Article |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A bridge to higher ground
A bridge to higher ground
Single-molecule magnets are coordination clusters with magnetic properties that are typically reliant on the coupling between pairs of metal centres. Now, a cluster in which magnetism arises from delocalized electrons — built using an imidazolate bridge, a common linker in metal–organic architectures — shows promise for molecular memory devices.
- Annie K. Powell
-
News & Views |
 Spinning into control
Spinning into control
Spin transitions are the most common mechanism for switching molecules between two distinct energy states, for uses as diverse as memory devices and displays. How the transition is triggered is crucial, and a pentanuclear cluster has now been reported in which the spin transition is promoted by redox transfer between different metal ions.
- Roberta Sessoli
-
Research Highlights |
 Behold the fold
Behold the fold
Folding techniques have been used on printed titanium hydride sheets to create three-dimensional structures.
- Neil Withers
-
Research Highlights |
 Protein under glass
Protein under glass
The water molecules surrounding a protein can be dissolved in an organic solvent to form dry, glassified microbeads of controllable size that preserve the protein's activity.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
 Assembly of a metal–organic framework by sextuple intercatenation of discrete adamantane-like cages
Assembly of a metal–organic framework by sextuple intercatenation of discrete adamantane-like cages
There has been much interest in the assembly and properties of metal–organic frameworks. Here, a new type is described in which an infinite three-dimensional polycatenane is assembled from a discrete octahedral nanocage through the interlocking of all its six vertices.
- Xiaofei Kuang
- , Xiaoyuan Wu
- & Can-Zhong Lu
-
Research Highlights |
 Peptides make the difference
Peptides make the difference
Microporous crystals formed by hydrogen-bonded dipeptides show different permeabilities for argon, nitrogen and oxygen.
- Anne Pichon
-
-
-
Article |
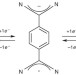 Charge-transfer-induced structural rearrangements at both sides of organic/metal interfaces
Charge-transfer-induced structural rearrangements at both sides of organic/metal interfaces
Interfaces between organic molecules and metal surfaces have a key role in determining the performance of many emerging technologies. Now an intensive experimental study — supported by calculations — of tetracyano-p-quinodimethane molecules on a copper surface, reveals structural rearrangement of both the organic molecules and the surface atoms after charge transfer across the interface.
- Tzu-Chun Tseng
- , Christian Urban
- & Rodolfo Miranda
-
Article |
 Self-assembly and optically triggered disassembly of hierarchical dendron–virus complexes
Self-assembly and optically triggered disassembly of hierarchical dendron–virus complexes
Viruses are ideal templates for engineering multifunctional materials. They can exhibit multiple copies of surface ligands and encapsulate inorganic and organic materials. Here, viruses are assembled into well-defined micrometre-sized objects by the addition of dendritic linkers. The linkers are designed to decompose on irradiation, which results in the release of the original virus particles.
- Mauri A. Kostiainen
- , Oksana Kasyutich
- & Roeland J. M. Nolte
-
Research Highlights |
 Turning on hydrocarbons
Turning on hydrocarbons
The intercalation of potassium into a simple aromatic hydrocarbon results in a new class of organic superconductors.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
 Face-directed self-assembly of an electronically active Archimedean polyoxometalate architecture
Face-directed self-assembly of an electronically active Archimedean polyoxometalate architecture
A wide range of porous framework materials has been assembled with a modular approach that takes advantage of prefabricated structural building units (SBUs). Now, it has been shown that functional all-inorganic frameworks can be made from a macrocyclic polyoxometalate SBU — that has a built-in aperture approximately 1 nm in diameter — linked together with redox-switchable metal ions.
- Scott G. Mitchell
- , Carsten Streb
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article |
 Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Nanotubular structures made from different materials are being investigated for applications ranging from sensing to drug delivery, but controlling how they interact with ‘cargo’ molecules has proved challenging. Now, the selective uptake, precise positioning and triggered release of gold nanoparticles has been achieved with nanotubes assembled from triangular DNA building blocks.
- Pik Kwan Lo
- , Pierre Karam
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
News & Views |
 Seizing the caesium
Seizing the caesium
Public acceptance of the expansion of nuclear power may hinge on the safe disposal of nuclear waste. Ion exchangers that remove radioactive metals — such as caesium ions — from the waste could provide part of the answer, so a flexible-framework material that selectively grab them from solution is a step in the right direction.
- Abraham Clearfield
-
News & Views |
 Building bridges
Building bridges
Supramolecular gels, which rely on non-covalent interactions, are typically fragile. Now, hydrogels that possess remarkable mechanical strength combined with the ability to rapidly self-heal have been built through multiple non-covalent interactions.
- David K. Smith
-
Research Highlights |
 An illuminating twist
An illuminating twist
The slow oxidation of tellurium in semiconductor cadmium telluride nanoparticles, accompanied by the replacement of tellurium by sulfur, has led to CdS/CdTe nanoparticles that self-assemble under visible light into twisted nanoribbons.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
 Exceptional ammonia uptake by a covalent organic framework
Exceptional ammonia uptake by a covalent organic framework
The uptake of ammonia by a covalent–organic framework (COF) containing a high density of Lewis-acidic boron sites has been found to be significantly greater than that exhibited by other state-of-the-art porous materials. The ammonia can be removed by heating under vacuum and the structural integrity of the COF is maintained during adsorption/desorption cycles.
- Christian J. Doonan
- , David J. Tranchemontagne
- & Omar M. Yaghi
-
Article |
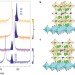 Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
The movement of oxygen ions through materials is important in electrolytes and separation membranes, but is rare at lower temperatures. Two different low-temperature diffusion pathways are revealed during the reduction process of CaFeO2.5 to CaFeO2. The two pathways are significantly different, resulting in anisotropy.
- Satoru Inoue
- , Masanori Kawai
- & Yuichi Shimakawa
-
Research Highlights |
 Practical honeycombs
Practical honeycombs
Silicon-based polymers have been assembled into honeycomb films that exhibit good flexibility, stability and thermal conductivity, showing great promise for industrial applications.
- Anne Pichon
-
-
Article |
 A facile route to ketene-functionalized polymers for general materials applications
A facile route to ketene-functionalized polymers for general materials applications
The ability to rapidly functionalize polymers is vital for application development. Here, a method for the introduction of masked ketenes into monomers for both ring-opening metathesis and radical-type polymerizations is described. These ketenes — a group previously underexploited in polymer chemistry — allow both crosslinking and post-polymerization functionalization of the polymers.
- Frank A. Leibfarth
- , Minhyuk Kang
- & Craig J. Hawker
-
Article |
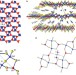 Selective incarceration of caesium ions by Venus flytrap action of a flexible framework sulfide
Selective incarceration of caesium ions by Venus flytrap action of a flexible framework sulfide
A perforated framework material of gallium antimony sulfide is able to selectively extract caesium ions from solution. After this capture, the holes close and prevent the ions leaching back out. This dynamic response could be used to remove caesium from nuclear waste.
- Nan Ding
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Research Highlights |
Particle particulars
Key intermediates and their roles in secondary organic aerosol formation from isoprene have been elucidated.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Analysis of the reactivity and selectivity of fullerene dimerization reactions at the atomic level
Analysis of the reactivity and selectivity of fullerene dimerization reactions at the atomic level
Well-resolved images of small molecules and their motions can be obtained with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. It has now been shown that this technique can also be used to visualize individual chemical reactions involving the dimerization of fullerenes and metallo-fullerenes trapped inside carbon nanotubes by monitoring how the positions of their atoms change over time.
- Masanori Koshino
- , Yoshiko Niimi
- & Sumio Iijima
-
Article |
 Random two-dimensional string networks based on divergent coordination assembly
Random two-dimensional string networks based on divergent coordination assembly
The bulk properties of materials that lack long-range order have been widely studied, but their local structures remain difficult to elucidate. Now, using scanning tunnelling microscopy, researchers have been able to look more closely at the structural motifs of robust, two-dimensional glassy networks assembled through metal–ligand interactions.
- Matthias Marschall
- , Joachim Reichert
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
News & Views |
 Producing 'perfect' particles
Producing 'perfect' particles
Synthetic procedures for making nanoparticles often result in samples that contain a range of different particle sizes. By using hollow self-assembled metal–organic spheres as templates, however, it is possible to make silica nanoparticles with uniform shapes and sizes in a precisely controlled fashion.
- Boris Breiner
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
News & Views |
 An electric effect
An electric effect
Electrically tunable materials are used to construct switches and memory devices. Applying an electric field within a specific temperature range to cyanometallate complexes triggers their charge-transfer phase transition, altering their optical and magnetic properties.
- Osamu Sato

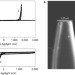 Electrochemistry through glass
Electrochemistry through glass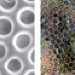 Practical honeycombs
Practical honeycombs Ice ice maybe
Ice ice maybe Tomography reveals all
Tomography reveals all