Featured
-
-
Article |
 Partitioning the interlayer space of covalent organic frameworks by embedding pseudorotaxanes in their backbones
Partitioning the interlayer space of covalent organic frameworks by embedding pseudorotaxanes in their backbones
Layered COFs are attractive precursors for two-dimensional materials but they are difficult to cleave into mono- or few-layer sheets. Pseudorotaxane moieties have now been embedded into layered COFs to facilitate their cleavage into sheets of uniform thickness. Crown-ether macrocycles within the COF backbone bind to ionic viologen guests, leading to electrostatic repulsion between layers.
- Xing Li
- , Hai-Sen Xu
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
News & Views |
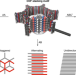 Taking stock of stacking
Taking stock of stacking
The manner in which adjacent sheets stack in layered covalent organic frameworks largely influences their material properties, including chemical stability, crystallinity and porosity. The layer stacking of a COF has now been probed locally, showing disorder that is not detected through long-range characterization.
- Andre Mähringer
- & Dana D. Medina
-
Article |
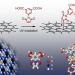 Long-range ordered and atomic-scale control of graphene hybridization by photocycloaddition
Long-range ordered and atomic-scale control of graphene hybridization by photocycloaddition
The controllable functionalization of graphene at the molecular level may prove useful for graphene-based electronics, but is difficult to do in a precise fashion. Now it has been shown that a photocycloaddition reaction between a hydrogen-bonded network of maleimide-derived molecules and single-layer graphene can produce a functionalized array with long-range order.
- Miao Yu
- , Chong Chen
- & Federico Rosei
-
News & Views |
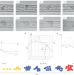 What atoms do when they get together
What atoms do when they get together
How atoms organize during the earliest stages of nucleation has been a subject of speculation for over a century. Using atomically resolved electron microscopy, the formation and ordering of metal clusters from individual atoms has now been observed in carbon nanotubes that serve as ‘test tubes’.
- J. J. De Yoreo
- & B. A. Legg
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry in the making
Symmetry in the making
After years of speculation on the origins of symmetry-making and -breaking during crystallization, time-resolved in situ scanning probe microscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations have shown that the formation of olanzapine crystals largely occurs by the incorporation of centrosymmetric dimers into growth sites.
- Susan M. Reutzel-Edens
-
Article |
 Olanzapine crystal symmetry originates in preformed centrosymmetric solute dimers
Olanzapine crystal symmetry originates in preformed centrosymmetric solute dimers
Crystal symmetry is notoriously uncorrelated to the symmetry of the constituent molecules that make up a crystal. Symmetry breaking is typically thought to occur during nucleation and growth, but a symmetry element of olanzapine crystals—an inversion centre—has now been shown to emerge in centrosymmetric dimers extant in solution prior to crystallization.
- Monika Warzecha
- , Lakshmanji Verma
- & Peter G. Vekilov
-
Article |
 Meta-DNA structures
Meta-DNA structures
A six-helix bundle DNA structure called meta-DNA has now been assembled and shown to possess some structural properties similar to those of single-stranded DNA. Two meta-DNAs containing complementary ‘meta-base pairs’ are shown to form double helices. Meta-DNA building blocks are also used to construct a series of DNA architectures and to perform a hierarchical strand-displacement reaction.
- Guangbao Yao
- , Fei Zhang
- & Hao Yan
-
Article |
 Atomic mechanism of metal crystal nucleus formation in a single-walled carbon nanotube
Atomic mechanism of metal crystal nucleus formation in a single-walled carbon nanotube
Crystal nucleation processes are difficult to probe experimentally because of the spatial and temporal scales involved. Now, the heterogeneous nucleation of three different metals has been observed by electron microscopy with atomic resolution—using single-walled carbon nanotube as test tubes—and, in each case, shown to adopt a two-step nucleation mechanism involving a metastable amorphous precursor.
- Kecheng Cao
- , Johannes Biskupek
- & Ute Kaiser
-
News & Views |
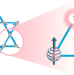 Taking titanium for a spin
Taking titanium for a spin
Spin-1/2 kagome lattice antiferromagnets are geometrically frustrated materials poised to host yet-unobserved behaviours. Now, such a lattice has been prepared that shows no structural distortions and hosts its spin in the dxy orbital of d1 Ti3+ centres, rather than the more-widely investigated d9 Cu2+ ions.
- Kelsey A. Collins
- & Danna E. Freedman
-
Article |
 Fast motion of molecular rotors in metal–organic framework struts at very low temperatures
Fast motion of molecular rotors in metal–organic framework struts at very low temperatures
Molecular rotors have been engineered within the bicyclopentane–dicarboxylate struts of a metal–organic framework—the bicyclic unit is the rotator and the carboxylate groups serve as the stator. In a zinc-based metal–organic framework, the crossed conformation of the strut–metal nodes enables fast rotation of the bicyclic moiety, but in the corresponding zirconium metal–organic framework a change in the conformation results in much slower rotation.
- Jacopo Perego
- , Silvia Bracco
- & Piero Sozzani
-
Article |
 Tunable exciton binding energy in 2D hybrid layered perovskites through donor–acceptor interactions within the organic layer
Tunable exciton binding energy in 2D hybrid layered perovskites through donor–acceptor interactions within the organic layer
The strength of electrostatic interactions in semiconductors strongly affects their performance in optoelectronic devices. Now, doping two-dimensional naphthalene-based lead halide perovskites with tetrachloro-1,2-benzoquinone has been shown to introduce donor–acceptor interactions within the organic network, without disrupting the inorganic sublattice. This in turn altered the energy of the materials’ electron–hole electrostatic Coulomb interactions.
- James V. Passarelli
- , Catherine M. Mauck
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Article |
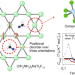 Synthesis of a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet
Synthesis of a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet
The highly frustrated spin-1/2 kagome lattice antiferromagnet, predicted to exhibit unconventional magnetic behaviours, has remained difficult to synthesize without structural imperfections. Now, a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet has been prepared in which there is only one crystallographically distinct Ti3+ site and one type of bridging fluoride, and it is shown to be a frustrated magnet with unusual magnetic properties.
- Ningxin Jiang
- , Arun Ramanathan
- & Henry S. La Pierre
-
News & Views |
 Photoswitching to the core
Photoswitching to the core
The potential applications of smart photoswitchable porous materials are currently limited by incomplete switching. Now, efficient bulk switching has been achieved by embedding a photoisomerizable overcrowded alkene in a highly porous aromatic framework, creating a material capable of photomodulated gas uptake.
- Jet-Sing M. Lee
- & Hiroshi Sato
-
Article |
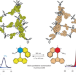 Modulation of porosity in a solid material enabled by bulk photoisomerization of an overcrowded alkene
Modulation of porosity in a solid material enabled by bulk photoisomerization of an overcrowded alkene
Despite numerous potential applications, the development of light-responsive solid materials based on molecular photoswitches is impeded by the low efficiency of photoisomerization in the solid environment. Now a robust, solid porous material made from tetraphenylmethane and a photoswitchable overcrowded alkene exhibits nearly quantitative photoisomerization in the bulk and in photomodulation of gas uptake.
- Fabio Castiglioni
- , Wojciech Danowski
- & Ben L. Feringa
-
Article |
 Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Single-atom catalysts maximize metal atom efficiency and exhibit properties that can be considerably different to their nanoparticle equivalent. Now a general host–guest strategy to make various single-atom catalysts on nitrogen-doped carbon has been developed; the iridium variant electrocatalyses the formic acid oxidation reaction with high mass activity and displays high tolerance to CO poisoning.
- Zhi Li
- , Yuanjun Chen
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 A photoswitchable polar crystal that exhibits superionic conduction
A photoswitchable polar crystal that exhibits superionic conduction
A material based on a three-dimensional –Fe–N≡C–Mo– anionic framework that hosts a Cs+ cation in every other pore has been shown to exhibit superionic conductivity, despite its polar crystal structure. It also exhibits second harmonic generation (SHG)—usually observed in insulators—and its ionic conductivity was reversibly altered under light irradiation.
- Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
- , Kosuke Nakagawa
- & Asuka Namai
-
Article |
 A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that responds to external and internal stimuli has been developed and used to fabricate a series of nanocarriers for drug release. The carriers respond to disease biomarkers, triggering self-immolative motifs and leading to the site-specific release of therapeutics both in vitro and in vivo.
- Penghui Zhang
- , Di Gao
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article |
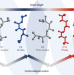 Odd–even alternations in helical propensity of a homologous series of hydrocarbons
Odd–even alternations in helical propensity of a homologous series of hydrocarbons
Even- and odd-numbered homologues of some hydrocarbons are known to exhibit different trends in solid-state properties. Now, experimental and computational investigations on a homologous series of a stereochemically well-defined hydrocarbon have revealed an odd–even effect in conformational behaviour in solution that is caused by a single gauche interaction.
- Johan A. Pradeilles
- , Siying Zhong
- & Varinder K. Aggarwal
-
Article |
 Vibrational coherences in manganese single-molecule magnets after ultrafast photoexcitation
Vibrational coherences in manganese single-molecule magnets after ultrafast photoexcitation
Controlling single-molecule magnets (SMMs) with ultrashort laser pulses could be key to future data storage devices, however, the photophysics of SMMs is complex. Now, using a monomer model system, it has been shown that optical excitation of Mn(iii)-SMMs leads to a modulation of the Jahn–Teller distortion, which is important for its magnetic anisotropy.
- Florian Liedy
- , Julien Eng
- & J. Olof Johansson
-
Article |
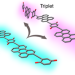 Spatial separation of triplet excitons drives endothermic singlet fission
Spatial separation of triplet excitons drives endothermic singlet fission
Generating high-energy triplet excitons from singlet fission without excess energy loss is a critical goal for potential applications. Now it is shown that molecular chromophores that are connected covalently can harbour multiple long-lived and high-energy triplets—created from one photon—only if more than two chromophoric units are present and they have sufficient flexibility to isolate the excitations upon torsional motion.
- Nadezhda V. Korovina
- , Christopher H. Chang
- & Justin C. Johnson
-
Article |
 Interface-mediated noble metal deposition on transition metal dichalcogenide nanostructures
Interface-mediated noble metal deposition on transition metal dichalcogenide nanostructures
The deposition of noble metals onto two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides is crucial for practical applications, including in catalysis and sensing, yet this process has remained difficult to control. Now, gold and silver have been shown to grow on colloidal transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets into either atomically thin layers or nanoparticles whose sizes and morphologies depend on the relative strengths of the interfacial noble metal–chalcogen bonds.
- Yifan Sun
- , Yuanxi Wang
- & Raymond E. Schaak
-
Article |
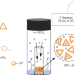 Coordination cages as permanently porous ionic liquids
Coordination cages as permanently porous ionic liquids
Porous liquids promise to combine the advantages of the porosity of solids with those of the fluidity of liquids. Now, a permanently porous ionic-liquid coordination cage has been assembled that encapsulates isomers of butanol and propanol with some size and shape selectivity, as well as three gaseous chlorofluorocarbons with a size-dependent affinity.
- Lillian Ma
- , Cally J. E. Haynes
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
News & Views |
 New stereocontrol on the block
New stereocontrol on the block
It is crucial to replace fossil fuel-based plastics with biodegradable ones that are made from renewable sources. Now, a new generation of bioplastics has been prepared through the stereoselective polymerization of diastereomeric monomers — a synthetic approach that allows tuning of the materials’ toughness, ductility and melting point.
- Sonja Herres-Pawlis
-
Article |
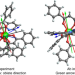 Observation of the asphericity of 4f-electron density and its relation to the magnetic anisotropy axis in single-molecule magnets
Observation of the asphericity of 4f-electron density and its relation to the magnetic anisotropy axis in single-molecule magnets
Gaining a better understanding of the complex electronic structure of single-molecule magnets is essential for their design and development. The 4f-electron density distribution of a dysprosium single-molecule magnet has now been experimentally determined using synchrotron diffraction data interpreted with a multipole model. The magnetic easy axes were recovered by analysis of the 4f-electron density shape, which is clearly oblate.
- Chen Gao
- , Alessandro Genoni
- & Jacob Overgaard
-
Article |
 Rapid desolvation-triggered domino lattice rearrangement in a metal–organic framework
Rapid desolvation-triggered domino lattice rearrangement in a metal–organic framework
A disordered metal–organic framework converts into a more porous, crystalline phase within 40 s following solvent exchange and desolvation. The rapid domino rearrangement of the whole lattice, which involves carboxylate migration on coordinatively unsaturated metal sites, is accompanied by a substantial increase in surface area.
- Sheng-Han Lo
- , Liang Feng
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article |
 In situ visualization of loading-dependent water effects in a stable metal–organic framework
In situ visualization of loading-dependent water effects in a stable metal–organic framework
A stable zinc-based metal–organic framework known to retain its porosity and crystallinity after exposure to moisture has been shown to undergo structural changes at the molecular level on adsorbing water. This dynamic and reversible response to the presence of water, including the rearrangement of bonds, is suggested to be the reason for the hydrolytic stability of this particular metal–organic framework.
- Nicholas C. Burtch
- , Ian M. Walton
- & Krista S. Walton
-
Article |
 Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Quantum dots functionalized with energy-accepting dyes hold promise for converting low-energy photons into higher-energy visible light for bioimaging, catalysis and solar energy harvesting. Now, it has been shown that non-toxic silicon quantum dots can be used in these systems; the transfer of spin-triplet excitons to molecules at their surface has been observed.
- Pan Xia
- , Emily K. Raulerson
- & Sean T. Roberts
-
Article |
 Efficient and tunable one-dimensional charge transport in layered lanthanide metal–organic frameworks
Efficient and tunable one-dimensional charge transport in layered lanthanide metal–organic frameworks
High electrical conductivities in metal–organic frameworks—attractive for applications in sensing and energy storage—typically arise in layered MOFs from metal–ligand bonds with strong covalent character. Now, lanthanide-based MOFs have shown high out-of-plane conductivities originating instead from the π-stacking of organic ligands.
- Grigorii Skorupskii
- , Benjamin A. Trump
- & Mircea Dincă
-
Article |
 A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
Gene-circuit-based sensors have, to date, largely relied on optical proteins (such as green fluorescent protein) to report the output, which limits the signalling bandwidth. Now, an electrochemical output has been developed and integrated with cell-free gene circuits. This approach enables multiplexing of sensors and introduces the possibility of electronic-based logic, memory and response elements to synthetic biology.
- Peivand Sadat Mousavi
- , Sarah J. Smith
- & Keith Pardee
-
Article |
 Capture of nitrogen dioxide and conversion to nitric acid in a porous metal–organic framework
Capture of nitrogen dioxide and conversion to nitric acid in a porous metal–organic framework
Nitrogen oxides are major air pollutants; capture and abatement technologies exist but they typically involve toxic species or precious-metal catalysts. Now, a metal–organic framework has been shown to store NO2 dimers selectively, and to separate NO2 from other gases under wet conditions. Treatment with water in air leads to conversion of NO2 into HNO3—an important feedstock for fertilizer production—with full recovery of the host.
- Jiangnan Li
- , Xue Han
- & Sihai Yang
-
News & Views |
 Of HOF hosts
Of HOF hosts
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks can readily encapsulate native enzymes and keep them active beyond biological conditions.
- Rui-Biao Lin
- & Banglin Chen
-
Article |
 Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
A solution-processing step has been used to prepare quantum-well structures that comprise a thin layer of perovskite sandwiched between two layers of conjugated oligothiophene derivatives. The band gap of the resulting 2D hybrid perovskites can be fine-tuned by functionalizing the organic component, which also improves the stability of the system.
- Yao Gao
- , Enzheng Shi
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
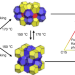 Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
The Z phase, one of three fundamental Frank–Kasper phases—topologically close-packed structures commonly found in metal alloys—is associated with a relatively large volume ratio between its constituents. This means it is typically not formed in single-component soft materials. Now, a shape amphiphile has been shown to self-assemble in a variety of unconventional structures, including the Z phase.
- Zebin Su
- , Chih-Hao Hsu
- & Stephen Z. D. Cheng
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 A closed cycle for esterifying aromatic hydrocarbons with CO2 and alcohol
A closed cycle for esterifying aromatic hydrocarbons with CO2 and alcohol
Previous methods for functionalizing hydrocarbons with CO2 to form carboxylic acid derivatives have required stoichiometric energy-intensive reagents such as strong bases or electrophilic activators. Now, a simple solid base has been developed that transforms aromatic hydrocarbons, CO2 and methanol into aromatic esters via a two-step cycle requiring no additional reagents.
- Dianne J. Xiao
- , Emma D. Chant
- & Matthew W. Kanan
-
Article |
 Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Although they are synthetically tunable, organic molecules that undergo singlet fission (the generation of two excitons from one photon) have not demonstrated the excited-state properties necessary to improve optoelectronic devices. Now, a general ‘energy cleft’ molecular design scheme has been demonstrated that enables rapid generation and long lifetimes of multiple triplet excitons that are for device applications.
- Andrew B. Pun
- , Amir Asadpoordarvish
- & Matthew Y. Sfeir
-
Article |
 Overcoming chemical equilibrium limitations using a thermodynamically reversible chemical reactor
Overcoming chemical equilibrium limitations using a thermodynamically reversible chemical reactor
Conventional chemical reactors are subject to the equilibrium limitations imposed by the overall reaction. It has now been shown that this limitation can be overcome if reactants are fed separately to a reactor and a non-stoichiometric oxygen carrier is used to transfer both oxygen and key chemical information across a reaction cycle.
- Ian S. Metcalfe
- , Brian Ray
- & John S. O. Evans
-
Article |
 Isotherms of individual pores by gas adsorption crystallography
Isotherms of individual pores by gas adsorption crystallography
Gas sorption studies in porous materials typically reflect their overall gas uptake. Now, using a ‘gas adsorption crystallography’ method, the gas adsorption isotherms of two metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been quantitatively decomposed into sub-isotherms that reflect the pore-filling behaviour of various guests in the different types of pores present in the MOFs.
- Hae Sung Cho
- , Jingjing Yang
- & Osamu Terasaki
-
Article |
 Imaging defects and their evolution in a metal–organic framework at sub-unit-cell resolution
Imaging defects and their evolution in a metal–organic framework at sub-unit-cell resolution
Structural defects are known to exist in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), and to affect the materials’ properties, but their exact structures have remained difficult to determine. Now, missing-linker and missing-cluster defects have been observed in a MOF using low-dose transmission electron microscopy, enabling their distributions, evolutions during crystallization and effects on the material’s catalytic activity to be explored.
- Lingmei Liu
- , Zhijie Chen
- & Yu Han
-
Article |
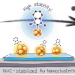 N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized magic-number gold nanoclusters
N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized magic-number gold nanoclusters
Magic-number Au11 clusters containing N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands are prepared by ligand exchange on known phosphine clusters and the introduction of even a single NHC results in improved cluster stability. The use of NHC-containing clusters in the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO is described and correlates with cluster stability.
- Mina R. Narouz
- , Kimberly M. Osten
- & Cathleen M. Crudden
-
Article |
 Radical polymerization inside living cells
Radical polymerization inside living cells
A strategy for directly synthesizing unnatural polymers in cells through radical polymerization has now been developed. This approach provides a platform to manipulate, track and control cellular behaviour by the in cellulo generation of macromolecules and a variety of nanostructures.
- Jin Geng
- , Weishuo Li
- & Mark Bradley
-
Article |
 Chemically stable polyarylether-based covalent organic frameworks
Chemically stable polyarylether-based covalent organic frameworks
The development of porous, crystalline materials with high chemical stability is crucial for their practical uses. Now, polyarylether-based covalent organic frameworks (PAE-COFs) have been synthesized that show high crystallinity and porosity, as well as good stability against harsh chemical environments including boiling water and strong acids and bases.
- Xinyu Guan
- , Hui Li
- & Shilun Qiu
-
Article |
 Shear-induced assembly of a transient yet highly stretchable hydrogel based on pseudopolyrotaxanes
Shear-induced assembly of a transient yet highly stretchable hydrogel based on pseudopolyrotaxanes
Synthetic dissipative systems, formed by out-of-equilibrium self-assembly processes, can mimic some of the properties of biological systems, but often show poor mechanical performance. Now, a shear-induced transient hydrogel has been prepared that is also highly stretchable. The system is based on coordination interactions between Cu(ii) centres and the pendant carboxylate groups of a pseudopolyrotaxane.
- Hua Ke
- , Liu-Pan Yang
- & Wei Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Pulling together to improve stability
Pulling together to improve stability
Maleimide–thiol adducts are popular in both bioconjugation and materials chemistry, however, they are unstable under physiological conditions. Now, a mechanochemical approach uses pulling forces to stabilize maleimide–thiol adducts and improve the stability of polymer–protein conjugates.
- Cody J. Higginson
- & Phillip B. Messersmith
-
Perspective |
 Molecular spins for quantum computation
Molecular spins for quantum computation
Spins in molecules provide a simple platform with which to encode a quantum bit (qubit), the elementary unit of future quantum computers. This Perspective discusses how chemistry can contribute to designing robust spin systems based, in particular, on mononuclear lanthanoid complexes.
- A. Gaita-Ariño
- , F. Luis
- & E. Coronado
-
News & Views |
 Two are better than one
Two are better than one
Finely tuned interactions in the second coordination sphere of enzymes or homogeneous catalysts can be essential for their function. Now, this concept has been applied to the surface of a catalytic material, utilizing pairs of Cu atoms for the selective electrochemical fixation of CO2.
- Benjamin S. Natinsky
- & Chong Liu
-
Article |
 Mesopolymer synthesis by ligand-modulated direct arylation polycondensation towards n-type and ambipolar conjugated systems
Mesopolymer synthesis by ligand-modulated direct arylation polycondensation towards n-type and ambipolar conjugated systems
Conjugated mesopolymers can combine the advantages of polymers and oligomers, but have received less attention as semiconducting materials. Now, such compounds have been synthesized by direct arylation polycondensation that exhibit high molecular regularity, solubility and solution processability. These mesopolymers also show electron mobilities that are significantly better than those of their polymer counterparts.
- Zhenjie Ni
- , Hanlin Wang
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article |
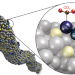 Copper atom-pair catalyst anchored on alloy nanowires for selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2
Copper atom-pair catalyst anchored on alloy nanowires for selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2
Anchored single-atom catalysts have recently been shown to be very active for various processes, however, a catalyst that features two adjacent copper atoms—which we call an atom-pair catalyst—is now reported. The Cu10–Cu1x+ pair structures work together to carry out the critical bimolecular step in CO2 reduction.
- Jiqing Jiao
- , Rui Lin
- & Yadong Li
-
News & Views |
 Surface anchors target golden bullets
Surface anchors target golden bullets
Gold nanomaterials are attractive for a variety of applications, including in medicine, but need to be made stable enough to operate in biological systems. Now, gold nanorods have been stabilized for photothermal therapy by sequential surface anchoring, using a bidendate PEG-based ligand that features a thiolate moiety and an Au–NHC moiety.
- Guillaume Médard
- & Anthoula C. Papageorgiou

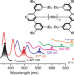 The loss of endgroup effects in long pyridyl-endcapped oligoynes on the way to carbyne
The loss of endgroup effects in long pyridyl-endcapped oligoynes on the way to carbyne