Featured
-
-
Comment |
 A UK perspective on tackling the geoscience racial diversity crisis in the Global North
A UK perspective on tackling the geoscience racial diversity crisis in the Global North
Geoscientists will play key roles in the grand challenges of the twenty-first century, but this requires our field to address its past when it comes to diversity and inclusion. Considering the bleak picture of racial diversity in the UK, we put forward steps institutions can take to break down barriers and make the geosciences equitable.
- Natasha Dowey
- , Jenni Barclay
- & Rebecca Williams
-
Article |
 Subslab heterogeneity and giant megathrust earthquakes
Subslab heterogeneity and giant megathrust earthquakes
Mantle heterogeneity beneath subducting plates may influence giant megathrust earthquakes, according to seismic tomography of the subslab structure beneath six megathrusts that have ruptured in M ≥ 9.0 earthquakes.
- Jianke Fan
- & Dapeng Zhao
-
Article |
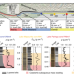 Spatiotemporal clustering of great earthquakes on a transform fault controlled by geometry
Spatiotemporal clustering of great earthquakes on a transform fault controlled by geometry
The rupture mode between major and great earthquakes is controlled by transform fault geometry, according to simulations of a reconstructed record of 20 palaeoearthquakes along the Alpine Fault, New Zealand.
- Jamie D. Howarth
- , Nicolas C. Barth
- & Rupert Sutherland
-
Article |
 Global dominance of tectonics over climate in shaping river longitudinal profiles
Global dominance of tectonics over climate in shaping river longitudinal profiles
Spatially varying uplift rates strongly influence the concavity of river profiles worldwide, with smaller contributions from hydrological factors, according to a comparison of river profile, tectonic and climatic datasets.
- Hansjörg Seybold
- , Wouter R. Berghuijs
- & James W. Kirchner
-
Editorial |
Hazard cascades
Interacting geological processes can cause complex hazard cascades that threaten life and property. Past events are instructive, but physical understanding must be paired with effective communication to minimize the risks posed by these events.
-
Article
| Open Access Co-variation of silicate, carbonate and sulfide weathering drives CO2 release with erosion
Co-variation of silicate, carbonate and sulfide weathering drives CO2 release with erosion
Unlike sulfide and carbonate, silicate weathering does not increase with physical erosion, which could result in a net release of carbon dioxide associated with uplift, according to stream-water chemistry of southern Taiwan.
- Aaron Bufe
- , Niels Hovius
- & Jui-Ming Chang
-
Article |
 Bedrock weathering contributes to subsurface reactive nitrogen and nitrous oxide emissions
Bedrock weathering contributes to subsurface reactive nitrogen and nitrous oxide emissions
Weathering of deep bedrock releases reactive nitrogen into the subsurface, which contributes to the flux of nitrous oxide to the atmosphere, according to a field study that combines soil, rock and groundwater data within a river catchment.
- Jiamin Wan
- , Tetsu K. Tokunaga
- & Kenneth H. Williams
-
News & Views |
 Magma behaving brittly
Magma behaving brittly
Low viscosities may not preclude brittle magma fragmentation under certain conditions, according to field observations and experimental evidence that suggest the conditions for brittle fragmentation may be met in many explosive mafic eruptions.
- Emma J. Liu
-
Article |
 Fracturing and healing of basaltic magmas during explosive volcanic eruptions
Fracturing and healing of basaltic magmas during explosive volcanic eruptions
In explosive basaltic eruptions, brittle fragmentation and subsequent healing by viscous melt are documented by textural analysis of products from ten disparate eruptions, suggesting that grain size may not reflect the initial fracture density of magma.
- J. Taddeucci
- , C. Cimarelli
- & F. Di Stefano
-
Article |
 Brittle fragmentation by rapid gas separation in a Hawaiian fountain
Brittle fragmentation by rapid gas separation in a Hawaiian fountain
In a Hawaiian fountain eruption, rapid gas expansion cools the melt below the glass transition temperature and causes brittle magma fragmentation, producing small, vesicular pyroclasts, according to observations of the 2018 eruption of Kīlauea.
- Atsuko Namiki
- , Matthew R. Patrick
- & Bruce F. Houghton
-
Article |
 Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Mountain glacier growth around the Mediterranean repeatedly stalled during cold, dry Heinrich Stadials, according to an analysis of cosmogenic isotope-dated glacial landforms from across the region.
- James L. Allard
- , Philip D. Hughes
- & Jamie C. Woodward
-
Article |
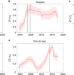 Large-scale thermal unrest of volcanoes for years prior to eruption
Large-scale thermal unrest of volcanoes for years prior to eruption
Large-scale radiant heat flux increased in the years prior to eruptions at five volcanoes, probably due to enhanced underground hydrothermal activity, according to an analysis of satellite infrared data.
- Társilo Girona
- , Vincent Realmuto
- & Paul Lundgren
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogen dances in the deep mantle
Hydrogen dances in the deep mantle
Hydrogen ions move freely within the crystal structure of a hydrous mineral under lower mantle conditions, resulting in high electrical conductivity that may make it possible to map water in the deep mantle.
- Tetsuya Komabayashi
-
Article |
 Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle
Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle
Under conditions of Earth’s deep lower mantle, hydrogen ions diffuse freely through the FeOOH lattice framework and electrical conductivity increases rapidly, according to electrical conductivity experiments and first-principles simulations.
- Mingqiang Hou
- , Yu He
- & Ho-Kwang Mao
-
Article |
 Oceanic crustal flow in Iceland observed using seismic anisotropy
Oceanic crustal flow in Iceland observed using seismic anisotropy
The lower oceanic crust beneath Iceland is flowing and internally deforming, according to constraints on seismic anisotropy in the Icelandic crust from an analysis of seismic surface waves.
- Omry Volk
- , Robert S. White
- & Nicholas Rawlinson
-
News & Views |
 Fidelity of turbidites as earthquake records
Fidelity of turbidites as earthquake records
Turbidites record ground motion in the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake. Recent events are now revealing how turbidites record earthquakes, but turbidites are triggered in many ways, and testing if ancient turbidites are earthquake-triggered remains challenging.
- Peter J. Talling
-
Article |
 Calibrating the marine turbidite palaeoseismometer using the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake
Calibrating the marine turbidite palaeoseismometer using the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake
Marine turbidite deposition is confirmed to relate to earthquake ground motions by an analysis of turbidite deposits and simulations of ground motions from the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake.
- Jamie D. Howarth
- , Alan R. Orpin
- & M. Namik Cağatay
-
Article |
 Earth’s long-term climate stabilized by clouds
Earth’s long-term climate stabilized by clouds
Reduced planetary albedo due to fewer low clouds on early Earth could explain some 40% of the required forcing to offset the faint young Sun, according to global climate model experiments.
- Colin Goldblatt
- , Victoria L. McDonald
- & Kelly E. McCusker
-
Article |
 Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
The presence of large rivers in North Africa critical for Quaternary human migrations were controlled by a combination of orbital forcing and Mediterranean storminess, according to terrestrial proxy records from a marine core off Libya integrated with paleoclimate modelling.
- Cécile L. Blanchet
- , Anne H. Osborne
- & Martin Frank
-
Article |
 Postseismic geodetic signature of cold forearc mantle in subduction zones
Postseismic geodetic signature of cold forearc mantle in subduction zones
Deformation after large subduction earthquakes reflects the thermal contrast between the mantle wedge and its nose, according to numerical simulations and a synthesis of postseismic uplift data from subduction zones.
- Haipeng Luo
- & Kelin Wang
-
Article |
 Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Constraints on the denudation of the Southern Alps over the last glacial cycle indicate a nonlinear influence of climate on landscape evolution in glaciated areas, according to a beryllium isotope record measured from quartz in a sequence of Mediterranean turbidites.
- Apolline Mariotti
- , Pierre-Henri Blard
- & Karim Keddadouche
-
Article |
 Archaean seafloors shallowed with age due to radiogenic heating in the mantle
Archaean seafloors shallowed with age due to radiogenic heating in the mantle
In contrast to present-day seafloor subsidence with age, there may have been Archaean seafloor shallowing and landmass exposure due to high internal heating in the mantle that halted subsidence, according to numerical models of mantle convection.
- Juan Carlos Rosas
- & Jun Korenaga
-
Article |
 Distinct slab interfaces imaged within the mantle transition zone
Distinct slab interfaces imaged within the mantle transition zone
Two seismic discontinuities in the mantle transition zone beneath the western Pacific represent subducted slab interfaces that could be the slab Moho and partially molten sub-slab asthenosphere, according to an analysis of seismic data.
- Xin Wang
- , Qi-Fu Chen
- & Lijun Liu
-
Article |
 Continuum of earthquake rupture speeds enabled by oblique slip
Continuum of earthquake rupture speeds enabled by oblique slip
Long fault ruptures that have both strike-slip and dip-slip components can propagate at a wide range of speeds, including those theoretically predicted to be unstable, according to numerical simulations.
- Huihui Weng
- & Jean-Paul Ampuero
-
Article |
 Active crustal differentiation beneath the Rio Grande Rift
Active crustal differentiation beneath the Rio Grande Rift
A link between post-thickening lithospheric extension and the differentiation of continental crust is implied by granulite conditions beneath the Rio Grande Rift, inferred from analysis of lower-crustal xenoliths and thermobarometric modelling.
- Jacob H. Cipar
- , Joshua M. Garber
- & Andrew J. Smye
-
News & Views |
 The magmatic forge
The magmatic forge
Time capsules of fluid, trapped within the oxide minerals from two iron ore deposits reveal an important role for sediment-derived carbonate–sulfate-rich melts in the concentration of iron, a crucial element for humanity’s development.
- James M. Brenan
-
Article |
 A fundamental role of carbonate–sulfate melts in the formation of iron oxide–apatite deposits
A fundamental role of carbonate–sulfate melts in the formation of iron oxide–apatite deposits
Iron-rich carbonate–sulfate melts are fundamental to the formation of iron oxide–apatite ore deposits, according to a detailed fluid-inclusion study that characterized the mineralizing fluids for two mineralizing systems in the United States.
- Wyatt M. Bain
- , Matthew Steele-MacInnis
- & Erin E. Marsh
-
News & Views |
 Inelastic earthquake damage
Inelastic earthquake damage
Permanent surface deformation caused by the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes has been directly measured, constraining the mechanics of surface damage in earthquakes.
- Wanpeng Feng
- & Rafael V. Almeida
-
Article |
 Localized fault-zone dilatancy and surface inelasticity of the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes
Localized fault-zone dilatancy and surface inelasticity of the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes
Inelastic failure in the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes was localized and influenced by mylonitic deformation of the fault damage zone, according to an analysis of surface displacements derived from satellite images.
- William D. Barnhart
- , Ryan D. Gold
- & James Hollingsworth
-
Article |
 Slip-rate-dependent friction as a universal mechanism for slow slip events
Slip-rate-dependent friction as a universal mechanism for slow slip events
A transition from rate-weakening to rate-strengthening frictional behaviour with increasing slip rate could explain the observed diversity of slow slip events on faults, according to numerical simulations.
- Kyungjae Im
- , Demian Saffer
- & Jean-Philippe Avouac
-
Article |
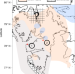 A nutrient control on marine anoxia during the end-Permian mass extinction
A nutrient control on marine anoxia during the end-Permian mass extinction
Phosphorus remobilized from seafloor sediments due to a reduced influx of iron-oxide from land led to widespread anoxia during the end-Permian mass extinction, according to palaeoredox and phosphorus speciation proxy records from Svalbard.
- Martin Schobben
- , William J. Foster
- & Simon W. Poulton
-
Article |
 Back-propagating supershear rupture in the 2016 Mw 7.1 Romanche transform fault earthquake
Back-propagating supershear rupture in the 2016 Mw 7.1 Romanche transform fault earthquake
In one earthquake, an oceanic transform fault ruptured in one direction and then backwards at a speed exceeding that of shear-wave propagation, according to an analysis of data recorded by nearby seafloor and global seismometers.
- Stephen P. Hicks
- , Ryo Okuwaki
- & Henriette Sudhaus
-
Article |
 The state of rock debris covering Earth’s glaciers
The state of rock debris covering Earth’s glaciers
A global map of rock-debris cover on mountain glaciers shows its spatial distribution and evolution.
- Sam Herreid
- & Francesca Pellicciotti
-
Review Article |
 Materials and pathways of the organic carbon cycle through time
Materials and pathways of the organic carbon cycle through time
A review of the organic carbon cycle explores the interactions between the Earth’s surface and deeper reservoirs, the expanding inorganic controls on the organic carbon cycle, and how these links have strengthened through geological time.
- Matthieu E. Galvez
- , Woodward W. Fischer
- & Timothy I. Eglinton
-
News & Views |
 Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
The Archaean atmosphere may have been well oxygenated, according to a reconsideration of sulfur cycling at that time. This challenges the view that sedimentary sulfur records oxygen-poor conditions during Earth’s first two billion years.
- Desiree Roerdink
-
Article |
 Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Increased river incision and landscape erosion can be attributed to late Cenozoic cooling/changes in hydroclimate, according to cosmogenic isotope and luminescence ages of a sequence of bedrock terraces in the Yukon River basin.
- Adrian M. Bender
- , Richard O. Lease
- & Tammy M. Rittenour
-
Article |
 Preferential localized thinning of lithospheric mantle in the melt-poor Malawi Rift
Preferential localized thinning of lithospheric mantle in the melt-poor Malawi Rift
The mantle lithosphere has thinned more than the crust beneath the Malawi Rift despite being melt-poor, according to seismic wave imaging; this suggests early melting of fusible mantle material.
- Emily Hopper
- , James B. Gaherty
- & Gabriel Mbogoni
-
Article |
 A seawater-sulfate origin for early Earth’s volcanic sulfur
A seawater-sulfate origin for early Earth’s volcanic sulfur
Formation of mass-independent isotope fractionation of sulfur signatures recorded in Archaean sedimentary rocks could have occurred in an oxygen-rich atmosphere, according to thermodynamic and kinetic calculations and analysis of Earth’s early sulfur cycle.
- Hiroshi Ohmoto
-
Article |
 Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus
Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus
Thermomechanical modelling shows that the formation and diverse morphologies of coronae on Venus can be explained by interactions between the lithosphere and impinging mantle plumes. Some corona structures are consistent with ongoing plume activity.
- Anna J. P. Gülcher
- , Taras V. Gerya
- & Jessica Munch
-
Article |
 Mud in rivers transported as flocculated and suspended bed material
Mud in rivers transported as flocculated and suspended bed material
Fast settling rates of suspended silt and clay particles suggest that mud in rivers is largely flocculated and part of suspended bed-material load.
- Michael P. Lamb
- , Jan de Leeuw
- & Gary Parker
-
News & Views |
 Plate tectonics from crust to core
Plate tectonics from crust to core
Compositional signatures of subducted crust in the deep-mantle sources of ocean island volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean but not the Pacific reveal that plate motions on Earth’s surface influence the characteristics of Earth’s deepest interior.
- Richard W. Carlson
-
Article |
 Global distribution of sediment-hosted metals controlled by craton edge stability
Global distribution of sediment-hosted metals controlled by craton edge stability
Major sediment-hosted base metal deposits are located within 200 km of the border between thick and thin lithosphere, according to statistical comparisons between global lithospheric thickness and known deposit locations.
- Mark J. Hoggard
- , Karol Czarnota
- & Sia Ghelichkhan
-
Article |
 Weak magnetic field changes over the Pacific due to high conductance in lowermost mantle
Weak magnetic field changes over the Pacific due to high conductance in lowermost mantle
High conductance in the lowermost mantle beneath the Pacific deflects the planetary gyre, which results in limited variation in the magnetic field in the region, according to numerical modelling of Earth’s core dynamics.
- Mathieu Dumberry
- & Colin More
-
Article |
 Distinct formation history for deep-mantle domains reflected in geochemical differences
Distinct formation history for deep-mantle domains reflected in geochemical differences
Earth’s deep-mantle domains are geochemically distinct. The African domain is enriched in subducted material, which suggests a different history from the Pacific domain and a dynamic relationship between plate tectonics and deep-mantle structures.
- Luc S. Doucet
- , Zheng-Xiang Li
- & Ross N. Mitchell
-
Article |
 Deep-sea eruptions boosted by induced fuel–coolant explosions
Deep-sea eruptions boosted by induced fuel–coolant explosions
Interactions between magma and water can drive explosive fragmentation eruptions of the type seen in the Havre volcanic eruption, New Zealand, in 2012, even under submarine conditions, according to laboratory fragmentation experiments.
- T. Dürig
- , J. D. L. White
- & N. Spitznagel
-
-
Article |
 Steady erosion rates in the Himalayas through late Cenozoic climatic changes
Steady erosion rates in the Himalayas through late Cenozoic climatic changes
Long-term Himalayan erosion rates remained stable through the global climatic changes of the past six million years, according to the cosmogenic nuclide composition of terrestrial sediments recovered from the Bay of Bengal.
- Sebastien J. P. Lenard
- , Jérôme Lavé
- & Karim Keddadouche
-
Article |
 The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core may host most of the planet’s water inventory, according to calculations of the partitioning behaviour of water at conditions of core formation.
- Yunguo Li
- , Lidunka Vočadlo
- & John P. Brodholt
-
Perspective |
 Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust
Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust
Migration of water from the slab to the surface during subduction is highlighted as a key process in the formation of continental crust.
- William J. Collins
- , J. Brendan Murphy
- & Hui-Qing Huang

 Topographic stress control on bedrock landslide size
Topographic stress control on bedrock landslide size