Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical signal activation of an organocatalyst enables control over soft material formation
Chemical signal activation of an organocatalyst enables control over soft material formation
Enzymes regulated by chemical signals are common in biology, but few such artificial catalysts exist. Here, the authors design an aniline catalyst that, when activated by a chemical trigger, catalyses formation of hydrazone-based gels, demonstrating signal response in a soft material.
- Fanny Trausel
- , Chandan Maity
- & Rienk Eelkema
-
Article
| Open Access Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Crystal growth is a fundamental process, important in a wide range of fields, but the interparticle forces responsible for molecule alignment are not well understood. Here, the authors measure the alignment forces in ZnO using dynamic force spectroscopy, highlighting the role of intervening water molecules.
- X. Zhang
- , Z. Shen
- & K. M. Rosso
-
Article
| Open Access Exact mass analysis of sulfur clusters upon encapsulation by a polyaromatic capsular matrix
Exact mass analysis of sulfur clusters upon encapsulation by a polyaromatic capsular matrix
The structures of inorganic clusters are commonly characterized by mass spectrometry (MS), but neutral sulfur clusters heavily fragment under MS conditions, preventing their exact mass determination. Here, the authors successfully perform MS on labile cyclic sulfur clusters by stabilizing them within ionic supramolecular capsules.
- Sho Matsuno
- , Masahiro Yamashina
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Continual reproduction of self-assembling oligotriazole peptide nanomaterials
Continual reproduction of self-assembling oligotriazole peptide nanomaterials
Molecules that act as both autocatalysts and material precursors offer exciting prospects for self-synthesizing materials. Here, the authors design a triazole peptide that self-replicates and then self-assembles into nanostructures, coupling autocatalytic and assembly pathways to realize a reproducing supramolecular system.
- Roberto J. Brea
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article
| Open Access A coordination polymer for the site-specific integration of semiconducting sequences into DNA-based materials
A coordination polymer for the site-specific integration of semiconducting sequences into DNA-based materials
Integration of semiconducting properties into the basic topological motif of DNA remains challenging. Here, the authors show a coordination polymer derived from 6-thioguanosine that complexes with Au(I) ions to form a wire-like material that can also integrate semiconducting sequences into the framework of DNA materials.
- Lamia L. G. Al-Mahamad
- , Osama El-Zubir
- & Andrew Houlton
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA nanoscope via auto-cycling proximity recording
A DNA nanoscope via auto-cycling proximity recording
The spatial organisation of nanostructures is fundamental to their function. Here, the authors develop a non-destructive, proximity-based method to record extensive spatial organization information in DNA molecules for later readout.
- Thomas E. Schaus
- , Sungwook Woo
- & Peng Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative colloidal self-assembly of metal-protein superlattice wires
Cooperative colloidal self-assembly of metal-protein superlattice wires
Colloidal self-assembly is a unique method to produce three-dimensional materials with well-defined hierarchical structures and functionalities. Liljeström et al. show controlled preparation of macroscopic chiral wires with helical plasmonic superlattice structure composed of metal nanoparticles and viruses.
- Ville Liljeström
- , Ari Ora
- & Mauri A. Kostiainen
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence-controlled supramolecular terpolymerization directed by specific molecular recognitions
Sequence-controlled supramolecular terpolymerization directed by specific molecular recognitions
Nature can precisely control monomer sequences in biopolymers, but this is somewhat problematic in the formation of synthetic polymers. Here the authors show sequence-controlled supramolecular terpolymerization via self-sorting behavior among three sets of monomers possessing mismatched host-guest pairs.
- Takehiro Hirao
- , Hiroaki Kudo
- & Takeharu Haino
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen bonds to Au atoms in coordinated gold clusters
Hydrogen bonds to Au atoms in coordinated gold clusters
Many transition metals can form hydrogen bonds to organic species, but experimental evidence for Au is still lacking. Here, the authors obtain crystallographic and NMR spectroscopic evidence of hydrogen bonding between C-H groups and Au atoms of gold clusters, suggesting that non-covalent interactions may play a role in gold cluster catalysis.
- Md. Abu Bakar
- , Mizuho Sugiuchi
- & Katsuaki Konishi
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of native peptide sequences in prebiotic replication networks
Emergence of native peptide sequences in prebiotic replication networks
The synthesis of biopolymers in living cells is perfected by complex machinery, however this was not the case on early Earth. Here the authors show the role of non-enzymatic replication in the enrichment of certain products within prebiotically relevant mixtures.
- Jayanta Nanda
- , Boris Rubinov
- & Gonen Ashkenasy
-
Article
| Open Access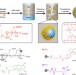 Higher-order assembly of crystalline cylindrical micelles into membrane-extendable colloidosomes
Higher-order assembly of crystalline cylindrical micelles into membrane-extendable colloidosomes
Functional nanoscale objects can be prepared via crystallization-driven self-assembly of diblock copolymers. Here the authors show the self-assembly of crystalline block copolymers into size-specific cylindrical micelles for the hierarchical construction of mechanically robust colloidosomes with a range of membrane textures.
- Hongjing Dou
- , Mei Li
- & Ian Manners
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the crystallographic orientation of two-dimensional atomic crystals with supramolecular self-assembly
Probing the crystallographic orientation of two-dimensional atomic crystals with supramolecular self-assembly
Identifying the crystallographic orientations of 2D materials is important, but methods to do so are typically destructive. Here, the authors show that the orientational dependency of self-assembled nanoribbons of oleamide molecules can be used to non-invasively probe the lattice orientations of various 2D substrates.
- Jinghui Wang
- , Hongde Yu
- & Liying Jiao
-
Article
| Open Access A light-regulated host–guest-based nanochannel system inspired by channelrhodopsins protein
A light-regulated host–guest-based nanochannel system inspired by channelrhodopsins protein
Light-controlled gating of ion transport across membranes occurs in nature via channelrhodopsin nanochannels. Here, the authors show facile non-covalent approach towards light-responsive biomimetic nanochannels using host–guest interactions between a negative pillararene host and a positive azobenzene guest.
- Yue Sun
- , Junkai Ma
- & Haibing Li
-
Article
| Open Access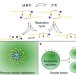 Autonomous model protocell division driven by molecular replication
Autonomous model protocell division driven by molecular replication
Coupling compartmentalisation and molecular replication is essential for the development of evolving chemical systems. Here the authors show an oil-in-water droplet containing a self-replicating amphiphilic imine that can undergo repeated droplet division.
- J. W. Taylor
- , S. A. Eghtesadi
- & L. Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular recognition by multiple metal coordination inside wavy-stacked macrocycles
Molecular recognition by multiple metal coordination inside wavy-stacked macrocycles
Synergistic use of coordination bonds that are strong and reversible realizes unique molecular recognition in artificial systems. Here, the authors show that a zinc-based metallomacrocyle can bind dicarboxylic acids of suitable length at specific metal sites by shape deformation and dimerization.
- Takashi Nakamura
- , Yuya Kaneko
- & Tatsuya Nabeshima
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Organizing photochromic molecules into 3D networks is a key strategy to access photoresponsive materials, but framework rigidity typically limits conversion efficiency. Here, the authors exploit a flexible metal-organic framework to achieve quantitative and reversible photoisomerization in a porous crystalline solid.
- Yongtai Zheng
- , Hiroshi Sato
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access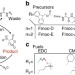 Non-equilibrium dissipative supramolecular materials with a tunable lifetime
Non-equilibrium dissipative supramolecular materials with a tunable lifetime
Biological systems vital functions are based on non-equilibrium states driven by consumption of chemical fuels. Here the authors show a spatiotemporal control over the formation of hydrophobic colloids, hydrogels or inks through a chemical reaction network of dicarboxylate compounds fuelled by carbodiimide.
- Marta Tena-Solsona
- , Benedikt Rieß
- & Job Boekhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Anion-capped metallohost allows extremely slow guest uptake and on-demand acceleration of guest exchange
Anion-capped metallohost allows extremely slow guest uptake and on-demand acceleration of guest exchange
Host—guest assemblies can exploit stimuli-responsive guest binding and release for molecular recognition, but are typically governed by thermodynamics alone. Here, the authors design macrocycles with removable and exchangeable anion caps, allowing for the kinetic trapping and on-demand exchange of guest ions.
- Yoko Sakata
- , Chiho Murata
- & Shigehisa Akine
-
Article
| Open Access Polyaromatic molecular peanuts
Polyaromatic molecular peanuts
The complex, multicomponent structures often found in nature are difficult to mimic synthetically. Here, the authors assemble a molecular analogue of a peanut through coordinative and π-stacking interactions, in which a polyaromatic double capsule ‘pod’ held together by metal ions encapsulates fullerene ‘beans’.
- Kohei Yazaki
- , Munetaka Akita
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondria localization induced self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles for cellular dysfunction
Mitochondria localization induced self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles for cellular dysfunction
Spatiotemporal control of intracellular molecular self-assembly holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here the authors develop a peptide consisting of a phenylalanine dipeptide with a mitochondrial targeting moiety to form self-assembling fibrous nanostructures within mitochondria, leading to apoptosis.
- M. T. Jeena
- , L. Palanikumar
- & Ja-Hyoung Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access Giant capsids from lattice self-assembly of cyclodextrin complexes
Giant capsids from lattice self-assembly of cyclodextrin complexes
Designing and synthesizing protein mimetic molecules to form crystalline structures can be a challenge. Here the authors show lattice self-assembly of cyclodextrin complexes into a variety of capsid like structures, such as, lamellae, helical tubes and hollow rhombic dodecahedra.
- Shenyu Yang
- , Yun Yan
- & Lingxiang Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Non-equilibrium steady states in supramolecular polymerization
Non-equilibrium steady states in supramolecular polymerization
Several cell functions are based on the fuel-driven assembly and disassembly of supramolecular polymers under non-equilibrium conditions. Here, the authors show controlled formation and breaking of a supramolecular polymer by enzymatic phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a building block by continuously adding ATP fuel and removing waste products.
- Alessandro Sorrenti
- , Jorge Leira-Iglesias
- & Thomas M. Hermans
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive self-assembly and induced-fit transformations of anion-binding metal-organic macrocycles
Adaptive self-assembly and induced-fit transformations of anion-binding metal-organic macrocycles
Container-molecules capable of recognizing charged species possess great potential as sensors, but are typically limited by their rigid frameworks. Here, Sun and co-workers design a family of adaptive metal-organic macrocycles that exhibit shape and size induced-fit transformations upon anion-binding.
- Ting Zhang
- , Li-Peng Zhou
- & Qing-Fu Sun
-
Article
| Open Access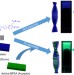 Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Energy and chirality transfer play a crucial role in living systems. Here, the authors show that achiral acceptors and chiral donor gelators can assemble in a chirally-controlled manner into a supramolecular nanohelix that can additionally harvest circularly polarized energy.
- Dong Yang
- , Pengfei Duan
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Reaction-diffusion controls the spatial formation of many natural structures but is rarely applied to organic materials. Here, the authors couple reaction-diffusion to the self-assembly of a supramolecular gelator, introducing a strategy to forming soft, free-standing objects with controlled shape and functionality.
- Matija Lovrak
- , Wouter E. J. Hendriksen
- & Jan H. van Esch
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Spiro compounds contain two or more rings linked together through one common atom. Here the authors provide a method to backfold both rings, producing spiro quasi[1]catenanes, via a strategy of temporarily linking the linear intermediates with covalent bonds.
- Luuk Steemers
- , Martin J. Wanner
- & Jan H. van Maarseveen
-
Article
| Open Access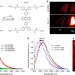 A high quantum yield molecule-protein complex fluorophore for near-infrared II imaging
A high quantum yield molecule-protein complex fluorophore for near-infrared II imaging
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging >1,000 nm allows deep tissue imaging, but available organic dyes display poor brightness and temporal resolution. Here, the authors synthesize a NIR dye that, upon binding serum proteins, exhibits a 110-fold increase in intensity, giving an 11% quantum yield.
- Alexander L. Antaris
- , Hao Chen
- & Zhen Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic diversity of synthetic supramolecular polymers in water as revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange
Dynamic diversity of synthetic supramolecular polymers in water as revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange
Understanding the dynamics of supramolecular architectures without using labels is crucial for developing advanced biosystems. Here, the authors show kinetic hydrogen/deuterium exchange profiles for a series of water-soluble supramolecular polymers.
- Xianwen Lou
- , René P. M. Lafleur
- & E W Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced unfolding and refolding of supramolecular polymer nanofibres
Light-induced unfolding and refolding of supramolecular polymer nanofibres
Dynamically controlling the conformations of 1D elongated supramolecular polymers can induce functions comparable to protein folding/unfolding. Here the authors show light-induced conformational changes of azobenzene-based supramolecular polymers from helically coiled to extended/randomly coiled conformations.
- Bimalendu Adhikari
- , Yuki Yamada
- & Shiki Yagai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-large supramolecular coordination cages composed of endohedral Archimedean and Platonic bodies
Ultra-large supramolecular coordination cages composed of endohedral Archimedean and Platonic bodies
Host–guest chemistry in hollow coordination cages can be exploited for a range of applications, but is often limited by inner cavity dimensions. Here, Schmitt and co-workers fabricate supramolecular keplerates that possess ultra-large cross-sectional diameters and are composed of multiple sub-cages.
- Kevin Byrne
- , Muhammad Zubair
- & Wolfgang Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Stimuli-controlled self-assembly of diverse tubular aggregates from one single small monomer
Stimuli-controlled self-assembly of diverse tubular aggregates from one single small monomer
Hydrogen bonds are powerful supramolecular motifs, owing to their selective and dynamic nature. Here, the authors build orthogonal hydrogen-bonding sites into a single molecule, allowing it to form diverse hierarchical assemblies and exhibit self-sorting behaviour in response to certain stimuli.
- Qixun Shi
- , Tomas Javorskis
- & Kenneth Wärnmark
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of aligned functional nanoribbons monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy and vibrational spectroscopy
On-surface synthesis of aligned functional nanoribbons monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy and vibrational spectroscopy
On-surface synthesis, in which molecular units assemble and couple on a defined surface, can access rare reaction pathways and products. Here, the authors synthesize functionalized organic nanoribbons on the Ag(110) surface, and monitor the evolution of the covalent reactions by an unorthodox vibrational spectroscopy approach.
- Nataliya Kalashnyk
- , Kawtar Mouhat
- & Sylvain Clair
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
In vivo, complex topologies have been identified in proteins and DNA, while their existence in RNA is still unclear. Here, the authors design synthetic topological structures containing single stranded RNA, offering tools for investigating biologically relevant questions about RNA topology.
- Di Liu
- , Yaming Shao
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence-selective encapsulation and protection of long peptides by a self-assembled FeII8L6 cubic cage
Sequence-selective encapsulation and protection of long peptides by a self-assembled FeII8L6 cubic cage
One of the challenges of synthetic self-assembled capsules is achieving selective recognition of specific cargoes. Here, authors synthesize a self-assembled porphyrin cubic cage that is capable of sequestering imidazole and thiazole-containing small molecules and peptides, protecting them from proteolysis.
- Jesús Mosquera
- , Bartosz Szyszko
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article
| Open Access Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Two-dimensional material heterostructures enable unique electronic features by introducing periodic potentials. Here, Gobbiet al. use a monolayer supramolecular lattice with a tunable one-dimensional periodic potential to modify the electronic structure of graphene.
- Marco Gobbi
- , Sara Bonacchi
- & Emanuele Orgiu
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Proteins can template the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles, but the formation mechanisms remain vague. Here, the authors directly observe, through a sequence of X-ray crystal structures, the stages of gold sub-nanocluster growth within the confined environment of a ferritin cage.
- Basudev Maity
- , Satoshi Abe
- & Takafumi Ueno
-
Article
| Open Access Templated bilayer self-assembly of fully conjugated π-expanded macrocyclic oligothiophenes complexed with fullerenes
Templated bilayer self-assembly of fully conjugated π-expanded macrocyclic oligothiophenes complexed with fullerenes
Controlling the self-assembly of oligothiophene complexes that are used in multi-functional thin films can be challenging. Here the authors show a hierarchy of non-covalent interactions for robust self-assembly that orders Saturn-like complexes of fullerenes with oligothiophene macrocycles.
- José D. Cojal González
- , Masahiko Iyoda
- & Jürgen P. Rabe
-
Article
| Open Access NO3− anions can act as Lewis acid in the solid state
NO3− anions can act as Lewis acid in the solid state
The nitrate anion, NO3−, is typically thought of as an electron-donating molecular moiety. Here the authors reveal, however, that when the negative charge on NO3−is smeared out over a large enough area, a positive potential emerges on N that can act as a Lewis acid in the solid state.
- Antonio Bauzá
- , Antonio Frontera
- & Tiddo J. Mooibroek
-
Article
| Open Access Dielectric and ferroelectric sensing based on molecular recognition in Cu(1,10-phenlothroline)2SeO4·(diol) systems
Dielectric and ferroelectric sensing based on molecular recognition in Cu(1,10-phenlothroline)2SeO4·(diol) systems
Molecular recognition is an important biological process where guest and host molecules interact through non-covalent bonding. Yeet al. show that this can be sensed by the dielectric and ferroelectric signals of the final complexes in a series of metal-coordination compounds with different diol molecules.
- Heng-Yun Ye
- , Wei-Qiang Liao
- & Ren-Gen Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular weaving via surface-templated epitaxy of crystalline coordination networks.
Molecular weaving via surface-templated epitaxy of crystalline coordination networks.
The self-assembly of polymer threads into interwoven textiles is an important goal in polymer chemistry. Here the authors assemble interwoven polymer chains by cross-linking acetylene functionalized ligands in surface-mounted MOFs and subsequent removal of the metal ions affords 2D textile sheets.
- Zhengbang Wang
- , Alfred Błaszczyk
- & Marcel Mayor
-
Article
| Open Access A metamorphic inorganic framework that can be switched between eight single-crystalline states
A metamorphic inorganic framework that can be switched between eight single-crystalline states
Crystal engineering is a powerful process for assembling complex materials but tends to require organic building blocks, which can limit stability. Here, the authors use inorganic polyoxometalates to assemble an all-inorganic metamorphic framework that can be switched between eight distinct states.
- Caihong Zhan
- , Jamie M. Cameron
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of solid–solid transitions in 3D crystals of colloidal superballs
Observation of solid–solid transitions in 3D crystals of colloidal superballs
Experimental understanding of anisotropic colloid self-organization has not yet caught up with theory. Here, the authors find that the experimental phase behaviour of superballs is more complex than predicted, revealing a solid-solid transition from a plastic crystal to two rhombohedral crystal phases with distinct stacking types.
- Janne-Mieke Meijer
- , Antara Pal
- & Andrei V. Petukhov
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-centred azaphosphatriptycene gear with a photo- and thermally driven mechanical switching function based on coordination isomerism
Metal-centred azaphosphatriptycene gear with a photo- and thermally driven mechanical switching function based on coordination isomerism
In metal-based molecular motors, the motion is generally triggered by changes in the ligand coordination around the metal centre. Here, the authors synthesize a molecular gear that switches between states through photo- and thermally driven geometrical isomerization around a platinum ion.
- Hitoshi Ube
- , Yoshihiro Yasuda
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-resolution imaging of water networks by atomic force microscopy
Ultrahigh-resolution imaging of water networks by atomic force microscopy
The structure of water in the first layer on surfaces is essential to our understanding of various phenomena, such as surface wettability and heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip to image water defects on copper surface at atomic resolution.
- Akitoshi Shiotari
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of form in metal–organic frameworks
Evolution of form in metal–organic frameworks
Self-assembly is a strategy for making metal-organic materials but controlling the interior of metal-organic crystals remains challenging. Here, the authors report a sequential self-assembly process for synthesizing various interior morphologies of metal-organic crystal demonstrating evolution of form.
- Jiyoung Lee
- , Ja Hun Kwak
- & Wonyoung Choe
-
Article
| Open Access Stacked antiaromatic porphyrins
Stacked antiaromatic porphyrins
It has been proposed that stacking antiaromatic molecules can build three-dimensional aromaticity, but this claim has lacked experimental validation. Here the authors report that π–π stacked antiaromatic porphyrins display significantly reduced antiaromaticity in solid state and in solution.
- Ryo Nozawa
- , Hiroko Tanaka
- & Hiroshi Shinokubo
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of bacterial pilus-like nanofibres by designed minimalistic self-assembling peptides
Formation of bacterial pilus-like nanofibres by designed minimalistic self-assembling peptides
The application of nanofibres formed from monomers of bacterial type IV pili in vitrohas proven to be complex. Here, the authors have overcome this limitation by using a reductionist approach to design a self-assembling pilin-based 20-mer peptide capable of forming a supramolecular beta sheet.
- Tom Guterman
- , Micha Kornreich
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access A metal-organic cage incorporating multiple light harvesting and catalytic centres for photochemical hydrogen production
A metal-organic cage incorporating multiple light harvesting and catalytic centres for photochemical hydrogen production
Photocatalytic water splitting is a promising route to hydrogen generation from renewable solar power. Here, the authors report a hydrogen-evolving photochemical molecular device based on a self-assembled coordination cage, which simultaneously incorporates multiple photosensitizing and catalytic metal centres.
- Sha Chen
- , Kang Li
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and reversible photoinduced switching of a rotaxane crystal
Rapid and reversible photoinduced switching of a rotaxane crystal
Crystalline phase transition can be used to detect changes in the solid state properties of materials. Here, the authors describe the mechanical response of a crystal composed of ferrocene-containing rotaxane to laser irradiation.
- Kai-Jen Chen
- , Ya-Ching Tsai
- & Masaki Horie

 Selective binding of choline by a phosphate-coordination-based triple helicate featuring an aromatic box
Selective binding of choline by a phosphate-coordination-based triple helicate featuring an aromatic box