Featured
-
-
Article |
 Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Nanocatalysts can undergo various dynamic phenomena that affect their activity, such as restructuring and spillover. Now, using spatially and temporally resolved imaging of individual catalytic reactions, cooperative communication between different sites within single palladium- and gold-based nanocatalysts, and between different nanocatalysts, has been observed during three distinct catalytic reactions.
- Ningmu Zou
- , Xiaochun Zhou
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Chemical evolution of atmospheric organic carbon over multiple generations of oxidation
Chemical evolution of atmospheric organic carbon over multiple generations of oxidation
Nearly all organic carbon has now been quantified and characterized in a highly complex evolving atmospheric system, specifically, the multigenerational oxidation of α-pinene. It has been observed that initial addition of functional groups quickly gives way to fragmentation reactions, with organic carbon ultimately becoming sequestered in chemically resistant reservoirs: organic aerosols and long-lived gas-phase species.
- Gabriel Isaacman-VanWertz
- , Paola Massoli
- & Jesse H. Kroll
-
Review Article |
 Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
The emergence of synthetic fluorescent nucleobases that can be incorporated into DNA and RNA in place of their natural counterparts has enabled new tools and technologies with applications in chemistry, biology and biomedicine. This Review discusses chemical insights into canonical and non-canonical nucleobase designs, relating structure to properties.
- Wang Xu
- , Ke Min Chan
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Thesis |
101 libations
Bruce C. Gibb takes a look at the complex cocktail of chemical compounds that make up gin.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
Article |
 Modular probes for enriching and detecting complex nucleic acid sequences
Modular probes for enriching and detecting complex nucleic acid sequences
Modular hybridization probes (M-Probes) have been developed that enable sequence-selective binding of complex nucleic acid targets. The M-probes can target sequences that: are hypervariable at prescribed loci, are long continuous sequences of over 500 nucleotides, or contain repetitive sequences. A hybrid-capture assay using the M-probes was developed that was capable of determining the exact triplet repeat expansion number in the Huntington's gene from genomic DNA.
- Juexiao Sherry Wang
- , Yan Helen Yan
- & David Yu Zhang
-
Article |
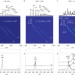 Infrared spectrum and structure of the homochiral serine octamer–dichloride complex
Infrared spectrum and structure of the homochiral serine octamer–dichloride complex
Octameric complexes of serine are long known for their special properties, such as their enhanced stability and preference for homochirality. Yet, there is no consensus on their structures. Now, experimental data on the serine octamer–dichloride complex is presented that supports a highly symmetrical, highly stable structure.
- Jongcheol Seo
- , Stephan Warnke
- & Gert von Helden
-
Article |
 Chelation and stabilization of berkelium in oxidation state +IV
Chelation and stabilization of berkelium in oxidation state +IV
Berkelium is the only transplutonium element predicted to be able to exhibit both +III and +IV oxidation states in solution. Bk(IV) has now been stabilized through chelation with a siderophore derivative. The resulting neutral coordination compound was characterized and compared with the negatively charged species obtained by chelation of neighbouring trivalent actinides.
- Gauthier J.-P. Deblonde
- , Manuel Sturzbecher-Hoehne
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
Article |
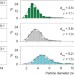 The structure and binding mode of citrate in the stabilization of gold nanoparticles
The structure and binding mode of citrate in the stabilization of gold nanoparticles
The manner in which carboxylates bind to the surface of nanoparticles has been an important question in materials science. Now, multinuclear magnetic resonance experiments — alongside DFT calculations, XPS and TEM measurements — have elucidated the three-dimensional ligand structures of gold nanoparticles capped with various ratios of carboxylate-containing ligands, and enabled the determination of the most probable binding modes.
- Hind Al-Johani
- , Edy Abou-Hamad
- & Jean-Marie Basset
-
Article |
 One-thousand-fold enhancement of high field liquid nuclear magnetic resonance signals at room temperature
One-thousand-fold enhancement of high field liquid nuclear magnetic resonance signals at room temperature
The analysis of complex (bio)molecules by NMR spectroscopy is often complicated by limitations in sensitivity. Now, it has been shown that 13C NMR signals are strongly enhanced in solution by resonant microwave irradiation of a nitroxide polarizer. This method exhibits up to one-thousand-fold improvements in sensitivity, which stands to greatly improve the detail with which small molecules and metabolites can be studied.
- Guoquan Liu
- , Marcel Levien
- & Marina Bennati
-
Article |
 Rational design of reversible fluorescent probes for live-cell imaging and quantification of fast glutathione dynamics
Rational design of reversible fluorescent probes for live-cell imaging and quantification of fast glutathione dynamics
Reversible fluorescent probes for intracellular glutathione (GSH) imaging have now been designed and synthesized based on Si-rhodamine fluorophores. These probes are shown to be capable of quantifying the GSH concentration in various living cell types and also for monitoring real-time live-cell imaging of GSH dynamics with a temporal resolution of seconds.
- Keitaro Umezawa
- , Masafumi Yoshida
- & Yasuteru Urano
-
Article |
 An infrared spectroscopy approach to follow β-sheet formation in peptide amyloid assemblies
An infrared spectroscopy approach to follow β-sheet formation in peptide amyloid assemblies
There is increasing evidence that highly dynamic, polydisperse peptide oligomers are the toxic species in amyloid-related diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Now, the secondary structure of individual amyloid oligomers has been analysed directly for the first time using a combination of ion-mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry and gas-phase infrared spectroscopy.
- Jongcheol Seo
- , Waldemar Hoffmann
- & Kevin Pagel
-
-
Article |
 Dynamic formation of a solid-liquid electrolyte interphase and its consequences for hybrid-battery concepts
Dynamic formation of a solid-liquid electrolyte interphase and its consequences for hybrid-battery concepts
Li+-selective solid electrolytes may enable next-generation battery systems, such as Li–S and Li–O2. Now, in an exemplar system, it is shown that a resistive interphase forms at the interface between solid and liquid electrolytes, termed the solid-liquid electrolyte interphase (SLEI). An in situ study of this undesirable effect is supported by state-of-the-art surface analysis.
- Martin R. Busche
- , Thomas Drossel
- & Jürgen Janek
-
News & Views |
 Eavesdropping on interactions
Eavesdropping on interactions
A method for directly probing binding interactions in free solution, without the need for chemical tagging, offers exciting opportunities for non-perturbative analyses of biomolecules in their native state.
- Enrique Valera
- & Ryan C. Bailey
-
Article |
 Organocatalytic removal of formaldehyde adducts from RNA and DNA bases
Organocatalytic removal of formaldehyde adducts from RNA and DNA bases
Formaldehyde is universally employed in the fixation of tissue specimens, where it forms adducts with biomolecules, but this hinders the analysis of nucleic acids in the specimen. Bifunctional organocatalysts that speed the reversal of formaldehyde adducts of RNA and DNA are now reported, and show promise for general use in clinical specimens.
- Saswata Karmakar
- , Emily M. Harcourt
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
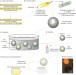 Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors
Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors
A method for high-throughput analysis of whole-cell biocatalysts for industrial biotechnology has been developed. The process relies on a combination of specifically tailored bacterial sensor cells that are incubated with biocatalyst variants within nanolitre-sized compartments. The product is secreted by the whole-cell biocatalysts and taken up by the sensor cells, which initiates a sequence of reactions that finish with the synthesis of green fluorescent protein.
- Andreas Meyer
- , René Pellaux
- & Martin Held
-
-
News & Views |
 Clamping down on cancer detection
Clamping down on cancer detection
An electrochemical clamp assay that enables the rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids containing single base mutations has now been developed. It has been shown to differentiate between cancer patient samples featuring a specific mutation, and controls from healthy donors or other cancer patients, all directly in unprocessed serum.
- Irina A. Gorodetskaya
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
 Through-space transfer of chiral information mediated by a plasmonic nanomaterial
Through-space transfer of chiral information mediated by a plasmonic nanomaterial
Surface-enhanced resonant Raman optical activity (SERROA) reveals the through-space transfer of chirality from biomolecules to achiral benzotriazole dye-conjugated nanotags. The chiroptical responses generated by the stereoisomers of ribose and tryptophan establish this as the basis for a stereoselective nanosensor platform.
- Saeideh Ostovar pour
- , Louise Rocks
- & Ewan W. Blanch
-
Article |
 An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
The analysis of circulating cell-free nucleic acids (cfNA) in the blood of cancer patients permits the analysis of tumour mutations without requiring invasive sampling of tissue. Now, the development of an electrochemical assay that uses a collection of clamp molecules to sequester interfering cfNAs enables the accurate detection of mutated sequences in serum collected from people with lung cancer or melanoma.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Ivaylo Ivanov
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article |
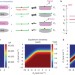 Simulation-guided DNA probe design for consistently ultraspecific hybridization
Simulation-guided DNA probe design for consistently ultraspecific hybridization
The use of kinetic simulations to guide the design of competitive hybridization probe systems is shown to enable high selectivity for single-nucleotide variants. Using this approach across 44 cancer mutation/wild-type sequence pairs showed between a 200- and 3,000-fold higher binding affinity than the corresponding wild-type sequence. In combination with PCR amplification this method enabled the detection of a 1% concentration of variant alleles in human genomic DNA.
- Juexiao Sherry Wang
- & David Yu Zhang
-
-
Thesis |
 The organic Solar System
The organic Solar System
In the second of two essays looking at organic chemistry that can be found in the Solar System, Bruce C. Gibb focuses on the gas and ice giants as well as their satellites — concluding the tour on Saturn's fascinating moon Titan.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
News & Views |
 Enzyme activity with a twist
Enzyme activity with a twist
A supramolecular polymer comprising stacked artificial chromophores to which zinc(II) complexes are appended is able to respond to enzymatic hydrolysis in aqueous solution. The assembly of molecules can twist reversibly and quickly in response to changes in the type of adenosine phosphate present.
- David B. Amabilino
-
News & Views |
 Bound in flight
Bound in flight
In their natural environment, membrane proteins are surrounded by lipids, but the effect that the lipids have on the proteins is not easy to assess. Now, controlling the extent of delipidation has enabled the study of these interactions.
- Sophie R. Harvey
- & Vicki H. Wysocki
-
Article |
 A subset of annular lipids is linked to the flippase activity of an ABC transporter
A subset of annular lipids is linked to the flippase activity of an ABC transporter
Defining the lipid composition that exists around a membrane protein complex in natural bilayers is a challenging task. Now, key lipids that are important for the structure and function of an ABC transporter have been revealed by systematically removing layers of lipids, and using mass spectrometry to monitor those that remained closely associated with the membrane protein.
- Chérine Bechara
- , Anne Nöll
- & Carol V. Robinson
-
News & Views |
 Zinc differently
Zinc differently
An extracellular ejection of zinc, known as a zinc spark, is triggered by the fertilization of a mammalian egg; however, the origin of this zinc was not clear. Now, a combination of four complementary techniques has revealed the source and provided an unprecedented quantification of the distribution of zinc in a maturing mammalian oocyte.
- Kyle P. Carter
- & Amy E. Palmer
-
Commentary |
 Remote-controlled experiments with cloud chemistry
Remote-controlled experiments with cloud chemistry
Developing cleaner chemical processes often involves sophisticated flow-chemistry equipment that is not available in many economically developing countries. For reactions where it is the data that are important rather than the physical product, the networking of chemists across the internet to allow remote experimentation offers a viable solution to this problem.
- Ryan A. Skilton
- , Richard A. Bourne
- & Martyn Poliakoff
-
Article |
 Screening and classifying small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid formation using ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry
Screening and classifying small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid formation using ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry
A method for rapidly screening small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid assembly has been developed. This method uses electrospray ionization–ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry to detect and identify the type of inhibition. A screen of this nature could help in the discovery of therapeutics for numerous diseases associated with aberrant protein aggregation.
- Lydia M. Young
- , Janet C. Saunders
- & Alison E. Ashcroft
-
News & Views |
 Another stable base in DNA
Another stable base in DNA
Oxidation of 5-methylcytosine has been proposed to mediate active and passive DNA demethylation. Tracking the history of DNA modifications has now provided the first solid evidence that 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is a stable epigenetic modification.
- Pijus Brazauskas
- & Skirmantas Kriaucionis
-
Thesis |
 Faith, chemistry and extraterrestrial life
Faith, chemistry and extraterrestrial life
Bruce Gibb wonders whether our faith in chemistry — and what it can teach us about the Universe beyond our Earthly bounds — will have a role to play in the search for alien life.
- Bruce C. Gibb
-
Article |
 Recognition and sensing of low-epitope targets via ternary complexes with oligonucleotides and synthetic receptors
Recognition and sensing of low-epitope targets via ternary complexes with oligonucleotides and synthetic receptors
Recognition, differentiation and sensing of small molecules displaying only sparse functionalities using artificial receptors is extremely challenging. Now a method to selectively bind and recognise low-epitope targets has been developed. The approach uses the formation of ternary complexes between small-molecule targets, their non-specific organic (or organometallic) receptors, and aptamers.
- Kyung-Ae Yang
- , Mihaela Barbu
- & Milan N. Stojanovic
-
Thesis |
 Seeding crystallography
Seeding crystallography
Michelle Francl wonders if the harem effect in crystallography is overrated.
- Michelle Francl
-
Article |
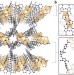 Capturing snapshots of post-synthetic metallation chemistry in metal–organic frameworks
Capturing snapshots of post-synthetic metallation chemistry in metal–organic frameworks
Obtaining precise structural information for metal-centred reactions that take place within the pores of metal–organic frameworks continues to be an elusive goal. Now, a flexible framework has been synthesized that enables the direct elucidation of the products of post-synthetic metallation reactions and subsequent chemical transformations by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. Camera image: © boyoglu/iStock/Thinkstock
- Witold M. Bloch
- , Alexandre Burgun
- & Christopher J. Sumby
-
Thesis |
 An ode to the atomic weights
An ode to the atomic weights
They might not be fundamental constants of nature, but atomic weights are one of the foundations on which modern chemistry is built, explains Juris Meija.
- Juris Meija
-
News & Views |
 Strategic blinking
Strategic blinking
For decades chemists have focused on increasing the brightness of fluorophores. In super-resolution microscopy, however, fluorophores that preferentially exist in a non-fluorescent state, but occasionally re-arrange into a fluorescent form, can give better results.
- Gražvydas Lukinavičius
- & Kai Johnsson
-
Article |
 A spontaneously blinking fluorophore based on intramolecular spirocyclization for live-cell super-resolution imaging
A spontaneously blinking fluorophore based on intramolecular spirocyclization for live-cell super-resolution imaging
A self-blinking fluorophore suitable for super-resolution imaging has been developed. The blinking arises from a reversible intramolecular spirocyclization in a rhodamine-based fluorophore that switches between a fluorescent open form and a non-fluorescent closed form. The advantages over existing methodologies are demonstrated using single-molecule localization microscopy imaging inside cells.
- Shin-nosuke Uno
- , Mako Kamiya
- & Yasuteru Urano
-
Article |
 Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering
Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are amongst the best known examples of targeted cancer therapeutics. Now, using hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering imaging, the label-free visualization and quantification of two TKI drugs inside living cells is reported. Significant trapping of TKI drugs in lysosomes was observed, which can be reversed by co-treatment with chloroquine through lysosome-mediated interactions.
- Dan Fu
- , Jing Zhou
- & X. Sunney Xie
-
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon magnetic resonance imaging
Genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging of gene expression has been limited by the low molecular sensitivity of conventional 1H-MRI. To overcome this limitation, the first genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon MRI have been developed. These expressible reporters, based on gas-filled protein nanostructures from buoyant microorganisms, are detectable at picomolar concentrations.
- Mikhail G. Shapiro
- , R. Matthew Ramirez
- & Vikram S. Bajaj
-
Article |
 Bioorthogonal cyclization-mediated in situ self-assembly of small-molecule probes for imaging caspase activity in vivo
Bioorthogonal cyclization-mediated in situ self-assembly of small-molecule probes for imaging caspase activity in vivo
Controlling the self-assembly of small molecules within living animals is complicated because of the complex and dynamic nature of the physiological environment. Here, a strategy for directing in situ self-assembly of small molecules into fluorescent nano-aggregates in living mice is demonstrated. The nano-aggregates can be used for imaging caspase-3/7 activity in human tumour xenograft mouse models.
- Deju Ye
- , Adam J. Shuhendler
- & Jianghong Rao
-
Review Article |
 The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics
The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics
Ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) is enhancing many areas of (bio)chemical analysis because it can separate ions both by their mass-to-charge ratio and differences in their cross-sectional area. IM-MS can be used for structural characterization, enhanced analysis of complex mixtures or to gain insights into conformational dynamics.
- Francesco Lanucara
- , Stephen W. Holman
- & Claire E. Eyers
-
News & Views |
 Flexibility leads to function
Flexibility leads to function
ATP synthase is an important enzyme for the storage and release of energy in cells. Ion-mobility mass spectrometry has now been used to study its structure, revealing important mechanistic details about its operation and regulation.
- Jianhua Zhao
- & John L. Rubinstein
-
Article |
 Ion mobility–mass spectrometry of a rotary ATPase reveals ATP-induced reduction in conformational flexibility
Ion mobility–mass spectrometry of a rotary ATPase reveals ATP-induced reduction in conformational flexibility
Ion mobility–mass spectrometry has enabled the study of conformation and dynamics of membrane proteins in the gas phase. Here, the enhanced flexibility of macromolecular ATPase was investigated by comparing arrival time distributions of distinct species and relating them to different solution conditions, leading to the proposal of a nucleotide-triggered regulatory mechanism.
- Min Zhou
- , Argyris Politis
- & Carol V. Robinson
-
Article |
 Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Identification of glycosylation patterns is complicated by the lack of sensitive analytical techniques that can distinguish between epimeric carbohydrates. It has now been shown that ion-mobility tandem mass spectrometry of ions derived from glycopeptides and oligosaccharides enables glycan stereochemistry to be determined, highlighting the potential of this technique for sequencing complex carbohydrates on cell surfaces.
- P. Both
- , A. P. Green
- & C. E. Eyers
-
Article |
 Layer-by-layer cell membrane assembly
Layer-by-layer cell membrane assembly
Immobilized microfluidic water-in-oil droplets serve as templates for layer-by-layer deposition of lipid monolayers to create vesicles of programmable lamellarity and content. Arrays of vesicles allow reproducible assembly and multi-vesicle probing of complex membrane-associated parameters, such as permeability, asymmetry and membrane protein function.
- Sandro Matosevic
- & Brian M. Paegel
-
-
-

 Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping Captivating COFs
Captivating COFs Weapon of ash destruction
Weapon of ash destruction A memorable reaction
A memorable reaction Non-classical crystals
Non-classical crystals