Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of synthetic RNA protein granules using engineered phage-coat-protein -RNA complexes
Formation of synthetic RNA protein granules using engineered phage-coat-protein -RNA complexes
Condensates composed of RNA and proteins are biologically vital but generally poorly understood. Here, the authors engineer synthetic RNA-protein condensates and show that gel-like condensates form as a result of liquid-gel phase separation in a specific and selective fashion.
- Naor Granik
- , Noa Katz
- & Roee Amit
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic characterization of cancer transcriptome at transcript resolution
Systematic characterization of cancer transcriptome at transcript resolution
Modification of transcribed mRNAs enables regulation of transcription but its extent in cancer cells is incompletely understood. Here, the authors analyse transcript assembly in over 1000 cancer cell lines and find unannotated transcripts are common, and are associated with drug sensitivity.
- Wei Hu
- , Yangjun Wu
- & Shengli Li
-
Article
| Open Access Circuit-guided population acclimation of a synthetic microbial consortium for improved biochemical production
Circuit-guided population acclimation of a synthetic microbial consortium for improved biochemical production
Achieving stable production by co-culturing multiple microorganisms is often challenging due to difficulties in controlling its population. Here, the authors develop a “population guider” that can acclimate a population to higher production.
- Chae Won Kang
- , Hyun Gyu Lim
- & Gyoo Yeol Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Inducible plasmid copy number control for synthetic biology in commonly used E. coli strains
Inducible plasmid copy number control for synthetic biology in commonly used E. coli strains
The ability to externally control gene expression has been important for all areas of biological research, especially for synthetic biology. Here the authors present plasmid TULIP which offers DNA copy number control via chemical induction to accelerate the design, prototyping, and reuse of gene circuits in diverse contexts.
- Shivang Hina-Nilesh Joshi
- , Chentao Yong
- & Andras Gyorgy
-
Article
| Open Access Absolute protein quantification using fluorescence measurements with FPCountR
Absolute protein quantification using fluorescence measurements with FPCountR
A challenge in synthetic biology is the empirical characterisation of genetic parts. Here the authors present FPCountR, a validated method and accompanying R package that enables the precise quantification of fluorescent protein reporters per bacterial cell to be enumerated in ‘proteins per cell’ or nanomolar units without requiring protein purification.
- Eszter Csibra
- & Guy-Bart Stan
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding fibrosis pathogenesis via modeling macrophage-fibroblast interplay in immune-metabolic context
Understanding fibrosis pathogenesis via modeling macrophage-fibroblast interplay in immune-metabolic context
Renal fibrosis is a progressive process with complex etiopathology, causing organ failure. Here authors present a mathematical model, based on an in vitro system faithfully contemplating macrophage-fibroblast interaction and the metabolic-immunologic signals that are affecting kidney fibrosis, that is applicable to kidney transplant failure.
- Elisa Setten
- , Alessandra Castagna
- & Massimo Locati
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing β-TrCP activity dynamics in live cells with a genetically encoded biosensor
Revealing β-TrCP activity dynamics in live cells with a genetically encoded biosensor
β-TrCP plays an important role in diverse cellular processes such as the cell cycle and inflammation. Here the authors develop a biosensor for β-TrCP activity and use it to investigate β-TrCP dynamics during the cell cycle, and to screen a small-molecule library for β-TrCP activators and inhibitors.
- Debasish Paul
- , Stephen C. Kales
- & Steven D. Cappell
-
Article
| Open Access Micro-scale functional modules in the human temporal lobe
Micro-scale functional modules in the human temporal lobe
The sensory cortices of many mammals consist of modules in the form of cortical columns. By analyzing functional connectivity and neural responses to visual stimuli, the authors show that this organization may extend to the human temporal lobe.
- Julio I. Chapeton
- , John H. Wittig Jr
- & Kareem A. Zaghloul
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome effects of genome-wide single gene perturbations
Proteome effects of genome-wide single gene perturbations
Protein abundance is controlled at the transcriptional, translational and posttranslational levels. Here, Öztürk et al. determine proteome changes resulting from individual knockout of 3308 nonessential genes in the yeast S. pombe, infer gene functionality, and show that protein upregulation under stable transcript expression utilizes optimal codons.
- Merve Öztürk
- , Anja Freiwald
- & Falk Butter
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic transcription platform for programmable gene expression in mammalian cells
A synthetic transcription platform for programmable gene expression in mammalian cells
Precise and scalable regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells is challenging. Here, the authors created a highly tunable CRISPR-based synthetic transcription system for programmable control of mammalian gene expression and cellular activity.
- William C. W. Chen
- , Leonid Gaidukov
- & Timothy K. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro assembly, positioning and contraction of a division ring in minimal cells
In vitro assembly, positioning and contraction of a division ring in minimal cells
Constructing a minimal protein machinery for self-division of membrane compartments is a major goal of bottom-up synthetic biology. Here, authors achieved the assembly, placement and onset of contraction of a minimal division ring in lipid vesicles.
- Shunshi Kohyama
- , Adrián Merino-Salomón
- & Petra Schwille
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring differential subcellular localisation in comparative spatial proteomics using BANDLE
Inferring differential subcellular localisation in comparative spatial proteomics using BANDLE
Changes in protein subcellular localization can be determined using mass spectrometry. Here, the authors present a statistical approach to determine relocalising proteins from spatial proteomics experiments.
- Oliver M. Crook
- , Colin T. R. Davies
- & Kathryn S. Lilley
-
Article
| Open Access Differential nuclear import sets the timing of protein access to the embryonic genome
Differential nuclear import sets the timing of protein access to the embryonic genome
Here the authors address how embryos control the timing of specific gene activation in early frog development. They find transcription factors for early gene activation are maternally loaded and remain at constant levels, and rather that order of activation is based on their sequential entry into the nucleus based largely on their respective affinity to importins.
- Thao Nguyen
- , Eli J. Costa
- & Martin Wühr
-
Article
| Open Access HOXA9 has the hallmarks of a biological switch with implications in blood cancers
HOXA9 has the hallmarks of a biological switch with implications in blood cancers
HOXA9 plays an important role in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), but its relevance for other blood malignancies is unclear. Here, the authors show that HOXA9 has a binary switch function that can clinically stratify AML patients, and model how the interactions with JAK2, TET2 and NOTCH impact myeloproliferative neoplasms.
- Laure Talarmain
- , Matthew A. Clarke
- & Benjamin A. Hall
-
Article
| Open Access A deeper understanding of system interactions can explain contradictory field results on pesticide impact on honey bees
A deeper understanding of system interactions can explain contradictory field results on pesticide impact on honey bees
Pesticide impact on honey bees under field conditions remains elusive. Here, the authors combine a systems biology approach and laboratory experiments to show that the immune suppressive effect of the pathogen deformed wing virus can be responsible for the disparity amongst honey bee experiments.
- Dimitri Breda
- , Davide Frizzera
- & Francesco Nazzi
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic neuromorphic computing in living cells
Synthetic neuromorphic computing in living cells
Computational properties of neuronal networks have been applied to computing systems using simplified models comprising repeated connected nodes. Here the authors create layered assemblies of genetically encoded devices that perform non-binary logic computation and signal processing using combinatorial promoters and feedback regulation.
- Luna Rizik
- , Loai Danial
- & Ramez Daniel
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial diet modulates tamoxifen-induced death via host fatty acid metabolism
Bacterial diet modulates tamoxifen-induced death via host fatty acid metabolism
Here, Diot et al. use the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model to identify off-target toxicity mechanisms for tamoxifen, and find that these include fatty acid metabolism and cell death, which can be modulated by different bacterial species.
- Cédric Diot
- , Aurian P. García-González
- & Albertha J. M. Walhout
-
Article
| Open Access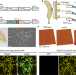 A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
Engineered living materials (ELMs) embed living cells in a biopolymer matrix to create novel materials with tailored functions. In this work, the authors engineered bacteria to grow novel macroscopic materials that can be reshaped, functionalized, and used to filter contaminated water while also showing that the stiffness of these materials can be tuned through genetic changes.
- Sara Molinari
- , Robert F. Tesoriero Jr.
- & Caroline M. Ajo-Franklin
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of plant hemostatic dencichine in Escherichia coli
Biosynthesis of plant hemostatic dencichine in Escherichia coli
Biosynthetic pathway of dencichine, a plant derived nature product that has found various pharmacological applications, is still elusive. Here, the authors design artificial pathways through retro-biosynthesis approaches and achieve its efficient production in E. coli by systematic metabolic and enzymatic engineering.
- Wenna Li
- , Zhao Zhou
- & Qipeng Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative fragmentomics allow affinity mapping of interactomes
Quantitative fragmentomics allow affinity mapping of interactomes
Protein networks have been widely explored but most binding affinities remain unknown, limiting the quantitative interpretation of interactomes. Here the authors measure affinities of 65,000 interactions involving human PDZ domains and target sequence motifs relevant for viral infection and cancer.
- Gergo Gogl
- , Boglarka Zambo
- & Gilles Travé
-
Article
| Open Access Phylogeographic analysis reveals an ancient East African origin of human herpes simplex virus 2 dispersal out-of-Africa
Phylogeographic analysis reveals an ancient East African origin of human herpes simplex virus 2 dispersal out-of-Africa
There are competing hypotheses for human herpes simplex virus 2’s migration out-of-Africa. Here, the authors sequence 65 new herpes simplex virus 2 genomes with a focus on under-sampled sub-Saharan African countries, suggesting an Eastern African origin for global dispersal the virus between 22-29 thousand years ago.
- Jennifer L. Havens
- , Sébastien Calvignac-Spencer
- & Joel O. Wertheim
-
Article
| Open Access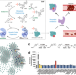 Unleashing the potential of noncanonical amino acid biosynthesis to create cells with precision tyrosine sulfation
Unleashing the potential of noncanonical amino acid biosynthesis to create cells with precision tyrosine sulfation
Incorporation of noncanonical amino acids into proteins holds great promise for altering structure and function of these proteins. Here the authors generate metabolically modified prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that can biosynthesize sTyr and incorporate it into proteins in a site-specific manner.
- Yuda Chen
- , Shikai Jin
- & Han Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access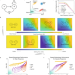 Layered feedback control overcomes performance trade-off in synthetic biomolecular networks
Layered feedback control overcomes performance trade-off in synthetic biomolecular networks
Layered feedback is an optimization strategy in feedback control designs widely used in engineering. Here, combining simulation and experimentation, the authors apply layered control - a powerful optimization strategy in engineering - to synthetic biomolecular networks in living bacteria to show layered control overcomes performance trade-offs in biology.
- Chelsea Y. Hu
- & Richard M. Murray
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic compartmentalization by unnatural reaction for itaconate production
Kinetic compartmentalization by unnatural reaction for itaconate production
Unlike eukaryotic system, bacterial hosts lack membranous system, which is one of the limitations for efficient metabolic engineering. Here, the authors report a kinetic compartmentalization strategy to increase substrate availability from competitive reactions for the efficient production of itaconate in E. coli.
- Dae-yeol Ye
- , Myung Hyun Noh
- & Gyoo Yeol Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating and formatting biomedical data as pre-calculated knowledge graph embeddings in the Bioteque
Integrating and formatting biomedical data as pre-calculated knowledge graph embeddings in the Bioteque
Biomedical data is accumulating at a fast pace and integrating it into a unified framework is a major challenge. Here, the authors present a resource that contains pre-calculated biomedical descriptors derived from a very large knowledge graph.
- Adrià Fernández-Torras
- , Miquel Duran-Frigola
- & Patrick Aloy
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of an Escherichia coli strain growing on methanol via the ribulose monophosphate cycle
Generation of an Escherichia coli strain growing on methanol via the ribulose monophosphate cycle
Using one carbon compounds as feedstock is a promising approach in abating climate change. Here, the authors report the conversion of E. coli into a synthetic methylotroph that assimilates methanol via the ribulose monophosphate cycle and a set of distinctive mutations.
- Philipp Keller
- , Michael A. Reiter
- & Julia A. Vorholt
-
Article
| Open Access MVsim is a toolset for quantifying and designing multivalent interactions
MVsim is a toolset for quantifying and designing multivalent interactions
Arising through multiple binding elements, multivalency can specify the avidity, duration, cooperativity, and selectivity of biomolecular interactions, but quantitative prediction and design of these properties has remained challenging. Here the authors enable facile analysis and engineering of multivalent binding by developing MVsim, a simulator that incorporates biochemical and biophysical parameters of interacting molecules and is accessible through a graphical user interface.
- Bence Bruncsics
- , Wesley J. Errington
- & Casim A. Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access Automated model-predictive design of synthetic promoters to control transcriptional profiles in bacteria
Automated model-predictive design of synthetic promoters to control transcriptional profiles in bacteria
Transcription rates are regulated by the interactions between RNA polymerase, sigma factor, and promoter DNA sequences in bacteria. Here the authors combine massively parallel experiments & machine learning to develop a predictive biophysical model of transcription, validated across 22132 bacterial promoters, and apply it to the design and debugging of genetic circuits.
- Travis L. LaFleur
- , Ayaan Hossain
- & Howard M. Salis
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling gene expression with deep generative design of regulatory DNA
Controlling gene expression with deep generative design of regulatory DNA
Design of de novo synthetic regulatory DNA is a promising avenue to control gene expression in biotechnology and medicine. Here the authors present EspressionGAN, a generative adversarial network that uses genomic and transcriptomic data to generate regulatory sequences.
- Jan Zrimec
- , Xiaozhi Fu
- & Aleksej Zelezniak
-
Article
| Open Access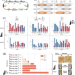 The automated Galaxy-SynBioCAD pipeline for synthetic biology design and engineering
The automated Galaxy-SynBioCAD pipeline for synthetic biology design and engineering
Automated design and build processes can rapidly accelerate work in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. Here the authors present Galaxy-SynBioCAD, a toolshed for synthetic biology, metabolic engineering, and industrial biotechnology that they use to build and execute Galaxy scientific workflows from pathway design to strain engineering through the automated generation of scripts driving robotic workstations.
- Joan Hérisson
- , Thomas Duigou
- & Jean-Loup Faulon
-
Article
| Open Access Rhythmic transcription of Bmal1 stabilizes the circadian timekeeping system in mammals
Rhythmic transcription of Bmal1 stabilizes the circadian timekeeping system in mammals
The mammalian circadian clock is composed of clock genes forming transcriptional feedback loops. Here, the authors identify a key role of the secondary feedback loop that is interlocked with the core loop to establish a perturbation-resilient clock system.
- Yasuko O. Abe
- , Hikari Yoshitane
- & Yoshitaka Fukada
-
Article
| Open Access Human acute inflammatory recovery is defined by co-regulatory dynamics of white blood cell and platelet populations
Human acute inflammatory recovery is defined by co-regulatory dynamics of white blood cell and platelet populations
Inflammation is a protective response of the body. Here, authors show that healthy inflammation induces remarkably consistent changes in white cell and platelet populations, regardless of the underlying cause, including heart attack, infection and trauma.
- Brody H. Foy
- , Thoralf M. Sundt
- & John M. Higgins
-
Article
| Open Access A nanopore interface for higher bandwidth DNA computing
A nanopore interface for higher bandwidth DNA computing
Toe-hold-mediated strand displacement (DSD) is a widely used molecular tool in applications such as DNA computing and nucleic acid diagnostics. Here the authors characterize dozens of orthogonal barcode sequences that can be used for monitoring the output kinetics of multiplexed DSD reactions in real-time using a commercially-available portable nanopore array device.
- Karen Zhang
- , Yuan-Jyue Chen
- & Jeff Nivala
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling the medium-term dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in England in the Omicron era
Modelling the medium-term dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in England in the Omicron era
This mathematical modelling study projects the dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in England until the end of 2022 assuming that the Omicron BA.2 sublineage remains dominant. They show that booster vaccination was highly effective in mitigating severe outcomes and that future dynamics will depend greatly on assumptions about waning immunity.
- Rosanna C. Barnard
- , Nicholas G. Davies
- & W. John Edmunds
-
Article
| Open Access Halogenation of tyrosine perturbs large-scale protein self-organization
Halogenation of tyrosine perturbs large-scale protein self-organization
Sun et al. has studied the genetically encodable halotyrosines in proteins of the prokaryotic cell division machinery to elucidate the general role of halogenation in cellular lifespan and oxidative damage-induced diseases such as aging and cancer.
- Huan Sun
- , Haiyang Jia
- & Nediljko Budisa
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic cybergenetic control of bacterial co-culture composition via optogenetic feedback
Dynamic cybergenetic control of bacterial co-culture composition via optogenetic feedback
Communities of microbes play important roles in natural environments and hold great potential for deploying division-of-labor strategies in synthetic biology and bioproduction. Here, in a community of two competing E. coli strains, the authors show that the relative abundances of the strains can be stabilized and steered dynamically with remarkable precision by coupling the cells to an automated computer-controlled feedback-loop.
- Joaquín Gutiérrez Mena
- , Sant Kumar
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access Chimeric GPCRs mimic distinct signaling pathways and modulate microglia responses
Chimeric GPCRs mimic distinct signaling pathways and modulate microglia responses
Understanding the function of GPCRs requires stimulation with their specific ligands. Here, the authors design chemogenetic G-protein coupled receptors that allows for the study of receptors without knowing the immediate ligand, and demonstrate its use for the β2-adrenergic receptor in microglia.
- Rouven Schulz
- , Medina Korkut-Demirbaş
- & Sandra Siegert
-
Article
| Open Access Proteotoxicity caused by perturbed protein complexes underlies hybrid incompatibility in yeast
Proteotoxicity caused by perturbed protein complexes underlies hybrid incompatibility in yeast
Hybrid incompatibility can be an important element of reproductive isolation and speciation. Using chromosome replacement lines of yeast, the authors show that perturbed proteostasis caused by destabilized hybrid protein complexes may represent a general mechanism of hybrid incompatibility.
- Krishna B. S. Swamy
- , Hsin-Yi Lee
- & Jun-Yi Leu
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency spectra and the color of cellular noise
Frequency spectra and the color of cellular noise
The invention of the Fourier integral in the 19th century laid the foundation for modern spectral analysis methods. Here the authors develop frequency-based methods for analyzing the reaction mechanisms within living cells from distinctively noisy single-cell output trajectories and present forward engineering of synthetic oscillators and controllers.
- Ankit Gupta
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access Model-guided engineering of DNA sequences with predictable site-specific recombination rates
Model-guided engineering of DNA sequences with predictable site-specific recombination rates
Site-specific recombination (SSR) is an important tool in synthetic biology, but its applications are limited by the inability to predictably tune SSR reaction rates. Here, using quantitative high-throughput experiments and machine learning, the authors achieve rational control of a DNA attachment site sequence to predictably modulate site-specific recombination rates both in vitro and in cells.
- Qiuge Zhang
- , Samira M. Azarin
- & Casim A. Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access Auxotrophic and prototrophic conditional genetic networks reveal the rewiring of transcription factors in Escherichia coli
Auxotrophic and prototrophic conditional genetic networks reveal the rewiring of transcription factors in Escherichia coli
The bacterium E. coli has around 300 transcriptional factors, but the functions of many of them, and the interactions between their respective regulatory networks, are unclear. Here, the authors study genetic interactions among all transcription factor genes in E. coli, revealing condition-dependent interactions and roles for uncharacterized transcription factors.
- Alla Gagarinova
- , Ali Hosseinnia
- & Mohan Babu
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying multicellular spatiotemporal organization of cells with SpaceFlow
Identifying multicellular spatiotemporal organization of cells with SpaceFlow
A critical task in spatial transcriptomics analysis is to understand inherently spatial relationships among cells. Here, the authors present a deep learning framework to integrate spatial and transcriptional information, spatially extending pseudotime and revealing spatiotemporal organization of cells.
- Honglei Ren
- , Benjamin L. Walker
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable multiplex co-fractionation/mass spectrometry platform for accelerated protein interactome discovery
Scalable multiplex co-fractionation/mass spectrometry platform for accelerated protein interactome discovery
Co-fractionation/mass spectrometry (CF/MS) allows mapping protein interactomes but efficiency and quantitative accuracy are limited. Here, the authors develop a reproducible multiplexed CF/MS method and apply it to characterize interactome rewiring in breast cancer cells.
- Pierre C. Havugimana
- , Raghuveera Kumar Goel
- & Andrew Emili
-
Article
| Open Access Massively targeted evaluation of therapeutic CRISPR off-targets in cells
Massively targeted evaluation of therapeutic CRISPR off-targets in cells
Thorough evaluation of CRISPR RNA-guided nucleases off-targets in cells is required for advancing gene therapies. Here the authors report SURRO-seq for the simultaneous investigation of thousands of off-target sites for therapeutic RNA-guided nucleases in cells.
- Xiaoguang Pan
- , Kunli Qu
- & Yonglun Luo
-
Article
| Open Access dia-PASEF data analysis using FragPipe and DIA-NN for deep proteomics of low sample amounts
dia-PASEF data analysis using FragPipe and DIA-NN for deep proteomics of low sample amounts
The dia-PASEF technology uses ion mobility separation to reduce signal interferences and increase sensitivity of mass spectrometry-based proteomics. The authors present algorithms and a software solution, which boost proteomic depth in dia-PASEF experiments by up to 83% compared to previous work, and are specifically beneficial for fast proteomic experiments and those with low sample amounts.
- Vadim Demichev
- , Lukasz Szyrwiel
- & Markus Ralser
-
Article
| Open Access Low-cost anti-mycobacterial drug discovery using engineered E. coli
Low-cost anti-mycobacterial drug discovery using engineered E. coli
Whole-cell screening for Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibitors is complicated by the pathogen’s slow growth and biocontainment requirements. Here the authors develop engineered E. coli as a synthetic biology tool to express and screen metabolic targets from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Nadine Bongaerts
- , Zainab Edoo
- & Edwin H. Wintermute
-
Article
| Open Access A plasmid system with tunable copy number
A plasmid system with tunable copy number
The range of available copy numbers for cloning vectors is largely restricted to the handful of ORIs that have been isolated from plasmids found in nature. Here the authors introduce a plasmid system that allow for the continuous, finely-tuned control of plasmid copy number between 1 and 800 copies per cell.
- Miles V. Rouches
- , Yasu Xu
- & Guillaume Lambert
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable synthetic cell networks regulated by tuneable reaction rates
Programmable synthetic cell networks regulated by tuneable reaction rates
Our understanding of how compartmentalisation and intercellular communication can tune enzyme reactions is still in its infancy. Here, the authors show that multi-enzyme reactions within semi-permeable compartments have distinct properties compared to reactions in buffer solution.
- Adrian Zambrano
- , Giorgio Fracasso
- & T-Y. Dora Tang
-
Article
| Open Access A versatile active learning workflow for optimization of genetic and metabolic networks
A versatile active learning workflow for optimization of genetic and metabolic networks
Optimization of biological networks is often limited by wet lab labor and cost, and the lack of convenient computational tools. Here, aimed at democratization and standardization, the authors describe METIS, a modular and versatile active machine learning workflow with a simple online interface for the optimization of biological target functions with minimal experimental datasets.
- Amir Pandi
- , Christoph Diehl
- & Tobias J. Erb
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 Integrase-mediated differentiation circuits improve evolutionary stability of burdensome and toxic functions in E. coli
Integrase-mediated differentiation circuits improve evolutionary stability of burdensome and toxic functions in E. coli