Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access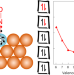 Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Single-atom alloys have emerged as highly active and selective catalysts that do not follow the traditional models of heterogeneous catalysis. Now it has been shown that the binding of adsorbates at their surface abides by a simple 10-electron count rule, which can identify promising catalysts for various applications.
- Julia Schumann
- , Michail Stamatakis
- & Romain Réocreux
-
Article |
 Structural characterization and reactivity of a room-temperature-stable, antiaromatic cyclopentadienyl cation salt
Structural characterization and reactivity of a room-temperature-stable, antiaromatic cyclopentadienyl cation salt
The synthesis, structure and reactivity of room-temperature-stable [Cp(C6F5)5]+[Sb3F16]− is presented. Coordination of the cyclopentadienyl cation by [Sb3F16]− or C6F6 stabilizes the antiaromatic singlet state in the solid state. Calculated hydride and fluoride ion affinities of the [Cp(C6F5)5]+ cation are higher than those of the tritylium cation [C(C6F5)3]+.
- Yannick Schulte
- , Christoph Wölper
- & Stephan Schulz
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
Article
| Open Access Janus-type emission from a cyclometalated iron(iii) complex
Janus-type emission from a cyclometalated iron(iii) complex
Noble metals dominate the field of photosensitizers and luminophores. Now, an approach incorporating cyclometalating and carbene functions into FeIII complexes has been shown to enable dual emission from the opposing ligand-to-metal and metal-to-ligand charge-transfer states. The latter shows an exceptionally long lifetime of 4.6 ns and is quenched by oxygen and other quenchers.
- Jakob Steube
- , Ayla Kruse
- & Matthias Bauer
-
Article
| Open Access φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
φ-Aromaticity in prismatic {Bi6}-based clusters
Aromaticity is a ubiquitous concept in organic chemistry yet it is less widespread for inorganic species. Now the cluster [(CpRu)3Bi6]–, obtained as part of a soluble salt, has been shown to exhibit aromatic behaviour referred to as φ-type, owing to a highly regular {Bi6} substructure causing a non-localizable molecular orbital of \(f_{z^3}\)-like symmetry.
- Benjamin Peerless
- , Andreas Schmidt
- & Stefanie Dehnen
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under an ambient atmosphere using a porous coordination polymer with bridging dinitrogen anions
The nitrogen reduction reaction is an extremely valuable but energy-intensive process. Now, a coordination polymer based on a [Zn–N2–Zn] unit has been shown to promote the formation of ammonia under ambient conditions by a photocatalytic reaction. The N2 moieties within the framework are reduced, creating unsaturated [Zn2+···Zn+] intermediates that are able to capture external N2 and sustain the cycle.
- Yan Xiong
- , Bang Li
- & Zhong Jin
-
News & Views |
 Isolating intermediates
Isolating intermediates
Noyori-type catalysts and inorganic bases are frequently used together for homogeneous hydrogenation, but key intermediates have not yet been isolated. Now, the structure and reactivity of a long-postulated intermediate — the alkali metal amidate complex — have been reported through experimental and computational studies.
- Pavel A. Dub
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Synthesis of a low-valent Al4+ cluster cation salt
Although neutral and anionic low-valent aluminium complexes are widespread, their cationic counterparts have remained rare. Now, a salt of [Al(AlCp*)3]+ featuring a formal low-valent Al+ cation has been isolated that dimerizes in concentrated solutions and the solid state, and also forms Al4 clusters on coordinating with Lewis bases.
- Philipp Dabringhaus
- , Julie Willrett
- & Ingo Krossing
-
Article |
 Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Most chemical glycosylation methods operate by acid-promoted, ionic activation of donors. Now, by exploiting the formation of a halogen-bond complex, the activation of glycosyl donors was achieved via a visible light-promoted radical cascade process, resulting in a general, simple and mild way to build challenging 1,2-cis-glycosidic bonds.
- Chen Zhang
- , Hao Zuo
- & Dawen Niu
-
Article |
 A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
A 9.2-GHz clock transition in a Lu(II) molecular spin qubit arising from a 3,467-MHz hyperfine interaction
The s-orbital mixing into the spin-bearing d orbital associated with a molecular Lu(II) complex is shown to both reduce spin–orbit coupling and increase electron–nuclear hyperfine interactions, which substantially improves electron spin coherence. Combined with the potential to tune interactions through coordination chemistry, it makes this system attractive for quantum information applications.
- Krishnendu Kundu
- , Jessica R. K. White
- & Stephen Hill
-
Article |
 Stereoelectronic effects in stabilizing protein–N-glycan interactions revealed by experiment and machine learning
Stereoelectronic effects in stabilizing protein–N-glycan interactions revealed by experiment and machine learning
Analysis of the thermodynamics of protein–N-glycan interactions perturbed by mutations has revealed an enthalpy–entropy compensation that depends on the electronics of the interacting side chains. Machine-learned and statistical models showed that protein–N-glycan interactions highly correlate with stereoelectronic effects, and that a major part of protein–N-glycan interactions can be explained using the energetic rules of frontier molecular orbital interactions.
- Maziar S. Ardejani
- , Louis Noodleman
- & Jeffery W. Kelly
-
Article |
 Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions
Unlike ferrocene and its cationic counterpart ferrocenium, the ferrocene monoanion is an unusual species that has been observed through low-temperature electrochemical studies. Now, a family of isostructural 3d metallocenates has been isolated that consists of a manganocene, a cobaltocene and a high-spin ferrocene anion stabilized by cyclopentadienyl ligands bearing bulky aliphatic groups.
- Conrad A. P. Goodwin
- , Marcus J. Giansiracusa
- & David P. Mills
-
News & Views |
 Fixing Jacob's ladder
Fixing Jacob's ladder
Density functional theory calculations can be carried out with different levels of accuracy, forming a hierarchy that is often represented by the rungs of a ladder. Now a new method has been developed that significantly improves the accuracy of the 'third rung' when calculating the properties of diversely bonded systems.
- Roberto Car
-
Article |
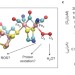 Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
FeFe hydrogenases are highly efficient H2 producing enzymes; however, they can be inactivated by O2. Now, a mechanism for O2 diffusion within FeFe hydrogenases and its reactions at the active site of the enzyme has been proposed. These findings could help with the design of hydrogenase mutants with increased resistance to oxidative damage.
- Adam Kubas
- , Christophe Orain
- & Christophe Léger
-
Article |
 Accurate first-principles structures and energies of diversely bonded systems from an efficient density functional
Accurate first-principles structures and energies of diversely bonded systems from an efficient density functional
Whether a molecule or material can exist, and with what structures and energies, is of critical importance. For demanding calculations the efficiency of density functional theory makes it the only practical electronic structure theory available to help answer these questions. Now, an efficient density functional is shown to have unprecedented accuracy for a diverse set of bonded systems.
- Jianwei Sun
- , Richard C. Remsing
- & John P. Perdew
-
Article |
 The structural and chemical origin of the oxygen redox activity in layered and cation-disordered Li-excess cathode materials
The structural and chemical origin of the oxygen redox activity in layered and cation-disordered Li-excess cathode materials
The chemistry of the transition metals within the oxide cathodes of lithium-ion batteries typically limits their capacity, however, reversible oxygen redox could potentially break this limit. It is now demonstrated that Li-excess and cation disorder create specific environments around oxygen atoms that lead to labile oxygen electrons that participate in the practical capacity of cathodes.
- Dong-Hwa Seo
- , Jinhyuk Lee
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
News & Views |
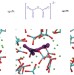 Catch the carbon dioxide
Catch the carbon dioxide
Understanding the minute details of CO2 transport is key to finding new technologies that reduce the hazardous levels of CO2 in our atmosphere. Now, the observation that the transport of CO2 in molten calcium carbonate occurs faster than standard molecular diffusion brings us one step closer.
- Barbara Kirchner
- & Barbara Intemann
-
Article |
 Carbon dioxide transport in molten calcium carbonate occurs through an oxo-Grotthuss mechanism via a pyrocarbonate anion
Carbon dioxide transport in molten calcium carbonate occurs through an oxo-Grotthuss mechanism via a pyrocarbonate anion
The solvation behaviour of CO2 in carbonate melts is important from both a geochemical point of view and with respect to its electroreduction. Now, simulations have shown that solvation of CO2 in molten CaCO3 leads to the formation of the pyrocarbonate anion, C2O52–, which significantly enhances the transport of CO2 via a Grotthuss-like mechanism.
- Dario Corradini
- , François-Xavier Coudert
- & Rodolphe Vuilleumier
-
Article |
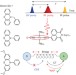 On the mechanism of vibrational control of light-induced charge transfer in donor–bridge–acceptor assemblies
On the mechanism of vibrational control of light-induced charge transfer in donor–bridge–acceptor assemblies
The ultrafast and mode-specific infrared excitation of several donor–bridge–acceptor (DBA) assemblies in solution has been shown to modulate their light-induced electron transfer properties. New insights are afforded into the role of vibrational processes immediately following light absorption in charge-transfer molecules and a recipe for efficient ‘vibrational control’ of electron transfer is proposed.
- Milan Delor
- , Theo Keane
- & Julia A. Weinstein
-
-
Article |
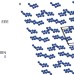 Calculations predict a stable molecular crystal of N8
Calculations predict a stable molecular crystal of N8
Polynitrogen compounds are of interest on a fundamental level and as potential high-energy-density materials. A crystalline solid that consists of two isomeric forms of N8 molecules held together by weak van der Waals interactions has now been predicted to exist, and to be stable even at low pressures.
- Barak Hirshberg
- , R. Benny Gerber
- & Anna I. Krylov
-
-
News & Views |
 Beyond state I
Beyond state I
Although caesium is well known in its oxidation state +I, many chemists have speculated about a possible higher state. Such a species has not yet been prepared, but based on quantum-chemical calculations CsFn compounds have now been predicted to be stable.
- Sebastian Riedel
- & Peter Schwerdtfeger
-
News & Views |
 A bright future for defects
A bright future for defects
Covalently bonding groups to the walls of carbon nanotubes has been previously observed to quench their photoluminescence. Now, it has been shown that, if you get the chemistry just right, their photoluminescence can in fact be significantly brightened by introducing defects through functionalization.
- Qing Hua Wang
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Caesium in high oxidation states and as a p-block element
Caesium in high oxidation states and as a p-block element
Caesium has so far not been found in oxidation states higher than +1, but quantum chemical calculations have now shown that, under high pressures, 5p inner shell electrons of caesium can participate in — and become the main components of — bonds. Caesium is predicted to form stable CsFn molecules that resemble isoelectronic XeFn.
- Mao-sheng Miao
-
Article |
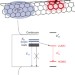 Brightening of carbon nanotube photoluminescence through the incorporation of sp3 defects
Brightening of carbon nanotube photoluminescence through the incorporation of sp3 defects
The controlled functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes has been shown to brighten their photoluminescence up to 28 times, which challenges our current understanding of how chemical defects affect low-dimensional carbon materials. This significantly improved photon conversion efficiency promises to advance a broad range of optoelectronic and imaging applications based on carbon nanotubes.
- Yanmei Piao
- , Brendan Meany
- & YuHuang Wang

 The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene
The anti-aromatic dianion and aromatic tetraanion of [18]annulene Molecular doormen
Molecular doormen