic promiscuity enabled by photoredox catalysis in nicotinamide-dependent oxidoreductases
Catalytic promiscuity enabled by photoredox catalysis in nicotinamide-dependent oxidoreductases
Enzymes are powerful catalysts for chemical synthesis because they are capable of providing unparalleled levels of selectivity; however, in nature they only catalyse a limited collection of reactions. Now, it has been shown that non-natural reactions that proceed via free-radical intermediates can be catalysed with high selectivity by using an exogenous photoredox catalyst in conjunction with enzymes.
- Kyle F. Biegasiewicz
- , Simon J. Cooper
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Article |
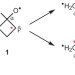 Labelling and determination of the energy in reactive intermediates in solution enabled by energy-dependent reaction selectivity
Labelling and determination of the energy in reactive intermediates in solution enabled by energy-dependent reaction selectivity
Short-lived intermediates in solution may react before undergoing thermal equilibration. This phenomenon is used here to achieve the ‘energy labelling’ of an alkoxy radical. The intermediate's excess energy varies broadly depending on how it is formed and can be determined from the observed reaction selectivity.
- Hiroaki Kurouchi
- & Daniel A. Singleton
-
Article |
 Iridium-catalysed arylation of C–H bonds enabled by oxidatively induced reductive elimination
Iridium-catalysed arylation of C–H bonds enabled by oxidatively induced reductive elimination
The direct arylation of C–H bonds is an attractive synthetic step, but the reductive elimination of an organometallic catalyst carrying the desired C–H and aryl functionalities has remained challenging. Now, this step has been achieved by first oxidizing the iridium centre of the catalyst, which facilitates the arylation of arene C–H bonds of a range of substrates.
- Kwangmin Shin
- , Yoonsu Park
- & Sukbok Chang
-
News & Views |
 Three is the magic number
Three is the magic number
Although predicted many years ago, chemically reactive termolecular reactions were thought to be unimportant in defining the behaviour of combustion systems. Now, calculations have shown that such reactions between radicals and long-lived bimolecular complexes can actually play an important role in hydrogen combustion.
- Rex T. Skodje

 Exploring the frontiers of condensed-phase chemistry with a general reactive machine learning potential
Exploring the frontiers of condensed-phase chemistry with a general reactive machine learning potential