Featured
-
-
Article |
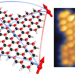 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
The design of open-shell nanographenes is commonly limited to systems featuring a single magnetic origin. Now a strategy that combines topological frustration and electron–electron interactions has been developed to generate a butterfly-shaped nanographene that hosts four highly entangled π-spins and exhibits both ferromagnetic and anti-ferromagnetic coupling.
- Shaotang Song
- , Andrés Pinar Solé
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access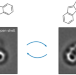 Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Switching the magnetic state of a polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon in a reversible and controlled manner is challenging. Now, by means of single-molecule scanning probe microscopy, an indenofluorene isomer on ultrathin NaCl films has been shown to adopt both open- and closed-shell states. Furthermore, bidirectional switching between the two states is achieved by changing the adsorption site of the molecule.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Manuel Vilas-Varela
- & Leo Gross
-
Article |
 Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers
Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers
Sequences of synthetic polymers are generally heterogeneous and dictate many of their physiochemical properties, but are challenging to determine. Now an imaging method, termed CREATS (coupled reaction approach toward super-resolution imaging), can count, localize and identify each monomer of single polymer chains during (co)polymerization.
- Rong Ye
- , Xiangcheng Sun
- & Peng Chen
-
Research Briefing |
 A multimodal imaging approach for interrogating energy-conversion pathways in biohybrids
A multimodal imaging approach for interrogating energy-conversion pathways in biohybrids
A multimodal imaging approach is developed to interrogate microorganism–semiconductor biohybrids at the single-cell and single-molecule level for light-driven CO2 fixation. Application to lithoautotrophic bacterium Ralstonia eutropha biohybrids reveals the roles of two hydrogenases in electron transport and bioplastic formation, the magnitude of semiconductor-to-single-cell electron transport and the associated pathways.
-
Article |
 Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Understanding interfacial and cellular electron transport is essential for guiding efficiency optimization in microbe–semiconductor biohybrids for energy conversion. A multimodal imaging platform that combines optical imaging and photocurrent mapping can now interrogate such electron-transport pathways at the single-cell level, uncovering different roles of hydrogenases and a microbe’s large electron-uptake capacity.
- Bing Fu
- , Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Time-resolved imaging and analysis of the electron beam-induced formation of an open-cage metallo-azafullerene
Time-resolved imaging and analysis of the electron beam-induced formation of an open-cage metallo-azafullerene
Visualizing single-molecule reactions using electron microscopy can be difficult because of potential radiation damage from the electron beam. Now, however, it has been shown that a high-energy electron beam can be used to synthesize metallo-azafullerenes. Atomic-resolution, time-resolved transmission electron microscopy, with the help of computational calculations, is used to monitor the metal-encapsulation dynamics.
- Helen Hoelzel
- , Sol Lee
- & Dominik Lungerich
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction is a powerful technique to determine structures from nanocrystals. A data treatment method that takes into account dynamical diffraction effects has now been shown to lead to more accurate structure models, better sensitivity to weak signals and a reliable determination of absolute configuration—even for materials containing only light atoms.
- Paul B. Klar
- , Yaşar Krysiak
- & Lukas Palatinus
-
Article
| Open Access Structural resolution of a small organic molecule by serial X-ray free-electron laser and electron crystallography
Structural resolution of a small organic molecule by serial X-ray free-electron laser and electron crystallography
The structural analysis of small crystals has remained challenging. Now, the structure of a small organic molecule, rhodamine-6G, has been resolved from microcrystals using an X-ray free-electron laser and electron diffraction. The former showed better reliability for atomic coordinates, whereas the latter was more sensitive to charges; both techniques accurately determined the position of hydrogen atoms.
- Kiyofumi Takaba
- , Saori Maki-Yonekura
- & Koji Yonekura
-
News & Views |
 Colouring by force
Colouring by force
Mechanical force has recently become a new tool for chemists to create colours, trigger reactions, and develop advanced fabrication techniques not possible using other methods. Force-induced multiple colouring has now been developed as a printing technique in soft lithography, enabling the colouring of polymeric materials without inks.
- Xiaocun Lu
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article |
 A dissipative pathway for the structural evolution of DNA fibres
A dissipative pathway for the structural evolution of DNA fibres
Nature uses out-of-equilibrium systems to control hierarchical assembly. Now, a dissipative chemical system has been shown to slowly release monomer DNA strands from a high-energy reservoir, regulating self-assembly by switching the mechanism of supramolecular polymerization at the single-molecule level. This process heals fibre defects, converting branched, heterogeneous networks into nanocable superstructures.
- Felix J. Rizzuto
- , Casey M. Platnich
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions via competition
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy techniques can interrogate entities that fluoresce; however, most chemical or biological processes do not involve fluorescent species. Now, the incorporation of a competitive reaction into a single-molecule fluorescence detection scheme has been shown to enable quantitative super-resolution imaging of non-fluorescent reactions.
- Xianwen Mao
- , Chunming Liu
- & Peng Chen
-
News & Views |
 Raw protein from the top down
Raw protein from the top down
Mass spectrometry is a powerful technique for analysing proteins, yet linking higher-order protein structure to amino acid sequence and post-translational modifications is far from simple. Now, a native top-down method has been developed that can provide information on higher-order protein structure and different proteoforms at the same time.
- Kathrin Breuker
-
Article |
 Theory-driven design of high-valence metal sites for water oxidation confirmed using in situ soft X-ray absorption
Theory-driven design of high-valence metal sites for water oxidation confirmed using in situ soft X-ray absorption
Water oxidation is key to the production of chemical fuels from electricity. Now, guided by theory, NiCoFeP oxyhydroxide catalysts have been developed that require an overpotential lower than that required by IrO2. In situ soft X-ray absorption studies of neutral-pH NiCoFeP catalysts indicate formation of Ni4+, which is favourable for water oxidation.
- Xueli Zheng
- , Bo Zhang
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Real-time molecular scale observation of crystal formation
Real-time molecular scale observation of crystal formation
Homogeneous crystal nucleation has now been observed by transmission electron microscopy in real time on a molecular scale. Countercation-dependent observations of polyoxometalate proto-crystal formation confirm existence of a higher energy classical molecular attachment mechanism, as well as a lower energy two-step mechanism via an intermediate dense phase.
- Roy E. Schreiber
- , Lothar Houben
- & Ronny Neumann
-
Thesis |
 Changing chemistry by degrees
Changing chemistry by degrees
It is easy to overlook just how important temperature is when it comes to chemistry and Michelle Francl wonders if thermometers had a role in turning alchemists into chemists.
- Michelle Francl
-
Article |
 Reversible Bergman cyclization by atomic manipulation
Reversible Bergman cyclization by atomic manipulation
The Bergman cyclization is a fascinating rearrangement reaction with implications beyond organic chemistry. It has now been shown that a reversible Bergman cyclization reaction in a single molecule sitting on an ultrathin NaCl film can be triggered and directly imaged using atomic force microscopy. The interconverted diradical and diyne products are shown to have distinct chemical and physical properties.
- Bruno Schuler
- , Shadi Fatayer
- & Leo Gross
-
Article |
 Real-time observation of multiexcitonic states in ultrafast singlet fission using coherent 2D electronic spectroscopy
Real-time observation of multiexcitonic states in ultrafast singlet fission using coherent 2D electronic spectroscopy
Singlet fission, a spin-allowed conversion of a spin-singlet state into a pair of spin-triplet excitons, may be useful for the development of next-generation photovoltaics. Ultrafast coherence measurements now show that vibrational motions play a critical role in fission as they facilitate the mixing of triplet-pair states with singlet excitons.
- Artem A. Bakulin
- , Sarah E. Morgan
- & Akshay Rao
-
-
-
Article |
 Quantitative mapping of zinc fluxes in the mammalian egg reveals the origin of fertilization-induced zinc sparks
Quantitative mapping of zinc fluxes in the mammalian egg reveals the origin of fertilization-induced zinc sparks
The mammalian oocyte cell cycle is regulated by massive zinc fluxes which culminate in coordinated ejections of ~1010 zinc ions at fertilization. Four single-cell physiochemical approaches (live-cell fluorescence imaging, scanning transmission electron microscopy with energy dispersive spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence microscopy and tomography) reveal that these ‘zinc sparks’ originate from thousands of cortical vesicles which each release ~106 zinc ions.
- Emily L. Que
- , Reiner Bleher
- & Thomas V. O'Halloran
-
-
-
-
Article |
 Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Non-noble-metal-based MoS2 nanostructures are hydrogen evolution catalysts whose active sites are known to be located at the edges. Supported thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− nanoclusters have now been prepared that exhibit a structural motif similar to that of MoS2 edges. The nanoclusters, synthesized by a scalable route, demonstrate a high turnover frequency.
- Jakob Kibsgaard
- , Thomas F. Jaramillo
- & Flemming Besenbacher
-
News & Views |
 Phase transition singled out
Phase transition singled out
Four-dimensional electron microscopy has been applied to the detailed characterization of metal–organic-framework nanoparticles undergoing an electronic transition. The transition characteristics of a single particle were found to differ from those of an ensemble, and also to vary from one nanoparticle to the next.
- Nigel D. Browning
-
Perspective |
 Design strategies for organic semiconductors beyond the molecular formula
Design strategies for organic semiconductors beyond the molecular formula
Although the molecular formula gives valuable information on the properties of isolated molecules or conjugated polymers, it fails to accurately predict their collective behaviour in the solid state. This Perspective highlights the importance of organization across multiple length scales on the optical and electronic properties of organic semiconductors, and how device performances poorly reflect the capabilities of a given material.
- Zachary B. Henson
- , Klaus Müllen
- & Guillermo C. Bazan
-
Article |
 Visualization of hierarchically structured zeolite bodies from macro to nano length scales
Visualization of hierarchically structured zeolite bodies from macro to nano length scales
Understanding the nature of complex zeolite particles, used as catalysts in industrial reactors, is vital for their further development. Now, an integrated approach to visualizing granules of a hierarchical MFI-type zeolite, on length scales from nanometres to millimetres, is reported.
- Sharon Mitchell
- , Nina-Luisa Michels
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article |
 Understanding and controlling the substrate effect on graphene electron-transfer chemistry via reactivity imprint lithography
Understanding and controlling the substrate effect on graphene electron-transfer chemistry via reactivity imprint lithography
The chemical modification of graphene is important for its use in many applications. Now it is shown that the reactivity of graphene towards covalent modification varies widely depending on its underlying support substrate, and that the substrate can be patterned to induce spatial control of chemical reactions in graphene.
- Qing Hua Wang
- , Zhong Jin
- & Michael S. Strano
-
-
News & Views |
 Autonomous propulsion
Autonomous propulsion
Polymer vesicles have been constructed that entrap platinum nanoparticles in their outer surface. These serve to break down a fuel of hydrogen peroxide, generating water and oxygen and in turn inducing a propulsive effect.
- Jonathan Howse
-
Article |
 Catalytic activity in individual cracking catalyst particles imaged throughout different life stages by selective staining
Catalytic activity in individual cracking catalyst particles imaged throughout different life stages by selective staining
Insight into the active zeolitic domains of catalyst particles used in fluid catalytic cracking is limited by the particles' complex nature, but is crucial to improving these billion dollar catalysts. Now, a staining method allows confocal fluorescence microscopy to probe within single catalyst particles, and correlate Brønsted acidity distributions to catalytic activity.
- Inge L. C. Buurmans
- , Javier Ruiz-Martínez
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 A microdroplet dilutor for high-throughput screening
A microdroplet dilutor for high-throughput screening
Droplet microfluidics offer a convenient platform for high-throughput experimentation. It has been difficult, however, to rapidly and controllably vary concentration — a key process used in macro-scale experiments. Here, a droplet dilution module is described that traps a mother droplet and then repeatedly dilutes it releasing a series of droplets that define a digital concentration gradient.
- Xize Niu
- , Fabrice Gielen
- & Andrew J. deMello
-
News & Views |
 On the right path
On the right path
Controlled energy-transfer on a molecular scale is a goal in many areas of science, from artificial photosynthesis to molecular electronics. Now, DNA origami has been used to direct the transfer of energy from an excited input dye down one of two paths by precisely arranging a mediator dye.
- Bo Albinsson
-
-
News & Views |
 From 2D to 3D
From 2D to 3D
The self-assembly of molecules into porous two-dimensional networks on surfaces has been well studied in recent years, but now the concept has been extended to three dimensions with a little help from fullerene molecules.
- Steven De Feyter
-
Article |
 Control and imaging of O(1D2) precession
Control and imaging of O(1D2) precession
Larmor precession of a quantum mechanical angular momentum vector about an applied magnetic field forms the basis for NMR spectroscopy, MRI and a range of other important analytical techniques. This precessional motion has now been imaged for the first time, using velocity-map imaging in a model system of strongly polarized oxygen atoms.
- Shiou-Min Wu
- , Dragana Č. Radenovic
- & Richard N. Zare
-
Research Highlights |
 Spiralling into control
Spiralling into control
Single crystals of chromium silicide have been prepared that grow into highly crystalline nanowebs.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
 Reversing the direction in a light-driven rotary molecular motor
Reversing the direction in a light-driven rotary molecular motor
Biological rotary motors can alter their mechanical function by changing the direction of rotary motion. Now, researchers have designed a synthetic light-driven rotary motor in which the direction of rotation can be reversed on command by changing the chirality of the molecular motor through base-induced epimerization.
- Nopporn Ruangsupapichat
- , Michael M. Pollard
- & Ben L. Feringa
-
Article |
 Spectroscopic visualization of sound-induced liquid vibrations using a supramolecular nanofibre
Spectroscopic visualization of sound-induced liquid vibrations using a supramolecular nanofibre
Although ultrasonic vibrations are known to be capable of aligning macromolecules in solution, the question of whether audible sound — which has much lower frequencies — can have such an effect is somewhat controversial. Now, however, it has been shown that supramolecular nanofibres can be preferentially aligned parallel to the propagation direction of audible sound.
- Akihiko Tsuda
- , Yuka Nagamine
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Article |
 Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
The phosphoric acid fuel cell is limited by its slow rate of oxygen reduction at the cathode, but now an approach to the rational design of improved catalysts for this process has been developed. Molecular patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide adsorbates is used to block the adsorption of spectator anions without hindering oxygen reduction, thus improving catalytic activity.
- Dusan Strmcnik
- , María Escudero-Escribano
- & Nenad M. Marković
-
Research Highlights |
 Petite patterns
Petite patterns
A heated AFM tip has been used to create nanoscale patterns of reduced graphene oxide.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Research Highlights |
 Zooming in zeolites
Zooming in zeolites
Single metal atoms can be identified within the pores of a zeolite catalyst.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
 Enhancement of anhydrous proton transport by supramolecular nanochannels in comb polymers
Enhancement of anhydrous proton transport by supramolecular nanochannels in comb polymers
Efficient conduction of protons on a micrometre scale is critical for the development of fuel cell membranes — a key component of clean energy sources. Now, self-assembling amphiphilic polymers have been shown to provide a nanoscale organization of proton-conducting functionalities that dramatically increases anhydrous proton conductivity.
- Yangbin Chen
- , Michael Thorn
- & S. Thayumanavan
-
News & Views |
 Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Chemical reactions of fullerenes and metallofullerenes lined up inside single-walled carbon nanotubes can be monitored at the atomic scale inside an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope.
- Mauricio Terrones

 Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging Tales from the cryptates
Tales from the cryptates A right tangle
A right tangle No limit
No limit Gold rush
Gold rush Jaws up close
Jaws up close Force microscopy takes charge
Force microscopy takes charge Spiralling into control
Spiralling into control