Featured
-
-
Perspective |
 Geological evidence for multiple climate transitions on Early Mars
Geological evidence for multiple climate transitions on Early Mars
Early Mars did not experience a single wet-to-dry transition, but seven such shifts in its palaeoclimatic history, as argued based on the planet’s stratigraphy, mineralogy and geomorphology.
- Edwin S. Kite
- & Susan Conway
-
Article |
 Coevolving aerodynamic and impact ripples on Earth
Coevolving aerodynamic and impact ripples on Earth
Wind tunnel experiments and numerical modelling reveal the existence of two distinct ripples on Earth: centimetre-scale impact ripples and decimetre-scale hydrodynamic ripples, akin to those in water and on Mars.
- Hezi Yizhaq
- , Katharina Tholen
- & Itzhak Katra
-
Comment |
 The case for a lunar anthropocene
The case for a lunar anthropocene
Human exploration of the Solar System began on the Moon during the space race of the mid-twentieth century. To facilitate documentation and study of the human influence on the Moon, we argue it is time to designate a ‘Lunar Anthropocene’.
- Justin Allen Holcomb
- , Rolfe David Mandel
- & Karl William Wegmann
-
Article
| Open Access Antarctic Peninsula glaciation patterns set by landscape evolution and dynamic topography
Antarctic Peninsula glaciation patterns set by landscape evolution and dynamic topography
Spatially distinct ice-sheet growth on the Antarctic Peninsula through the Pleistocene was the result of dynamic topography and pre-glacial landscape evolution, not climate, according to a palaeotopographic reconstruction and ice-sheet modelling.
- Matthew Fox
- , Anna Clinger
- & Frederic Herman
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread small grabens consistent with recent tectonism on Mercury
Widespread small grabens consistent with recent tectonism on Mercury
The widespread occurrence of young grabens associated with larger compressional structures on Mercury’s surface suggests contractional tectonism has continued on the planet into geologically recent times.
- Benjamin Man
- , David A. Rothery
- & Jack Wright
-
Research Briefing |
 The sinuosity patterns of lowland meandering rivers on Earth and Mars
The sinuosity patterns of lowland meandering rivers on Earth and Mars
Two contrasting sinuosity patterns were identified in lowland rivers on Earth and Mars. The channel sinuosity either substantially increases or remains constant towards the coast. These bimodal patterns reflect the age of the channels and their lateral migration rates, which are associated with sediment supply and discharge variability.
-
Article |
 Lowland river sinuosity on Earth and Mars set by the pace of meandering and avulsion
Lowland river sinuosity on Earth and Mars set by the pace of meandering and avulsion
Spatial patterns of channel sinuosity near river outlets reflect the interplay between the channel migration rate and the avulsion timescale, according to sinuosity measurements of lowland rivers on Earth and Mars and channel evolution simulations.
- Chenliang Wu
- , Wonsuck Kim
- & An Li
-
Article
| Open Access Himalayan valley-floor widths controlled by tectonically driven exhumation
Himalayan valley-floor widths controlled by tectonically driven exhumation
Himalayan valley-floor widths are controlled by long-term tectonically driven exhumation, rather than by water discharge, according to an analysis of valley-floor width and exhumation rate observations.
- Fiona J. Clubb
- , Simon M. Mudd
- & Hugh D. Sinclair
-
News & Views |
 Mantle driven mountains
Mantle driven mountains
Deciphering the contribution of mantle convection to Earth’s surface elevation remains challenging, but it may have a dominant influence on mountain-building at subduction zones, according to a new study reconstructing the topographic evolution of Calabria.
- Gregory A. Ruetenik
-
Article |
 Calabrian forearc uplift paced by slab–mantle interactions during subduction retreat
Calabrian forearc uplift paced by slab–mantle interactions during subduction retreat
Interactions between subducting slabs and the 660-km mantle transition zone can influence mantle convection and forearc uplift, according to rock uplift histories of the Calabrian forearc spanning the past 30 million years.
- Sean F. Gallen
- , Nikki M. Seymour
- & Paul O’Sullivan
-
Article
| Open Access Mixing dynamics at river confluences governed by intermodal behaviour
Mixing dynamics at river confluences governed by intermodal behaviour
Mixing dynamics at river confluences where shallow flows merge in rivers consist of switching between wake and mixing-layer modes, as shown in theoretical and field-scale physical modelling.
- A. N. Sukhodolov
- , O. O. Shumilova
- & B. L. Rhoads
-
Article |
 Acceleration of a large deep-seated tropical landslide due to urbanization feedbacks
Acceleration of a large deep-seated tropical landslide due to urbanization feedbacks
A large, slow-moving landslide underlying the city of Bukavu in the Democratic Republic of the Congo has accelerated in recent decades due to hydrological modifications related to urbanization, according to an analysis of aerial photographs and remote-sensing data.
- Antoine Dille
- , Olivier Dewitte
- & François Kervyn
-
Article
| Open Access Fraser Island (K'gari) and initiation of the Great Barrier Reef linked by Middle Pleistocene sea-level change
Fraser Island (K'gari) and initiation of the Great Barrier Reef linked by Middle Pleistocene sea-level change
Disruption of sediment flows along the eastern Australia coast due to the Middle Pleistocene formation of Fraser Island set the stage for Great Barrier Reef initiation, according to optically stimulated luminescence and palaeomagnetic dating of sand dunes.
- D. Ellerton
- , T. M. Rittenour
- & X. Zhao
-
Article |
 Martian landscapes of fluvial ridges carved from ancient sedimentary basin fill
Martian landscapes of fluvial ridges carved from ancient sedimentary basin fill
Numerical simulations of the exhumation of basin-filling river deposits suggest that ridge networks observed in Martian landscapes may represent erosional windows into sedimentary basins on Mars.
- Benjamin T. Cardenas
- , Michael P. Lamb
- & John P. Grotzinger
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon and sediment fluxes inhibited in the submarine Congo Canyon by landslide-damming
Carbon and sediment fluxes inhibited in the submarine Congo Canyon by landslide-damming
Bathymetric surveys of the submarine Congo Canyon show damming by canyon-flank landslides led to the temporary storage of substantial masses of sediment and organic carbon, interrupting their transport to the deep sea.
- Ed L. Pope
- , Maarten S. Heijnen
- & Morelia Urlaub
-
Article |
 Forest vulnerability to drought controlled by bedrock composition
Forest vulnerability to drought controlled by bedrock composition
Spatial variability in forest dieback during the severe drought in California between 2011 and 2017 can be explained by variations in bedrock composition and thus weatherability, according to analyses of the drought responses a series of geologically distinct sites.
- Russell P. Callahan
- , Clifford S. Riebe
- & W. Steven Holbrook
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid retreat of Thwaites Glacier in the pre-satellite era
Rapid retreat of Thwaites Glacier in the pre-satellite era
The Thwaites Glacier grounding zone has experienced sustained pulses of rapid retreat over the past two centuries, according to sea floor observations obtained by an autonomous underwater vehicle.
- Alastair G. C. Graham
- , Anna Wåhlin
- & Robert D. Larter
-
News & Views |
 Islands on the move
Islands on the move
Sea level rise causes barrier islands to migrate landward. Coastal evolution modelling reveals a centennial-scale lag in island response time and suggests migration rates will increase by 50% within the next century, even if sea level were to stabilize.
- Laura J. Moore
- & A. Brad Murray
-
Article |
 Lag in response of coastal barrier-island retreat to sea-level rise
Lag in response of coastal barrier-island retreat to sea-level rise
Coastal evolution simulations suggest that the modern retreat of coastal barrier islands is controlled by cumulative sea-level rise over the past several centuries and will accelerate by 50% within a century, even if sea-level rise remains at present rates.
- Giulio Mariotti
- & Christopher J. Hein
-
Editorial |
 Rumbling rubble-pile asteroids
Rumbling rubble-pile asteroids
Recent missions to the rubble-pile asteroids Bennu and Ryugu have revealed asteroid surfaces that continue to be actively modified by a variety of processes while also recording the geologic history of these small bodies.
-
Article
| Open Access Relative sea-level data preclude major late Holocene ice-mass change in Pine Island Bay
Relative sea-level data preclude major late Holocene ice-mass change in Pine Island Bay
The Pine Island Glacier, a locus of ice loss from the modern West Antarctic Ice Sheet, had previously been stable since at least the mid-Holocene, according to records tracking ice extent based on radiocarbon and cosmogenic exposure dating.
- Scott Braddock
- , Brenda L. Hall
- & John Woodward
-
News & Views |
 A weak and active surface of Bennu
A weak and active surface of Bennu
The surface of the asteroid Bennu is so weakly bonded that rockslide avalanches are easily triggered by small body impacts, and boulders fractured due to diurnal heating and cooling are readily dislodged. The result is a surface under continuous renewal.
- Masahiko Arakawa
-
Article |
 Low surface strength of the asteroid Bennu inferred from impact ejecta deposit
Low surface strength of the asteroid Bennu inferred from impact ejecta deposit
Observations of deposits associated with a crater on the rubble-pile asteroid Bennu indicate a surface with low strength that is readily reworked by impact processes.
- M. E. Perry
- , O. S. Barnouin
- & D. S. Lauretta
-
Article |
 Alignment of fractures on Bennu’s boulders indicative of rapid asteroid surface evolution
Alignment of fractures on Bennu’s boulders indicative of rapid asteroid surface evolution
Fractures on the asteroid Bennu imaged by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft are consistent with cracking induced by diurnal temperature variations over geologically rapid timescales.
- Marco Delbo
- , Kevin J. Walsh
- & Dante S. Lauretta
-
Article |
 Crater population on asteroid (101955) Bennu indicates impact armouring and a young surface
Crater population on asteroid (101955) Bennu indicates impact armouring and a young surface
Boulder armouring inhibits small-crater formation on the rubble-pile asteroid Bennu, substantially reducing surface age estimates, according to an analysis of the crater size–frequency distribution.
- E. B. Bierhaus
- , D. Trang
- & D. S. Lauretta
-
Article |
 Surface characteristics of the Zhurong Mars rover traverse at Utopia Planitia
Surface characteristics of the Zhurong Mars rover traverse at Utopia Planitia
Analysis of interactions between the wheels of the Zhurong rover and the terrain along the rover’s traverse reveals soils with high bearing strength and cohesion.
- L. Ding
- , R. Zhou
- & K. Di
-
Article |
 Tributary channel networks formed by depositional processes
Tributary channel networks formed by depositional processes
Drainage divides between coastal plain channel networks can be constructed through depositional, rather than erosional, processes according to a lidar-based topographic analysis of the Gulf of Mexico coastal plain.
- John M. Swartz
- , Benjamin T. Cardenas
- & Paola Passalacqua
-
Article |
 Contribution of background seismicity to forearc uplift
Contribution of background seismicity to forearc uplift
Frequent and dispersed small earthquakes may contribute substantially to uplift of subduction margins, according to an analysis of such seismicity in the Peru–Chile and Japan margins.
- Andrea Madella
- & Todd A. Ehlers
-
News & Views |
 Stressed rocks cause big landslides
Stressed rocks cause big landslides
Near-surface stress patterns, influenced by topography, control the size and location of the largest landslides — but not necessarily smaller ones — according to a study of mountains at the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau.
- Peter van der Beek
-
Article |
 Topographic stress control on bedrock landslide size
Topographic stress control on bedrock landslide size
Stress from tectonics and topography may be the primary control on the size of bedrock landslides, according to a comparison of a stress model with landslide inventories for a mountainous area in eastern Tibet.
- Gen K. Li
- & Seulgi Moon
-
Article |
 Global dominance of tectonics over climate in shaping river longitudinal profiles
Global dominance of tectonics over climate in shaping river longitudinal profiles
Spatially varying uplift rates strongly influence the concavity of river profiles worldwide, with smaller contributions from hydrological factors, according to a comparison of river profile, tectonic and climatic datasets.
- Hansjörg Seybold
- , Wouter R. Berghuijs
- & James W. Kirchner
-
Editorial |
Hazard cascades
Interacting geological processes can cause complex hazard cascades that threaten life and property. Past events are instructive, but physical understanding must be paired with effective communication to minimize the risks posed by these events.
-
Article
| Open Access Co-variation of silicate, carbonate and sulfide weathering drives CO2 release with erosion
Co-variation of silicate, carbonate and sulfide weathering drives CO2 release with erosion
Unlike sulfide and carbonate, silicate weathering does not increase with physical erosion, which could result in a net release of carbon dioxide associated with uplift, according to stream-water chemistry of southern Taiwan.
- Aaron Bufe
- , Niels Hovius
- & Jui-Ming Chang
-
Article |
 Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Mountain glacier growth around the Mediterranean repeatedly stalled during cold, dry Heinrich Stadials, according to an analysis of cosmogenic isotope-dated glacial landforms from across the region.
- James L. Allard
- , Philip D. Hughes
- & Jamie C. Woodward
-
Article |
 Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Constraints on the denudation of the Southern Alps over the last glacial cycle indicate a nonlinear influence of climate on landscape evolution in glaciated areas, according to a beryllium isotope record measured from quartz in a sequence of Mediterranean turbidites.
- Apolline Mariotti
- , Pierre-Henri Blard
- & Karim Keddadouche
-
Article |
 Post-impact cryo-hydrologic formation of small mounds and hills in Ceres’s Occator crater
Post-impact cryo-hydrologic formation of small mounds and hills in Ceres’s Occator crater
Mounds within Ceres’s Occator crater may have formed by freezing of water-rich impact-induced melt, by a process analogous to that of pingo formation on Earth, according to an analysis of data from NASA’s Dawn mission.
- B. E. Schmidt
- , H. G. Sizemore
- & C. T. Russell
-
Article |
 The state of rock debris covering Earth’s glaciers
The state of rock debris covering Earth’s glaciers
A global map of rock-debris cover on mountain glaciers shows its spatial distribution and evolution.
- Sam Herreid
- & Francesca Pellicciotti
-
Article |
 Valley formation on early Mars by subglacial and fluvial erosion
Valley formation on early Mars by subglacial and fluvial erosion
Some valleys in the southern highlands of Mars may have formed by subglacial erosion, consistent with a cold and icy early Mars, according to a statistical analysis of valley morphometry.
- Anna Grau Galofre
- , A. Mark Jellinek
- & Gordon R. Osinski
-
Article |
 Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Increased river incision and landscape erosion can be attributed to late Cenozoic cooling/changes in hydroclimate, according to cosmogenic isotope and luminescence ages of a sequence of bedrock terraces in the Yukon River basin.
- Adrian M. Bender
- , Richard O. Lease
- & Tammy M. Rittenour
-
Article |
 Mud in rivers transported as flocculated and suspended bed material
Mud in rivers transported as flocculated and suspended bed material
Fast settling rates of suspended silt and clay particles suggest that mud in rivers is largely flocculated and part of suspended bed-material load.
- Michael P. Lamb
- , Jan de Leeuw
- & Gary Parker
-
Article |
 Geomorphological evidence for a dry dust avalanche origin of slope streaks on Mars
Geomorphological evidence for a dry dust avalanche origin of slope streaks on Mars
Patterns of erosion and deposition by some slope streaks on Mars are consistent with a dry dust avalanche origin, according to an analysis of orbital images before and after new streaks formed.
- Colin M. Dundas
-
Article |
 Experimental evidence for lava-like mud flows under Martian surface conditions
Experimental evidence for lava-like mud flows under Martian surface conditions
Experimental mudflows under Martian surface conditions propagate similarly to terrestrial pahoehoe lava flows, suggesting mud (rather than igneous) volcanism can explain some flow morphologies on Mars.
- Petr Brož
- , Ondřej Krýza
- & Manish R. Patel
-
Article |
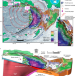 Earthquakes and tsunamis caused by low-angle normal faulting in the Banda Sea, Indonesia
Earthquakes and tsunamis caused by low-angle normal faulting in the Banda Sea, Indonesia
Low-angle normal faults in the Banda Sea have caused large earthquakes that indirectly generated tsunamis due to earthquake-triggered submarine slumping, according to an analysis of historical earthquake and tsunami events and GPS observations.
- Phil R. Cummins
- , Ignatius R. Pranantyo
- & Siyuan Zhao
-
Perspective |
 Initial results from the InSight mission on Mars
Initial results from the InSight mission on Mars
Geophysical and meteorological measurements by NASA’s InSight lander on Mars reveal a planet that is seismically active and provide information about the interior, surface and atmospheric workings of Mars.
- W. Bruce Banerdt
- , Suzanne E. Smrekar
- & Mark Wieczorek
-
Article |
 Constraints on the shallow elastic and anelastic structure of Mars from InSight seismic data
Constraints on the shallow elastic and anelastic structure of Mars from InSight seismic data
The crust beneath the InSight lander on Mars is altered or fractured to 8–11 km depth and may bear volatiles, according to an analysis of seismic noise and wave scattering recorded by InSight’s seismometer.
- P. Lognonné
- , W. B. Banerdt
- & P. Zweifel
-
Article |
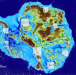 Deep glacial troughs and stabilizing ridges unveiled beneath the margins of the Antarctic ice sheet
Deep glacial troughs and stabilizing ridges unveiled beneath the margins of the Antarctic ice sheet
A high-resolution update of Antarctic bed topography using mass conservation reveals broad stabilizing ridges for glaciers flowing across the Transantarctic Mountains, and stabilizing slopes beneath Moscow University, Totten and Lambert glacier system.
- Mathieu Morlighem
- , Eric Rignot
- & Duncan A. Young
-
Article |
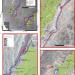 Irrigation-triggered landslides in a Peruvian desert caused by modern intensive farming
Irrigation-triggered landslides in a Peruvian desert caused by modern intensive farming
Slow-moving landslides in two valleys in Peru were initiated by irrigation programmes in the region, suggest analyses of 40 years of satellite data.
- Pascal Lacroix
- , Amaury Dehecq
- & Edu Taipe
-
Article |
 A tenfold slowdown in river meander migration driven by plant life
A tenfold slowdown in river meander migration driven by plant life
River meanders migrate much faster in barren than in vegetated landscapes, according to global analyses of active meander migration of both unvegetated and vegetated rivers. The difference in migration rates suggests that the rise of land plants had a significant influence on landscapes.
- Alessandro Ielpi
- & Mathieu G. A. Lapôtre
-

 Critical turbidity thresholds for maintenance of estuarine tidal flats worldwide
Critical turbidity thresholds for maintenance of estuarine tidal flats worldwide Penitente formation is unlikely on Europa
Penitente formation is unlikely on Europa