Q&A |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Methods to detect and identify bacteria typically rely on enrichment steps such as bacterial culture and nucleic acid amplification. Now, an assay for detecting bacteria based on a two-channel electrical chip that combines electroactive DNAzymes with an electrochemical readout, has been developed. This assay enables reagentless and culture-free detection of bacteria in clinical samples.
- Richa Pandey
- , Dingran Chang
- & Leyla Soleymani
-
Article |
 Reagentless biomolecular analysis using a molecular pendulum
Reagentless biomolecular analysis using a molecular pendulum
A reagentless method for detecting analytes based on the motion of an inverted molecular pendulum has now been developed. The sensor is capable of detecting important physiological markers of stress, allergy, cardiovascular health, inflammation and cancer and works in blood, saliva, urine, tears and sweat. The sensor is also capable of collecting data in living animals.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Surath Gomis
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
News & Views |
 Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
The tumour microenvironment has a specific enzymatic fingerprint, which provides opportunities for cancer therapy. Now, two studies show how this unique chemical environment can be used to produce reporter molecules or nanoclusters within the tumour that can subsequently be identified in urine or breath, enabling cancer detection and monitoring.
- Alexander N. Zelikin
-
News & Views |
 Interfacing electronic and genetic circuits
Interfacing electronic and genetic circuits
Synthetic genetic circuits leverage the information processing capability of biological machinery to tackle complex sensing tasks, yet they lack many of the advantages inherent to electrical computation. Now, an interface has been designed that provides an electrical output for synthetic genetic circuits.
- Robbyn K. Anand
- & Kira L. Rahn
-
-
News & Views |
 Clamping down on cancer detection
Clamping down on cancer detection
An electrochemical clamp assay that enables the rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids containing single base mutations has now been developed. It has been shown to differentiate between cancer patient samples featuring a specific mutation, and controls from healthy donors or other cancer patients, all directly in unprocessed serum.
- Irina A. Gorodetskaya
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
 Through-space transfer of chiral information mediated by a plasmonic nanomaterial
Through-space transfer of chiral information mediated by a plasmonic nanomaterial
Surface-enhanced resonant Raman optical activity (SERROA) reveals the through-space transfer of chirality from biomolecules to achiral benzotriazole dye-conjugated nanotags. The chiroptical responses generated by the stereoisomers of ribose and tryptophan establish this as the basis for a stereoselective nanosensor platform.
- Saeideh Ostovar pour
- , Louise Rocks
- & Ewan W. Blanch
-
Article |
 An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum
The analysis of circulating cell-free nucleic acids (cfNA) in the blood of cancer patients permits the analysis of tumour mutations without requiring invasive sampling of tissue. Now, the development of an electrochemical assay that uses a collection of clamp molecules to sequester interfering cfNAs enables the accurate detection of mutated sequences in serum collected from people with lung cancer or melanoma.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Ivaylo Ivanov
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
-
News & Views |
 Enzyme activity with a twist
Enzyme activity with a twist
A supramolecular polymer comprising stacked artificial chromophores to which zinc(II) complexes are appended is able to respond to enzymatic hydrolysis in aqueous solution. The assembly of molecules can twist reversibly and quickly in response to changes in the type of adenosine phosphate present.
- David B. Amabilino
-
Article |
 End-to-end conformational communication through a synthetic purinergic receptor by ligand-induced helicity switching
End-to-end conformational communication through a synthetic purinergic receptor by ligand-induced helicity switching
Biological receptors communicate information through ligand-induced conformational changes. A synthetic receptor with a boron-containing binding site that can selectively and reversibly complex a ligand (such as a purine nucleoside) is shown to function in a similar fashion. The resulting conformational change is relayed through the receptor, communicating structural information about the ligand to a spectroscopic reporter more than 2 nm away.
- Robert A. Brown
- , Vincent Diemer
- & Jonathan Clayden
-
News & Views |
 Blue-chip binding
Blue-chip binding
Heparin is an anionic polysaccharide that has tremendous clinical importance as an anticoagulant. Several dyes have been developed that can detect heparin, and the latest example — named Mallard Blue — has now been shown to have excellent sensing properties under biologically relevant conditions.
- Zachary Shriver
- & Ram Sasisekharan
-
News & Views |
 Breaking the rules
Breaking the rules
Chemists have long been interested in synthesizing compounds that push the boundaries of conventional molecular structure. Incorporating metal centres into the ring unit of highly strained and unsaturated cyclic molecules can help reduce strain — a tactic that has now been used to render a previously inaccessible metallapentalyne isolable.
- Torsten Beweries
- & Uwe Rosenthal
-
News & Views |
 Taking charge of detection
Taking charge of detection
An electrochemical sensor that relies on displacement of a 'neutralizer' from a surface-bound, charged probe molecule by the analyte enables the use of a single platform for the detection of multiple analytes irrespective of their charge.
- Anthony M. Burke
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
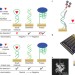 An ultrasensitive universal detector based on neutralizer displacement
An ultrasensitive universal detector based on neutralizer displacement
A universal detector of small molecules, proteins and nucleic acids is described that relies on the displacement of a neutralizer molecule from a sensor surface. When the neutralizer is displaced by an analyte, an electrochemical signal is generated. Ultrasensitive limits of detection are achieved, and a new record for the electrochemical detection of bacteria (0.15 colony-forming units per microlitre) is reported.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Kristin B. Cederquist
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
-
-
Article |
 In situ quantitative imaging of cellular lipids using molecular sensors
In situ quantitative imaging of cellular lipids using molecular sensors
Cellular membrane lipids play key roles in cell regulation. Here, an environmentally sensitive fluorophore is attached to a protein that binds to a key signalling lipid to produce a membrane lipid sensor. This strategy allows sensitive, quantitative, spatiotemporal imaging of the lipid concentration in mammalian cells.
- Youngdae Yoon
- , Park J. Lee
- & Wonhwa Cho
-
News & Views |
 Sweet solution to sensing
Sweet solution to sensing
Glucose meters allow rapid and quantitative measurement of blood sugar levels for diabetes sufferers worldwide. Now a new method allows this proven technology to be used to quantify a much wider range of analytes.
- Samuel K. Sia
- & Curtis D. Chin
-
Article |
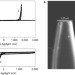 Electrochemistry through glass
Electrochemistry through glass
Glass is widely used as an electrical insulator in electrodes, but in spite of its high resistance, 100-nm-thick layers of glass have now been shown to be sufficiently conductive for electrochemical measurements. Obtaining redox couples through glass-covered nanoelectrodes suggests that the pH response of the glass is due to the formation of a hydrogel layer in acidic solution.
- Jeyavel Velmurugan
- , Dongping Zhan
- & Michael V. Mirkin

 Making commercial sense
Making commercial sense Captivating COFs
Captivating COFs Spoiler alert
Spoiler alert Attoreactor arrays
Attoreactor arrays