Featured
-
-
Article |
 A heparin-mimicking polymer conjugate stabilizes basic fibroblast growth factor
A heparin-mimicking polymer conjugate stabilizes basic fibroblast growth factor
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is crucial for a range of diverse cellular processes, from wound healing to bone regeneration, yet is inherently unstable. This important biologic has now been covalently linked to a polymer that mimics the polysaccharide heparin to produce a conjugate that shows remarkable stability to a wide range of therapeutically and environmentally relevant stressors.
- Thi H. Nguyen
- , Sung-Hye Kim
- & Heather D. Maynard
-
News & Views |
 Packing polymers in protein cages
Packing polymers in protein cages
The combination of addressable synthetic macromolecules with proteins of precise structure and function often leads to materials with unique properties, as is now shown by the efficient multi-site initiation of polymer growth inside the cavity of a virus capsid.
- Jeroen J. L. M. Cornelissen
-
Article |
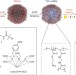 Use of the interior cavity of the P22 capsid for site-specific initiation of atom-transfer radical polymerization with high-density cargo loading
Use of the interior cavity of the P22 capsid for site-specific initiation of atom-transfer radical polymerization with high-density cargo loading
The site-selective initiation and propagation of an atom-transfer radical polymerization reaction forms an addressable crosslinked polymer constrained within the interior cavity of a virus-like particle derived from the bacteriophage P22. This protein–polymer hybrid is useful as a new vehicle for high-density delivery of small-molecule cargos.
- Janice Lucon
- , Shefah Qazi
- & Trevor Douglas
-
-
-
Research Highlights |
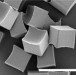 Silyl ether linkers
Silyl ether linkers
Polymeric particles based on silyl ether crosslinkers create acid-sensitive biomaterials whose degradation is controlled in vivo by natural pH gradients.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
 Mineralization of the metre-long biosilica structures of glass sponges is templated on hydroxylated collagen
Mineralization of the metre-long biosilica structures of glass sponges is templated on hydroxylated collagen
Understanding how biosilica forms is crucial to our knowledge of this important biomaterial. Now, the role of collagen as structuring agent for the metre-long spicules of a primitive glass sponge has been revealed and found to have an unusual peptide motif.
- Hermann Ehrlich
- , Rainer Deutzmann
- & Matthew J. Collins
-
Research Highlights |
 Flexible magnetic aerogels
Flexible magnetic aerogels
A nanocomposite of bacterial cellulose nanofibrils and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles combines the flexibility of the former with the magnetic properties of the latter.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
 Efficient water oxidation at carbon nanotube–polyoxometalate electrocatalytic interfaces
Efficient water oxidation at carbon nanotube–polyoxometalate electrocatalytic interfaces
Catalytically oxidizing water to produce oxygen is so challenging that even the enzyme that performs the task in nature must be regenerated every 30 mins. Now, stable oxygen-evolving anodes have been made by tethering a polyoxometalate catalyst to a conducting bed of carbon nanotubes.
- Francesca M. Toma
- , Andrea Sartorel
- & Marcella Bonchio
-
Article |
 Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Nanotubular structures made from different materials are being investigated for applications ranging from sensing to drug delivery, but controlling how they interact with ‘cargo’ molecules has proved challenging. Now, the selective uptake, precise positioning and triggered release of gold nanoparticles has been achieved with nanotubes assembled from triangular DNA building blocks.
- Pik Kwan Lo
- , Pierre Karam
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-

 Conversion of light into macroscopic helical motion
Conversion of light into macroscopic helical motion Pitcher plant perfect
Pitcher plant perfect Silyl ether linkers
Silyl ether linkers Tomography reveals all
Tomography reveals all