Featured
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Enzymatically crosslinked scaffolds
Enzymatically crosslinked scaffolds
Microgel particle precursors bearing peptide substrates for human enzymes crosslink in wound sites to produce bioactive scaffolds in situ that rapidly recruit cells and promote dermal healing.
- David W. Grainger
-
News & Views |
 Low-energy electron therapy
Low-energy electron therapy
The fabrication of a self-sustaining source of low-energy electrons in a single-atom layer could help unravel fundamental mechanisms of radiobiological damage and lead to improved cancer therapies.
- Léon Sanche
-
-
Article |
 Designer amphiphilic proteins as building blocks for the intracellular formation of organelle-like compartments
Designer amphiphilic proteins as building blocks for the intracellular formation of organelle-like compartments
Amphiphilic proteins act as building blocks for the de novo formation of membrane-based organelles within Escherichia coli. The organelles can be selectively functionalized in vivo with unnatural amino acids and hence may permit chemical reactions inside the cell that have not been possible so far.
- Matthias C. Huber
- , Andreas Schreiber
- & Stefan M. Schiller
-
Article |
 Interplay of matrix stiffness and protein tethering in stem cell differentiation
Interplay of matrix stiffness and protein tethering in stem cell differentiation
Recent work has proposed that both protein tethering to the extracellular matrix and matrix porosity can regulate stem cell differentiation. It is now shown that differentiation is driven by matrix stiffness independently of tethering and porosity.
- Jessica H. Wen
- , Ludovic G. Vincent
- & Adam J. Engler
-
-
-
Article |
 Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Peptide-based nanofibres with bioactive proteins attached can now be made such that the protein ligands are introduced in a controlled manner. This tailoring of the nanofibre’s composition enables the ratio of multiple different proteins to be highly tuned within the assemblies. By changing the protein content of the nanofibres, it is possible to adjust the antibody responses in mice to the different nanofibres.
- Gregory A. Hudalla
- , Tao Sun
- & Joel H. Collier
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Boosting plant biology
Boosting plant biology
Chloroplasts with extended photosynthetic activity beyond the visible absorption spectrum, and living leaves that perform non-biological functions, are made possible by localizing nanoparticles within plant organelles.
- Gregory D. Scholes
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing
Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing
Imparting non-native functions to living plants using nanoparticles opens the possibility of creating synthetic materials that can grow and repair themselves using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. It is now shown that, both in plant extracts and living leaves, carbon nanotubes traverse and localize within the lipid envelope of plant chloroplasts, enhance their photosynthetic activity, and enable near-infrared fluorescence monitoring of nitric oxide.
- Juan Pablo Giraldo
- , Markita P. Landry
- & Michael S. Strano
-
-
Article |
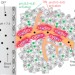 A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
The imaging of tumours is challenging because of the wide range of different cancers. Now, the rapid detection of tumours, independent of type, is achieved using a nonlinear amplification strategy that employs ultrasensitive pH-responsive fluorescent nanoparticles that illuminate within tumour neovasculature or in response to the tumour’s acidic extracellular environment.
- Yiguang Wang
- , Kejin Zhou
- & Jinming Gao
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
Commentary |
 Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Cancer nanomedicines approved so far minimize toxicity, but their efficacy is often limited by physiological barriers posed by the tumour microenvironment. Here, we discuss how these barriers can be overcome through innovative nanomedicine design and through creative manipulation of the tumour microenvironment.
- Vikash P. Chauhan
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Differential stickiness
Differential stickiness
Technologies to isolate colonies of human pluripotent stem cells from other cell types in a high-throughput manner are lacking. A microfluidic-based approach that exploits differences in the adhesion strength between these cells and a substrate may soon fill the gap.
- Oscar J. Abilez
- & Joseph C. Wu
-
Letter |
 Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
A highly selective and efficient approach to covalently bond complementary DNA strands in solution and on surfaces on demand is shown. The approach involves the substitution of a pair of complementary bases by cinnamate-based crosslinks, which can be activated on exposure to ultraviolet light, and allows chemical patterning of flat and curved surfaces down to micrometre and potentially submicrometre resolutions.
- Lang Feng
- , Joy Romulus
- & Paul Chaikin
-
Article |
 Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues
Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues
Three-dimensional bioactive scaffolds can support tissue growth for studies in cellular biophysics and regenerative medicine. Such scaffolds have now been integrated with semiconductor nanowires to probe their porous interior, allowing for real-time monitoring of signals such as the response of neural and cardiac tissue models to drugs.
- Bozhi Tian
- , Jia Liu
- & Charles M. Lieber
-
News & Views |
 Still in control
Still in control
The development of synthetic strategies enabling the fabrication of well-defined polymer–biomolecule conjugates, together with advances in top-down nanofabrication, are two highlights from a recent meeting of polymer scientists.
- Jeffrey Pyun
-
Article |
 Fano-resonant asymmetric metamaterials for ultrasensitive spectroscopy and identification of molecular monolayers
Fano-resonant asymmetric metamaterials for ultrasensitive spectroscopy and identification of molecular monolayers
Plasmonic nanostructures are known to be an attractive platform for highly sensitive molecular sensors, although they often lack specificity. A plasmonic device with a sharp optical resonance tuned to biomolecules selectively captured on the surface of the device now offers a versatile yet highly specific platform for molecular sensing.
- Chihhui Wu
- , Alexander B. Khanikaev
- & Gennady Shvets
-
-
Article |
 Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency
Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency
On standard tissue culture platforms, mesenchymal stem cells tend to spontaneously differentiate with the loss of multi-lineage potential. Now, a robust and reproducible nanotopographical platform has been shown to maintain stem cell phenotype and promote stem cell growth over several months whilst implicating mechanisms for the observed stem cell behaviour
- Rebecca J. McMurray
- , Nikolaj Gadegaard
- & Matthew J. Dalby
-
News & Views |
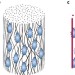 Noodle gels for cells
Noodle gels for cells
Heating and cooling of peptide amphiphile suspensions converts disorganized nanofibres into liquid-crystalline nanofibre bundles that gel on addition of salts. The noodle-shaped strings of gel can entrap and align cells.
- Timothy J. Deming
-
Article |
 Nanopatterning Si(111) surfaces as a selective surface-chemistry route
Nanopatterning Si(111) surfaces as a selective surface-chemistry route
The ability to control the surface chemistry of silicon is important for microelectronic applications. Chemical species can now be stabilized on Si(111) surfaces using a partially alkoxylated surface as a nanopatterning template.
- David J. Michalak
- , Sandrine Rivillon Amy
- & Yves J. Chabal

 Phage-mediated counting by the naked eye of miRNA molecules at attomolar concentrations in a Petri dish
Phage-mediated counting by the naked eye of miRNA molecules at attomolar concentrations in a Petri dish Changing domains
Changing domains