Abstract
Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) is widely used in disease models to examine the contribution of receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK) 1 in cell death and inflammation. We studied three Nec-1 analogs: Nec-1, the active inhibitor of RIPK1, Nec-1 inactive (Nec-1i), its inactive variant, and Nec-1 stable (Nec-1s), its more stable variant. We report that Nec-1 is identical to methyl-thiohydantoin-tryptophan, an inhibitor of the potent immunomodulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Both Nec-1 and Nec-1i inhibited human IDO, but Nec-1s did not, as predicted by molecular modeling. Therefore, Nec-1s is a more specific RIPK1 inhibitor lacking the IDO-targeting effect. Next, although Nec-1i was ∼100 × less effective than Nec-1 in inhibiting human RIPK1 kinase activity in vitro, it was only 10 times less potent than Nec-1 and Nec-1s in a mouse necroptosis assay and became even equipotent at high concentrations. Along the same line, in vivo, high doses of Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s prevented tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced mortality equally well, excluding the use of Nec-1i as an inactive control. Paradoxically, low doses of Nec-1 or Nec-1i, but not Nec -1s, even sensitized mice to TNF-induced mortality. Importantly, Nec-1s did not exhibit this low dose toxicity, stressing again the preferred use of Nec-1s in vivo. Our findings have important implications for the interpretation of Nec-1-based data in experimental disease models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Depending on the cellular context, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induces receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK)-1 and RIPK3 kinase-dependent necrotic cell death (regulated necrosis or necroptosis).1, 2, 3, 4, 5 In certain conditions, such as deficiency or inhibition of cIAPs, RIPK1 kinase activity can mediate apoptosis.6, 7, 8 RIPK1 and RIPK3 interact through their RIP homotypic interaction motif domain and initiate necroptosis via phosphorylation-driven formation of a signaling complex within TNFR1-induced complex II (the necrosome).4, 7 Necrostatin-1 ((Nec-1; 5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one), originally identified in a screen for chemical inhibitors of necrotic cell death in human U937 cells,9 is an allosteric inhibitor of RIPK1.10 Nec-1 does not affect RIPK1-mediated nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation,10 in line with the dispensable role of RIPK1 kinase activity in this process.11 For several kinases, the catalytic activity is regulated by the phosphorylation status of the activation segment (T-loop), located in the kinase domain.12 The unphosphorylated activation segment, locked into an inactive conformation, is converted by phosphorylation into an active conformation. Homology modeling using B-RAF as a template, structure–activity relationship (SAR) and mutant analysis showed that Nec-1 stabilizes the inactive conformation of RIPK1, functioning as an allosteric inhibitor.10
Because RIPK1 deficiency in mice causes postnatal death due to its indispensable platform function leading to NF-κB13 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling,14 Nec-1 has been instrumental in studying the contribution of RIPK1 kinase-dependent necroptosis in various pathologies involving cell death.9, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 We previously reported that treatment with Nec-1 or genetic ablation of RIPK3 protected mice from lethality associated with TNF-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), suggesting that a RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent pathway drives TNF-induced mortality.21 However, literature and our own observations raised some critical issues regarding Nec-1’s specificity, its appropriate control and the effective concentration especially in murine experimental disease models. Regarding the kinase specificity of Nec-1, of 98 human kinases, only PAK1 and PKAcα are partially inhibited by Nec-1.22 Targets of Nec-1 activity other than RIPK1 have also been suggested, for example, in T-cell receptor signaling.23 The Nec-1 analog, Nec-1 stable (Nec-1s) (7-Cl-O-Nec-1) was >1000-fold more selective for RIPK1 than for any other kinase out of 485 human kinases.24 Another issue is that RIPK1 kinase activity is not only confined to necroptosis but is also involved in ERK activation25 and in apoptosis when IAP is depleted.6, 7, 8 Altogether, these results argue for a careful interpretation of the biological effect after in vivo Nec-1 administration. Moreover, a selection of appropriate controls and consideration of the effective concentrations is very important in interpreting the results obtained using Nec-1. Strikingly, before being identified as a RIPK1 kinase inhibitor, Nec-1 under its alternative name methyl-thiohydantoin-tryptophan (MTH-Trp) had been described as an inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO).26 IDO, which is an immune regulator,27 catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step of tryptophan catabolism, leading to the formation of kynurenine.28 IDO activity is induced by several pro-inflammatory stimuli, including lipopolysaccharides, bacterial DNA and type I/II interferons.29, 30, 31 Mounting data suggest that IDO controls the flux between the pathways leading to pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokine production.32 IDO activity is induced in patients with shock and trauma,33 and blockage or deficiency of IDO partially protects mice against endotoxemia.34 Kynurenine has also been identified as an ‘endothelium-derived relaxing factor’ mediating inflammation-induced pathological hypotension.35 Clearly, targeting IDO by Nec-1/MTH-Trp might be important in some in vivo models of inflammation. Therefore, we examined IDO inhibitory activity of Nec-1 and its derivatives.
The second issue relates to differential RIPK1 inhibitory potencies of Nec-1 derivatives. Nec-1 consists of an indoleamine and a thiohydantoin moiety, also called thioxo-imidazolidinone. The SAR analyses of Nec-1 revealed that elimination of the methyl group in the thiohydantoin moiety completely abolished its inhibition of human RIPK1 and of TNF-induced necroptosis in Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD)-deficient Jurkat cells, a human T cell line.10 Demethylated Nec-1 is referred to as Nec-1 inactive (Nec-1i) (5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one). It is often used as an inactive control in studies using Nec-1 to exclude nonspecific off-target effects inherent to inhibitors. Moreover, a small group substitution at the seventh position of the indole of Nec-1 and a change from thiohydantoin to hydantoin strongly enhanced its inhibitory activity.10, 36 One variant also improved in vivo stability: Nec-1s or 7-Cl-O-Nec-1 (5-((7-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-3-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione) was effective in reducing brain injuries.9, 18 Surprisingly, we found that the ‘inactive’ Nec-1i still inhibited TNF-induced necroptosis in mouse cells and became equipotent at higher concentrations. Furthermore, it was equipotent to Nec-1 in protecting against lethal TNF-induced SIRS in vivo. As Nec-1i is inactive on purified recombinant human RIPK1 but active in cellular and in vivo conditions, at least in the mouse system, a third issue is raised. What is the optimal concentration for administering Nec-1 in vivo and how to discriminate it from its ‘inactive’ variant Nec-1i? These issues prompted us to compare the inhibitory activities of Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s on human RIPK1 kinase, human IDO, mouse cellular necroptosis and in an in vivo necroptosis model, namely TNF-induced SIRS.21
Results
Characterization of Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s on a RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinase assay and on TNF-induced necroptosis
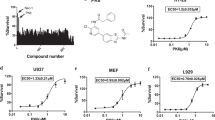
SAR analysis revealed that Nec-1i, which lacks a methyl group on the thiohydantoin moiety, lost its RIPK1 inhibitory activity, whereas substitution of thiohydantoin with hydantoin and introduction of chlorine at position 7 of the indoleamine moiety yielded a more stable inhibitor, Nec-1s, also called 7-Cl-O-Nec-1.9, 10, 36 We performed an in vitro kinase assay using recombinant human RIPK1or RIPK3 in the presence and absence of these compounds. RIPK1 autophosphorylation was evident and was potently inhibited by Nec-1 and Nec-1s in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1b). Nec-1s was equipotent to Nec-1, confirming published results.9, 10, 36 The demethylated variant of Nec-1, Nec-1i, only showed minor inhibitory activity on human RIPK1 autophosphorylation at the highest concentration (100 μM) (Figure 1c), indicating a more than 100-fold lower inhibitory activity of Nec-1i as compared with Nec-1. In addition, none of the compounds was able to block RIPK3 autophosphorylation (Figure 1c), confirming that these compounds specifically target RIPK1 and not RIPK3 in the necroptotic pathway.10
Activity of Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s in an in vitro RIPK kinase assay and a cellular assay for necroptosis. (a) Chemical structures of Nec-1/MTH-Trp, Nec-1i and Nec-1s (b) Effect of Nec-1 variants on human RIPK1 kinase activity. Recombinant GST-hRIPK1 was preincubated with the indicated amount of inhibitor, and autophosphorylation was determined by a radioactive ATP assay, followed by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose membrane. All reactions contained the same amount of DMSO. The autophosphorylation observed in the presence of only DMSO was set to 100%. (c). Effect of Nec-1 variants on human RIPK3 kinase activity. The procedure was identical to b, but GST-hRIPK3 was used instead of GST-hRIPK1. (d). Effect of Nec-1 variants on TNF-induced necrosis. L929sA cells were preincubated for 1 h with the indicated amounts of inhibitor or an equal amount of DMSO, and then treated with 1000 IU/ml of mTNF for 6 h. Cell death was measured as percentage of propidium iodide (PI)-positive nuclei on images acquired with BD pathway
Next, we compared the efficiency of these compounds to modulate TNF-induced necroptosis in mouse L929sA cells. This cellular assay surprisingly revealed only about 10-fold lower inhibitory activity of Nec-1i compared with Nec-1 (Figure 1d). This relatively minor difference between Nec-1 and Nec-1i on mouse cells is in contrast with the absence of any inhibitory activity of Nec-1i on human FADD-deficient Jurkat cells.10 From these experiments, we conclude that Nec-1i retains some inhibitory activity on TNF-induced necroptosis on mouse cells, which becomes equipotent at higher concentrations (10–100 μM) (Figure 1d). Although the exact mechanism of this protection by Nec-1i is not known, it may either reflect a species specificity, the existence of additional targets or metabolization of Nec-1i resulting in an active compound. Whatever the reason may be, it is obvious that this observation has important implications for the use of Nec-1i as a control in mouse experimental disease models.
Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, are predicted to inhibit IDO with similar potency
Nec-1 has been identified as a specific inhibitor of RIPK1 kinase activity.9, 10 However, Nec-1 is identical to MTH-Trp, which has been described as a potent inhibitor of IDO.26 The substrates of IDO are indoleamines, such as tryptophan, serotonin, melatonin and tryptamine.37 Hence, typical IDO inhibitors are indoleamine-containing compounds, including 1-methyl-tryptophan (1-MT)38 and MTH-Trp.26 Ample studies have used Nec-1 to inhibit RIPK1 kinase activity, but a potential IDO-inhibiting effect in cellular or experimental disease models has not been addressed before.
Nec-1, Nec-1i, Nec-1s and 1-MT contain an indole moiety also present in L-tryptophan, the substrate of IDO (Figure 2a). The crystal structures of human IDO (pdb-entries 2D0T and 2D0U) reveal the active site as a small distal pocket located adjacent to the heme. The orientation of the ligand’s indole moiety within this pocket is expected to be near-perpendicular versus the heme, with N1 and C2 in the vicinity of the iron ion, as to allow iron-bound dioxygen to react with the indole ring in accordance with the proposed mechanism.39 We suspected that the chlorine substituent of Nec-1s/7-Cl-O-Nec-1 might no longer allow the indole ring to fit properly in the enzyme’s narrow pocket. Subsequently, we have docked the substrate L-tryptophan (L-Trp), the known IDO inhibitors (1-MT and Nec-1/1-MTH-Trp) and the Nec-1 derivatives (Nec-1i and Nec-1s) into the active site of human IDO pdb-entry 2D0T, using the automated docking program AutoDock-Vina.40 This crystal structure contains 4-phenylimidazole nitrogen-bound to the heme’s iron ion. In preparing the enzyme’s structure model for docking, this ligand was removed, leaving the heme unoccupied. Given the enzyme’s mechanism, ligand docking poses that leave no room for iron-bound molecular oxygen were dismissed.
Molecular docking of substrates, inhibitors and Nec-1 variants on human IDO. (a) Chemical structures of L-Trp, 1-MT, Nec-1/MTH-Trp, Nec-1i and Nec-1s. (b) Surface view of IDO’s pocket-like active site, with the docked pose of L-Trp as seen from the enzyme’s heme in the foreground. (c) Same viewing position partly surfaced, now showing Ser167 in relation to the ligand’s indole ring. (d) Same docking pose of L-Trp (amino-acid moiety clipped off for clarity) now as seen from the pocket entrance with the heme on the right, with meshed surface showing the narrow pocket. The gap between the heme’s iron versus positions 1 and 2 of the indole ring leaves sufficient space for the missing iron-bound dioxygen. (e) The docked pose of Nec-1 shows a symmetrical distance between the heme’s iron and position 1 or 2 of the indole ring, also allowing sufficient space for dioxygen. (f) For the analogous pose of Nec-1s, the indole ring is slightly tilted due to a steric clash of Ser167 with the indole’s 7-Cl substituent. This brings the indole ring substantially closer to the heme, suggesting that this pose no longer leaves sufficient space for molecular oxygen, or that Nec-1s may be unable to fit into the pocket of dioxygen-bound IDO
With L-Trp, a docking pose was obtained, showing an indole position and orientation within the active site’s pocket that corroborates the proposed mechanism (Figure 2b); its amino-acid moiety resides in the tunnel-like entrance to the pocket. Ser167 protruding from the surface of the pocket is in the vicinity (4.6Å) of C7 of the indole moiety (Figure 2c). This docking pose allows sufficient space for molecular oxygen (Figure 2d). A similar overall pose was obtained with Nec-1 (Figure 2e) and at first sight also with Nec-1s (Figure 2f). Next, we docked the L enantiomer of all ligands (L-Trp, 1-MT, Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s) (Figure 3a) and calculated the distances of the respective indole’s H1 and C2 to the heme’s iron to assess the spatial relationship between the ligand and the molecular oxygen (red-mesh lines in Figures 2e and f; Figure 3). The D enantiomer of all ligands docked in a similar fashion (result not shown). The positioning of the indole ring of all ligands, except for Nec-1s, allows the accommodation of iron-bound dioxygen (Figure 3b), which is a prerequisite for substrate and competitive inhibitor binding.39 However, a similar pose with Nec-1s results in a smaller H1-Fe distance as compared with the other ligands (Figure 3b). Indeed, the 7-Cl substitution in Nec-1s induces steric hindrance with the protruding Ser167 at the pocket’s surface, causing a tilt of the indole ring, thereby bringing its H1 closer to the iron ion of the heme, leaving no room for molecular oxygen. This suggests that Nec-1s, in contrast to Nec-1 and Nec-1i, will not bind and inhibit IDO, a prediction that was experimentally tested (next section).
Molecular docking of substrates, inhibitors and Nec-1 variants on human IDO representing a similar docking pose for all ligands. (a) Vina dockings on human IDO yielded highly similar poses for all ligands whether as L or D enantioner; only L enantiomers are shown. Top left: L-Trp with amino-acid moiety and meshed surface clipped off, showing the narrow pocket; top center: L-Trp complete view; top right: L-1-MT; bottom left: L-Nec-1; bottom center: L-Nec-1i; and bottom right: L-Nec-1s. The latter shows a larger tilt of the indole ring with respect to the pocket, due to a steric clash between Ser167 and the indole’s 7-Cl substituent. (b) Table with calculated distances between IDO’s heme iron versus positions 1 and 2 of the respective indoles of the docked ligand poses. The red highlight indicates the smaller gap for molecular oxygen with the pose of Nec-1s
Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, inhibit IDO enzyme activity
As docking predicted differential binding of Nec-1 and its variants on IDO (Figure 3), we tested these compounds together with a prototype IDO inhibitor 1-MT in an IDO enzyme assay. Both Nec-1 and Nec-1i inhibited IDO with a comparable EC50 to 1-MT (Figure 4a). In contrast, Nec-1s did not inhibit IDO (Figure 4a), as predicted by molecular docking (Figure 3b). These results indicate caution when interpreting results using these compounds in cellular assays or in vivo because Nec-1 is not only a RIPK1 inhibitor but also a potent IDO inhibitor. Also, Nec-1i potently inhibits IDO, as predicted by the docking model. In contrast, Nec-1s is a more specific and therefore superior RIPK1 inhibitor. As all these compounds share the indole moiety, we questioned whether IDO inhibitors, such as 1-MT, would interfere with cellular necroptosis. 1-MT did not show any inhibitory activity on TNF-induced cytotoxicity on L929 cells at any concentration tested, ruling out that IDO inhibitors in general could directly interfere with necrotic cell death (Figures 4b and c).
Nec-1/1-M-Trp and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, inhibit IDO activity. (a) IDO enzymatic assay using recombinant IDO shows IDO inhibitory activities of Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not of Nec-1s, which is in accordance with the predictions of the docking experiment. (b) Prototype IDO inhibitor D-1-MT has no inhibitory activity on cellular necroptosis assay using L929 cells. Cell survival was measured by MTT colorimetric method. (c) Increasing the concentration of 1-MT up to 100 μM has no effect on necroptosis. Cell survival was measured by MTT colorimetric method
In vivo Nec-1i is as protective as Nec-1 against lethality associated with TNF-induced SIRS
We have reported that pretreatment with Nec-1 protected against lethal SIRS caused by in vivo administration of TNF.21 Because both Nec-1 and Nec-1i possess IDO inhibitory activity and IDO is an important immunomodulatory molecule, we tested Nec-1i in this model as well. Mice were pretreated with Nec-1 or Nec-1i before challenge with a lethal dose of mTNF using the same dose regimen as described before.21 Nec-1 protected against TNF-induced hypothermia and lethality as reported earlier (Figures 5a and b). Rather surprisingly, Nec-1i protected equally well (Figures 5a and b), which is in line with the equipotent inhibition in the cellular necroptosis assay at higher concentrations (Figure 1d). Thus, the inhibitory effect of Nec-1i might be due to the high dose of compounds reaching equipotent concentrations in target organs, which could mask the difference in the effective dose. In addition, in vivo pharmacodynamics and metabolization may also contribute to the equal protection. In order to discriminate between Nec-1 and Nec-1i in vivo activities, we examined the dose response in this model.
Nec-1 and Nec-1i show a paradoxical dose response in TNF-induced SIRS. (a) Effect of Nec-1 and Nec-1i on TNF shock-associated hypothermia. DMSO, Nec-1 or Nec-1i were injected i.v. at a dose of 6 mg/kg b.w. 17 min before challenge with 10 μg mTNF i.v. (about LD100); Nec-1 and Nec-1i were equipotent in protection. (b) Survival curve for the experiment described in a. (c) TNF shock-associated hypothermia for different doses of Nec-1 and Nec-1i. Both compounds were injected at different doses with the same regimen as above, before injection with 7.5 μg mTNF (about LD50). Hi: 6 mg/kg b.w; Mo: 3 mg/kg b.w; and Lo: 0.6 mg/kg b.w. Nec-1 and Nec-1i paradoxically sensitized mice to TNF-induced SIRS. (d) Survival curve for different doses of Nec-1 and Nec-1i. (e) Levels of damage-associated markers detected in the plasma of mice treated as indicated with TNF and different doses of Nec-1 and Nec-1i. A cumulative result of two independent experiments is represented (a–d). Number of mice is indicated between brackets. *P<0.05, **P<0.001 and ***P<0.0001
Nec-1 and Nec-1i sensitize towards TNF-induced SIRS when administered at a lower dose
We evaluated the dose response of both compounds using half (3 mg/kg, designated moderate (Mo)) and one-tenth (0.6 mg/kg, designated low (Lo)) of the initial dose (6 mg/kg, designated high (Hi)), assuming that the lower doses might reveal a differential protective effect between Nec-1 and Nec-1i. The half dose was still as protective as the initial dose (Figures 5c and d). Surprisingly, at the lowest dose both Nec-1 and Nec-1i even sensitized mice to TNF-induced shock, evidenced by accelerated hypothermia and decreased survival rate (Figures 5c and d). Importantly, these results indicate that at a lower dose both Nec-1 and Nec-1i gain a toxic effect, making it impossible to establish differences by subsaturating doses. The toxic effect is a specific in vivo phenomenon as it was not observed in vitro in the cellular necroptosis assay (Figure 1d).
Next, we questioned whether the sensitizing effect of Nec-1 involved cell death processes. We have shown earlier that inhibition of necroptosis by Nec-1 or RIPK3 deletion resulted in reduced release of cellular content into circulation.21 The levels of the liver enzymes aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase, as well as the cellular disintegration marker lactate dehydrogenase, increased by TNF administration in the control group in a highly significant manner, as reported earlier.21 Creatinine levels rather declined after TNF administration, most likely reflecting muscle catabolism (Figure 5e). Pretreatment with Nec-1 at high dose reversed these changes almost completely (Figure 5e), indicating protection against cytolysis, as reported previously.21 Pretreatment with Nec-1 at low dose did not increase the levels of most of these soluble markers, suggesting that mechanisms other than cellular damage are involved in sensitization.
Nec-1s protects against TNF-induced SIRS without sensitization effect
As Nec-1s is a potent inhibitor of RIPK1 and cellular necroptosis (Figures 1b and c) while lacking IDO inhibitory activity (Figure 4a), we tested it in the TNF-induced SIRS model with doses that were protective (Hi: 6 mg/kg) and sensitizing for Nec-1 (Lo: 0.6 mg/kg). Nec-1s protected as well as Nec-1 at the high dose, but did not sensitize at the low dose. In the same experimental set-up, Nec-1 exhibited protection or sensitization pending on the dose used (Figures 6a and b), confirming previous findings (Figures 5c and d). Pretreatment with Nec-1s at high dose provided statistically significant protection. Pretreatment at a lower dose was comparable to the control group. Therefore, Nec-1s is not only a more specific inhibitor that does not interfere with IDO but is also a superior inhibitor suitable for use in vivo lacking a paradoxical sensitizing effect in TNF-induced lethality. As all Nec-1 derivatives were protective at high dose, this effect most probably is mediated by RIPK1 inhibition. On the other hand, because Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, were able to block IDO in vitro, we speculate that the sensitizing effect of Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, at lower dose in vivo may involve IDO targeting, although further research is required to support this hypothesis.
Nec-1s does not show a paradoxical dose response in TNF-induced SIRS. (a) TNF shock-associated hypothermia. Nec-1 and Nec-1s were injected i.v. at a dose of Hi: 6 mg/kg b.w. or Lo: 0.6 mg/kg b.w. 17 min before the challenge with mTNF; i.v. Nec-1s was as protective as Nec-1 but lacked the sensitizing effect of Nec-1 at the lower dose. (b) Survival curve for the experiment described in a. Symbols of Nec-1 Hi and Nec-1s Hi coincide and are both completely protective. A cumulative result of two independent experiments is represented. Number of mice is indicated between brackets. *P<0.05, **P<0.001 and ***P<0.0001
Discussion
Nec-1 has been described as a specific inhibitor of RIPK1 activity, efficiently protecting cells from TNF-induced necroptosis.9, 10 Nec-1 has been widely used to examine the involvement of RIPK1 activity in cell death and inflammation in murine disease models. However, some critical issues concerning its in vivo use are emerging. We addressed three major questions on the specificity, the appropriate control and the effective dose of Nec-1 and its derivates, Nec-1i and Nec-1s.
Nec-1s is >1000-fold more selective than any other kinase out of 485 human kinases.24 Nec-1 was recently found to inhibit two other kinases,22 indicating that Nec-1-mediated protection may involve targets other than RIPK1 activity. NO-induced necroptosis41 and inhibition of T-cell proliferation23 are inhibited by Nec-1 independently of RIPK1 kinase activity, suggesting also in vivo the existence of additional targets. The chemical identity of Nec-1 and MTH-Trp as RIPK1 inhibitor9, 10 and as IDO inhibitor26 may complicate the interpretation of the in vivo effects of Nec-1. As IDO is upregulated in inflammation and has a major immunomodulatory role, double reactivity on RIPK1 and IDO may have important in vivo implications. Molecular modeling predicted that Nec-1 and Nec-1i, but not Nec-1s, would inhibit IDO. The 7-Cl on the indole in Nec-1s probably causes steric hindrance, resulting in a tilting of the indole ring in the IDO catalytic pocket. The first step of the IDO reaction requires substrate binding involving the iron dioxygen at the heme of the catalytic pocket. The tilted indole ring of Nec-1s probably no longer competes with the substrate (Figure 2d and Figure 3a). This prediction was confirmed by an enzymatic IDO assay. The differential inhibition of IDO by Nec-1/1-MTH-Trp and Nec-1i versus Nec-1s provides a good avenue to avoid interference of IDO targeting. However, 1-MT, a classical IDO inhibitor,26 had no effect in the cellular necroptosis assay, excluding the direct implication of IDO in necroptosis.
A second important issue is the use of Nec-1i, a demethylated variant of Nec-1, as an inactive control. Nec-1i is >100-fold less active on human recombinant RIPK1 than Nec-1 and Nec-1s, in line with previous reports.9, 10, 36 In contrast to the absence of any effect on necroptosis in human FADD-deficient Jurkat cells,9, 10, 36 in mouse L929 cells, Nec-1i consistently inhibited necroptosis only 10-fold less than Nec-1, even resulting in complete inhibition at higher concentrations. This surprising observation may reflect species specificity of Nec-1i. By methylation of its thiohydantoin moiety in some cells or even in vivo, Nec-1i might be converted to a Nec-1-like inhibitory compound. In line with this partial necroptosis blocking activity of Nec-1i in cellular systems, we found that Nec-1i administration in vivo also inhibits TNF-induced SIRS. These findings argue against the in vivo use of Nec-1i as a ‘silent’ control because Nec-1i can still target IDO, and in mice, it is apparently equipotent to Nec-1 in blocking TNF-induced SIRS. It would be worthwhile to check whether the demethylated form of Nec-1s could be a negative control for RIPK1 targeting on cells and in vivo.
There is a third issue. Mice were sensitized to TNF-induced SIRS when 10-fold lower doses of Nec-1/MTH-Trp or Nec-1i were administered (0.6 mg/kg). This paradoxical finding has major implications for the interpretation of dose-dependent effects of Nec-1 in murine experimental disease models and may also explain some controversies in the literature. Indeed, in contrast to our earlier publication,21 Nec-1 was reported to exacerbate TNF-induced SIRS.42 Another group also reported that Nec-1 worsens the outcome of a peritoneal sepsis model.43 Both publications concluded that RIPK1 kinase activity is necessary for survival from sepsis. However, in these reports, the dose of Nec-1 used was comparable to the low dose in Figures 5 and 6, explaining the sensitizing effect. From the current study, we argue that this sensitization is not the result of RIPK1 targeting and necroptosis. First, cellular necroptosis assays at low concentrations of Nec-1 and Nec-1i do not show such sensitization. Second, Nec-1s, which is an equipotent RIPK1 inhibitor,9, 10, 36 does not sensitize TNF-induced SIRS. Third, sensitization at these low doses of Nec-1 and Nec-1i is not accompanied by the enhanced presence of tissue-damage markers, suggesting that toxicity mechanisms other than RIPK1-mediated necroptosis may be involved. This sensitization was not shared by Nec-1s. Therefore, the involvement of RIPK1 can be excluded. Because both Nec-1 and Nec-1i target IDO, whereas Nec-1s does not, the blocking of IDO could be implicated. This remains to be investigated. Another issue is that these compounds may be metabolized differently, generating toxicity in one case and not in the other. In this regard, it is interesting to note that hydantoinase activity has been reported in mammalian cells, which corresponds to dihydropyrimidinase activity.44 Such enzymes can partly hydrolyze thiohydantoin compounds, and thiohydantoins have been described as unstable under typical biochemical incubation conditions.45, 46 That thiohydantoin-containing necrostatins, such as Nec-1 and Nec-1i, exhibit a sensitizing phenotype at a low dose is in contrast to the nonsensitizing phenotype of Nec-1s, a hydantoin variant. Thiohydantoins and hydantoins might be metabolized differently, generating different metabolites.
Our data indicate some major issues concerning the specificity, the appropriate control and the dose of Nec-1 and its derivatives, and may have major implications for the use in experimental disease models and the interpretation of the published data. Many conclusions drawn on the use of Nec-1 in experimental disease models may require reevaluation. The use of Nec-1s, which does not target IDO, provides a perfect alternative. Moreover, considering the increasing number of pathological conditions involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent necroptosis, Nec-1s may offer a promising therapeutic option for the treatment of these conditions. Nec-1 is still a commercially available option, which can only be used in conditions where involvement of IDO is clearly excluded by use of 1-MT.
Material and Methods
Cells, cytokines and reagents
L929sAhFas cells were generated as previously described47 and are referred to as L929sA cells for simplicity. Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, penicillin (100 IU/ml), streptomycin (0.1 mg/ml) and L-glutamine (0.03%). The recombinant mouse TNF used for in vivo experiments and human TNF for in vitro experiments were produced in Escherichia coli and purified in our laboratories. The activity and endotoxin contamination of mTNF, determined by MTT assay and the Limulus amebocyte lysate assay (Kabivitrum, Trenton, NJ, USA), was 1.7 × 108 IU/mg and 0.47 EU/mg, respectively. Activity of human TNF used in vitro was 3.3 × 108IU/mg. The 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used at 500 mg/ml. Nec-1 (full name, 5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one) and Nec-1i (full name 5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one) were purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA, USA). Nec-1s (full name, 5-((7-Cl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-3-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione) was prepared and kindly provided by Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Inc, Boston. See website for structures and nomenclature (http://www.nature.com/nchembio/journal/v1/n2/compound/nchembio711_ci.html). 1-MT (Sigma Aldrich) was dissolved in PBS.
In vitro kinase assay
Recombinant human RIPK1 (aa 1–497) and RIPK3 (aa 1–439) were produced in Sf9 insect cells as GST-fusion proteins. GST-fusion constructs were obtained by cloning hRIPK1 and hRIPK3 cDNA into the BamHI restriction site of the pAcGHLT vector (BD Bioscience Benelux N.V., Erembodegem, Belgium), and recombinant baculovirus was obtained after cotransfection of these constructs with BaculoGold linearized baculovirus (BD Biosciences) into Sf9 cells according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sf9 cell pellets were resuspended in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% (v/v) Igepal CA-630 and EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Tablets (Roche Diagnostics Belgium N.V., Vilvoorde, Belgium). Lysates were incubated on ice for 30 min. Insoluble proteins were removed by centrifugation. The supernatant was applied to a Glutathione Sepharose 4FF column (GE Healthcare, Diegem, Belgium) preequilibrated with PBS pH 7.4. The GST-tagged RIP kinase was eluted from the column with 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl and 10 mM reduced glutathione. Fractions containing the RIP kinase were pooled and further purified using a Superdex 75pg column (GE Healthcare; running buffer: 20 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0 and 100 mM NaCl). The purity of the fractions was checked by means of SDS-PAGE, and the RIP kinase fractions were pooled and stored at −70 °C. For in vitro kinase assays, recombinant human RIPK1 and RIPK3 (0.2 and 0.75 μg, respectively) were incubated in 30 μl kinase assay buffer (20 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 7.5, 2 mM DTT and 10 mM MnCl2 (for RIPK1) or 10 mM MgCl2 (for RIPK3, respectively) supplemented with 10 mM cold ATP and 10 μCi 32P-γ-ATP for 30 min at 30 °C in the presence of different concentrations of Nec-1, Nec-1i and Nec-1s. The amount of DMSO was equal in all samples. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and exposed to chemiluminescence films (Amersham Hyperfilm ECL, Amersham, GE Healthcare, Diegem, Belgium). After obtaining the autoradiogram, GST-hRIPK1 and GST-hRIPK3 levels were revealed with an anti-GST western blot on the radioactive membrane (image acquired on an Odyssey infrared scanner, Odyssey LI-COR Biosciences GmbH, Bad Homburg, Germany).
IDO enzymatic assay
The assay has been described in detail elsewhere.48 Recombinant human IDO was expressed and purified as described.49 The IC50 inhibition assays were performed in a 96-well microtiter plate as described before.49 Briefly, the reaction mixture contained 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5), 40 mM ascorbic acid, 400 μg/ml catalase, 20 μM methylene blue and ∼27 nM purified recombinant IDO per reaction. The reaction mixture was added to the substrate, L-tryptophan (L-Trp), and the inhibitor. The Nec-1/MTH-Trp, Nec-1i and Nec-1s compounds were serially diluted in three-fold increments, ranging from 100 μM to 1.69 nM, and the L-Trp was tested at 100 μM (Km=80 μM). The reaction was carried out at 37 °C for 60 min and stopped by the addition of 30% (w/v) trichloroacetic acid. The plate was incubated at 65 °C for 15 min to convert N-formylkynurenine to kynurenine and was then centrifuged at 1250 × g for 10 min. Finally, 100 μl supernatant from each well was transferred to a new 96-well plate and mixed at equal volume with 2% (w/v) p-dimethylamino-benzaldehyde in acetic acid. The yellow color generated from the reaction with kynurenine was measured at 490 nm using a Synergy HT microtiter plate reader (Bio-Tek, Winooski, VT, USA). The data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 4 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
In vitro cell death assay
L929 cells were seeded the day before analysis at 1 × 104 cells in 100 μl per well in 96-well adherent plates suitable for imaging purposes. The next day, cells should have a confluence rate of maximal 80% upon induction of cell death. For short-term assays (<6 h), nuclear staining with, for example, PI (3 μM final concentration) and Hoechst (1 μM) was included with the treatment. For long-term assays, PI/Hoechst staining was performed at least 30 min before measurement. Image acquisition was performed using a BD Pathway 885. Images of at least 1000 cells were taken using a × 10 objective and the image montage feature of the equipment. Data acquisition and data analysis were performed using the Attovision software package, BD Bioscience Benelux N.V. A segmentation mask, identifying each single nucleus as region of interest was set on the Hoechst image. The measurement parameter for cell death is the % of PI-positive nuclei.
Molecular docking
Protein molecule A of the human IDO crystal structure 2D0T,39 containing the inhibitor 4-phenylimidazole as well as two molecules of 2-(N-cyclohexylamino)ethane sulfonic acid in its active site, was selected for docking experiments with AutoDock-Vina40 using AutoDockTools50 for preparations of enzyme and ligands. Except for the heme group and its central iron ion, all waters and non-covalent ligands were removed. Both enantiomers of all ligands were docked, these were drawn in 3D with Avogadro51 and were minimized with the MMFF94 force field.52 Vina box settings were: size x, y=16 Å and z=18 Å centered at x=59.2, y=53.2 and z=20.7; docking exhaustiveness was set at 32. Only those poses were evaluated of which the indole group was found in the small cavity where the original 4-phenylimidazole resides.
Mice
Female C57BL/6J WT mice matched for gender and age were purchased from Janvier (Le Genest, France). All mice were bred and housed at the VIB Department for Molecular Biomedical Research in the specific pathogen-free animal facility. All experiments on mice were conducted according to institutional, national and European animal regulations. Animal protocols were approved by the ethics committee of Ghent University. Mice were used at the age of 8–14 weeks.
Injections and monitoring
mTNF and inhibitors were diluted in endotoxin-free PBS and injected in a volume of 0.2 ml. Nec-1, Nec-1i and mTNF (7,5 μg) were injected intravenously unless otherwise indicated. Inhibitors were given 17 min before mTNF injection. Control mice received an equal amount of DMSO (6%) dissolved in PBS before the mTNF challenge. Rectal body temperature was recorded with an electric thermometer (model 2001; Comark Electronics, Norwich, UK). Body temperature and mortality were monitored for 48 and 72 h, respectively.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Prism software (GraphPad Software, Inc.). Body temperature is shown as means±S.E.M. and compared with one-way analysis of variance with Bonferoni posttest. Survival curves were compared using log-rank Mantel–Cox test.
Abbreviations
- 1-MT:
-
1-methyl-tryptophan
- 1-MTH-Trp:
-
methyl-thiohydantoin-tryptophan
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated protein with death domain
- Hi:
-
high dose
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- IDO:
-
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- Lo:
-
low dose
- Mo:
-
moderate dose
- Nec-1:
-
necrostatin-1
- Nec-1i:
-
necrostatin-1 inactive
- Nec-1s:
-
necrostatin-1 stable
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor κB
- RIPK:
-
receptor-interacting protein kinase
- SAR:
-
structure–activity relationship
- SIRS:
-
systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M et al. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009; 137: 1112–1123.
Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P . RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and survival. Cell 2009; 138: 229–232.
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 2009; 137: 1100–1111.
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G . Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 700–714.
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC et al. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science 2009; 325: 332–336.
Bertrand MJ, Vandenabeele P . The ripoptosome: death decision in the cytosol. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 323–325.
Feoktistova M, Geserick P, Kellert B, Dimitrova DP, Langlais C, Hupe M et al. cIAPs block ripoptosome formation, a RIP1/caspase-8 containing intracellular cell death complex differentially regulated by cFLIP isoforms. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 449–463.
Tenev T, Bianchi K, Darding M, Broemer M, Langlais C, Wallberg F et al. The Ripoptosome, a signaling platform that assembles in response to genotoxic stress and loss of IAPs. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 432–448.
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 2005; 1: 112–119.
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch’en IL, Korkina O, Teng X et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 2008; 4: 313–321.
Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N, Kelliher MA . The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 33185–33191.
Oliver AW, Knapp S, Pearl LH . Activation segment exchange: a common mechanism of kinase autophosphorylation? Trends Biochem Sci 2007; 32: 351–356.
Kelliher MA, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F, Stanger BZ, Leder P . The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity 1998; 8: 297–303.
Lee TH, Huang Q, Oikemus S, Shank J, Ventura JJ, Cusson N et al. The death domain kinase RIP1 is essential for tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling to p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 8377–8385.
Lim SY, Davidson SM, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM, Smith CC . The cardioprotective effect of necrostatin requires the cyclophilin-D component of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2007; 21: 467–469.
Northington FJ, Chavez-Valdez R, Graham EM, Razdan S, Gauda EB, Martin LJ . Necrostatin decreases oxidative damage, inflammation, and injury after neonatal HI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2011; 31: 178–189.
Smith CC, Davidson SM, Lim SY, Simpkin JC, Hothersall JS, Yellon DM . Necrostatin: a potentially novel cardioprotective agent? Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2007; 21: 227–233.
You Z, Savitz SI, Yang J, Degterev A, Yuan J, Cuny GD et al. Necrostatin-1 reduces histopathology and improves functional outcome after controlled cortical impact in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008; 28: 1564–1573.
Trichonas G, Murakami Y, Thanos A, Morizane Y, Kayama M, Debouck CM et al. Receptor interacting protein kinases mediate retinal detachment-induced photoreceptor necrosis and compensate for inhibition of apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21695–21700.
Linkermann A, Brasen JH, Himmerkus N, Liu S, Huber TB, Kunzendorf U et al. Rip1 (receptor-interacting protein kinase 1) mediates necroptosis and contributes to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 2012; 81: 751–761.
Duprez L, Takahashi N, Van Hauwermeiren F, Vandendriessche B, Goossens V, Vanden Berghe T et al. RIP kinase-dependent necrosis drives lethal systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Immunity 2011; 35: 908–918.
Biton S, Ashkenazi A . NEMO and RIP1 control cell fate in response to extensive DNA damage via TNF-alpha feedforward signaling. Cell 2011; 145: 92–103.
Cho Y, McQuade T, Zhang H, Zhang J, Chan FK . RIP1-dependent and independent effects of necrostatin-1 in necrosis and T cell activation. PLoS One 2011; 6: e23209.
Christofferson DE, Li Y, Hitomi J, Zhou W, Upperman C, Zhu H et al. A novel role for RIP1 kinase in mediating TNFalpha production. Cell Death Dis 2012; 3: e320.
Vanlangenakker N, Vanden Berghe T, Bogaert P, Laukens B, Zobel K, Deshayes K et al. cIAP1 and TAK1 protect cells from TNF-induced necrosis by preventing RIP1/RIP3-dependent reactive oxygen species production. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 656–665.
Muller AJ, DuHadaway JB, Donover PS, Sutanto-Ward E, Prendergast GC . Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1, potentiates cancer chemotherapy. Nat Med 2005; 11: 312–319.
Soliman H, Mediavilla-Varela M, Antonia S . Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: is it an immune suppressor? Cancer J 2010; 16: 354–359.
Thackray SJ, Mowat CG, Chapman SK . Exploring the mechanism of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem Soc Trans 2008; 36: 1120–1123.
Heikenwalder M, Polymenidou M, Junt T, Sigurdson C, Wagner H, Akira S et al. Lymphoid follicle destruction and immunosuppression after repeated CpG oligodeoxynucleotide administration. Nat Med 2004; 10: 187–192.
Puccetti P, Grohmann U . IDO and regulatory T cells: a role for reverse signalling and non-canonical NF-kappaB activation. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 817–823.
Zelante T, Fallarino F, Bistoni F, Puccetti P, Romani L . Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in infection: the paradox of an evasive strategy that benefits the host. Microbes Infect 2009; 11: 133–141.
Hill M, Tanguy-Royer S, Royer P, Chauveau C, Asghar K, Tesson L et al. IDO expands human CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells by promoting maturation of LPS-treated dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 3054–3062.
Tattevin P, Monnier D, Tribut O, Dulong J, Bescher N, Mourcin F et al. Enhanced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J Infect Dis 2010; 201: 956–966.
Jung ID, Lee MG, Chang JH, Lee JS, Jeong YI, Lee CM et al. Blockade of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase protects mice against lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxin shock. J Immunol 2009; 182: 3146–3154.
Wang Y, Liu H, McKenzie G, Witting PK, Stasch JP, Hahn M et al. Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation. Nat Med 2010; 16: 279–285.
Teng X, Degterev A, Jagtap P, Xing X, Choi S, Denu R et al. Structure-activity relationship study of novel necroptosis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2005; 15: 5039–5044.
Shimizu T, Nomiyama S, Hirata F, Hayaishi O . Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem 1978; 253: 4700–4706.
Cady SG, Sono M . 1-Methyl-DL-tryptophan, beta-(3-benzofuranyl)-DL-alanine (the oxygen analog of tryptophan), and beta-[3-benzo(b)thienyl]-DL-alanine (the sulfur analog of tryptophan) are competitive inhibitors for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 1991; 291: 326–333.
Sugimoto H, Oda S, Otsuki T, Hino T, Yoshida T, Shiro Y . Crystal structure of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: catalytic mechanism of O2 incorporation by a heme-containing dioxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2611–2616.
Trott O, Olson AJ . AutoDock vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 2010; 31: 455–461.
Tamura Y, Chiba Y, Tanioka T, Shimizu N, Shinozaki S, Yamada M et al. NO donor induces Nec-1-inhibitable, but RIP1-independent, necrotic cell death in pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett 2011; 585: 3058–3064.
Linkermann A, Brasen JH, De Zen F, Weinlich R, Schwendener RA, Green DR et al. Dichotomy between RIP1- and RIP3-mediated necroptosis in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced shock. Mol Med 2012; 18: 577–586.
McNeal SI, LeGolvan MP, Chung CS, Ayala A . The dual functions of receptor interacting protein 1 in fas-induced hepatocyte death during sepsis. Shock 2011; 35: 499–505.
Dudley KH, Butler TC, Bius DL . The role of dihydropyrimidinase in the metabolism of some hydantoin and succinimide drugs. Drug Metab Dispos 1974; 2: 103–112.
Andersen G . Uracil and beta-alanine degradation in Saccharomyces kluyveri—discovery of a novel catabolic pathway. Ph.D. Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2006.
Waniek T . Untersuchungen zur Substratspezifität und Enantioselektivität mikrobieller Hydantoinasen. Ph.D. University Stuttgart: Stuttgart, 2000.
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G, Van de Craen M, Declercq W, Fiers W et al. Dual signaling of the Fas receptor: initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 919–930.
Kumar S, Jaller D, Patel B, LaLonde JM, DuHadaway JB, Malachowski WP et al. Structure based development of phenylimidazole-derived inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 4968–4977.
Littlejohn TK, Takikawa O, Skylas D, Jamie JF, Walker MJ, Truscott RJ . Expression and purification of recombinant human indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase. Protein Expr Purif 2000; 19: 22–29.
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 2009; 30: 2785–2791.
Hanwell MD, Curtis DE, Lonie DC, Vandermeersch T, Zurek E, Hutchison GR . Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J Cheminform 2012; 4: 17.
Halgren TA . Merck molecular force field.1. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J Comput Chem 1996; 17: 490–519.
Acknowledgements
We thank Amin Bredan for editorial help. Research in the Vandenabeele group is supported by European grants (FP6 ApopTrain, MRTN-CT-035624; FP7 EC RTD Integrated Project, Apo-Sys, FP7-200767; Euregional PACT II), Belgian grants (Interuniversity Attraction Poles, IAP 6/18, IAP 7/32), Flemish grants (Research Foundation Flanders, FWO G.0875.11, FWO G.0973.11 and FWO G.0A45.12N), Ghent University grants (MRP, GROUP-ID consortium) and grants from Flanders Institute for Biotechnology (VIB). PV holds a Methusalem grant (BOF09/01M00709) from the Flemish Government. SG was supported by the ‘Institute for the promotion of Innovation by Science and Technology in Flanders’ (IWT SB63424), a ‘Special Research Fund’ from Ghent University (BOF B/09683/02), and a university contract as part of a Methusalem grant awarded to professor PV by the Flemish Government (BOF09/01M00709).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, N., Duprez, L., Grootjans, S. et al. Necrostatin-1 analogues: critical issues on the specificity, activity and in vivo use in experimental disease models. Cell Death Dis 3, e437 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2012.176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2012.176
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis and evaluation of a novel PET ligand, a GSK’963 analog, aiming at autoradiography and imaging of the receptor interacting protein kinase 1 in the brain
EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry (2023)
-
The therapeutic potential of targeting regulated non-apoptotic cell death
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2023)
-
Ferroptotic mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation in the kidney
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2023)
-
Protective Effect of a Novel RIPK1 Inhibitor, Compound 4–155, in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Sepsis
Inflammation (2023)
-
An in vitro evaluation of the antioxidant activities of necroptosis and apoptosis inhibitors: the potential of necrostatin-1 and necrostatin-1i to have radical scavenging activities
Pharmacological Reports (2023)