Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfiguring hydrogel assemblies using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive for multiple customized functions
Reconfiguring hydrogel assemblies using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive for multiple customized functions
Although hydrogels with complex, heterogeneous and reconfigurable structures are promising materials for use in intelligent systems, fabricating such hydrogels is challenging. Now it has been shown that they can be fabricated by reversibly gluing different hydrogel units using a photocontrolled metallopolymer adhesive. This method can be used to design hydrogels with customized functions.
- Jiahui Liu
- , Yun-Shuai Huang
- & Si Wu
-
Article |
 Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks
Bottom-up assembly of protocells into networking superstructures represents a further key step towards rudimentary formation of life. Now it has been shown that a pool of biomolecules can self-organize into an interactive binary population of protocell coacervates with a self-sorting chain-like configuration, allowing for biomolecular extraction, translocation and macroscale separation.
- Wenjing Mu
- , Liyan Jia
- & Yan Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Droplet slipperiness despite surface heterogeneity at molecular scale
Surface heterogeneity is generally acknowledged as the major cause of liquid–solid friction, affecting whether droplets slide off the surface or stick to it. Now, a model surface of self-assembled monolayers has been used to investigate how molecular-scale surface heterogeneity affects water contact angle hysteresis and contact line friction. The high-coverage hydrophobic surface is slippery, as—counter-intuitively—is the low-coverage hydrophilic surface.
- Sakari Lepikko
- , Ygor Morais Jaques
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article |
 Chemical upcycling of commodity thermoset polyurethane foams towards high-performance 3D photo-printing resins
Chemical upcycling of commodity thermoset polyurethane foams towards high-performance 3D photo-printing resins
Current strategies for recycling cross-linked polyurethane foam waste are economically unattractive and/or lead to recycled products with inferior properties. Now it has been shown that a cost-effective chemical strategy can be used to turn the foam into high-performance value-added three-dimensional photo-printing resins.
- Zenghe Liu
- , Zizheng Fang
- & Tao Xie
-
Article |
 Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
The kinetics of liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) in cell-like confinements remains poorly understood. Now it has been shown that it involves complex interplay between the incipient phases and the membrane boundary, which arrests phase coarsening, deforms the membrane and couples LLPS with lipid phase separation.
- Wan-Chih Su
- , James C. S. Ho
- & Atul N. Parikh
-
Article
| Open Access Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
The synthesis of two-dimensional nanostructures with controlled dimensions from polymeric precursors remains challenging. Now, two-dimensional nanoparticles with chemically different spatially defined cores have been fabricated through seeded growth and are shown to undergo a programmable degradation process.
- Zaizai Tong
- , Yujie Xie
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
Article |
 Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have remained difficult to grow as single crystals. Now, amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives that assemble in micelles in aqueous solutions have been shown to promote the growth of a variety of imine-bridged COFs into single crystals, in a step-by-step fashion, within their hydrophobic compartment.
- Zhipeng Zhou
- , Lei Zhang
- & Zhikun Zheng
-
Article |
 Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Crystals of hexachlorobenzene have now been shown to support the autonomous motion of water and particulate matter over their surface. Parallel microchannels present at the surface of the crystal gradually widen by sublimation, propelling droplets of condensed ambient water that can also transport microscopic amounts of material such as silver microparticles.
- Patrick Commins
- , Marieh B. Al-Handawi
- & Panče Naumov
-
Article |
 Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Identifying and quantifying the biodistribution of synthetic polymeric nanoparticles in biological milieu is crucial for biomedical applications. Now, it has been shown that encoded polymeric amphiphiles with discrete molar masses undergo sequence- and length-dependent self-assembly into precise digital micelles that can be used in direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification assays.
- Qiangqiang Shi
- , Hao Yin
- & Shiyong Liu
-
Article |
 Photoinduced inverse vulcanization
Photoinduced inverse vulcanization
Inverse vulcanization (IV) generates sulfur-rich functional polymers from elemental sulfur and organic crosslinkers, but the harsh reaction conditions required limit the scope of suitable crosslinkers. Now, a photoinduced IV has been shown to proceed at ambient temperatures, enabling the use of volatile and gaseous alkenes and alkynes as crosslinkers and broadening the range of products.
- Jinhong Jia
- , Jingjiang Liu
- & Zheng-Jun Quan
-
Article |
 Phase-specific RNA accumulation and duplex thermodynamics in multiphase coacervate models for membraneless organelles
Phase-specific RNA accumulation and duplex thermodynamics in multiphase coacervate models for membraneless organelles
The biochemical roles and mechanisms of multiphase membraneless organelles are not yet well understood. Now, multiphase peptide droplets have been shown to sort RNA based on whether it is single- or double-stranded, as well as impact RNA duplexation through in-droplet thermodynamic equilibria. This work provides insight into possible primitive mechanisms for multicompartment intracellular condensates and can aid in the design of functional artificial membraneless organelles.
- Saehyun Choi
- , McCauley O. Meyer
- & Christine D. Keating
-
Article |
 Parallel transmission in a synthetic nerve
Parallel transmission in a synthetic nerve
Soft bioelectronic devices have exciting potential applications in robotics, computing and medicine, but they are typically restricted by the requirement for tethers or stiff electrodes. Now, a synthetic nerve has been developed that is bioinspired, wireless and powered by light. By patterning functionalized lipid membrane compartments, information was directionally conveyed using electrochemical signals.
- Charlotte E. G. Hoskin
- , Vanessa Restrepo Schild
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article |
 Continuous, autonomous subsurface cargo shuttling by nature-inspired meniscus-climbing systems
Continuous, autonomous subsurface cargo shuttling by nature-inspired meniscus-climbing systems
Water-walking insects harness capillary forces by changing body posture to climb or descend the meniscus between water and a solid object. Now, autonomous aqueous-based synthetic systems have been shown to overcome the meniscus barrier and shuttle cargo subsurface between a landing site and targeted drop-off sites.
- Ganhua Xie
- , Pei Li
- & Thomas P. Russell
-
Article |
 A versatile approach for the synthesis of degradable polymers via controlled ring-opening metathesis copolymerization
A versatile approach for the synthesis of degradable polymers via controlled ring-opening metathesis copolymerization
Degradable polymers are important for technological applications and sustainability, but they remain difficult to access via ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP). Now, commercial 2,3-dihydrofuran is shown to be an effective ROMP comonomer for various norbornenes. This copolymerization generates new acid-degradable polymers with controlled molecular weights, different functionalities and tunable properties.
- John D. Feist
- , Daniel C. Lee
- & Yan Xia
-
News & Views |
 Just a click away
Just a click away
The precisely ordered helical structures of biomacromolecules have long-inspired chemists to create synthetic helical polymers. Now, a new step-growth approach has enabled facile synthesis of helical polymers through the highly efficient sulfur(vi) fluoride exchange click chemistry.
- Cangjie Yang
- & Jia Niu
-
Article |
 Olefin metathesis-based chemically recyclable polymers enabled by fused-ring monomers
Olefin metathesis-based chemically recyclable polymers enabled by fused-ring monomers
Depolymerizable polymers can potentially address challenges in polymer sustainability, but most existing systems lack the useful thermomechanical properties of traditional ones. Now, it has been shown that depolymerizable polymers based on olefin metathesis show good thermal stability as well as versatile mechanical properties and that the monomers used to make them can be prepared from abundant materials.
- Devavrat Sathe
- , Junfeng Zhou
- & Junpeng Wang
-
Article |
 Chemical-mediated translocation in protocell-based microactuators
Chemical-mediated translocation in protocell-based microactuators
Although many systems that involve protocell–protocell interactions have been developed, there are fewer reports of protocell–environment interactive systems. Now, helical hydrogel filaments—in which enzyme-containing proteinosomes are immobilized—have been shown to contract and expand as the local chemical environment changes. Enzyme processing regulates the chemomechanical responses to generate different modes of actuation in the soft microstructures.
- Ning Gao
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
News & Views |
 Colloidal metallurgy
Colloidal metallurgy
Colloidal self-assembly requires carefully balanced particle interactions that are often incompatible with the mechanical disturbances associated with macroscopic-scale manufacturing. Now, a practical bottom-up route has enabled the production of bulk solid materials with nanoscale components.
- Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article |
 Enzyme-mediated nitric oxide production in vasoactive erythrocyte membrane-enclosed coacervate protocells
Enzyme-mediated nitric oxide production in vasoactive erythrocyte membrane-enclosed coacervate protocells
The self-assembly of haemoglobin-containing erythrocyte membrane fragments onto the surface of preformed coacervates has been used to make hybrid synthetic cells that can initiate nitric-oxide-induced vasodilation. These synthetic cells encapsulate enzymes that generate a flux of nitric oxide, as well as exhibiting high haemocompatibility and increased blood circulation times.
- Songyang Liu
- , Yanwen Zhang
- & Stephen Mann
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry in the making
Symmetry in the making
After years of speculation on the origins of symmetry-making and -breaking during crystallization, time-resolved in situ scanning probe microscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations have shown that the formation of olanzapine crystals largely occurs by the incorporation of centrosymmetric dimers into growth sites.
- Susan M. Reutzel-Edens
-
Article |
 Olanzapine crystal symmetry originates in preformed centrosymmetric solute dimers
Olanzapine crystal symmetry originates in preformed centrosymmetric solute dimers
Crystal symmetry is notoriously uncorrelated to the symmetry of the constituent molecules that make up a crystal. Symmetry breaking is typically thought to occur during nucleation and growth, but a symmetry element of olanzapine crystals—an inversion centre—has now been shown to emerge in centrosymmetric dimers extant in solution prior to crystallization.
- Monika Warzecha
- , Lakshmanji Verma
- & Peter G. Vekilov
-
Article |
 Meta-DNA structures
Meta-DNA structures
A six-helix bundle DNA structure called meta-DNA has now been assembled and shown to possess some structural properties similar to those of single-stranded DNA. Two meta-DNAs containing complementary ‘meta-base pairs’ are shown to form double helices. Meta-DNA building blocks are also used to construct a series of DNA architectures and to perform a hierarchical strand-displacement reaction.
- Guangbao Yao
- , Fei Zhang
- & Hao Yan
-
News & Views |
 New stereocontrol on the block
New stereocontrol on the block
It is crucial to replace fossil fuel-based plastics with biodegradable ones that are made from renewable sources. Now, a new generation of bioplastics has been prepared through the stereoselective polymerization of diastereomeric monomers — a synthetic approach that allows tuning of the materials’ toughness, ductility and melting point.
- Sonja Herres-Pawlis
-
News & Views |
 Of HOF hosts
Of HOF hosts
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks can readily encapsulate native enzymes and keep them active beyond biological conditions.
- Rui-Biao Lin
- & Banglin Chen
-
News & Views |
 A cornerstone of complex crystals
A cornerstone of complex crystals
Frank–Kasper phases are topologically close-packed structures typically found in ordered mixtures of ‘hard particles’ such as metallic alloys. Now, a shape amphiphile has been shown to self-assemble into a Frank–Kasper Z phase, which had so far remained elusive in soft materials.
- Abhiram Reddy
- & Gregory M. Grason
-
Article |
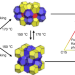 Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
Identification of a Frank–Kasper Z phase from shape amphiphile self-assembly
The Z phase, one of three fundamental Frank–Kasper phases—topologically close-packed structures commonly found in metal alloys—is associated with a relatively large volume ratio between its constituents. This means it is typically not formed in single-component soft materials. Now, a shape amphiphile has been shown to self-assemble in a variety of unconventional structures, including the Z phase.
- Zebin Su
- , Chih-Hao Hsu
- & Stephen Z. D. Cheng
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Shear-induced assembly of a transient yet highly stretchable hydrogel based on pseudopolyrotaxanes
Shear-induced assembly of a transient yet highly stretchable hydrogel based on pseudopolyrotaxanes
Synthetic dissipative systems, formed by out-of-equilibrium self-assembly processes, can mimic some of the properties of biological systems, but often show poor mechanical performance. Now, a shear-induced transient hydrogel has been prepared that is also highly stretchable. The system is based on coordination interactions between Cu(ii) centres and the pendant carboxylate groups of a pseudopolyrotaxane.
- Hua Ke
- , Liu-Pan Yang
- & Wei Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Pulling together to improve stability
Pulling together to improve stability
Maleimide–thiol adducts are popular in both bioconjugation and materials chemistry, however, they are unstable under physiological conditions. Now, a mechanochemical approach uses pulling forces to stabilize maleimide–thiol adducts and improve the stability of polymer–protein conjugates.
- Cody J. Higginson
- & Phillip B. Messersmith
-
Article |
 Enzyme-powered motility in buoyant organoclay/DNA protocells
Enzyme-powered motility in buoyant organoclay/DNA protocells
Organoclay/DNA semipermeable microcapsules with catalase-powered oxygen gas bubble-dependent buoyancy are prepared and exploited as synthetic protocells capable of programmed motility and sustained oscillatory movement.
- B. V. V. S. Pavan Kumar
- , Avinash J. Patil
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
Living systems rely on externally tuneable and stimuli-responsive conformational changes of proteins and protein assemblies for a wide range of essential functions. A combination of experimental and computational analyses has now enabled the fabrication of a rationally designed, synthetic, stimuli-responsive protein assembly through modulation of its free-energy landscape.
- Robert Alberstein
- , Yuta Suzuki
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Article |
 Amino-acid-encoded biocatalytic self-assembly enables the formation of transient conducting nanostructures
Amino-acid-encoded biocatalytic self-assembly enables the formation of transient conducting nanostructures
Amino acids have now been used as chemical inputs to provide control over self-assembly in semiconducting structures. This approach enables temporal control over the formation of nanostructures and consequently control over their transient electronic conductivity.
- Mohit Kumar
- , Nicole L. Ing
- & Rein V. Ulijn
-
News & Views |
 Intercalation without altercation
Intercalation without altercation
Building materials with clusters instead of atoms promises unconventional properties, but those 'superatomic solids' are often too fragile to manipulate. Now, intercalating a guest within an ionic layered solid made of fullerenes and metal chalcogenide clusters greatly alters its conductivity and optical properties without disrupting its crystalline structure.
- Shiv N. Khanna
- & Arthur C. Reber
-
Article |
 Single-crystal-to-single-crystal intercalation of a low-bandgap superatomic crystal
Single-crystal-to-single-crystal intercalation of a low-bandgap superatomic crystal
Intercalation — a cornerstone of materials science with wide-ranging applications — has now been demonstrated in a superatomic crystal. A redox-active tetracyanoethylene guest was inserted into the lattice of a material consisting of alternate layers of {Co6Te8} clusters and C60 fullerenes, leading to a single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation that significantly modulates the material's optical and electrical transport properties.
- Evan S. O'Brien
- , M. Tuan Trinh
- & Xavier Roy
-
Article |
 Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
A scalable, one-pot, solution-based protocol for the controlled synthesis of uniform non-spherical block copolymer micelles is a desirable but challenging target. Now, a polymerization-induced crystallization-driven self-assembly process has been developed that offers facile access to 1D and platelet micelle morphologies and to near monodisperse cylinders of controlled length.
- Charlotte E. Boott
- , Jessica Gwyther
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation–π interactions
Tuning underwater adhesion with cation–π interactions
Cation–π interactions are critical for the adhesion proteins of marine organisms, yet the energetics of cation–π interactions in underwater environments remains uncharted. Nanoscale force measurements and NMR spectroscopy reveal that interfacial confinement fundamentally alters the energetics of cation–π mediated assembly.
- Matthew A. Gebbie
- , Wei Wei
- & Jacob N. Israelachvili
-
Article |
 Programming molecular self-assembly of intrinsically disordered proteins containing sequences of low complexity
Programming molecular self-assembly of intrinsically disordered proteins containing sequences of low complexity
A programmable model of membraneless organelles comprised of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) containing sequences of low complexity has now been developed. The rules governing the assembly of archetypal IDPs into biologically inspired mixed, layered and size-controlled configurations provides a new means for understanding intracellular phase behaviour of IDPs.
- Joseph R. Simon
- , Nick J. Carroll
- & Gabriel P. López
-
Article |
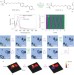 Photoswitching of glass transition temperatures of azobenzene-containing polymers induces reversible solid-to-liquid transitions
Photoswitching of glass transition temperatures of azobenzene-containing polymers induces reversible solid-to-liquid transitions
Reversibly inducing solid-to-liquid transitions of polymers at room temperature represents a challenge for enhanced processability and applications of polymers. Now, three azopolymers have been shown to exhibit photoswitchable glass transition temperatures, resulting in reversible solid-to-liquid transitions. Light exposure can heal cracks in hard azopolymers, reduce surface roughness of azopolymer films and control azopolymer adhesion.
- Hongwei Zhou
- , Changguo Xue
- & Si Wu
-
Article |
 Fast response dry-type artificial molecular muscles with [c2]daisy chains
Fast response dry-type artificial molecular muscles with [c2]daisy chains
Photoresponsive wet- and dry-type actuators can be built up from rotaxane-like structures through the polycondensation of four-armed polyethylene glycols with [c2]daisy chains comprised of cyclodextrin rings and azobenzene side chains. The response of the dry-type (xerogel) actuator to UV light was found to be more than 10,000 times faster than the wet-type (hydrogel) actuator.
- Kazuhisa Iwaso
- , Yoshinori Takashima
- & Akira Harada
-
Article |
 Dissipative self-assembly of vesicular nanoreactors
Dissipative self-assembly of vesicular nanoreactors
Dissipative self-assembly processes are energetically uphill and require the continuous consumption of energy. Now, by using ATP as a chemical fuel, the dissipative self-assembly of vesicles has been demonstrated. These transiently formed supramolecular assemblies are able to sustain a chemical reaction and it is shown that the yield depends on the lifetime of the vesicles.
- Subhabrata Maiti
- , Ilaria Fortunati
- & Leonard J. Prins
-
Article |
 A highly stretchable autonomous self-healing elastomer
A highly stretchable autonomous self-healing elastomer
Polymers that are both elastic and self-healing are desirable for a variety of applications, but often rely on hydrogen bonding which makes them moisture-sensitive. Now, by incorporating metal–ligand interactions with different bond strengths into flexible polymer backbones, an elastomer has been devised that combines high stretchability and high dielectric strength with autonomous self-healing and mechanical actuation capabilities.
- Cheng-Hui Li
- , Chao Wang
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article |
 Highly branched and loop-rich gels via formation of metal–organic cages linked by polymers
Highly branched and loop-rich gels via formation of metal–organic cages linked by polymers
Gels formed by metal–ligand coordination typically consist of single metal ions linked together by polymer chains. Now, metal–organic cages have been used as junctions instead. A gel was prepared that features a large number of polymer chains at each junction, including loops that further serve to functionalize the material.
- Aleksandr V. Zhukhovitskiy
- , Mingjiang Zhong
- & Jeremiah A. Johnson
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

 Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations
Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations Coordination driven gelation
Coordination driven gelation Tales from the cryptates
Tales from the cryptates A right tangle
A right tangle Falling to pieces faster
Falling to pieces faster Bursting bubbles
Bursting bubbles At the crease
At the crease