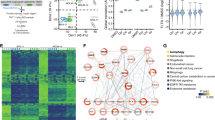
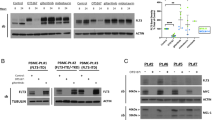
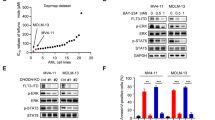
Abstract
More than one-third of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) harbor aberrant mutations in Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). Among them, the internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutation predicts poor prognosis. MZH29 is a novel FLT3 inhibitor synthesized in our laboratory that showed that cellular and kinase assays sustained inhibitory effects on wild-type and mutant FLT3, including the FLT3-ITD, FLT3-D835H/Y/V and FLT3-K663Q mutants. More importantly, MZH29 retained its potent inhibitory effect against the FLT3-ITD/F691L mutation, a drug resistance mutation against the well-known FLT3 inhibitor, AC220. MZH29 is a type II FLT3 inhibitor that tolerated the F691L mutation in molecular docking studies. Oral administration of 10 mg/kg MZH29 caused complete tumor regression and extended survival in a mouse model of AML with less toxicity. Subsequent proteomics study revealed less proteome perturbation in the MZH29-treated group than in the AC220-treated group. MZH29 demonstrates potential and potent novel FLT3 inhibitory effects for the treatment of AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estey E, Döhner H . Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2006; 368: 1894–1907.
Patel JP, Gonen M, Figueroa ME, Fernandez H, Sun Z, Racevskis J et al. Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1079–1089.
Drexler HG . Expression of FLT3 receptor and response to FLT3 ligand by leukemic cells. Leukemia 1996; 10: 588–599.
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 2059–2074.
Smith CC, Wang Q, Chin C-S, Salerno S, Damon LE, Levis MJ et al. Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2012; 485: 260–263.
Ke YY, Singh VK, Coumar MS, Hsu YC, Wang WC, Song JS et al. Homology modeling of DFG-in FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and structure-based virtual screening for inhibitor identification. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 11702.
Wander SA, Levis MJ, Fathi AT . The evolving role of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia: quizartinib and beyond. Ther Adv Hematol 2014; 5: 65–77.
Cortes JE, Kantarjian H, Foran JM, Ghirdaladze D, Zodelava M, Borthakur G et al. Phase I study of quizartinib administered daily to patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia irrespective of FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication status. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 3681–3687.
Smith CC, Zhang C, Lin KC, Lasater EA, Zhang Y, Massi E et al. Characterizing and overriding the structural mechanism of the quizartinib-resistant FLT3 'Gatekeeper' F691L mutation with PLX3397. Cancer Discov 2015; 5: 668–679.
Ma H, Nguyen B, Li L, Greenblatt S, Williams A, Zhao M et al. TTT-3002 is a novel FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor with activity against FLT3-associated leukemias in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2014; 123: 1525–1534.
Lee HK, Kim HW, Lee IY, Lee J, Lee J, Jung DS et al. G-749, a novel FLT3 kinase inhibitor, can overcome drug resistance for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2014; 123: 2209–2219.
Takahashi S . Downstream molecular pathways of FLT3 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: biology and therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol 2011; 4: 13.
Wu H, Hu C, Wang A, Weisberg EL, Wang W, Chen C et al. Ibrutinib selectively targets FLT3-ITD in mutant FLT3-positive AML. Leukemia 2016; 30: 754–757.
Smith CC, Lasater EA, Zhu X, Lin KC, Stewart WK, Damon LE et al. Activity of ponatinib against clinically-relevant AC220-resistant kinase domain mutants of FLT3-ITD. Blood 2013; 121: 3165–3171.
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 2004; 25: 1605–1612.
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 2009; 30: 2785–2791.
Schuttelkopf AW, van Aalten DM . PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2004; 60: 1355–1363.
Xu B, Gao Y, Zhan S, Xiong F, Qiu W, Qian X et al. Quantitative protein profiling of hippocampus during human aging. Neurobiol Aging 2016; 39: 46–56.
Vizcaino JA, Csordas A, del-Toro N, Dianes JA, Griss J, Lavidas I et al. Update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res 2016; 44: D447–D456.
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H, Xue Y . HemI: a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PloS One 2014; 9: e111988.
Levis MJ, Perl AE, Dombret H, Döhner H, Steffen B, Rousselot P et al. Final results of a phase 2 open-label, monotherapy efficacy and safety study of quizartinib (AC220) in patients with FLT3-ITD positive or negative relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia after second-line chemotherapy or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 120: 673–673.
Kim Y, Ko J, Cui Z, Abolhoda A, Ahn JS, Ou SH et al. The EGFR T790M mutation in acquired resistance to an irreversible second-generation EGFR inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 784–791.
Albers C, Leischner H, Verbeek M, Yu C, Illert A, Peschel C et al. The secondary FLT3-ITD F691L mutation induces resistance to AC220 in FLT3-ITD+ AML but retains in vitro sensitivity to PKC412 and Sunitinib. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1416–1418.
Smith CC, Lasater EA, Lin KC, Wang Q, McCreery MQ, Stewart WK et al. Crenolanib is a selective type I pan-FLT3 inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 5319–5324.
Treiber Daniel K, Shah Neil P . Ins and outs of kinase DFG motifs. Chem Biol 2013; 20: 745–746.
Zhao Z, Wu H, Wang L, Liu Y, Knapp S, Liu Q et al. Exploration of type II binding mode: a privileged approach for kinase inhibitor focused drug discovery? ACS Chem Biol 2014; 9: 1230–1241.
Nagar B, Bornmann WG, Pellicena P, Schindler T, Veach DR, Miller WT et al. Crystal structures of the kinase domain of c-Abl in complex with the small molecule inhibitors PD173955 and imatinib (STI-571). Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4236–4243.
Wan PT, Garnett MJ, Roe SM, Lee S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Good VM et al. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004; 116: 855–867.
Zorn JA, Wang Q, Fujimura E, Barros T, Kuriyan J . Crystal structure of the FLT3 kinase domain bound to the inhibitor quizartinib (AC220). PloS one 2015; 10: e0121177.
Yun C-H, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV, Woo MS, Greulich H, Wong K-K et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 2070–2075.
Noble MEM, Endicott JA, Johnson LN . Protein kinase inhibitors: insights into drug design from structure. Science 2004; 303: 1800–1805.
Green AS, Maciel TT, Yin C, Mazed F, Townsend EC, Pilorge S et al. Pim kinases modulate resistance to FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Adv 2015; 1: e1500221.
Li L, Osdal T, Ho Y, Chun S, McDonald T, Agarwal P et al. SIRT1 activation by a c-MYC oncogenic network promotes the maintenance and drug resistance of human FLT3-ITD acute Myeloid Leukemia stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2014; 15: 431–446.
Puissant A, Fenouille N, Alexe G, Pikman Y, Bassil CF, Mehta S et al. SYK is a critical regulator of FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 226–242.
Carnevale J, Ross L, Puissant A, Banerji V, Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ et al. SYK regulates mTOR signaling in AML. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2118–2128.
Kasper S, Breitenbuecher F, Heidel F, Hoffarth S, Markova B, Schuler M et al. Targeting MCL-1 sensitizes FLT3-ITD-positive leukemias to cytotoxic therapies. Blood Cancer J 2012; 2: e60.
Yoshimoto G, Miyamoto T, Jabbarzadeh-Tabrizi S, Iino T, Rocnik JL, Kikushige Y et al. FLT3-ITD up-regulates MCL-1 to promote survival of stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia via FLT3-ITD-specific STAT5 activation. Blood 2009; 114: 5034–5043.
Secchiero P, Melloni E, Voltan R, Norcio A, Celeghini C, Zauli G . MCL1 down-regulation plays a critical role in mediating the higher anti-leukaemic activity of the multi-kinase inhibitor Sorafenib with respect to Dasatinib. Br J Haematol 2012; 157: 510–514.
Zhang W, Borthakur G, Gao C, Chen Y, Mu H, Ruvolo VR et al. The dual MEK/FLT3 inhibitor E6201 exerts cytotoxic activity against acute myeloid leukemia cells harboring resistance-conferring FLT3 mutations. Cancer Res 2016; 76: 1528–1537.
Acknowledgements
We thank Qingsong Liu’s group for proving the cell lines stably expressed the FLT3 mutants. We thank Professor Haiteng Deng and the Protein Chemistry Facility at the Center for Biomedical Analysis of Tsinghua University for the sample analysis. We also thank Yu Wang for sorting the compounds chemical data. This study was supported by the Novo Nordisk Union Diabetes Research Talent Fund 2013 to WG, CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine (CAMS-I2M) 2016-I2M-3 to WG, PUMC Youth Fund, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332015020 to BHX).
Author contributions
BX and WG designed the studies and wrote the paper. BX performed the experiments and docking. YZ and PG designed and synthesized the chemical structures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they own the intellectual property of the new synthesized compound in this paper. No additional conflicts of interest exist.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Zhao, Y., Wang, X. et al. MZH29 is a novel potent inhibitor that overcomes drug resistance FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 31, 913–921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.297
This article is cited by
-
NADPH oxidase mediated oxidative stress signaling in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Update on Small Molecule Targeted Therapies for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2023)
-
Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: advances, challenges, and future perspectives
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)