Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Two-dimensional hybrid perovskites have gained substantial interest recently due to their controllable optoelectronic properties; however precise control over layer thickness has been synthetically challenging. Now a crystal growth method is shown to achieve high-quality single crystals of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites with control over their thickness and length through judicious solvent choice, affording precisely tuned optoelectronic properties.
- Jee Yung Park
- , Ruyi Song
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
On-surface synthesis enables highly reactive structures to be produced under vacuum, but they need to be passivated to be incorporated into practical devices. Here, the facile protection of air-sensitive chiral graphene nanoribbons has been shown, by either hydrogenation or synthesis of an oxidized form. The chemically stable forms can subsequently be deprotected.
- James Lawrence
- , Alejandro Berdonces-Layunta
- & Dimas G. de Oteyza
-
Article |
 Stoichiometric two-dimensional non-van der Waals AgCrS2 with superionic behaviour at room temperature
Stoichiometric two-dimensional non-van der Waals AgCrS2 with superionic behaviour at room temperature
Layered materials held together by weak interactions can be exfoliated into monolayers that retain the structure and composition of their bulk counterpart, but this has remained challenging to achieve for non-van der Waals materials. Now, AgCrS2 has been exfoliated into such [CrS2]Ag[CrS2] nanosheets through intercalation with tetraalkylammonium cations chosen for their suitable redox potential. The nanosheets show superionic behaviour at room temperature.
- Jing Peng
- , Yuhua Liu
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Superatomic solid solutions
Superatomic solid solutions
In atomic solids, substitutional doping is a powerful approach to modulating materials properties. Now, three substitutional mixtures of {Co6Se8} and {Cr6Te8} clusters in a crystal lattice with C60 fullerenes have been prepared. At two Co:Cr mixing ratios, the solid solutions showed particularly high electrical conductivities and low activation barriers for electron transport, owing to their structural heterogeneity.
- Jingjing Yang
- , Jake C. Russell
- & Colin Nuckolls
-
Article |
 Mechanochemical synthesis of an elusive fluorinated polyacetylene
Mechanochemical synthesis of an elusive fluorinated polyacetylene
Fluorinated polyacetylene has typically proven to be inaccessible using traditional polymer synthesis, but there is much interest in its predicted properties. Now, a mechanochemical unzipping strategy has succeeded in the synthesis of a gold-coloured, semiconducting fluorinated polyacetylene with improved stability in air compared to polyacetylene.
- Benjamin R. Boswell
- , Carl M. F. Mansson
- & Noah Z. Burns
-
News & Views |
 What atoms do when they get together
What atoms do when they get together
How atoms organize during the earliest stages of nucleation has been a subject of speculation for over a century. Using atomically resolved electron microscopy, the formation and ordering of metal clusters from individual atoms has now been observed in carbon nanotubes that serve as ‘test tubes’.
- J. J. De Yoreo
- & B. A. Legg
-
Article |
 Tunable exciton binding energy in 2D hybrid layered perovskites through donor–acceptor interactions within the organic layer
Tunable exciton binding energy in 2D hybrid layered perovskites through donor–acceptor interactions within the organic layer
The strength of electrostatic interactions in semiconductors strongly affects their performance in optoelectronic devices. Now, doping two-dimensional naphthalene-based lead halide perovskites with tetrachloro-1,2-benzoquinone has been shown to introduce donor–acceptor interactions within the organic network, without disrupting the inorganic sublattice. This in turn altered the energy of the materials’ electron–hole electrostatic Coulomb interactions.
- James V. Passarelli
- , Catherine M. Mauck
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Article |
 Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
Molecular engineering of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites quantum wells
A solution-processing step has been used to prepare quantum-well structures that comprise a thin layer of perovskite sandwiched between two layers of conjugated oligothiophene derivatives. The band gap of the resulting 2D hybrid perovskites can be fine-tuned by functionalizing the organic component, which also improves the stability of the system.
- Yao Gao
- , Enzheng Shi
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
 Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Although they are synthetically tunable, organic molecules that undergo singlet fission (the generation of two excitons from one photon) have not demonstrated the excited-state properties necessary to improve optoelectronic devices. Now, a general ‘energy cleft’ molecular design scheme has been demonstrated that enables rapid generation and long lifetimes of multiple triplet excitons that are for device applications.
- Andrew B. Pun
- , Amir Asadpoordarvish
- & Matthew Y. Sfeir
-
Article |
 Thiophene and its sulfur inhibit indenoindenodibenzothiophene diradicals from low-energy lying thermal triplets
Thiophene and its sulfur inhibit indenoindenodibenzothiophene diradicals from low-energy lying thermal triplets
A paradoxical case of a well-defined diradicaloid that has an unusually large singlet–triplet energy gap (ΔES-T) imparted by the thiophene sulfur atom is reported. Quantum chemistry, organic synthesis, molecular spectroscopies, X-ray crystal analysis and high-temperature magnetic measurements help account for the dichotomy between the large diradical character and large ΔEST.
- Justin J. Dressler
- , Mitsuru Teraoka
- & Michael M. Haley
-
Article |
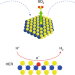 Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
MoS2 single layers spontaneously undergo a slow oxygen substitution reaction under ambient conditions giving rise to solid-solution-type 2D molybdenum oxy-sulfide crystals. The oxygen substitution sites of the 2D MoS2−xOx crystals act as efficient single-atom catalytic centres for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- János Pető
- , Tamás Ollár
- & Levente Tapasztó
-
Article |
 Formation of the layered conductive magnet CrCl2(pyrazine)2 through redox-active coordination chemistry
Formation of the layered conductive magnet CrCl2(pyrazine)2 through redox-active coordination chemistry
Layered coordination polymers are attractive for the preparation of advanced 2D materials but they are typically non-magnetic insulators. Now such a layered network, CrCl2(pyrazine)2, has been prepared that comprises a paramagnetic metal ion and a redox-active ligand. The material exhibits both magnetism — with a ferrimagnetic ground state — and high electrical conductivity.
- Kasper S. Pedersen
- , Panagiota Perlepe
- & Rodolphe Clérac
-
Article |
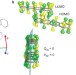 Coherent singlet fission activated by symmetry breaking
Coherent singlet fission activated by symmetry breaking
Singlet fission — converting a singlet exciton to two triplet excitons — may be useful for improving photovoltaic efficiency. Ultrafast spectroscopic measurements and quantum chemical calculations have now uncovered aspects of the process critical to it occurring efficiently, including the role of intermolecular vibrations and symmetry breaking, and the location of a conical intersection on the excited-state potential-energy surface.
- Kiyoshi Miyata
- , Yuki Kurashige
- & Yoshiyasu Matsumoto
-
News & Views |
 Fixing Jacob's ladder
Fixing Jacob's ladder
Density functional theory calculations can be carried out with different levels of accuracy, forming a hierarchy that is often represented by the rungs of a ladder. Now a new method has been developed that significantly improves the accuracy of the 'third rung' when calculating the properties of diversely bonded systems.
- Roberto Car
-
Article |
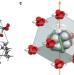 Directionally tunable and mechanically deformable ferroelectric crystals from rotating polar globular ionic molecules
Directionally tunable and mechanically deformable ferroelectric crystals from rotating polar globular ionic molecules
A major drawback of molecular ferroelectric crystals, low dimensionality, has now been overcome by ionic plastic crystals. Molecular rotation and phase transitions intrinsic to the crystals make the materials unique molecular ferroelectrics, where the polarization axis direction in a grown crystal can be flexibly altered by applying an electric field.
- Jun Harada
- , Takafumi Shimojo
- & Tamotsu Inabe
-
Review Article |
 Dynamic molecular crystals with switchable physical properties
Dynamic molecular crystals with switchable physical properties
Numerous dynamic molecular crystals whose physical properties can be switched by external stimuli have recently been developed. This Review discusses how the precise control of the electron, proton and molecular movement within the crystals through the application of external stimuli can lead to considerable changes in their properties.
- Osamu Sato
-
Article |
 Accurate first-principles structures and energies of diversely bonded systems from an efficient density functional
Accurate first-principles structures and energies of diversely bonded systems from an efficient density functional
Whether a molecule or material can exist, and with what structures and energies, is of critical importance. For demanding calculations the efficiency of density functional theory makes it the only practical electronic structure theory available to help answer these questions. Now, an efficient density functional is shown to have unprecedented accuracy for a diverse set of bonded systems.
- Jianwei Sun
- , Richard C. Remsing
- & John P. Perdew
-
Article |
 Diindeno-fusion of an anthracene as a design strategy for stable organic biradicals
Diindeno-fusion of an anthracene as a design strategy for stable organic biradicals
Biradical polycyclic hydrocarbons are promising materials for organic spintronic and photovoltaic applications. The efficient and scalable synthesis of a diindenoanthracene derivative that exhibits moderate biradical character, yet is remarkably stable towards oxygen and heat, is now reported. A thermally accessible magnetic triplet state was studied through variable temperature techniques.
- Gabriel E. Rudebusch
- , José L. Zafra
- & Michael M. Haley
-
Article |
 Charge-compensation in 3d-transition-metal-oxide intercalation cathodes through the generation of localized electron holes on oxygen
Charge-compensation in 3d-transition-metal-oxide intercalation cathodes through the generation of localized electron holes on oxygen
The energy that can be stored in lithium-ion batteries is typically limited by the redox chemistry of the transition metals within the cathodes. Now it is shown that for Li1.2[Ni2+0.13Co3+0.13Mn4+0.54]O2, a 3d-transition-metal oxide that breaks this limit, Li-ion extraction is charge compensated not just by transition-metal oxidation but also through the generation of localized electron-holes on oxygen.
- Kun Luo
- , Matthew R. Roberts
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 A labile hydride strategy for the synthesis of heavily nitridized BaTiO3
A labile hydride strategy for the synthesis of heavily nitridized BaTiO3
Oxynitrides are garnering interest because of their variety of novel properties, but their synthesis has typically involved highly reducing conditions that put significant constraints on their composition, structure and properties. Now, the lability of H− in perovskite oxyhydride BaTiO3−xHx has enabled H–/N3– exchange at a lower temperature, yielding a ferroelectric oxynitride BaTiO3−xN2x/3.
- Takeshi Yajima
- , Fumitaka Takeiri
- & Hiroshi Kageyama
-
-
Article |
 Molecular length dictates the nature of charge carriers in single-molecule junctions of oxidized oligothiophenes
Molecular length dictates the nature of charge carriers in single-molecule junctions of oxidized oligothiophenes
Understanding the intrinsic electronic properties of building blocks in conjugated materials can provide powerful design guidelines to control charge transport, such as tuning the nature of the charge carriers. Now, single-molecule transport studies of a family of oxidized oligothiophenes have shown that their molecular length determines the dominant carrier type.
- Emma J. Dell
- , Brian Capozzi
- & Luis M. Campos
-
News & Views |
 A positive future for squid proteins
A positive future for squid proteins
Protein-based protonic conductivity plays an important role in nature, but has been explored little outside of a biological setting. Now, proton conductors have been developed based on the squid protein reflectin, and integrated with devices for potential bioelectronic applications.
- Marco Rolandi
-
Article |
 Bulk protonic conductivity in a cephalopod structural protein
Bulk protonic conductivity in a cephalopod structural protein
Proton-conducting materials have proved useful for renewable energy applications and bioelectronics technologies. The proton conductivity of thin films made from reflectin — a cephalopod structural protein — is now reported. Reflectin's electrical properties compare favourably to those of artificial materials, and have enabled the demonstration of protein-based protonic transistors.
- David D. Ordinario
- , Long Phan
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
 Self-healing chemistry enables the stable operation of silicon microparticle anodes for high-energy lithium-ion batteries
Self-healing chemistry enables the stable operation of silicon microparticle anodes for high-energy lithium-ion batteries
The ability to self-heal is an important survival feature in nature, with in-built systems working to correct faults and extend the lifetimes of organisms. Now, self-healing chemistry has been applied to overcome the short cycling lifetime of high-capacity rechargeable lithium-ion batteries with silicon-microparticle anodes that suffer from mechanical fractures.
- Chao Wang
- , Hui Wu
- & Zhenan Bao
-
News & Views |
 A bright future for defects
A bright future for defects
Covalently bonding groups to the walls of carbon nanotubes has been previously observed to quench their photoluminescence. Now, it has been shown that, if you get the chemistry just right, their photoluminescence can in fact be significantly brightened by introducing defects through functionalization.
- Qing Hua Wang
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Brightening of carbon nanotube photoluminescence through the incorporation of sp3 defects
Brightening of carbon nanotube photoluminescence through the incorporation of sp3 defects
The controlled functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes has been shown to brighten their photoluminescence up to 28 times, which challenges our current understanding of how chemical defects affect low-dimensional carbon materials. This significantly improved photon conversion efficiency promises to advance a broad range of optoelectronic and imaging applications based on carbon nanotubes.
- Yanmei Piao
- , Brendan Meany
- & YuHuang Wang
-
News & Views |
 Highly charged
Highly charged
Tying molecules together in a link results in tremendous stabilization of the radical species they can form. Six clearly distinguishable charged states — which can be interconverted reversibly — have now been observed in a densely cationic system.
- David B. Amabilino
-
Review Article |
 The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets
The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets
Two-dimensional materials have recently garnered much interest in the scientific and technology communities. This Review describes how ultrathin transition metal dichalcogenides combine tunable structure and electronic properties, achieved through altering their composition, with versatile chemistry. This makes them attractive in various fields, for example as lithium-ion battery electrodes and electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- Manish Chhowalla
- , Hyeon Suk Shin
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Charged and metallic molecular monolayers through surface-induced aromatic stabilization
Charged and metallic molecular monolayers through surface-induced aromatic stabilization
When monolayers of π-conjugated organic semiconductors interact with metal surfaces, most remain semiconducting. In some cases, however, the metallic character of the substrate is seen to extend onto the molecules. A mechanism for this intriguing phenomenon is now suggested and new strategies for chemical surface engineering are proposed.
- G. Heimel
- , S. Duhm
- & N. Koch
-
Perspective |
 Design strategies for organic semiconductors beyond the molecular formula
Design strategies for organic semiconductors beyond the molecular formula
Although the molecular formula gives valuable information on the properties of isolated molecules or conjugated polymers, it fails to accurately predict their collective behaviour in the solid state. This Perspective highlights the importance of organization across multiple length scales on the optical and electronic properties of organic semiconductors, and how device performances poorly reflect the capabilities of a given material.
- Zachary B. Henson
- , Klaus Müllen
- & Guillermo C. Bazan
-
News & Views |
 Electronic perturbations
Electronic perturbations
Oxide materials typically used as supports for the active metal nanoparticles of heterogeneous catalysts are known to influence catalytic activity through strong metal–support interactions. Researchers have now revealed electronic interactions between platinum and ceria that go well beyond known effects and lead to excellent catalytic activity.
- Charles T. Campbell
-
Article |
 Optically switchable transistor via energy-level phototuning in a bicomponent organic semiconductor
Optically switchable transistor via energy-level phototuning in a bicomponent organic semiconductor
One of the goals for devices using organic semiconductors is to make the materials themselves multifunctional or tunable, reducing the complexity of the device. Now, a film created by blending two components is shown to be phototunable with bistable energy levels and has been used in an organic thin-film transistor.
- Emanuele Orgiu
- , Núria Crivillers
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article |
 Light-triggered self-construction of supramolecular organic nanowires as metallic interconnects
Light-triggered self-construction of supramolecular organic nanowires as metallic interconnects
Triarylamine derivatives in solution have been self-assembled into organic nanowires between two electrodes, under white-light irradiation and in the presence of a voltage. The resulting fibres possess a very high electric conductivity as well as a metallic behaviour when cooled down to a temperature of 1.5 K.
- Vina Faramarzi
- , Frédéric Niess
- & Nicolas Giuseppone
-
News & Views |
 Flexibility with a metallic skin
Flexibility with a metallic skin
Transparent, metallic conducting thin films are key for applications such as flatpanel displays and solar cells, and heavily electron-doped ionic oxide materials have been intensively studied for this purpose. A class of conductors that are transparent in the near-infrared region has now been developed using a topological insulator.
- Hideo Hosono
-
Article |
 Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes
Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes
Transparent conductive electrodes are widely used in modern optoelectronic devices, but they are rarely transparent in the near-infrared, limiting their use. Nanostructured bismuth selenide, a topological insulator, is now shown to be a flexible near-infrared transparent electrode.
- Hailin Peng
- , Wenhui Dang
- & Zhongfan Liu

 Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons
Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons Spoiler alert
Spoiler alert