All Minerals Considered |
Featured
-
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Out of sight burbankite
Out of sight burbankite
Burbankite is a rare sodium carbonate mineral that is easily dissolved away in its host igneous rocks. Its formation and dissolution can help concentrate rare earth elements that are vital for a low-carbon future, as Sam Broom-Fendley explains.
- Sam Broom-Fendley
-
Comment |
 Seismic methodologies key to unlocking Earth’s lowermost mantle
Seismic methodologies key to unlocking Earth’s lowermost mantle
Advances in seismological observational and modelling techniques are needed to constrain complex lowermost mantle structures and understand their influence on the global dynamics and evolution of Earth’s interior.
- Lauren Waszek
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Phosphorus’s cosmic courier
Phosphorus’s cosmic courier
Schreibersite is found in meteorites and thought to dwell in planetary cores. Tingting Gu explains how it may also have supported life on the early Earth.
- Tingting Gu
-
Article |
 Detections of ultralow velocity zones in high-velocity lowermost mantle linked to subducted slabs
Detections of ultralow velocity zones in high-velocity lowermost mantle linked to subducted slabs
Global detections of ultralow velocity zones in high-velocity lowermost mantle regions are associated with thermochemical anomalies linked to subducted slabs, according to analysis of SKKKP B-caustic diffractions with anomalous seismic structures in the mantle and outer core.
- Yulong Su
- , Sidao Ni
- & Daoyuan Sun
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Amphibole interlocking into jade
Amphibole interlocking into jade
Nephrite jade is a semi-precious gemstone composed of tiny crystals and needles of amphibole. Here, Matthew Tarling and Steven Smith describe how its origins lead to inner toughness and beauty.
- Matthew S. Tarling
- & Steven A. F. Smith
-
Article |
 Regional rare-earth element supply and demand balanced with circular economy strategies
Regional rare-earth element supply and demand balanced with circular economy strategies
Mobilization of in-use rare-earth element stocks in regions of high consumption can ease dependence on regions of rare-earth extraction, according to dynamic integrated modelling combining material flow and scenario analysis.
- Peng Wang
- , Yu-Yao Yang
- & Wei-Qiang Chen
-
Article |
 A hydrogen-enriched layer in the topmost outer core sourced from deeply subducted water
A hydrogen-enriched layer in the topmost outer core sourced from deeply subducted water
Deeply subducted water may have enabled the exchange of hydrogen and silicon between the mantle and core, according to high-pressure and -temperature experiments.
- Taehyun Kim
- , Joseph G. O’Rourke
- & Yongjae Lee
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Carbonate’s fluid history
Carbonate’s fluid history
Carbonates are key minerals for understanding fluids and their interactions with near-surface environments. Ashley King explores their significance on Earth, and beyond.
- Ashley J. King
-
All Minerals Considered |
 The crystal timekeeper zircon
The crystal timekeeper zircon
Recording 4.3 billion years of Earth’s history, Jesse Reimink explores the many ways that zircon allows geologists to keep track of the past.
- Jesse Reimink
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Rutile’s fiery brilliance
Rutile’s fiery brilliance
From pressure indicator to paint brightener, Alicia Cruz-Uribe examines the many uses of rutile.
- Alicia M. Cruz-Uribe
-
Research Briefing |
 A curved post-garnet boundary enhances slab and plume dynamics in the Earth’s mantle
A curved post-garnet boundary enhances slab and plume dynamics in the Earth’s mantle
The post-garnet transition has been found to have a curved phase boundary, with negative slopes in cold regions and positive slopes in hot regions of the Earth’s mantle. This varying slope could be a reason for the puzzling dynamics of subducting slabs and upwelling plumes observed seismically in the upper part of the lower mantle.
-
Article |
 Buoyancy of slabs and plumes enhanced by curved post-garnet phase boundary
Buoyancy of slabs and plumes enhanced by curved post-garnet phase boundary
Experimental determination of how the post-garnet phase transition pressure varies with temperature suggests a downward-convex phase boundary with potential implications for mantle dynamics.
- Takayuki Ishii
- , Daniel J. Frost
- & Tomoo Katsura
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Garnet the gift that keeps on giving
Garnet the gift that keeps on giving
More than just a gemstone, Jon Pownall and Kathryn Cutts explore the history and future directions of garnet as a recorder of pressure, temperature, and time.
- Jonathan M. Pownall
- & Kathryn A. Cutts
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Scorched minerals in sedimentary rocks
Scorched minerals in sedimentary rocks
Inspired by the mineralogist Shulamit Gross’s studies of one of the world’s unique mineral factories, Michael Anenburg discusses the pyrometamorphic minerals formed by fire in the Dead Sea desert.
- Michael Anenburg
-
Article |
 Primordial helium extracted from the Earth’s core through magnesium oxide exsolution
Primordial helium extracted from the Earth’s core through magnesium oxide exsolution
Primordial helium in the deep mantle may be supplied continuously from Earth’s core, according to first-principles calculations and modelling of helium partitioning into exsolved magnesium oxide at core–mantle boundary conditions
- Jie Deng
- & Zhixue Du
-
Article |
 Increasing complexity in magmatic architecture of volcanoes along a waning hotspot
Increasing complexity in magmatic architecture of volcanoes along a waning hotspot
Intraplate volcanoes erupt lower volumes of more diverse magma and have increasingly complex magmatic architectures as the heat flux from the driving mantle plume wanes, according to an analysis of a continental hotspot chain in eastern Australia.
- A. T. Tapu
- , T. Ubide
- & P. M. Vasconcelos
-
Article |
 The magmatic architecture and evolution of the Chang’e-5 lunar basalts
The magmatic architecture and evolution of the Chang’e-5 lunar basalts
The lunar basalts sampled by the Chang’e-5 mission originated from melting of a clinopyroxene-rich mantle source enhanced in radioactive elements, potentially explaining this late lunar volcanism, according to sample analysis and crystallization modelling.
- Biji Luo
- , Zaicong Wang
- & Hongfei Zhang
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Tetrataenite’s magnetic personality
Tetrataenite’s magnetic personality
Following on from insights gleaned from iron meteorites, Claire Nichols explains why tetrataenite, with its unique magnetic properties, could be key for future renewable energy technologies.
- Claire I. O. Nichols
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Quartz for all time
Quartz for all time
From the tools of Stone Age ancestors to records of Earth’s history, Yang Li and Xian-Hua Li explore how the properties of quartz place it at the heart of human innovation.
- Yang Li
- & Xian-Hua Li
-
Article |
 Formation of manganese oxides on early Mars due to active halogen cycling
Formation of manganese oxides on early Mars due to active halogen cycling
Manganese oxidation experiments in Mars-like fluids suggest that chlorate and bromate may have been more effective oxidants of manganese on early Mars than atmospheric oxygen and explain observed manganese oxide deposits.
- Kaushik Mitra
- , Eleanor L. Moreland
- & Jeffrey G. Catalano
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Bridgmanite across the lower mantle
Bridgmanite across the lower mantle
Earth’s most abundant mineral — bridgmanite — lies hidden in the lower mantle, but Li Zhang is hopeful that advances in analytical techniques may reveal the inner workings of our world.
- Li Zhang
-
Article |
 Mineral-catalysed formation of marine NO and N2O on the anoxic early Earth
Mineral-catalysed formation of marine NO and N2O on the anoxic early Earth
Marine emissions of N2O could have sustained an early Archaean atmosphere of 0.8–6.0 ppb N2O without a protective ozone layer, according to mineral incubations combined with diffusion and photochemical modelling.
- Steffen Buessecker
- , Hiroshi Imanaka
- & Hinsby Cadillo-Quiroz
-
Article |
 Formation of oxidized sulfur-rich magmas in Neoarchaean subduction zones
Formation of oxidized sulfur-rich magmas in Neoarchaean subduction zones
Neoarchaean arc magmas in Superior Province, Canada, were relatively oxidized and sulfur rich, reaching compositions comparable to modern subduction zones by approximately 2.7 Ga, according to analysis of sulfur speciation in zircon-hosted apatite grains.
- Xuyang Meng
- , Adam C. Simon
- & Jeremy P. Richards
-
Q&A |
 Digging into deep water
Digging into deep water
Nature Geoscience spoke with Dr Qingyang Hu, a high-pressure mineralogist at HPSTAR; Prof. Suzan van der Lee, a geophysicist at Northwestern University; and Prof. Katherine Kelley, a geochemist at the University of Rhode Island about their work and what the future of deep-water research might bring.
- Rebecca Neely
-
Editorial |
 Deep Earth bound by water
Deep Earth bound by water
Research efforts from across the geosciences are uncovering how water deep within the Earth affects its fundamental workings.
-
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Cycles of serpentines
Cycles of serpentines
Jörg Hermann suggests that as the process of serpentinization leads to clean energy generation, metal separation and carbon sequestration, it could serve as a natural analogue for a sequential economy.
- Jörg Hermann
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Diamonds as windows to deep Earth
Diamonds as windows to deep Earth
Delving into recent and historical discoveries, Ananya Mallik explains how diamonds track the workings of the deep Earth that are hidden from view.
- Ananya Mallik
-
Editorial |
 Minerals matter
Minerals matter
Permeating every aspect of life – and each with a multitude of stories to tell – we celebrate the utility, beauty and wonder of minerals in a new column: all minerals considered.
-
Article |
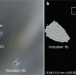 Hydrous peridotitic fragments of Earth’s mantle 660 km discontinuity sampled by a diamond
Hydrous peridotitic fragments of Earth’s mantle 660 km discontinuity sampled by a diamond
Hydrous conditions extend across the 660 km discontinuity between Earth’s mantle transition zone and lower mantle, according to analysis of a polyphase mineral inclusion in a gem diamond from the Karowe mine, Botswana
- Tingting Gu
- , Martha G. Pamato
- & Fabrizio Nestola
-
Article |
 Fluocerite as a precursor to rare earth element fractionation in ore-forming systems
Fluocerite as a precursor to rare earth element fractionation in ore-forming systems
Experiments under simulated hydrothermal conditions suggest that the mineral fluocerite may serve as an intermediate phase that fractionates the rare earth elements in ore-forming systems.
- Andrew C. Strzelecki
- , Artas Migdisov
- & Xiaofeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Metasedimentary rocks atop the downgoing slab oxidize ascending slab-derived dehydration fluids by removing reduced species, according to petrological analysis of subduction complex metasedimentary rocks and reactive transport modelling.
- Jay J. Ague
- , Santiago Tassara
- & Timm John
-
Article |
 Earth’s missing argon paradox resolved by recycling of oceanic crust
Earth’s missing argon paradox resolved by recycling of oceanic crust
Oceanic crust subduction sequesters substantial amounts of argon in the Earth’s mantle, while atmosphere-derived argon affects only the isotopic composition and not the overall budget, according to geodynamic–geochemical models of mantle convection.
- Jonathan M. Tucker
- , Peter E. van Keken
- & Chris J. Ballentine
-
Article |
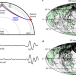 A poorly mixed mantle transition zone and its thermal state inferred from seismic waves
A poorly mixed mantle transition zone and its thermal state inferred from seismic waves
The mantle transition zone is poorly, mechanically mixed, and acts to impede mantle flow, according to seismic observations integrated with detailed mineral-physics models.
- Lauren Waszek
- , Benoit Tauzin
- & Juan Carlos Afonso
-
Article |
 Oceanic transform fault seismicity and slip mode influenced by seawater infiltration
Oceanic transform fault seismicity and slip mode influenced by seawater infiltration
Seawater infiltration into oceanic transform faults may control their seismicity extent and slip mode variations, according to numerical models of the mechanical and thermal structure of these faults that account for hydration effects.
- Arjun Kohli
- , Monica Wolfson-Schwehr
- & Jessica M. Warren
-
Article |
 Dynamic history of the inner core constrained by seismic anisotropy
Dynamic history of the inner core constrained by seismic anisotropy
The inner core underwent preferential equatorial growth and translation after nucleation ~0.5–1.5 billion years ago, according to an analysis of its seismic anisotropy and self-consistent geodynamic simulations.
- Daniel A. Frost
- , Marine Lasbleis
- & Barbara Romanowicz
-
Article |
 Dry metastable olivine and slab deformation in a wet subducting slab
Dry metastable olivine and slab deformation in a wet subducting slab
Transformation kinetics of olivine may be a cause of deep-focus earthquakes even in wet slabs, according to water-partitioning experiments, which show that olivine remains relatively dry even under wet subducting slab conditions.
- Takayuki Ishii
- & Eiji Ohtani
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogen dances in the deep mantle
Hydrogen dances in the deep mantle
Hydrogen ions move freely within the crystal structure of a hydrous mineral under lower mantle conditions, resulting in high electrical conductivity that may make it possible to map water in the deep mantle.
- Tetsuya Komabayashi
-
Article |
 Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle
Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle
Under conditions of Earth’s deep lower mantle, hydrogen ions diffuse freely through the FeOOH lattice framework and electrical conductivity increases rapidly, according to electrical conductivity experiments and first-principles simulations.
- Mingqiang Hou
- , Yu He
- & Ho-Kwang Mao
-
Article |
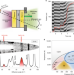 Implications of the iron oxide phase transition on the interiors of rocky exoplanets
Implications of the iron oxide phase transition on the interiors of rocky exoplanets
The interior structure and rheology of large terrestrial exoplanets is strongly affected by the phase transition of iron-oxide, according to dynamic compression and X-ray diffraction FeO experiments up to 700 GPa and calculation of the binary MgO–FeO phase diagram.
- F. Coppari
- , R. F. Smith
- & T. S. Duffy
-
Article |
 The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core may host most of the planet’s water inventory, according to calculations of the partitioning behaviour of water at conditions of core formation.
- Yunguo Li
- , Lidunka Vočadlo
- & John P. Brodholt
-
Article |
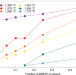 Early crust building enhanced on the Moon’s nearside by mantle melting-point depression
Early crust building enhanced on the Moon’s nearside by mantle melting-point depression
Early magmatism on the Moon’s nearside may have been enhanced by a geochemical anomaly lowering the melting point of the mantle source region, according to high-temperature experiments and thermal numerical modelling.
- Stephen M. Elardo
- , Matthieu Laneuville
- & Charles K. Shearer
-
Article |
 Instantaneous rock transformations in the deep crust driven by reactive fluid flow
Instantaneous rock transformations in the deep crust driven by reactive fluid flow
Fluid-mediated reaction fronts in rocks can propagate up to 10 centimetres per year, according to a transport model informed by observations of an ophiolite in Norway.
- A. Beinlich
- , T. John
- & Y. Y. Podladchikov
-
Article |
 Slab weakening during the olivine to ringwoodite transition in the mantle
Slab weakening during the olivine to ringwoodite transition in the mantle
In relatively cold subducted slabs, olivine may transform to finer-grained, weaker ringwoodite than in warm slabs, according to deformation experiments under conditions analogous to those in the mantle transition zone and scaling analysis.
- Anwar Mohiuddin
- , Shun-ichiro Karato
- & Jennifer Girard
-
Article |
 Release of oxidizing fluids in subduction zones recorded by iron isotope zonation in garnet
Release of oxidizing fluids in subduction zones recorded by iron isotope zonation in garnet
Lawsonite dehydration and release of oxidizing fluids could play an important role in sub-arc mantle oxidation in subduction zones, suggest measurements of changing oxygen fugacity in zoned garnets from Sifnos, Greece.
- Anna R. Gerrits
- , Edward C. Inglis
- & Kevin W. Burton
-
Article |
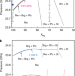 Sharp 660-km discontinuity controlled by extremely narrow binary post-spinel transition
Sharp 660-km discontinuity controlled by extremely narrow binary post-spinel transition
The post-spinel transition in mantle composition, which occurs at 660-km depth in Earth’s mantle, takes place over a pressure range equivalent to 250 m in depth, according to multi-anvil experiments for realistic mantle compositions and temperatures.
- Takayuki Ishii
- , Rong Huang
- & Tomoo Katsura
-
Article |
 Arc magmas oxidized by water dissociation and hydrogen incorporation in orthopyroxene
Arc magmas oxidized by water dissociation and hydrogen incorporation in orthopyroxene
Oxidation of arc magmas may be a secondary feature, acquired as hydrogen from magmatic water is incorporated into anhydrous minerals in the mantle wedge, according to analyses of orthopyroxenes in mantle xenoliths from an arc setting.
- Peter Tollan
- & Jörg Hermann
-
Article |
 Decline of giant impacts on Mars by 4.48 billion years ago and an early opportunity for habitability
Decline of giant impacts on Mars by 4.48 billion years ago and an early opportunity for habitability
The oldest known minerals from Mars have no strong shock features, indicating early cessation of giant impacts there, according to microanalysis of zircon and baddeleyite grains in meteorites.
- D. E. Moser
- , G. A. Arcuri
- & C. Davis
-

 Dense hydrous minerals under pressure
Dense hydrous minerals under pressure Look between the grains
Look between the grains Deep-sea ore deposits
Deep-sea ore deposits