Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 High-throughput and proteome-wide discovery of endogenous biomolecular condensates
High-throughput and proteome-wide discovery of endogenous biomolecular condensates
High-throughput proteome-wide methods for identifying endogenous proteins that phase separate or partition into condensates during certain physiological events are needed but remain a challenge. Now, a high-throughput, unbiased and quantitative strategy can identify endogenous biomolecular condensates and screen proteins involved in phase separation on a proteome-wide scale.
- Pengjie Li
- , Peng Chen
- & Yiwei Li
-
Review Article |
 Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics
Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics
Nanopore label-free sequencing of DNA and RNA at the single-molecule level offers rapid readout, high accuracy, low cost and portability. This Review surveys technologies underpinning commercial and academic nanopore sequencing, and examines how underlying biochemical advances can fuel future developments in nanopore-based protein sequencing.
- Adam Dorey
- & Stefan Howorka
-
News & Views |
 Discovering cryptic natural products by substrate manipulation
Discovering cryptic natural products by substrate manipulation
Cryptic halogenation reactions result in natural products with diverse structural motifs and bioactivities. However, these halogenated species are difficult to detect with current analytical methods because the final products are often not halogenated. An approach to identify products of cryptic halogenation using halide depletion has now been discovered, opening up space for more effective natural product discovery.
- Ludek Sehnal
- , Libera Lo Presti
- & Nadine Ziemert
-
Article |
 Heteromultivalency enables enhanced detection of nucleic acid mutations
Heteromultivalency enables enhanced detection of nucleic acid mutations
Detecting genetic mutations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), is essential for disease diagnostics but can be difficult using homomultivalent DNA hybridization-based approaches. Now, heteromultivalent hybridization is used to fine-tune binding specificity for the detection of one or two SNPs in a single target, enabling straightforward discrimination between adjacent and distant mutations and different viral strains.
- Brendan R. Deal
- , Rong Ma
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article |
 DNAzyme-based faithful probing and pulldown to identify candidate biomarkers of low abundance
DNAzyme-based faithful probing and pulldown to identify candidate biomarkers of low abundance
The discovery of biomarkers remains challenging owing to a lack of methods sensitive enough to identify such rare molecules. Now, by simultaneously exploiting the catalysis and affinity of a DNAzyme, candidate biomarkers with low abundance in cancers can be pulled down for identification and validation.
- Qinqin Hu
- , Zongxuan Tong
- & Hongzhou Gu
-
Article |
 Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Stabilization of RNAs for storage, transport and biological application remains a profound challenge. Now, it has been shown that reversible 2′-OH acylation with easily accessible acylimidazoles unlocks efficient protection of RNA. RNA can be deprotected by non-basic nucleophiles or spontaneously in cells to restore RNA functions.
- Linglan Fang
- , Lu Xiao
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
 Protein nanopore reveals the renin–angiotensin system crosstalk with single-amino-acid resolution
Protein nanopore reveals the renin–angiotensin system crosstalk with single-amino-acid resolution
A nanopore framework has been developed to reveal the crosstalk effect on the renin–angiotensin system. By reading the single-amino-acid differences in angiotensin peptides with high accuracy and high efficiency, the selective inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 was revealed. This activity was shown to be suppressed by the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
- Jie Jiang
- , Meng-Yin Li
- & Yi-Tao Long
-
Article |
 Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
A method has been developed to identify RNA transcript isoforms at the single-molecule level using solid-state nanopore microscopy. In this method, target RNA is refolded into RNA identifiers with designed sets of complementary DNA strands. Each reshaped molecule carries a unique sequence of structural (pseudo)colours that enables identification and quantification using solid-state nanopore microscopy.
- Filip Bošković
- & Ulrich Felix Keyser
-
Article |
 Structure-specific amyloid precipitation in biofluids
Structure-specific amyloid precipitation in biofluids
The composition of toxic protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative diseases is difficult to determine. Now, a method has been developed that can capture amyloid-containing aggregates in human biofluids using a structure-specific chemical dimer. This method—known as amyloid precipitation—enables unbiased determination of the molecular composition and structural features of the in vivo aggregates.
- M. Rodrigues
- , P. Bhattacharjee
- & D. Klenerman
-
Q&A |
 Making commercial sense
Making commercial sense
In 2017 Professor Frances S. Ligler was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame for her inventions in portable optical biosensors. Professor Ligler now talks to Nature Chemistry about the challenge of developing new sensor designs into reliable products, and some of the pitfalls to avoid in the development process.
- Russell Johnson
-
Article |
 Reagentless biomolecular analysis using a molecular pendulum
Reagentless biomolecular analysis using a molecular pendulum
A reagentless method for detecting analytes based on the motion of an inverted molecular pendulum has now been developed. The sensor is capable of detecting important physiological markers of stress, allergy, cardiovascular health, inflammation and cancer and works in blood, saliva, urine, tears and sweat. The sensor is also capable of collecting data in living animals.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Surath Gomis
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Meeting Report |
 No small matter
No small matter
The confined geometry of nanopores enables a wealth of chemistry and analysis to be conducted at the single-molecule scale. Yi-Lun Ying, Aleksandar P. Ivanov and Vincent Tabard-Cossa report on recent developments discussed at the 2020 Nanopore Electrochemistry Meeting.
- Yi-Lun Ying
- , Aleksandar P. Ivanov
- & Vincent Tabard-Cossa
-
Q&A |
 A dream to sequence life
A dream to sequence life
Yujia Qing, an early-career researcher at the University of Oxford, talks to Nature Chemistry about winning the Dream Chemistry Award 2019, her chemistry dream of ‘Sequencing Life’, and the challenge this represents.
- Russell Johnson
-
News & Views |
 Interfacing electronic and genetic circuits
Interfacing electronic and genetic circuits
Synthetic genetic circuits leverage the information processing capability of biological machinery to tackle complex sensing tasks, yet they lack many of the advantages inherent to electrical computation. Now, an interface has been designed that provides an electrical output for synthetic genetic circuits.
- Robbyn K. Anand
- & Kira L. Rahn
-
Article |
 A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
A multiplexed, electrochemical interface for gene-circuit-based sensors
Gene-circuit-based sensors have, to date, largely relied on optical proteins (such as green fluorescent protein) to report the output, which limits the signalling bandwidth. Now, an electrochemical output has been developed and integrated with cell-free gene circuits. This approach enables multiplexing of sensors and introduces the possibility of electronic-based logic, memory and response elements to synthetic biology.
- Peivand Sadat Mousavi
- , Sarah J. Smith
- & Keith Pardee
-
Article |
 I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells
I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells
I-motif DNA structures are thought to form in cytosine-rich regions of the genome and to have regulatory functions; however, in vivo evidence for the existence of such structures has so far remained elusive. Now an engineered antibody that is selective for i-motif structures has been developed and used to detect i-motifs in the nuclei of human cells.
- Mahdi Zeraati
- , David B. Langley
- & Daniel Christ
-
Article |
 Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that characterize expression at the level of individual cells. Now, a technique for characterizing mRNA expression has been developed. The technique uses the intracellular self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles to quantitate RNA levels at the single-cell level.
- Mahmoud Labib
- , Reza M. Mohamadi
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Review Article |
 Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
The emergence of synthetic fluorescent nucleobases that can be incorporated into DNA and RNA in place of their natural counterparts has enabled new tools and technologies with applications in chemistry, biology and biomedicine. This Review discusses chemical insights into canonical and non-canonical nucleobase designs, relating structure to properties.
- Wang Xu
- , Ke Min Chan
- & Eric T. Kool
-
News & Views |
 Eavesdropping on interactions
Eavesdropping on interactions
A method for directly probing binding interactions in free solution, without the need for chemical tagging, offers exciting opportunities for non-perturbative analyses of biomolecules in their native state.
- Enrique Valera
- & Ryan C. Bailey
-
Article |
 Organocatalytic removal of formaldehyde adducts from RNA and DNA bases
Organocatalytic removal of formaldehyde adducts from RNA and DNA bases
Formaldehyde is universally employed in the fixation of tissue specimens, where it forms adducts with biomolecules, but this hinders the analysis of nucleic acids in the specimen. Bifunctional organocatalysts that speed the reversal of formaldehyde adducts of RNA and DNA are now reported, and show promise for general use in clinical specimens.
- Saswata Karmakar
- , Emily M. Harcourt
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
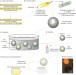 Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors
Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors
A method for high-throughput analysis of whole-cell biocatalysts for industrial biotechnology has been developed. The process relies on a combination of specifically tailored bacterial sensor cells that are incubated with biocatalyst variants within nanolitre-sized compartments. The product is secreted by the whole-cell biocatalysts and taken up by the sensor cells, which initiates a sequence of reactions that finish with the synthesis of green fluorescent protein.
- Andreas Meyer
- , René Pellaux
- & Martin Held
-
-
News & Views |
 Clamping down on cancer detection
Clamping down on cancer detection
An electrochemical clamp assay that enables the rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids containing single base mutations has now been developed. It has been shown to differentiate between cancer patient samples featuring a specific mutation, and controls from healthy donors or other cancer patients, all directly in unprocessed serum.
- Irina A. Gorodetskaya
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
 An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
The analysis of circulating cell-free nucleic acids (cfNA) in the blood of cancer patients permits the analysis of tumour mutations without requiring invasive sampling of tissue. Now, the development of an electrochemical assay that uses a collection of clamp molecules to sequester interfering cfNAs enables the accurate detection of mutated sequences in serum collected from people with lung cancer or melanoma.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Ivaylo Ivanov
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
-
News & Views |
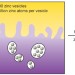 Zinc differently
Zinc differently
An extracellular ejection of zinc, known as a zinc spark, is triggered by the fertilization of a mammalian egg; however, the origin of this zinc was not clear. Now, a combination of four complementary techniques has revealed the source and provided an unprecedented quantification of the distribution of zinc in a maturing mammalian oocyte.
- Kyle P. Carter
- & Amy E. Palmer
-
News & Views |
 Another stable base in DNA
Another stable base in DNA
Oxidation of 5-methylcytosine has been proposed to mediate active and passive DNA demethylation. Tracking the history of DNA modifications has now provided the first solid evidence that 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is a stable epigenetic modification.
- Pijus Brazauskas
- & Skirmantas Kriaucionis
-
Article |
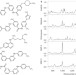 Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering
Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are amongst the best known examples of targeted cancer therapeutics. Now, using hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering imaging, the label-free visualization and quantification of two TKI drugs inside living cells is reported. Significant trapping of TKI drugs in lysosomes was observed, which can be reversed by co-treatment with chloroquine through lysosome-mediated interactions.
- Dan Fu
- , Jing Zhou
- & X. Sunney Xie
-
-
Review Article |
 The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics
The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics
Ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) is enhancing many areas of (bio)chemical analysis because it can separate ions both by their mass-to-charge ratio and differences in their cross-sectional area. IM-MS can be used for structural characterization, enhanced analysis of complex mixtures or to gain insights into conformational dynamics.
- Francesco Lanucara
- , Stephen W. Holman
- & Claire E. Eyers
-
News & Views |
 Flexibility leads to function
Flexibility leads to function
ATP synthase is an important enzyme for the storage and release of energy in cells. Ion-mobility mass spectrometry has now been used to study its structure, revealing important mechanistic details about its operation and regulation.
- Jianhua Zhao
- & John L. Rubinstein
-
Article |
 Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Identification of glycosylation patterns is complicated by the lack of sensitive analytical techniques that can distinguish between epimeric carbohydrates. It has now been shown that ion-mobility tandem mass spectrometry of ions derived from glycopeptides and oligosaccharides enables glycan stereochemistry to be determined, highlighting the potential of this technique for sequencing complex carbohydrates on cell surfaces.
- P. Both
- , A. P. Green
- & C. E. Eyers
-
News & Views |
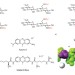 Blue-chip binding
Blue-chip binding
Heparin is an anionic polysaccharide that has tremendous clinical importance as an anticoagulant. Several dyes have been developed that can detect heparin, and the latest example — named Mallard Blue — has now been shown to have excellent sensing properties under biologically relevant conditions.
- Zachary Shriver
- & Ram Sasisekharan
-
News & Views |
 Breaking the rules
Breaking the rules
Chemists have long been interested in synthesizing compounds that push the boundaries of conventional molecular structure. Incorporating metal centres into the ring unit of highly strained and unsaturated cyclic molecules can help reduce strain — a tactic that has now been used to render a previously inaccessible metallapentalyne isolable.
- Torsten Beweries
- & Uwe Rosenthal
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Virulence caught green-handed
Virulence caught green-handed
Many of us eat mushrooms, but few of us have probably ever thought about — let alone witnessed — the epic battle of kingdoms that can occur between this delicacy and its bacterial pathogens. Now, imaging mass spectrometry has enabled the identification of a bacterium's potent antifungal weapon of choice.
- Laura M. Sanchez
- & Pieter C. Dorrestein
-
Article |
 Key stabilizing elements of protein structure identified through pressure and temperature perturbation of its hydrogen bond network
Key stabilizing elements of protein structure identified through pressure and temperature perturbation of its hydrogen bond network
The pressure- and temperature-dependent changes of various hydrogen bonds within ubiquitin have been determined at very high resolution using NMR H-bond scalar couplings. The measured perturbations show a correlation with the sequence separation between donor and acceptor residues, and indicate that certain topologically crucial H-bonds are specifically stabilized.
- Lydia Nisius
- & Stephan Grzesiek
-
News & Views |
 Robust sequence discrimination
Robust sequence discrimination
Careful consideration of thermodynamics has allowed the design of nucleic acid probes that are highly specific and virtually unaffected by changes in reaction conditions.
- Grégoire Altan-Bonnet
- & Fred Russell Kramer
-
Article |
 In situ quantitative imaging of cellular lipids using molecular sensors
In situ quantitative imaging of cellular lipids using molecular sensors
Cellular membrane lipids play key roles in cell regulation. Here, an environmentally sensitive fluorophore is attached to a protein that binds to a key signalling lipid to produce a membrane lipid sensor. This strategy allows sensitive, quantitative, spatiotemporal imaging of the lipid concentration in mammalian cells.
- Youngdae Yoon
- , Park J. Lee
- & Wonhwa Cho
-
News & Views |
 Sweet solution to sensing
Sweet solution to sensing
Glucose meters allow rapid and quantitative measurement of blood sugar levels for diabetes sufferers worldwide. Now a new method allows this proven technology to be used to quantify a much wider range of analytes.
- Samuel K. Sia
- & Curtis D. Chin
-
Article |
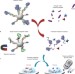 Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets
Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets
Portable sensors for the rapid quantitation of a variety of analytical targets could revolutionize both medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring. Here, functional DNA sensors that release the enzyme invertase in response to an analyte of choice are described. The enzyme converts sucrose to glucose which can then be easily detected using a widely available personal glucose meter.
- Yu Xiang
- & Yi Lu
-
News & Views |
 Detection by failure
Detection by failure
Testing for enzymes is important for diagnosing various medical conditions but can be problematic because of the complexity of physiological media such as blood. Now, a method of detecting phospholipases has been developed that neatly couples their concentration with the aggregation of gold nanoparticles.
- Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Article |
 Organic structure determination using atomic-resolution scanning probe microscopy
Organic structure determination using atomic-resolution scanning probe microscopy
The structure of many natural products can often only be confirmed by comparison with a synthetic sample. Here, scanning probe microscopy techniques allow the ultimate discrimination between structures suggested by the standard range of analytical techniques, proving the power of single-molecule imaging for molecular structure determination.
- Leo Gross
- , Fabian Mohn
- & Marcel Jaspars

 Identifying phase-separating biomolecular condensates in cells
Identifying phase-separating biomolecular condensates in cells Weapon of ash destruction
Weapon of ash destruction Crowning achievement
Crowning achievement Two-millennia-old tablets
Two-millennia-old tablets