News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
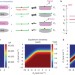 Simulation-guided DNA probe design for consistently ultraspecific hybridization
Simulation-guided DNA probe design for consistently ultraspecific hybridization
The use of kinetic simulations to guide the design of competitive hybridization probe systems is shown to enable high selectivity for single-nucleotide variants. Using this approach across 44 cancer mutation/wild-type sequence pairs showed between a 200- and 3,000-fold higher binding affinity than the corresponding wild-type sequence. In combination with PCR amplification this method enabled the detection of a 1% concentration of variant alleles in human genomic DNA.
- Juexiao Sherry Wang
- & David Yu Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Blue-chip binding
Blue-chip binding
Heparin is an anionic polysaccharide that has tremendous clinical importance as an anticoagulant. Several dyes have been developed that can detect heparin, and the latest example — named Mallard Blue — has now been shown to have excellent sensing properties under biologically relevant conditions.
- Zachary Shriver
- & Ram Sasisekharan
-
News & Views |
 Breaking the rules
Breaking the rules
Chemists have long been interested in synthesizing compounds that push the boundaries of conventional molecular structure. Incorporating metal centres into the ring unit of highly strained and unsaturated cyclic molecules can help reduce strain — a tactic that has now been used to render a previously inaccessible metallapentalyne isolable.
- Torsten Beweries
- & Uwe Rosenthal
-
Article |
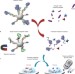 Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets
Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets
Portable sensors for the rapid quantitation of a variety of analytical targets could revolutionize both medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring. Here, functional DNA sensors that release the enzyme invertase in response to an analyte of choice are described. The enzyme converts sucrose to glucose which can then be easily detected using a widely available personal glucose meter.
- Yu Xiang
- & Yi Lu

 Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour