Abstract
Background:
REV-ERBα has been shown to regulate adipogenesis and lipid metabolism as well as to link the circadian timing system to whole body metabolic homeostasis. We thus tested whether polymorphisms in REV-ERBα could be associated with metabolic phenotypes in human population samples.
Methods:
We analyzed the associations between 5 REV-ERBα polymorphisms and anthropometric (body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist and hip circumferences), biochemical (plasma lipid, glucose and insulin levels) and clinical (systolic and diastolic blood pressure) variables in three population-based studies (MONICA Lille n=1155 adults, MONA LISA Lille n=1170 adults and HELENA n=1155 adolescents). We assessed in vitro, the potential influence of one REV-ERBα polymorphism in transient transfection assays using two different cell lines.
Results:
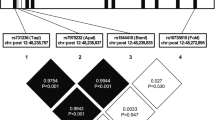
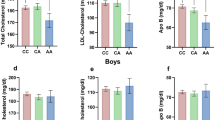
We observed significant and consistent associations between the T minor allele of the REV-ERBα rs2071427 polymorphism (located in intron 1) and higher BMI (mean allele effect=+0.33 kg m−2) in the MONICA Lille (P=0.02), MONA LISA (P=0.02) and HELENA (P=0.03) studies. The odds ratios for obesity associated with this allele were 1.67 (1.00–2.79) (P=0.05) in MONICA Lille, 1.29 (1.01–1.65) (P=0.04) in MONA LISA Lille and the odds ratio for overweight was 1.48 (1.08–2.03) (P=0.01) in HELENA. In transfection experiments in human hepatocyte-derived cell lines, the REV-ERBα intron 1 directed the transcription of a luciferase reporter gene independently of the rs2071427 polymorphism.
Conclusion:
Our results suggest that the REV-ERBα rs2071427 polymorphism modulates body fat mass in both adult and young people.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowrey PL, Takahashi JS . Genetics of circadian rhythms in Mammalian model organisms. Adv Genet 2011; 74: 175–230.
Scheer FA, Hu K, Evoniuk H, Kelly EE, Malhotra A, Hilton MF, Shea SA . Impact of the human circadian system, exercise, and their interaction on cardiovascular function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010; 107: 20541–20546.
Maury E, Ramsey KM, Bass J . Circadian rhythms and metabolic syndrome: from experimental genetics to human disease. Circ Res 2010; 106: 447–462.
Turek FW, Joshu C, Kohsaka A, Lin E, Ivanova G, McDearmon E et al. Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science 2005; 308: 1043–1045.
Marcheva B, Ramsey KM, Buhr ED, Kobayashi Y, Su H, Ko CH et al. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature 2010; 466: 627–631.
Huang W, Ramsey KM, Marcheva B, Bass J . Circadian rhythms, sleep, and metabolism. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 2133–2141.
Kohsaka A, Laposky AD, Ramsey KM, Estrada C, Joshu C, Kobayashi Y et al. High-fat diet disrupts behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in mice. Cell Metab 2007; 6: 414–421.
Kato S, Yokoyama A, Fujiki R . Nuclear receptor coregulators merge transcriptional coregulation with epigenetic regulation. Trends Biochem Sci 2011; 36: 272–281.
Lazar MA, Hodin RA, Darling DS, Chin WW . A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol 1989; 9: 1128–1136.
Preitner N, Damiola F, Lopez-Molina L, Zakany J, Duboule D, Albrecht U, Schibler U . The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell 2002; 110: 251–260.
Fontaine C, Dubois G, Duguay Y, Helledie T, Vu-Dac N, Gervois P et al. The orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erbalpha is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma target gene and promotes PPARgamma-induced adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 37672–37680.
Coste H, Rodriguez JC . Orphan nuclear hormone receptor Rev-erbalpha regulates the human apolipoprotein CIII promoter. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 27120–27129.
Raspe E, Duez H, Mansen A, Fontaine C, Fievet C, Fruchart JC et al. Identification of Rev-erbalpha as a physiological repressor of apoC-III gene transcription. J Lipid Res 2002; 43: 2172–2179.
Yin L, Wu N, Curtin JC, Qatanani M, Szwergold NR, Reid RA et al. Rev-erbalpha, a heme sensor that coordinates metabolic and circadian pathways. Science 2007; 318: 1786–1789.
Anzulovich A, Mir A, Brewer M, Ferreyra G, Vinson C, Baler R . Elovl3: a model gene to dissect homeostatic links between the circadian clock and nutritional status. J Lipid Res 2006; 47: 2690–2700.
Feng D, Liu T, Sun Z, Bugge A, Mullican SE, Alenghat T et al. A circadian rhythm orchestrated by histone deacetylase 3 controls hepatic lipid metabolism. Science 2011; 331: 1315–1319.
Le Martelot G, Claudel T, Gatfield D, Schaad O, Kornmann B, Sasso GL et al. REV-ERBalpha participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile acid homeostasis. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e1000181.
Teboul M, Guillaumond F, Grechez-Cassiau A, Delaunay F . The nuclear hormone receptor family round the clock. Mol Endocrinol 2008; 22: 2573–2582.
Duez H, Staels B . Rev-erb-alpha: an integrator of circadian rhythms and metabolism. J Appl Physiol 2009; 107: 1972–1980.
Cho H, Zhao X, Hatori M, Yu RT, Barish GD, Lam MT et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-alpha and REV-ERB-beta. Nature 2012; 485: 123–127.
Bugge A, Feng D, Everett LJ, Briggs ER, Mullican SE, Wang F et al. Rev-erbalpha and Rev-erbbeta coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 657–667.
Raghuram S, Stayrook KR, Huang P, Rogers PM, Nosie AK, McClure DB et al. Identification of heme as the ligand for the orphan nuclear receptors REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERBbeta. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2007; 14: 1207–1213.
Pardee KI, Xu X, Reinking J, Schuetz A, Dong A, Liu S et al. The structural basis of gas-responsive transcription by the human nuclear hormone receptor REV-ERBbeta. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e43.
Kojetin DJ, Burris TP . A role for rev-erbalpha ligands in regulation of adipogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 2011; 17: 320–324.
Solt LA, Wang Y, Banerjee S, Hughes T, Kojetin DJ, Lundasen T et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature 2012; 485: 62–68.
Severino G, Manchia M, Contu P, Squassina A, Lampus S, Ardau R et al. Association study in a Sardinian sample between bipolar disorder and the nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha gene, a critical component of the circadian clock system. Bipolar Disord 2009; 11: 215–220.
Shi J, Wittke-Thompson JK, Badner JA, Hattori E, Potash JB, Willour VL et al. Clock genes may influence bipolar disorder susceptibility and dysfunctional circadian rhythm. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008; 147B: 1047–1055.
Kishi T, Kitajima T, Ikeda M, Yamanouchi Y, Kinoshita Y, Kawashima K et al. Association analysis of nuclear receptor Rev-erb alpha gene (NR1D1) with mood disorders in the Japanese population. Neurosci Res 2008; 62: 211–215.
Manchia M, Squassina A, Congiu D, Chillotti C, Ardau R, Severino G, Del Zompo M . Interacting genes in lithium prophylaxis: preliminary results of an exploratory analysis on the role of DGKH and NR1D1 gene polymorphisms in 199 Sardinian bipolar patients. Neurosci Lett 2009; 467: 67–71.
Campos-de-Sousa S, Guindalini C, Tondo L, Munro J, Osborne S, Floris G et al. Nuclear receptor rev-erb-{alpha} circadian gene variants and lithium carbonate prophylaxis in bipolar affective disorder. J Biol Rhythms 2010; 25: 132–137.
The World Health Organization MONICA Project. Ecological analysis of the association between mortality and major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Int J Epidemiol 1994; 23: 505–516.
Dallongeville J, Delcroix AG, Wagner A, Ducimetiere P, Ruidavets JB, Arveiler D et al. The APOA4 Thr347->Ser347 polymorphism is not a major risk factor of obesity. Obes Res 2005; 13: 2132–2138.
Lambert JC, Dallongeville J, Ellis KA, Schraen-Maschke S, Lui J, Laws S et al. Association of plasma ass peptides with blood pressure in the elderly. PLoS One 2011; 6: e18536.
Moreno LA, De Henauw S, Gonzalez-Gross M, Kersting M, Molnar D, Gottrand F et al. Design and implementation of the Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32 (Suppl 5): S4–11.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH . Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 2000; 320: 1240–1243.
Mueller WH, Martorell R . Reliability and accuracy of measurements. In: Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R, (eds) Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Human Kinetics Books. Champaign: IL, USA, 1988; pp 83–86.
Nagy E, Vicente-Rodriguez G, Manios Y, Beghin L, Iliescu C, Censi et al. Harmonization process and reliability assessment of anthropometric measurements in a multicenter study in adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32 (Suppl 5): S58–S65.
Parizkova J, Roth Z . The assessment of depot fat in children from skinfold thickness measurements by Holtain (Tanner-Whitehouse) caliper. Hum Biol 1972; 44: 613–620.
Sun SS, Chumlea WC, Heymsfield SB, Lukaski HC, Schoeller D, Friedl K et al. Development of bioelectrical impedance analysis prediction equations for body composition with the use of a multicomponent model for use in epidemiologic surveys. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 331–340.
Nakabayashi H, Taketa K, Miyano K, Yamane T, Sato J . Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res 1982; 42: 3858–3863.
Viechtbauer W . Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Soft 2010; 36: 1–48.
Tregouet DA, Garelle V . A new JAVA interface implementation of THESIAS: testing haplotype effects in association studies. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 1038–1039.
Triqueneaux G, Thenot S, Kakizawa T, Antoch MP, Safi R, Takahashi JS et al. The orphan receptor Rev-erbalpha gene is a target of the circadian clock pacemaker. J Mol Endocrinol 2004; 33: 585–608.
Kumar N, Solt LA, Wang Y, Rogers PM, Bhattacharyya G, Kamenecka TM et al. Regulation of adipogenesis by natural and synthetic REV-ERB ligands. Endocrinology 2010; 151: 3015–3025.
Wang J, Lazar MA . Bifunctional role of Rev-erbalpha in adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 2213–2220.
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU et al. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 937–948.
Acknowledgements
This study is part of the CRESCENDO (Consortium for Research into Nuclear Receptors in Development and Aging) consortium funded by the Commission′s Sixth Framework Program (integrated project LSHM-CT-2005-018652). The HELENA study received funding from the European Union′s Sixth RTD Framework Program (Contract FOOD-CT-2005-007034). The French arm of the WHO-MONICA population study was funded by grants from the Conseil Régional du Nord-Pas de Calais, the Caisse Primaire d′Assurance Maladie de Sélestat, the Association Régionale de Cardiologie d′Alsace, ONIVINS, Parke-Davis, the Mutuelle Générale de l′Education Nationale (MGEN), the Réseau National de Santé Publique, the Direction Générale de la Santé, the INSERM, the Institut Pasteur de Lille and the Unité d′Evaluation du Center Hospitalier et Universitaire de Lille. The MONA LISA Study was made possible by an unrestricted grant of Pfizer and by a grant from ANR (ANR-05-PNRA-018). The University of Nice Sophia-Antipolis and the CNRS are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goumidi, L., Grechez, A., Dumont, J. et al. Impact of REV-ERB alpha gene polymorphisms on obesity phenotypes in adult and adolescent samples. Int J Obes 37, 666–672 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.117
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.117