Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 RNA returns to the fold
RNA returns to the fold
RNA has multiple roles in biology, enabled by its structural diversity. Now, artificially grafted RNA motifs have been encoded in a single RNA strand to form self-assembling nanostructures with controlled geometry and function.
- Qi Shen
- & Chenxiang Lin
-
Article |
 Interface-mediated noble metal deposition on transition metal dichalcogenide nanostructures
Interface-mediated noble metal deposition on transition metal dichalcogenide nanostructures
The deposition of noble metals onto two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides is crucial for practical applications, including in catalysis and sensing, yet this process has remained difficult to control. Now, gold and silver have been shown to grow on colloidal transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets into either atomically thin layers or nanoparticles whose sizes and morphologies depend on the relative strengths of the interfacial noble metal–chalcogen bonds.
- Yifan Sun
- , Yuanxi Wang
- & Raymond E. Schaak
-
Article |
 Branched kissing loops for the construction of diverse RNA homooligomeric nanostructures
Branched kissing loops for the construction of diverse RNA homooligomeric nanostructures
Homooligomerization systems can be used to construct nanoarchitectures and to aid understanding of natural analogues. But the formation of such artificial systems with structural diversity and complexity comparable to that of biological systems is challenging. Now, an artificial branched kissing-loop motif has been designed, which links tiles folded from a single strand of RNA to give diverse homooligomeric nanostructures.
- Di Liu
- , Cody W. Geary
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
News & Views |
 Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
The tumour microenvironment has a specific enzymatic fingerprint, which provides opportunities for cancer therapy. Now, two studies show how this unique chemical environment can be used to produce reporter molecules or nanoclusters within the tumour that can subsequently be identified in urine or breath, enabling cancer detection and monitoring.
- Alexander N. Zelikin
-
Article |
 Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Quantum dots functionalized with energy-accepting dyes hold promise for converting low-energy photons into higher-energy visible light for bioimaging, catalysis and solar energy harvesting. Now, it has been shown that non-toxic silicon quantum dots can be used in these systems; the transfer of spin-triplet excitons to molecules at their surface has been observed.
- Pan Xia
- , Emily K. Raulerson
- & Sean T. Roberts
-
Article |
 Designer DNA architecture offers precise and multivalent spatial pattern-recognition for viral sensing and inhibition
Designer DNA architecture offers precise and multivalent spatial pattern-recognition for viral sensing and inhibition
DNA is capable of self-assembling into a wide range of user-defined structures and so can be used as a scaffold to arrange binding motifs with nanometre precision. Now, DNA has been used to accurately display aptamers that fit the repeated epitope pattern of a dengue viral antigen to produce a nanostructure that can be a potent viral inhibitor or a fluorescent sensor.
- Paul S. Kwon
- , Shaokang Ren
- & Xing Wang
-
Article |
 Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
A solution-processing step has been used to prepare quantum-well structures that comprise a thin layer of perovskite sandwiched between two layers of conjugated oligothiophene derivatives. The band gap of the resulting 2D hybrid perovskites can be fine-tuned by functionalizing the organic component, which also improves the stability of the system.
- Yao Gao
- , Enzheng Shi
- & Letian Dou
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution writing
Super-resolution writing
The in situ, nanoscale positioning of a single molecule below the diffraction limit remains a challenge for chemists. Now, two approaches show how this can be accomplished through a combination of super-resolution microscopy and photo-inducible crosslinking chemistry.
- Limin Xiang
- & Ke Xu
-
Article |
 Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Tuning the selectivity for [2+2] photocycloadditions remains challenging. Now, triplet–triplet energy transfer from CdSe quantum dots enables the homo- and heterocouplings of 4-vinylbenzoic acid derivatives via [2+2] photocycloaddition. Preorganization of substrates on the quantum dots reverses intrinsic stereoelectronic preferences to yield cyclobutane products with unprecedented diastereo- and regioselectivity.
- Yishu Jiang
- , Chen Wang
- & Emily A. Weiss
-
Article |
 Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Generating stable single-atom catalysts is far from straightforward and can involve complicated preparation procedures. Now, mononuclear gold oxo-clusters formed in alkaline solutions through a facile one-pot synthesis are shown to catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reaction to methyl formate and hydrogen. The intrinsic activity is the same for both supported and unsupported gold catalysts.
- Sufeng Cao
- , Ming Yang
- & Maria Flytzani-Stephanopoulos
-
News & Views |
 A cornerstone of complex crystals
A cornerstone of complex crystals
Frank–Kasper phases are topologically close-packed structures typically found in ordered mixtures of ‘hard particles’ such as metallic alloys. Now, a shape amphiphile has been shown to self-assemble into a Frank–Kasper Z phase, which had so far remained elusive in soft materials.
- Abhiram Reddy
- & Gregory M. Grason
-
Article |
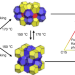 Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
The Z phase, one of three fundamental Frank–Kasper phases—topologically close-packed structures commonly found in metal alloys—is associated with a relatively large volume ratio between its constituents. This means it is typically not formed in single-component soft materials. Now, a shape amphiphile has been shown to self-assemble in a variety of unconventional structures, including the Z phase.
- Zebin Su
- , Chih-Hao Hsu
- & Stephen Z. D. Cheng
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Super-resolution labelling with Action-PAINT
Super-resolution labelling with Action-PAINT
Super-resolution microscopy has enabled optical imaging of individual biomolecules on the nanometre scale. Now, a new method has been developed that allows active manipulation of single-molecule targets on visualization in a sequential manner. This method, called ‘Action-PAINT’, combines real-time super-resolution microscopy (DNA-PAINT) and photoinducible crosslinking chemistry to deliver a single-molecule cargo with <30 nm selectivity.
- Ninning Liu
- , Mingjie Dai
- & Peng Yin
-
Article |
 On-surface synthesis and characterization of individual polyacetylene chains
On-surface synthesis and characterization of individual polyacetylene chains
Polyacetylene is an ideal system to probe to gain a better understanding of the nature of charge transport in conducting polymers. Now, individual atomically precise polyacetylene chains have been synthesized on a copper surface and characterized using a range of techniques, revealing a doping-induced semiconductor-to-metal transition.
- Shiyong Wang
- , Qiang Sun
- & Wei Xu
-
Article |
 Building in vitro transcriptional regulatory networks by successively integrating multiple functional circuit modules
Building in vitro transcriptional regulatory networks by successively integrating multiple functional circuit modules
The regulation of cellular response to stimuli by genetic regulatory networks (GRNs) suggests how in vitro chemical reaction networks might be used to direct the dynamics of synthetic materials or chemical reactions. Now, multiple functional in vitro transcriptional circuit modules have been integrated to form composite regulatory networks capable of complex features analogous to those found in cellular GRNs.
- Samuel W. Schaffter
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
Article |
 Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Precipitation enables the straightforward production of a variety of inorganic materials, but the rapid reaction rates involved typically make controlling their morphologies difficult. Now, the growth of either one-, two- or three-dimensional materials has been promoted by tuning of the reactants’ electrolytic dissociation and solution supersaturation, without the need for capping agents and templates.
- Wei-Hong Lai
- , Yun-Xiao Wang
- & Shi-Xue Dou
-
Article |
 Kinetic modulation of graphene growth by fluorine through spatially confined decomposition of metal fluorides
Kinetic modulation of graphene growth by fluorine through spatially confined decomposition of metal fluorides
Active species such as hydrogen and oxygen are commonly introduced into reactors to control the growth of two-dimensional materials. Now, the presence of fluorine—released by the decomposition of a metal fluoride sheet—has also been shown to modulate the growth kinetics of graphene, h-BN and WS2.
- Can Liu
- , Xiaozhi Xu
- & Kaihui Liu
-
Article |
 Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy techniques can interrogate entities that fluoresce; however, most chemical or biological processes do not involve fluorescent species. Now, the incorporation of a competitive reaction into a single-molecule fluorescence detection scheme has been shown to enable quantitative super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions.
- Xianwen Mao
- , Chunming Liu
- & Peng Chen
-
News & Views |
 Clocking growth and collapse
Clocking growth and collapse
In biological systems, order typically emerges from out-of-equilibrium molecular processes that control both static patterns and dynamic changes. Now, the self-regulating assembly and disassembly of a synthetic system has been achieved on the micrometre scale, by coupling the growth of a DNA nanotube to a biochemical oscillator.
- Tim Liedl
-
Article |
 Autonomous dynamic control of DNA nanostructure self-assembly
Autonomous dynamic control of DNA nanostructure self-assembly
Nucleic acid nanotechnology offers a promising route towards the design and synthesis of reconfigurable biomolecular materials. Now, the combination of dynamic and structural DNA nanotechnology has enabled the dynamic control of the assembly and disassembly of DNA nanotubes. The process involves minimal synthetic gene systems, including an autonomous molecular oscillator.
- Leopold N. Green
- , Hari K. K. Subramanian
- & Elisa Franco
-
Perspective |
 Molecular spins for quantum computation
Molecular spins for quantum computation
Spins in molecules provide a simple platform with which to encode a quantum bit (qubit), the elementary unit of future quantum computers. This Perspective discusses how chemistry can contribute to designing robust spin systems based, in particular, on mononuclear lanthanoid complexes.
- A. Gaita-Ariño
- , F. Luis
- & E. Coronado
-
Article |
 Non-chemisorbed gold–sulfur binding prevails in self-assembled monolayers
Non-chemisorbed gold–sulfur binding prevails in self-assembled monolayers
Gold–thiol contacts are ubiquitous across the physical and biological sciences, connecting organic molecules to surfaces. Now, conductance measurements of different sulfur-bound single-molecule junctions show that thiols—in contrast to the prevailing view—are not chemisorbed on gold, which strongly suggests that the thiol hydrogen is retained.
- Michael S. Inkpen
- , Zhen–Fei Liu
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
Article |
 Catalytic transport of molecular cargo using diffusive binding along a polymer track
Catalytic transport of molecular cargo using diffusive binding along a polymer track
One-dimensional diffusive binding represents an important mechanism used by nature to facilitate many fundamental biochemical processes. Now, a completely synthetic system with similar capabilities has been constructed. The system was exploited to significantly speed up bimolecular reactions and to catalytically transport molecular cargo in solution and within physically separated compartments.
- Lifei Zheng
- , Hui Zhao
- & Wilhelm T. S. Huck
-
News & Views |
 Talking across the membrane
Talking across the membrane
One goal of synthetic biologists is to develop artificial systems to help study biological processes. Now, cell communication and differentiation have been demonstrated using spatiotemporal patterns created in artificial multicellular compartments.
- Yi Li
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
Article |
 Hierarchical organization of perylene bisimides and polyoxometalates for photo-assisted water oxidation
Hierarchical organization of perylene bisimides and polyoxometalates for photo-assisted water oxidation
In native photosystem II (PSII), multi-chromophore antennas surround the reaction centre, capturing light and triggering the quantized (four-flashes) photo-oxidation of water to oxygen. The PSII ‘quantasome’ is the most efficient photo-electrolyser built so far. An artificial quantasome has now been developed; it is specifically designed for oxygen evolution by self-assembling light-harvesting-perylene bisimides with a ruthenium polyoxometalate water-oxidation catalyst.
- Marcella Bonchio
- , Zois Syrgiannis
- & Maurizio Prato
-
Article |
 Signalling and differentiation in emulsion-based multi-compartmentalized in vitro gene circuits
Signalling and differentiation in emulsion-based multi-compartmentalized in vitro gene circuits
Synthetic gene circuits encapsulated in lipid membrane compartments are often employed as artificial cell mimics, but these lack the complex behaviour of biological tissues. Now, spatial information based on chemical gradients has been used to engineer non-trivial dynamics such as signal propagation and differentiation in an artificial multicellular system.
- Aurore Dupin
- & Friedrich C. Simmel
-
News & Views |
 SNAr stands corrected
SNAr stands corrected
Dynamic covalent chemistry combines the error-correcting behaviour of supramolecular chemistry with the robustness of covalent bonding, but relies on a somewhat limited set of reactions. Now, the classic nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) reaction has been shown to be reversible and self-correcting.
- Yinghua Jin
- & Wei Zhang
-
Article |
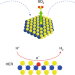 Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
MoS2 single layers spontaneously undergo a slow oxygen substitution reaction under ambient conditions giving rise to solid-solution-type 2D molybdenum oxy-sulfide crystals. The oxygen substitution sites of the 2D MoS2−xOx crystals act as efficient single-atom catalytic centres for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- János Pető
- , Tamás Ollár
- & Levente Tapasztó
-
Article |
 Narrow-band single-photon emission through selective aryl functionalization of zigzag carbon nanotubes
Narrow-band single-photon emission through selective aryl functionalization of zigzag carbon nanotubes
Aryl functionalization of carbon nanotubes generates sp3 defects capable of quantum light emission. A multiplicity of possible binding configurations, however, leads to spectrally diverse emission bands. Now, it is shown that the structural symmetry of zigzag nanotubes and a high chemical selectivity for ortho configurations results in defect-state emission from a single narrow band.
- Avishek Saha
- , Brendan J. Gifford
- & Stephen K. Doorn
-
Article |
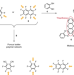 Dynamic self-correcting nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Dynamic self-correcting nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Dynamic covalent chemistry offers promise for the formation of elaborate extended network materials in high yields, but the limited number of reactions available confines the scope and functionality of the materials synthesized. Now, nucleophilic aromatic substitution has been shown to be reversible, and thus self-correcting, enabling the easy synthesis of sulfur-rich materials.
- Wen Jie Ong
- & Timothy M. Swager
-
Article |
 Isoreticular two-dimensional magnetic coordination polymers prepared through pre-synthetic ligand functionalization
Isoreticular two-dimensional magnetic coordination polymers prepared through pre-synthetic ligand functionalization
Surface engineering is an attractive route to tune the processability, stability and functionalities of 2D materials, but typically introduces defects in the resulting structures. Now, the issue has been circumvented through pre-synthetic functionalization instead; an isoreticular family of robust layered coordination polymers has been mechanically exfoliated to give functionalized crystalline magnetic monolayers.
- J. López-Cabrelles
- , S. Mañas-Valero
- & E. Coronado
-
News & Views |
 Scissoring genes with light
Scissoring genes with light
Enzymes can perform various biological functions because of their delicately and precisely organized structures. Now, simple inorganic nanoparticles with a rationally designed recognition capability can mimic restriction enzymes and selectively cut specific DNA sequences.
- Aleksandar P. Ivanov
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Article |
 Site-selective photoinduced cleavage and profiling of DNA by chiral semiconductor nanoparticles
Site-selective photoinduced cleavage and profiling of DNA by chiral semiconductor nanoparticles
Genome editing relies on engineered nucleases to change an organism’s DNA, but has not yet been achieved using abiotic materials. Now, chiral cysteine-capped CdTe nanoparticles are found to specifically recognize and, following photoirradiation, cut between bases T and A at the GATATC restriction site in DNA with over 90 base pairs.
- Maozhong Sun
- , Liguang Xu
- & Hua Kuang
-
Article |
 Structure–performance descriptors and the role of Lewis acidity in the methanol-to-propylene process
Structure–performance descriptors and the role of Lewis acidity in the methanol-to-propylene process
As of yet, no clear structure–performance descriptors have been developed to tune the catalytic activity of zeolitic methanol-to-olefin catalysts. Now it has been shown that introducing Lewis acidity into Brønsted acidic zeolites boosts their performance. Although Brønsted acidity is found to define propylene selectivity, Lewis acidity is responsible for prolonging lifetime.
- Irina Yarulina
- , Kristof De Wispelaere
- & Jorge Gascon
-
News & Views |
 Communicating catalysts
Communicating catalysts
The beauty and activity of enzymes inspire chemists to tailor new and better non-biological catalysts. Now, a study reveals that the active sites within heterogeneous catalysts actively cooperate in a fashion phenomenologically similar to, but mechanistically distinct, from enzymes.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional Na–Cl crystals of unconventional stoichiometries on graphene surface from dilute solution at ambient conditions
Two-dimensional Na–Cl crystals of unconventional stoichiometries on graphene surface from dilute solution at ambient conditions
The common form of salt has a 1:1 ratio of Na+ and Cl−; however, species that deviate from this can be found under extreme conditions, such as high pressure. Now, as a result of cation–π interactions that promote ion–surface adsorption, Na2Cl and Na3Cl have been observed as two-dimensional crystals on graphene at ambient conditions.
- Guosheng Shi
- , Liang Chen
- & Haiping Fang
-
Article |
 Harvesting multiple electron–hole pairs generated through plasmonic excitation of Au nanoparticles
Harvesting multiple electron–hole pairs generated through plasmonic excitation of Au nanoparticles
Multi-electron redox reactions are kinetically sluggish; however, plasmonic nanoparticles have shown promise as multi-electron reduction catalysts. Now, the principles that govern the harvesting of multiple electron–hole pairs from plasmonically excited gold nanoparticle photocatalysts are elucidated, providing a general foundation for the plasmonic catalysis of challenging multi-electron, multi-proton chemistry, such as N2 fixation and CO2 reduction.
- Youngsoo Kim
- , Jeremy G. Smith
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article |
 A molecular multi-gene classifier for disease diagnostics
A molecular multi-gene classifier for disease diagnostics
Gene expression profiling remains cost-prohibitive and challenging to implement in a clinical setting. Now, a molecular computation strategy for classifying complex gene expression signatures has been developed. Classification occurs through a series of molecular interactions between RNA inputs and engineered DNA probes designed to implement a relevant linear classification model.
- Randolph Lopez
- , Ruofan Wang
- & Georg Seelig
-
Article |
 Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
Living systems rely on externally tuneable and stimuli-responsive conformational changes of proteins and protein assemblies for a wide range of essential functions. A combination of experimental and computational analyses has now enabled the fabrication of a rationally designed, synthetic, stimuli-responsive protein assembly through modulation of its free-energy landscape.
- Robert Alberstein
- , Yuta Suzuki
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Article |
 Amino-acid-encoded biocatalytic self-assembly enables the formation of transient conducting nanostructures
Amino-acid-encoded biocatalytic self-assembly enables the formation of transient conducting nanostructures
Amino acids have now been used as chemical inputs to provide control over self-assembly in semiconducting structures. This approach enables temporal control over the formation of nanostructures and consequently control over their transient electronic conductivity.
- Mohit Kumar
- , Nicole L. Ing
- & Rein V. Ulijn
-
News & Views |
 Claim to FAME
Claim to FAME
Proteins are attractive material building blocks, yet their intrinsic functionality has remained largely untapped. Now, a protein-based material that exhibits controllable self-assembling behaviour has been prepared in a one-pot synthesis by simultaneous use of recombinant expression and post-translational modification.
- Alvaro Mata
-
Article |
 High phase-purity 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals
High phase-purity 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals
The phase in which a crystal exists can have a direct influence over its properties; however, it is usually difficult to control during synthesis. Now it has been shown that micrometre-sized metallic 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals can be prepared in high phase purity on a large scale, and that they display promising electrocatalytic activity towards the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- Yifu Yu
- , Gwang-Hyeon Nam
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that characterize expression at the level of individual cells. Now, a technique for characterizing mRNA expression has been developed. The technique uses the intracellular self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles to quantitate RNA levels at the single-cell level.
- Mahmoud Labib
- , Reza M. Mohamadi
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article |
 Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Nanocatalysts can undergo various dynamic phenomena that affect their activity, such as restructuring and spillover. Now, using spatially and temporally resolved imaging of individual catalytic reactions, cooperative communication between different sites within single palladium- and gold-based nanocatalysts, and between different nanocatalysts, has been observed during three distinct catalytic reactions.
- Ningmu Zou
- , Xiaochun Zhou
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded lipid–polypeptide hybrid biomaterials that exhibit temperature-triggered hierarchical self-assembly
Genetically encoded lipid–polypeptide hybrid biomaterials that exhibit temperature-triggered hierarchical self-assembly
Inspired by the post-translational modifications of polypeptides widespread in biological systems, the one-pot synthesis of biohybrid materials was engineered within Escherichia coli using a recombinant expression and post-translational lipidation. The fatty-acid-modified elastin-like polypeptides (FAMEs) prepared, which comprise peptide-amphiphile segments prone to self-assembly fused to a thermally responsive elastin-like polypeptide, exhibit temperature-triggered hierarchical assembly.
- Davoud Mozhdehi
- , Kelli M. Luginbuhl
- & Ashutosh Chilkoti
-
Article |
 Crystal phase-based epitaxial growth of hybrid noble metal nanostructures on 4H/fcc Au nanowires
Crystal phase-based epitaxial growth of hybrid noble metal nanostructures on 4H/fcc Au nanowires
Heterometallic nanomaterials in unusual crystal phases that are impossible to form in the bulk state can show interesting physical and chemical properties. Here, crystal-phase heterostructured 4H/fcc Au nanowires are used as seeds to epitaxially grow a variety of binary and ternary hybrid noble metal nanostructures on the phase boundary.
- Qipeng Lu
- , An-Liang Wang
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Complex supramolecular interfacial tessellation through convergent multi-step reaction of a dissymmetric simple organic precursor
Complex supramolecular interfacial tessellation through convergent multi-step reaction of a dissymmetric simple organic precursor
Complex interfacial supramolecular architectures promise unique physical and chemical properties, but are challenging to make. Now, it has been shown that a simple organic precursor can undergo a convergent multi-step on-surface transformation to give more complex building blocks that assemble into a semi-regular Archimedean tessellation with long-range order.
- Yi-Qi Zhang
- , Mateusz Paszkiewicz
- & Florian Klappenberger
-
Article |
 Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C–H activation
Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C–H activation
A renewed interest in C–H bond activation has developed on account of the recent increased availability of shale gas. Now, using a combination of surface science, microscopy, theory and nanoparticle studies, the ability of coke-resistant Pt/Cu single-atom alloys to efficiently activate C–H bonds in alkanes has been demonstrated under realistic catalytic conditions.
- Matthew D. Marcinkowski
- , Matthew T. Darby
- & E. Charles H. Sykes

 Vibrational coherences in manganese single-molecule magnets after ultrafast photoexcitation
Vibrational coherences in manganese single-molecule magnets after ultrafast photoexcitation