Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Concerted pulsatile and graded neural dynamics enables efficient chemotaxis in C. elegans
Concerted pulsatile and graded neural dynamics enables efficient chemotaxis in C. elegans
Finding one’s way to a food source along a complex gradient is central to survival for many animals. Here, the authors report that in C. elegans, the distinct response dynamics of two sensory neurons to odor gradients can support a navigation model more efficient than the biased-random walk.
- Eyal Itskovits
- , Rotem Ruach
- & Alon Zaslaver
-
Article
| Open Access Cell fate potentials and switching kinetics uncovered in a classic bistable genetic switch
Cell fate potentials and switching kinetics uncovered in a classic bistable genetic switch
Bistable switches are a common regulatory motif in cell fate decision-making circuits with two mutually exclusive expression states. Here the authors develop a bistable reporter system and report two additional expression states.
- Xiaona Fang
- , Qiong Liu
- & Jie Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access TCM visualizes trajectories and cell populations from single cell data
TCM visualizes trajectories and cell populations from single cell data
Time series single cell expression data has large variance between time points and is challenging for analysis. Here, the authors develop a new dimension reduction and data visualization tool for large scale temporal scRNA-seq data which identifies trajectories and subpopulations.
- Wuming Gong
- , Il-Youp Kwak
- & Daniel J. Garry
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage marker synchrony in hematopoietic genealogies refutes the PU.1/GATA1 toggle switch paradigm
Lineage marker synchrony in hematopoietic genealogies refutes the PU.1/GATA1 toggle switch paradigm
The timing of cell fate choices is usually unknown, because we have to rely on indirect evidence of their molecular basis. Here, the authors introduce a method to infer decision times from marker onset in cell genealogies, and find evidence refuting the paradigmatic PU.1/GATA1 cell fate switch.
- Michael K. Strasser
- , Philipp S. Hoppe
- & Carsten Marr
-
Article
| Open Access Network-based approach to prediction and population-based validation of in silico drug repurposing
Network-based approach to prediction and population-based validation of in silico drug repurposing
Repurposing approved drugs could accelerate treatment options for various diseases. Here, the authors use network proximity of disease gene products and drug targets in the human protein interactome to identify drug-disease associations for cardiovascular disease, and validate these using longitudinal healthcare data.
- Feixiong Cheng
- , Rishi J. Desai
- & Joseph Loscalzo
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale genetic analysis reveals mammalian mtDNA heteroplasmy dynamics and variance increase through lifetimes and generations
Large-scale genetic analysis reveals mammalian mtDNA heteroplasmy dynamics and variance increase through lifetimes and generations
Mitochondrial populations in cells may consist of heteroplasmic mixtures of mtDNA types, and their evolution through development, aging and generations is central to genetic diseases. Here the authors dissect these population dynamics using a large mouse-based data set to characterise the dynamics of heteroplasmy mean and variance throughout life and across generations.
- Joerg P. Burgstaller
- , Thomas Kolbe
- & Iain G. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access Caffeine-inducible gene switches controlling experimental diabetes
Caffeine-inducible gene switches controlling experimental diabetes
Control of transgene expression should ideally be easy and with minimal side effects. Here the authors present a synthetic biology-based approach in which the caffeine in coffee regulates a genetic circuit controlling glucagon-like peptide 1 expression in diabetic mice.
- Daniel Bojar
- , Leo Scheller
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access Out-of-equilibrium microcompartments for the bottom-up integration of metabolic functions
Out-of-equilibrium microcompartments for the bottom-up integration of metabolic functions
Generating artificial cells able to carry out metabolic activities out-of-equilibrium is a current challenge in synthetic biology. Here the authors use a microfluidic platform for integration and analysis of minimal metabolic reactions in artificial microcompartments formed of water-in-oil droplets.
- Thomas Beneyton
- , Dorothee Krafft
- & Jean-Christophe Baret
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean acidification conditions increase resilience of marine diatoms
Ocean acidification conditions increase resilience of marine diatoms
Diatoms account for 40% of marine primary production and their sensitivity to ocean acidification could have ecosystem-wide consequences. Here, the authors developed and applied a stress test, demonstrating that resilience of diatoms increases significantly in ocean acidification conditions.
- Jacob J. Valenzuela
- , Adrián López García de Lomana
- & Nitin S. Baliga
-
Article
| Open Access Network biology discovers pathogen contact points in host protein-protein interactomes
Network biology discovers pathogen contact points in host protein-protein interactomes
Nodes with high centrality in protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks are known to be essential in some organisms. Here, the authors in contrast find that in the interactome of A. thaliana central nodes are enriched in conditional and immune phenotypes and are preferred targets of pathogens.
- Hadia Ahmed
- , T. C. Howton
- & M. Shahid Mukhtar
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidized phospholipids regulate amino acid metabolism through MTHFD2 to facilitate nucleotide release in endothelial cells
Oxidized phospholipids regulate amino acid metabolism through MTHFD2 to facilitate nucleotide release in endothelial cells
During atherosclerosis, endothelial cells release purines in response to oxidized phospholipids. Here, Hitzel et al. show that oxidized phospholipids activate an MTHFD2-regulated gene network in endothelial cells which reprograms amino acid metabolism towards production of purines and thus compensates for their loss.
- Juliane Hitzel
- , Eunjee Lee
- & Ralf P. Brandes
-
Article
| Open Access Map of synthetic rescue interactions for the Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway identifies USP48
Map of synthetic rescue interactions for the Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway identifies USP48
Fanconi anemia is a rare disease caused by defective DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Here the authors observe that USP48 deficiencies reduce chromosomal instability in FA-defective cells, suggesting it might be a potential therapeutic target.
- Georgia Velimezi
- , Lydia Robinson-Garcia
- & Joanna I. Loizou
-
Article
| Open Access Phylodynamic assessment of intervention strategies for the West African Ebola virus outbreak
Phylodynamic assessment of intervention strategies for the West African Ebola virus outbreak
During the last Ebola virus outbreak in West Africa, a large amount of viral genomic data was obtained. Here, Dellicour et al. use phylodynamic approaches to assess effect of intervention strategies such as border closures.
- Simon Dellicour
- , Guy Baele
- & Philippe Lemey
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple communication mechanisms between sensor kinases are crucial for virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Multiple communication mechanisms between sensor kinases are crucial for virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacteria respond to stresses using two-component systems consisting of sensor kinases (SKs) and response regulators. Here, Francis et al. reveal three specific interaction mechanisms between a pair of SKs that are important for regulation of virulence in the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Vanessa I. Francis
- , Elaine M. Waters
- & Steven L. Porter
-
Article
| Open Access Precise temporal regulation of alternative splicing during neural development
Precise temporal regulation of alternative splicing during neural development
The precise timing of neurodevelopmental splicing switches and the underlying regulatory mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study identifies two major waves of developmental switches under the control of distinct combinations of RNA-binding proteins in central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Sebastien M. Weyn-Vanhentenryck
- , Huijuan Feng
- & Chaolin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial self-organization resolves conflicts between individuality and collective migration
Spatial self-organization resolves conflicts between individuality and collective migration
How bacteria migrate collectively despite individual phenotypic variation is not understood. Here, the authors show that cells spontaneously sort themselves within moving bands such that variations in individual tumble bias, a determinant of gradient climbing speed, are compensated by the local gradient steepness experienced by individuals.
- X. Fu
- , S. Kato
- & T. Emonet
-
Comment
| Open Access SCRaMbLEing to understand and exploit structural variation in genomes
SCRaMbLEing to understand and exploit structural variation in genomes
- Jan Steensels
- , Anton Gorkovskiy
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid host strain improvement by in vivo rearrangement of a synthetic yeast chromosome
Rapid host strain improvement by in vivo rearrangement of a synthetic yeast chromosome
The Sc2.0 project has built the Synthetic Chromosome Rearrangement and Modification by LoxP-mediated Evolution (SCRaMbLE) system into their synthetic chromosomes. Here the authors use SCRaMbLE to rapidly develop, diversify and screen strains for diverse production and growth characteristics.
- B. A. Blount
- , G-O. F. Gowers
- & T. Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid pathway prototyping and engineering using in vitro and in vivo synthetic genome SCRaMbLE-in methods
Rapid pathway prototyping and engineering using in vitro and in vivo synthetic genome SCRaMbLE-in methods
Pathway optimization and chassis engineering are usually carried out in a step-wise and trial-and-error manner. Here the authors present ’SCRaMbLE-in’ that combines in-vitro pathway rapid prototyping with in-vivo genome integration and optimization.
- Wei Liu
- , Zhouqing Luo
- & Yizhi Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying and characterizing SCRaMbLEd synthetic yeast using ReSCuES
Identifying and characterizing SCRaMbLEd synthetic yeast using ReSCuES
The use of synthetic chromosomes and the recombinase-based SCRaMbLE system could enable rapid strain evolution through massive chromosome rearrangements. Here the authors present ReSCuES, which uses auxotrophic markers to rapidly identify yeast with rearrangements for strain engineering.
- Zhouqing Luo
- , Lihui Wang
- & Junbiao Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Heterozygous diploid and interspecies SCRaMbLEing
Heterozygous diploid and interspecies SCRaMbLEing
SCRaMbLE has been used to rearrange synthetic chromosomes that have been introduced into host yeast. Here the authors produce semi-synthetic heterozygous diploid strains for rapid selection of phenotypes and map the rearrangements underlying selected phenotypes such as thermoresistance and caffeine resistance.
- Michael J. Shen
- , Yi Wu
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Review Article
| Open Access The CRISPR tool kit for genome editing and beyond
The CRISPR tool kit for genome editing and beyond
CRISPR has rapidly become an indispensable tool for biological research. Here Mazhar Adli reviews the current toolbox for editing and manipulating the genome and looks toward future developments in this fast moving field.
- Mazhar Adli
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering modular intracellular protein sensor-actuator devices
Engineering modular intracellular protein sensor-actuator devices
Synthetic biology principles are often used to design circuits that tune gene expression in response to changes in intracellular environments. Here the authors design a modular platform for intracellular protein sensing devices with transcriptional output.
- Velia Siciliano
- , Breanna DiAndreth
- & Ron Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access Designer cells programming quorum-sensing interference with microbes
Designer cells programming quorum-sensing interference with microbes
Bacterial populations communicate with AI-2 signaling molecules, helping to coordinate biofilm development and other group behaviors. Here the authors design a genetic circuit for mammalian cells that allows them to sense bacterial populations and interfere with quorum communication.
- Ferdinand Sedlmayer
- , Dennis Hell
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access The topological requirements for robust perfect adaptation in networks of any size
The topological requirements for robust perfect adaptation in networks of any size
Robust perfect adaptation (RPA), the ability of a system to return to its pre-stimulus state in the presence of a new signal, enables organisms to respond to further changes in stimuli. Here, the authors identify the modular structure of the full set of network topologies that can confer RPA on complex networks.
- Robyn P. Araujo
- & Lance A. Liotta
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvolution of subcellular protrusion heterogeneity and the underlying actin regulator dynamics from live cell imaging
Deconvolution of subcellular protrusion heterogeneity and the underlying actin regulator dynamics from live cell imaging
Cell protrusion dynamics are heterogeneous at the subcellular level, but current analyses operate at the cellular or ensemble level. Here the authors develop a computational framework to quantify subcellular protrusion phenotypes and reveal the underlying actin regulator dynamics at the leading edge.
- Chuangqi Wang
- , Hee June Choi
- & Kwonmoo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access The transcription-repair coupling factor Mfd associates with RNA polymerase in the absence of exogenous damage
The transcription-repair coupling factor Mfd associates with RNA polymerase in the absence of exogenous damage
The bacterial transcription-repair coupling factor Mfd displaces stalled RNA polymerase (RNAP) by promoting transcription termination at sites of DNA lesions. Here the authors find—using single molecule imaging in live Escherichia coli—that RNAP stalls frequently during transcription, and needs to be rescued by Mfd during normal growth.
- Han N. Ho
- , Antoine M. van Oijen
- & Harshad Ghodke
-
Article
| Open Access Random sequences rapidly evolve into de novo promoters
Random sequences rapidly evolve into de novo promoters
Bacterial promoters initiate gene transcription and have distinct sequence features. Here, the authors show that random sequences that contain no information are just on the verge of functioning as promoters in Escherichia coli.
- Avihu H. Yona
- , Eric J. Alm
- & Jeff Gore
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative assessment of protein activity in orphan tissues and single cells using the metaVIPER algorithm
Quantitative assessment of protein activity in orphan tissues and single cells using the metaVIPER algorithm
VIPER has been successfully used to assess the regulatory activities of proteins from gene expression data, but its dependence on tissue-specific molecular profiles limits its applicability. MetaVIPER, introduced here, enables inference of the protein activities in orphan tissues and single cells.
- Hongxu Ding
- , Eugene F. Douglass Jr.
- & Andrea Califano
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-free prediction of protein expression costs for growing cells
Cell-free prediction of protein expression costs for growing cells
The translation of heterologous proteins places a burden on host cell resources, affecting growth and productivity. Here the authors develop a cell-free assay to measure resource consumption and predict in vivo burden.
- Olivier Borkowski
- , Carlos Bricio
- & Tom Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access Sign epistasis caused by hierarchy within signalling cascades
Sign epistasis caused by hierarchy within signalling cascades
Sign epistasis clearly constrains evolution, but its causes are difficult to decipher. Here, the authors study epistasis in a signalling cascade, and arrive at a general criterion and understanding of sign epistasis as arising from the inherent hierarchy between signalling cascade components.
- Philippe Nghe
- , Manjunatha Kogenaru
- & Sander J. Tans
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphatase activity tunes two-component system sensor detection threshold
Phosphatase activity tunes two-component system sensor detection threshold
Two-component systems are a major family of signal transduction pathways and a rich source of sensors for biotechnology. Here, the authors develop a general method for rationally tuning two-component system input detection thresholds via specific point mutations in sensor histidine kinase proteins.
- Brian P. Landry
- , Rohan Palanki
- & Jeffrey J. Tabor
-
Article
| Open Access Design principles for enhancing phase sensitivity and suppressing phase fluctuations simultaneously in biochemical oscillatory systems
Design principles for enhancing phase sensitivity and suppressing phase fluctuations simultaneously in biochemical oscillatory systems
Biochemical processes require both high sensitivity and low fluctuation which is incompatible with the fluctuation dissipation theorem. Here Fei et al. model biochemical oscillators to show how free energy dissipation leads to both a suppression of phase fluctuation and an enhancement of phase sensitivity.
- Chenyi Fei
- , Yuansheng Cao
- & Yuhai Tu
-
Article
| Open Access Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse
Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse
Publicly available RNA-seq data is provided mostly in raw form, resulting in a barrier for integrative analyses. Here, Lachmann et al. develop a high-throughput processing infrastructure and search database (ARCHS4) that provides processed RNA-seq data for 187,946 publicly available mouse and human samples to support exploration and reuse.
- Alexander Lachmann
- , Denis Torre
- & Avi Ma’ayan
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-omics analysis reveals neoantigen-independent immune cell infiltration in copy-number driven cancers
Multi-omics analysis reveals neoantigen-independent immune cell infiltration in copy-number driven cancers
Neoantigen load has been associated with tumour immune infiltration. Here, the authors show that while this is true for tumours with recurrent mutations, cancers with recurrent CNAs show neoantigen-independent infiltration driven by cytokine production downstream of the DNA damage sensor ATM.
- Daniel J. McGrail
- , Lorenzo Federico
- & Nidhi Sahni
-
Article
| Open Access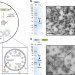 Prokaryotic nanocompartments form synthetic organelles in a eukaryote
Prokaryotic nanocompartments form synthetic organelles in a eukaryote
Compartmentalization of proteins can potentially increase the productivity of engineered metabolic pathways. Here the authors use encapsulins to build non-endogenous organelles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Yu Heng Lau
- , Tobias W. Giessen
- & Pamela A. Silver
-
Article
| Open Access Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment
Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment
Exosomes function as intercellular information transmitters and are candidates for delivery of therapeutic agents. Here the authors present EXOtic, a synthetic biology device for in-situ production of designer exosomes and demonstrate in vivo application in models of Parkinson's disease.
- Ryosuke Kojima
- , Daniel Bojar
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access A semi-synthetic regulon enables rapid growth of yeast on xylose
A semi-synthetic regulon enables rapid growth of yeast on xylose
Efficient assimilation of nutrients is essential for the production of value-added products in microbial fermentation. Here the authors design a semi-synthetic xylose regulon to improve growth characteristics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on this non-native sugar.
- Venkatesh Endalur Gopinarayanan
- & Nikhil U. Nair
-
Article
| Open Access The choroid plexus is an important circadian clock component
The choroid plexus is an important circadian clock component
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) has been thought of as the master circadian clock, but peripheral circadian clocks do exist. Here, the authors show that the choroid plexus displays oscillations more robust than the SCN and that can be described as a Poincaré oscillator with negative twist.
- Jihwan Myung
- , Christoph Schmal
- & Toru Takumi
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of complex single-cell trajectories using CellRouter
Reconstruction of complex single-cell trajectories using CellRouter
Single cell analysis provides insight into cell states and transitions, but to interpret the data, improved algorithms are needed. Here, the authors present CellRouter as a method to analyse single-cell trajectories from RNA-sequencing data, and provide insight into erythroid, myeloid and lymphoid differentiation.
- Edroaldo Lummertz da Rocha
- , R. Grant Rowe
- & George Q. Daley
-
Article
| Open Access High capacity in G protein-coupled receptor signaling
High capacity in G protein-coupled receptor signaling
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) activate intracellular signalling pathways upon extracellular stimulation. Here authors record single cell responses of GPCR signalling which allows the direct estimation of its channel capacity for each cell along with the reproducibility of its response.
- Amiran Keshelava
- , Gonzalo P. Solis
- & Vladimir L. Katanaev
-
Article
| Open Access Sheep genome functional annotation reveals proximal regulatory elements contributed to the evolution of modern breeds
Sheep genome functional annotation reveals proximal regulatory elements contributed to the evolution of modern breeds
The domestication of plants and animals causes genomic changes underlying various morphologic, physiologic and behavioral changes. Here, Naval-Sanchez et al. provide a ChIP-Seq validated comparative functional annotation of the sheep genome, and show widespread evolution of proximal regulatory elements.
- Marina Naval-Sanchez
- , Quan Nguyen
- & James Kijas
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing the replicability of cell types defined by single cell RNA-sequencing data using MetaNeighbor
Characterizing the replicability of cell types defined by single cell RNA-sequencing data using MetaNeighbor
Single cell RNA-sequencing analysis poses challenges in replication due to technical biases and analytic variability among bioinformatics pipelines. Here, Crow et al develop MetaNeighbor for measuring cell-type replication across datasets, and use it to identify marker genes for neuron subtypes with evidence of replication.
- Megan Crow
- , Anirban Paul
- & Jesse Gillis
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed hierarchical patterning of bacterial populations
Programmed hierarchical patterning of bacterial populations
Biological self-organization uses hierarchical induction of gene expression but this has not been exploited by synthetic biology. Here the authors use an AND gate based on a split T7 RNA polymerase to organize programmed hierarchical patterning of gene expression across a bacterial population.
- Christian R. Boehm
- , Paul K. Grant
- & Jim Haseloff
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying noncoding risk variants using disease-relevant gene regulatory networks
Identifying noncoding risk variants using disease-relevant gene regulatory networks
Current methods for prioritization of non-coding genetic risk variants are based on sequence and chromatin features. Here, Gao et al. develop ARVIN, which predicts causal regulatory variants using disease-relevant gene-regulatory networks, and validate this approach in reporter gene assays.
- Long Gao
- , Yasin Uzun
- & Kai Tan
-
Article
| Open Access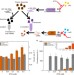 Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling of co-expressed genes
Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling of co-expressed genes
Competition between synthetic genetic circuits and host genes for shared resources can complicate circuit design and lead to failure. Here the authors demonstrate, mathematically and experimentally, the use of orthogonal ribosomes to decouple competing genes.
- Alexander P. S. Darlington
- , Juhyun Kim
- & Declan G. Bates
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic network biomarker indicates pulmonary metastasis at the tipping point of hepatocellular carcinoma
Dynamic network biomarker indicates pulmonary metastasis at the tipping point of hepatocellular carcinoma
Biomarkers of the tipping point before metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) could help stratify patient treatment. Here, the authors study dynamic network biomarkers to identify CALM3 as a potential suppressor of metastasis, the level of which can predict overall survival and relapse-free survival in postoperative HCC.
- Biwei Yang
- , Meiyi Li
- & Jinglin Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Cell fate in antiviral response arises in the crosstalk of IRF, NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways
Cell fate in antiviral response arises in the crosstalk of IRF, NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways
Innate immunity combines intra- and intercellular signalling to develop responses that limit pathogen spread. Here the authors analyse feedback and feedforward loops connecting IRF3, NF-κB and STAT pathways, and suggest they allow coordinating cell fate decisions in cellular populations in response to the virus-mimicking agent poly(I:C).
- Maciej Czerkies
- , Zbigniew Korwek
- & Tomasz Lipniacki
-
Article
| Open Access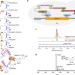 Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Breviscapine is the flavonoid extract from medical plant Erigeron breviscapus for the treatment of cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Here, the authors identify the key enzymes of the biosynthetic pathway from the plant genome and engineer yeast to produce breviscapine from glucose.
- Xiaonan Liu
- , Jian Cheng
- & Huifeng Jiang
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 Statistical mechanics for metabolic networks during steady state growth
Statistical mechanics for metabolic networks during steady state growth