News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Hazardous explosive eruptions of a recharging multi-cyclic island arc caldera
Hazardous explosive eruptions of a recharging multi-cyclic island arc caldera
Evidence for a past large explosive eruption within the Santorini caldera suggests that early stages of silicic caldera cycles can be more hazardous than previously assumed, according to analyses of intra-caldera deposits from the Kameni Volcano.
- Jonas Preine
- , Jens Karstens
- & Dimitrios Papanikolaou
-
Article |
 Stress-driven recurrence and precursory moment-rate surge in caldera collapse earthquakes
Stress-driven recurrence and precursory moment-rate surge in caldera collapse earthquakes
The initiation and rupture extent of earthquakes are controlled by stress heterogeneity, according to analysis of seismicity and deformation during caldera collapse of Kilauea Volcano.
- Paul Segall
- , Mark V. Matthews
- & Kyle R. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Mercury fluxes from hydrothermal venting at mid-ocean ridges constrained by measurements
Mercury fluxes from hydrothermal venting at mid-ocean ridges constrained by measurements
Hydrothermal venting makes limited contribution to the inventory of oceanic mercury compared with anthropogenic inputs, according to measurements at mid-ocean ridges.
- Natalia Torres-Rodriguez
- , Jingjing Yuan
- & Lars-Eric Heimbürger-Boavida
-
Research Briefing |
 The Shatsky Rise oceanic plateau formed through plume–ridge interaction
The Shatsky Rise oceanic plateau formed through plume–ridge interaction
There are two competing hypotheses for the origin of oceanic plateaus: plume versus plate. Thermodynamic modelling of magmatism at Shatsky Rise, in the Pacific Ocean, now suggests that neither mechanism is adequate on its own and in fact plume–ridge interaction is required to explain the formation of this ocean plateau.
-
Article |
 Magmatism of Shatsky Rise controlled by plume–ridge interaction
Magmatism of Shatsky Rise controlled by plume–ridge interaction
Thermodynamic simulations suggest that Shatsky Rise magmatism is controlled by the interaction between mantle plume and mid-ocean ridge.
- Xubo Zhang
- , Eric L. Brown
- & William W. Sager
-
Matters Arising |
 Sensitivity of Santorini eruption model predictions to input conditions
Sensitivity of Santorini eruption model predictions to input conditions
- R. J. Walker
- , S. P. A. Gill
- & T. L. Stephens
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: Sensitivity of Santorini eruption model predictions to input conditions
- A. Gudmundsson
- , M. Bazargan
- & C. Satow
-
Article
| Open Access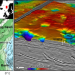 Shallow-water hydrothermal venting linked to the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
Shallow-water hydrothermal venting linked to the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
Widespread shallow-water hydrothermal venting in the North Atlantic, probably a source of methane, coincided with the onset of the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum, according to borehole proxy records and seismic imaging.
- Christian Berndt
- , Sverre Planke
- & Stacy L. Yager
-
Article |
 A primary magmatic source of nitrogen to Earth’s crust
A primary magmatic source of nitrogen to Earth’s crust
The formation of continental crust may have trapped —and thus not degassed—substantial amounts of magmatic nitrogen over Earth’s history, according to geochemical analyses of igneous rocks from the Hekla volcanic system in Iceland.
- Toby J. Boocock
- , Sami Mikhail
- & Eva E. Stüeken
-
Article |
 Large-scale volcanic deposit fluidization by dilute pyroclastic density currents
Large-scale volcanic deposit fluidization by dilute pyroclastic density currents
Fine-grained pyroclastic deposits can be fluidized by decompression following the passage of dilute pyroclastic density currents, generating hazardous, highly mobile flows, according to analogue experiments and numerical simulations.
- Karim Kelfoun
- & Antonio Proaño
-
Research Briefing |
 Underwater terraced deposits chronicle volcanic eruptions
Underwater terraced deposits chronicle volcanic eruptions
Analogue experiments show that powerful eruption columns deliver material to the sea surface and seabed in periodic annular sedimentation waves. Depending on the water depth, the impact and spread of these waves at the sea surface and seabed can excite tsunamis, drive radial pyroclastic density currents, and build concentric terraces.
-
Article |
 Submarine terraced deposits linked to periodic collapse of caldera-forming eruption columns
Submarine terraced deposits linked to periodic collapse of caldera-forming eruption columns
Submarine terraced deposits of some caldera-forming explosive eruptions result from periodic collapses of the eruption column and can be used to estimate their source eruption rate, according to an analysis of such terraces and analogue experiments.
- Johan T. Gilchrist
- , A. Mark Jellinek
- & Sean Wanket
-
News & Views |
 Eruptions from the deep
Eruptions from the deep
Long-lasting eruptions of some subduction zone volcanoes may be regulated by their magma sources in the mantle. This suggests that direct connections between the mantle and surface are possible through a relatively thick crust.
- Jorge E. Romero
-
Article |
 Arc volcano activity driven by small-scale metasomatism of the magma source
Arc volcano activity driven by small-scale metasomatism of the magma source
Small-scale compositional alteration of the mantle wedge by fluids may regulate eruptive activity of individual arc volcanoes, according to an analysis of the isotopic composition of ashes erupted by Tungurahua volcano in Ecuador from 1999 to 2016.
- I. Vlastélic
- , N. Sainlot
- & A. Gannoun
-
Article |
 Increasing complexity in magmatic architecture of volcanoes along a waning hotspot
Increasing complexity in magmatic architecture of volcanoes along a waning hotspot
Intraplate volcanoes erupt lower volumes of more diverse magma and have increasingly complex magmatic architectures as the heat flux from the driving mantle plume wanes, according to an analysis of a continental hotspot chain in eastern Australia.
- A. T. Tapu
- , T. Ubide
- & P. M. Vasconcelos
-
Article |
 The magmatic architecture and evolution of the Chang’e-5 lunar basalts
The magmatic architecture and evolution of the Chang’e-5 lunar basalts
The lunar basalts sampled by the Chang’e-5 mission originated from melting of a clinopyroxene-rich mantle source enhanced in radioactive elements, potentially explaining this late lunar volcanism, according to sample analysis and crystallization modelling.
- Biji Luo
- , Zaicong Wang
- & Hongfei Zhang
-
Q&A |
 Digging into deep water
Digging into deep water
Nature Geoscience spoke with Dr Qingyang Hu, a high-pressure mineralogist at HPSTAR; Prof. Suzan van der Lee, a geophysicist at Northwestern University; and Prof. Katherine Kelley, a geochemist at the University of Rhode Island about their work and what the future of deep-water research might bring.
- Rebecca Neely
-
Editorial |
 Hazard perception
Hazard perception
A limited number of earthquakes and volcanoes, primarily located in global north countries, dominate the collective research output on these geohazards. Efforts to improve monitoring at both local and global levels can address this disparity and reduce the associated risk.
-
Article |
 Eruption at basaltic calderas forecast by magma flow rate
Eruption at basaltic calderas forecast by magma flow rate
Using magma inflow rate improves eruption forecasting on timescales of weeks to months for basaltic caldera systems, compared with using surface deformation alone, according to analysis of 45 unrest case studies and viscoelastic modelling.
- Federico Galetto
- , Valerio Acocella
- & Marco Bagnardi
-
Article |
 Transient mobilization of subcrustal carbon coincident with Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
Transient mobilization of subcrustal carbon coincident with Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
A change in the style of rifting in the North Atlantic led to carbon fluxes from subcrustal melting that helped trigger the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum, according to geochemical analyses of volcanic sequences as well as melting and tectonic modelling.
- Thomas M. Gernon
- , Ryan Barr
- & Martin R. Palmer
-
Article |
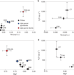 High water content of arc magmas recorded in cumulates from subduction zone lower crust
High water content of arc magmas recorded in cumulates from subduction zone lower crust
The water content of arc magmas in the lower crust can reach up to 20 wt% during crystallization, according to geochemical analyses of minerals from the Kohistan palaeo-arc, Pakistan, underscoring the role of water in porphyry deposits formation.
- B. M. Urann
- , V. Le Roux
- & E. J. Chin
-
News & Views |
 Flood basalt buildup warms climate
Flood basalt buildup warms climate
Flood basalts are connected to Earth’s most extreme environmental crises, yet warming is sometimes observed before surface eruptions. Modelling reveals that a complex buildup of basalt intrusions into the crust releases enough CO2 to cause this pre-eruptive warming.
- Jennifer Kasbohm
-
Article |
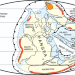 Pulses in silicic arc magmatism initiate end-Permian climate instability and extinction
Pulses in silicic arc magmatism initiate end-Permian climate instability and extinction
Pulses of silicic arc magmatism—and associated volatile emissions—helped set the timing and magnitude of the environmental disruptions that caused the end-Permian mass extinction, according to U–Pb zircon dating of silicic volcanic and related tephra sequences in eastern Australia.
- Timothy Chapman
- , Luke A. Milan
- & Jim Crowley
-
Article |
 Intrusions induce global warming before continental flood basalt volcanism
Intrusions induce global warming before continental flood basalt volcanism
Continental flood basalt emplacement is facilitated by basaltic intrusions, which crystalize and release carbon dioxide leading to pre-eruptive global warming, according to numerical models and a comparison with Deccan Traps and Columbia River Basalt records.
- Xiaochuan Tian
- & W. Roger Buck
-
Article |
 Cyclical geothermal unrest as a precursor to Iceland’s 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption
Cyclical geothermal unrest as a precursor to Iceland’s 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption
Ingression of magmatic gas into a geothermal aquifer generated cyclical deformation and primed the system for the 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption, Iceland, according to a catalogue of 39,500 precursory earthquakes combined with a poroelastic model.
- Ólafur G. Flóvenz
- , Rongjiang Wang
- & Claus Milkereit
-
Article
| Open Access Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Metasedimentary rocks atop the downgoing slab oxidize ascending slab-derived dehydration fluids by removing reduced species, according to petrological analysis of subduction complex metasedimentary rocks and reactive transport modelling.
- Jay J. Ague
- , Santiago Tassara
- & Timm John
-
Article |
 Deformation-controlled long-period seismicity in low-cohesion volcanic sediments
Deformation-controlled long-period seismicity in low-cohesion volcanic sediments
Long-period seismicity at volcanoes may be generated by deformation of weak material in the subsurface, not solely by fluid movement, according to rock deformation experiments.
- Pete Rowley
- , Philip M. Benson
- & Christopher J. Bean
-
Article |
 Explosive or effusive style of volcanic eruption determined by magma storage conditions
Explosive or effusive style of volcanic eruption determined by magma storage conditions
The effusive or explosive nature of a volcanic eruption may be determined by the crystallinity, water content and presence of exsolved volatiles in subvolcanic chambers, according to analysis of the pre-eruptive storage conditions of global volcanoes.
- Răzvan-Gabriel Popa
- , Olivier Bachmann
- & Christian Huber
-
Article |
 Birth of a large volcanic edifice offshore Mayotte via lithosphere-scale dyke intrusion
Birth of a large volcanic edifice offshore Mayotte via lithosphere-scale dyke intrusion
An ~5 km³ volcanic edifice offshore Mayotte formed between May 2018 and May 2019 by rapid magma intrusion through the entire lithosphere, according to an analysis of marine observations and geophysical data.
- Nathalie Feuillet
- , Stephan Jorry
- & Jérome Van der Woerd
-
Article |
 Carbon concentration increases with depth of melting in Earth’s upper mantle
Carbon concentration increases with depth of melting in Earth’s upper mantle
The carbon concentration of Earth’s upper mantle increases with depth, indicating a role for carbon in melt formation, according to data on magmatic gases and volcanic rocks from ocean island and continental rift settings around the world.
- Alessandro Aiuppa
- , Federico Casetta
- & Giancarlo Tamburello
-
Article |
 Eruptive activity of the Santorini Volcano controlled by sea-level rise and fall
Eruptive activity of the Santorini Volcano controlled by sea-level rise and fall
Sea-level lowstands over the last 360,000 years strongly controlled the timing of eruptions of the Santorini Volcano, according to an analysis of tephras and sea-level records, as well as numerical modelling of the underlying magma chamber.
- Chris Satow
- , Agust Gudmundsson
- & Mark Hardiman
-
Article |
 Rapid recycling of subducted sedimentary carbon revealed by Afghanistan carbonatite volcano
Rapid recycling of subducted sedimentary carbon revealed by Afghanistan carbonatite volcano
Sedimentary carbon is subducted to, and returned from, mantle depths in less than 27 million years, according strontium isotope analysis and geochronology of lavas from southern Afghanistan.
- Forrest Horton
-
Editorial |
Hazard cascades
Interacting geological processes can cause complex hazard cascades that threaten life and property. Past events are instructive, but physical understanding must be paired with effective communication to minimize the risks posed by these events.
-
News & Views |
 Magma behaving brittly
Magma behaving brittly
Low viscosities may not preclude brittle magma fragmentation under certain conditions, according to field observations and experimental evidence that suggest the conditions for brittle fragmentation may be met in many explosive mafic eruptions.
- Emma J. Liu
-
Article |
 Fracturing and healing of basaltic magmas during explosive volcanic eruptions
Fracturing and healing of basaltic magmas during explosive volcanic eruptions
In explosive basaltic eruptions, brittle fragmentation and subsequent healing by viscous melt are documented by textural analysis of products from ten disparate eruptions, suggesting that grain size may not reflect the initial fracture density of magma.
- J. Taddeucci
- , C. Cimarelli
- & F. Di Stefano
-
Article |
 Brittle fragmentation by rapid gas separation in a Hawaiian fountain
Brittle fragmentation by rapid gas separation in a Hawaiian fountain
In a Hawaiian fountain eruption, rapid gas expansion cools the melt below the glass transition temperature and causes brittle magma fragmentation, producing small, vesicular pyroclasts, according to observations of the 2018 eruption of Kīlauea.
- Atsuko Namiki
- , Matthew R. Patrick
- & Bruce F. Houghton
-
Article |
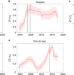 Large-scale thermal unrest of volcanoes for years prior to eruption
Large-scale thermal unrest of volcanoes for years prior to eruption
Large-scale radiant heat flux increased in the years prior to eruptions at five volcanoes, probably due to enhanced underground hydrothermal activity, according to an analysis of satellite infrared data.
- Társilo Girona
- , Vincent Realmuto
- & Paul Lundgren
-
News & Views |
 Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
The Archaean atmosphere may have been well oxygenated, according to a reconsideration of sulfur cycling at that time. This challenges the view that sedimentary sulfur records oxygen-poor conditions during Earth’s first two billion years.
- Desiree Roerdink
-
Article |
 Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus
Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus
Thermomechanical modelling shows that the formation and diverse morphologies of coronae on Venus can be explained by interactions between the lithosphere and impinging mantle plumes. Some corona structures are consistent with ongoing plume activity.
- Anna J. P. Gülcher
- , Taras V. Gerya
- & Jessica Munch
-
Article |
 Deep-sea eruptions boosted by induced fuel–coolant explosions
Deep-sea eruptions boosted by induced fuel–coolant explosions
Interactions between magma and water can drive explosive fragmentation eruptions of the type seen in the Havre volcanic eruption, New Zealand, in 2012, even under submarine conditions, according to laboratory fragmentation experiments.
- T. Dürig
- , J. D. L. White
- & N. Spitznagel
-
Article |
 Experimental evidence for lava-like mud flows under Martian surface conditions
Experimental evidence for lava-like mud flows under Martian surface conditions
Experimental mudflows under Martian surface conditions propagate similarly to terrestrial pahoehoe lava flows, suggesting mud (rather than igneous) volcanism can explain some flow morphologies on Mars.
- Petr Brož
- , Ondřej Krýza
- & Manish R. Patel
-
Article |
 Earth’s earliest granitoids are crystal-rich magma reservoirs tapped by silicic eruptions
Earth’s earliest granitoids are crystal-rich magma reservoirs tapped by silicic eruptions
The chemical diversity of Earth’s early continental building blocks can be explained by differentiation of a single melt, without complex geodynamic settings, according to petrological and geochemical analysis of samples from South Africa.
- Oscar Laurent
- , Jana Björnsen
- & Olivier Bachmann
-
News & Views |
 What goes down must come up
What goes down must come up
Differential cycling of carbonate and organic carbon in the mantle may link the Great Oxidation Event and the subsequent increase in carbon isotope values, according to a model that links the Earth’s surface and interior.
- Jeremy K. Caves Rugenstein
-
Article |
 Drainage of a deep magma reservoir near Mayotte inferred from seismicity and deformation
Drainage of a deep magma reservoir near Mayotte inferred from seismicity and deformation
Recent seismicity near Mayotte in the Indian Ocean is due to dyke propagation from and drainage of a 25–35 km deep magma reservoir, according to an analysis of earthquake and deformation data.
- Simone Cesca
- , Jean Letort
- & Torsten Dahm
-
Article |
 Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events linked by deep cycling and enhanced degassing of carbon
Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events linked by deep cycling and enhanced degassing of carbon
Carbon cycling in the mantle may be a common mechanism that links the Great Oxidation Event and the subsequent Lomagundi increase in carbon isotope values, according to a box model that accounts for carbon and oxygen fluxes and reservoirs.
- James Eguchi
- , Johnny Seales
- & Rajdeep Dasgupta
-
Article |
 Magma fragmentation in highly explosive basaltic eruptions induced by rapid crystallization
Magma fragmentation in highly explosive basaltic eruptions induced by rapid crystallization
Volcanoes that typically erupt effusively can generate highly explosive eruptions of basaltic lava under specific temperature and viscosity conditions, suggest crystallization experiments combined with numerical models of magma fragmentation.
- Fabio Arzilli
- , Giuseppe La Spina
- & Peter D. Lee
-
Article |
 Infrasound from giant bubbles during explosive submarine eruptions
Infrasound from giant bubbles during explosive submarine eruptions
During the submarine eruption of gas-rich magma into shallow water, a gas-tight seal forms, breaks and reseals, a process that results in violent explosions and the release of large gas bubbles, suggest low-frequency sound data from Bogoslof volcano, Alaska.
- John J. Lyons
- , Matthew M. Haney
- & Christopher F. Waythomas
-
News & Views |
 Building mountains on Ceres
Building mountains on Ceres
The large domes found on the dwarf planet Ceres may not result from cryovolcanism, but from solid-state flow analogous to salt doming on Earth, according to numerical simulations of gravitational loading.
- Michael Küppers
-
Article |
 Optimal depth of subvolcanic magma chamber growth controlled by volatiles and crust rheology
Optimal depth of subvolcanic magma chamber growth controlled by volatiles and crust rheology
Volatile exsolution and crustal viscosity dictate that the optimum pressure for the growth of an eruptible magma reservoir is 2 kbar in all tectonic settings and crustal compositions, according to thermomechanical modelling.
- Christian Huber
- , Meredith Townsend
- & Olivier Bachmann

 Underestimated volcanic hazard of Santorini
Underestimated volcanic hazard of Santorini