Abstract
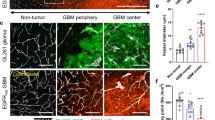
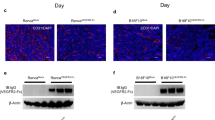
Oncolytic viral (OV) therapy has been considered as a promising treatment modality for brain tumors. Vasculostatin, the fragment of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor-1, shows anti-angiogenic activity against malignant gliomas. Previously, a vasculostatin-expressing oncolytic herpes simplex virus-1, Rapid Antiangiogenesis Mediated By Oncolytic virus (RAMBO), was reported to have a potent antitumor effect. Here, we investigated the therapeutic efficacy of RAMBO and cilengitide, an integrin inhibitor, combination therapy for malignant glioma. In vitro, tube formation was significantly decreased in RAMBO and cilengitide combination treatment compared with RAMBO or cilengitide monotherapy. Moreover, combination treatment induced a synergistic suppressive effect on endothelial cell migration compared with the control virus. RAMBO, combined with cilengitide, induced synergistic cytotoxicity on glioma cells. In the caspase-8 and -9 assays, the relative absorption of U87ΔEGFR cell clusters treated with cilengitide and with RAMBO was significantly higher than that of those treated with control. In addition, the activity of caspase 3/7 was significantly increased with combination therapy. In vivo, there was a significant increase in the survival of mice treated with combination therapy compared with RAMBO or cilengitide monotherapy. These results indicate that cilengitide enhanced vasculostatin-expressing OV therapy for malignant glioma and provide a rationale for designing future clinical trials combining these two agents.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P . Epidemiology and etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 2005; 109: 93–108.
Haseley A, Alvarez-Breckenridge C, Chaudhury AR, Kaur B . Advances in oncolytic virus therapy for glioma. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 2009; 4: 1–13.
Kurozumi K, Hardcastle J, Thakur R, Shroll J, Nowicki M, Otsuki A et al. Oncolytic HSV-1 infection of tumors induces angiogenesis and upregulates CYR61. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1382–1391.
Kaur B, Cork SM, Sandberg EM, Devi NS, Zhang Z, Klenotic PA et al. Vasculostatin inhibits intracranial glioma growth and negatively regulates in vivo angiogenesis through a CD36-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1212–1220.
Hardcastle J, Kurozumi K, Dmitrieva N, Sayers MP, Ahmad S, Waterman P et al. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of vasculostatin (Vstat120) expressing oncolytic HSV-1. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 285–294.
Hynes RO . Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002; 110: 673–687.
Varner JA, Cheresh DA . Integrins and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996; 8: 724–730.
Varner JA, Cheresh DA . Tumor angiogenesis and the role of vascular cell integrin alphavbeta3. Important Adv Oncol 1996: 69–87.
Varner JA, Emerson DA, Juliano RL . Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 expression negatively regulates cell growth: reversal by attachment to fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell 1995; 6: 725–740.
Friedlander M, Brooks PC, Shaffer RW, Kincaid CM, Varner JA, Cheresh DA . Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science 1995; 270: 1500–1502.
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA . Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 1994; 264: 569–571.
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 1994; 79: 1157–1164.
Hodivala-Dilke KM, Reynolds AR, Reynolds LE . Integrins in angiogenesis: multitalented molecules in a balancing act. Cell Tissue Res 2003; 314: 131–144.
Leavesley DI, Ferguson GD, Wayner EA, Cheresh DA . Requirement of the integrin beta 3 subunit for carcinoma cell spreading or migration on vitronectin and fibrinogen. J Cell Biol 1992; 117: 1101–1107.
MacDonald TJ, Taga T, Shimada H, Tabrizi P, Zlokovic BV, Cheresh DA et al. Preferential susceptibility of brain tumors to the antiangiogenic effects of an alpha(v) integrin antagonist. Neurosurgery 2001; 48: 151–157.
Xiong JP, Stehle T, Diefenbach B, Zhang R, Dunker R, Scott DL et al. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alpha Vbeta3. Science 2001; 294: 339–345.
Burke PA, DeNardo SJ, Miers LA, Lamborn KR, Matzku S, DeNardo GL . Cilengitide targeting of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptor synergizes with radioimmunotherapy to increase efficacy and apoptosis in breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4263–4272.
Abdollahi A, Griggs DW, Zieher H, Roth A, Lipson KE, Saffrich R et al. Inhibition of alpha(v)beta3 integrin survival signaling enhances antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 6270–6279.
Tentori L, Dorio AS, Muzi A, Lacal PM, Ruffini F, Navarra P et al. The integrin antagonist cilengitide increases the antitumor activity of temozolomide against malignant melanoma. Oncol Rep 2008; 19: 1039–1043.
Reardon DA, Fink KL, Mikkelsen T, Cloughesy TF, O'Neill A, Plotkin S et al. Randomized phase II study of cilengitide, an integrin-targeting arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide, in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5610–5617.
Kurozumi K, Hardcastle J, Thakur R, Yang M, Christoforidis G, Fulci G et al. Effect of tumor microenvironment modulation on the efficacy of oncolytic virus therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007; 99: 1768–1781.
Fulci G, Dmitrieva N, Gianni D, Fontana EJ, Pan X, Lu Y et al. Depletion of peripheral macrophages and brain microglia increases brain tumor titers of oncolytic viruses. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 9398–9406.
Fulci G, Breymann L, Gianni D, Kurozomi K, Rhee SS, Yu J et al. Cyclophosphamide enhances glioma virotherapy by inhibiting innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 12873–12878.
Kambara H, Okano H, Chiocca EA, Saeki Y . An oncolytic HSV-1 mutant expressing ICP34.5 under control of a nestin promoter increases survival of animals even when symptomatic from a brain tumor. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 2832–2839.
Terada K, Wakimoto H, Tyminski E, Chiocca EA, Saeki Y . Development of a rapid method to generate multiple oncolytic HSV vectors and their in vivo evaluation using syngeneic mouse tumor models. Gene Ther 2006; 13: 705–714.
Bishop ET, Bell GT, Bloor S, Broom IJ, Hendry NF, Wheatley DN . An in vitro model of angiogenesis: basic features. Angiogenesis 1999; 3: 335–344.
Mikkelsen T, Brodie C, Finniss S, Berens ME, Rennert JL, Nelson K et al. Radiation sensitization of glioblastoma by cilengitide has unanticipated schedule-dependency. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 2719–2727.
Maubant S, Saint-Dizier D, Boutillon M, Perron-Sierra F, Casara PJ, Hickman JA et al. Blockade of alpha v beta3 and alpha v beta5 integrins by RGD mimetics induces anoikis and not integrin-mediated death in human endothelial cells. Blood 2006; 108: 3035–3044.
Onishi M, Kurozumi K, Ichikawa T, Michiue H, Fujii K, Ishida J et al. Gene expression profiling of the anti-glioma effect of Cilengitide. Springerplus 2013; 2: 160.
Spear MA, Sun F, Eling DJ, Gilpin E, Kipps TJ, Chiocca EA et al. Cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and viral replication in tumor cells treated with oncolytic ribonucleotide reductase-defective herpes simplex type 1 virus (hrR3) combined with ionizing radiation. Cancer Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1051–1059.
Reardon DA, Nabors LB, Stupp R, Mikkelsen T . Cilengitide: an integrin-targeting arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide with promising activity for glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2008; 17: 1225–1235.
Nabors LB, Mikkelsen T, Hegi ME, Ye X, Batchelor T, Lesser G et al. A safety run-in and randomized phase 2 study of cilengitide combined with chemoradiation for newly diagnosed glioblastoma (NABTT 0306). Cancer 2012; 118: 5601–5607.
Walsh CT, Radeff-Huang J, Matteo R, Hsiao A, Subramaniam S, Stupack D et al. Thrombin receptor and RhoA mediate cell proliferation through integrins and cysteine-rich protein 61. FASEB J 2008; 22: 4011–4021.
Haseley A, Boone S, Wojton J, Yu L, Yoo JY, Yu J et al. Extracellular matrix protein CCN1 limits oncolytic efficacy in glioma. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 1353–1362.
Yoo JY, Haseley A, Bratasz A, Chiocca EA, Zhang J, Powell K et al. Antitumor efficacy of 34.5ENVE: a transcriptionally retargeted and “Vstat120”-expressing oncolytic virus. Mol Ther 2012; 20: 287–297.
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Wakimoto, M. Arao, and A. Ishikawa for their technical assistance. This study was supported by Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology to KK (No. 20890133; No. 21791364), and to TI (No. 19591675; No. 22591611).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cancer Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, K., Kurozumi, K., Ichikawa, T. et al. The integrin inhibitor cilengitide enhances the anti-glioma efficacy of vasculostatin-expressing oncolytic virus. Cancer Gene Ther 20, 437–444 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2013.38
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2013.38
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Implications of immune cells in oncolytic herpes simplex virotherapy for glioma
Brain Tumor Pathology (2022)
-
A super gene expression system enhances the anti-glioma effects of adenovirus-mediated REIC/Dkk-3 gene therapy
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Adhesion molecules and the extracellular matrix as drug targets for glioma
Brain Tumor Pathology (2016)
-
Integrin antagonist augments the therapeutic effect of adenovirus-mediated REIC/Dkk-3 gene therapy for malignant glioma
Gene Therapy (2015)
-
Evaluation of extracellular matrix protein CCN1 as a prognostic factor for glioblastoma
Brain Tumor Pathology (2015)