Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ceramic nanowelding
Ceramic nanowelding
Fabricating complex nanodevices requires joining techniques such as welding, common for metals but still out of reach for ceramics. Here the authors use MgO as a solder in a transmission electron microscope with a CO2 atmosphere to weld ceramic nanowires, and show their novel technique can also weld bulk ceramics.
- Liqiang Zhang
- , Yushu Tang
- & Jianyu Huang
-
Article
| Open Access New twinning route in face-centered cubic nanocrystalline metals
New twinning route in face-centered cubic nanocrystalline metals
Twin nucleation in face-centered cubic metals with high twin-fault energies should theoretically be unfavourable, but instead twinning is very often observed. Here, the authors report a new twinning route in nanocrystalline platinum that bypasses the high twin-fault energy barrier using closely spaced partial dislocations.
- Lihua Wang
- , Pengfei Guan
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptional increase in the creep life of magnesium rare-earth alloys due to localized bond stiffening
Exceptional increase in the creep life of magnesium rare-earth alloys due to localized bond stiffening
Adding very small amounts of zinc to magnesium alloys containing rare earth elements dramatically improves their creep life. Here, the authors use first principles calculations and atomic-scale characterization to show that this is due to stiff covalent bonding of zinc and rare earth elements such as neodymium.
- Deep Choudhuri
- , Srivilliputhur G. Srinivasan
- & Rajarshi Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring crystallization phases in metallic glass nanorods via nucleus starvation
Tailoring crystallization phases in metallic glass nanorods via nucleus starvation
Crystallising a bulk metallic glass usually results in separate phases. Here, the authors use metallic glass nanorods to show that as the sample size approaches the nucleation scale lengths, the crystallization behavior is dictated by the lack of nuclei and nanorods crystallise into a single phase.
- Sungwoo Sohn
- , Yujun Xie
- & Judy J. Cha
-
Article
| Open Access High-velocity projectile impact induced 9R phase in ultrafine-grained aluminium
High-velocity projectile impact induced 9R phase in ultrafine-grained aluminium
Deformation-induced defects with high formation energy are difficult to nucleate in aluminium. Here, the authors use a miniaturized projectile impact to nucleate the high stacking fault energy 9R phase in a thin film of ultrafine-grained aluminium, and show sessile Frank loops stabilize it.
- Sichuang Xue
- , Zhe Fan
- & Xinghang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mixing instabilities during shearing of metals
Mixing instabilities during shearing of metals
The mechanisms behind deformation of multiphase solids are elusive. Here, the authors use X-rays and simulations to show that the same mechanisms causing rocks to fold occur at the micrometer scale in dual-metal lamellas of Ag/Cu and Al/Cu under high-pressure torsion, leading to vortices formation.
- Mohsen Pouryazdan
- , Boris J. P. Kaus
- & Horst Hahn
-
Article
| Open Access Probing dopant segregation in distinct cation sites at perovskite oxide polycrystal interfaces
Probing dopant segregation in distinct cation sites at perovskite oxide polycrystal interfaces
Space-charges in polycrystalline materials can drive segregation of dopants, however an in-depth understanding of this process is still missing. Here, the authors show that in polycrystalline perovskites the space-charge segregation and interfacial structure are nearly identical irrespective of the interface type.
- Hye-In Yoon
- , Dong-Kyu Lee
- & Sung-Yoon Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Giant thermal expansion and α-precipitation pathways in Ti-alloys
Giant thermal expansion and α-precipitation pathways in Ti-alloys
Complex phase transformations in β-stabilised titanium alloys can dramatically change their α and β microstructures, providing tailorability for aerospace or biomaterial applications. Here the authors show that Ti-Nb alloys exhibit giant thermal expansions and identify two new pathways that lead to α phase formation.
- Matthias Bönisch
- , Ajit Panigrahi
- & Jürgen Eckert
-
Article
| Open Access Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
The exterior layers of mollusk shells are prismatic in nature, endowing them with stiffness and wear resistance. Inspired by these biominerals, here, Jiang and colleagues grow structurally similar prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films with comparable stiffness and hardness.
- Chuanlian Xiao
- , Ming Li
- & Helmut Cölfen
-
Article
| Open Access A highly flexible and sensitive piezoresistive sensor based on MXene with greatly changed interlayer distances
A highly flexible and sensitive piezoresistive sensor based on MXene with greatly changed interlayer distances
MXenes are a family of layered materials which show promise for a variety of (opto-)electronic applications. Here, the authors leverage the variations of the interlayer distance in Ti3C2 under external pressure to devise a piezoresistive sensor.
- Yanan Ma
- , Nishuang Liu
- & Yihua Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical self-entangled carbon nanotube tube networks
Hierarchical self-entangled carbon nanotube tube networks
Low-dimensional nanomaterials are crucial conducting components of stretchable electronics, but their mechanical reinforcement remains challenging. Here, the authors infiltrate carbon nanotubes into a porous ceramic network to produce a 3D nanofelted self-entangled assembly with high conductivity and mechanical stability.
- Fabian Schütt
- , Stefano Signetti
- & Rainer Adelung
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous elastic properties across the γ to α volume collapse in cerium
Anomalous elastic properties across the γ to α volume collapse in cerium
The origin of the volume collapse of cerium, the only elemental metal with a critical point in the solid phase, remains elusive. Here the authors show that, near the critical point, the f-electrons make cerium lose its compressive strength while maintaining a finite shear strength—which makes cerium unexpectedly auxetic.
- Magnus J. Lipp
- , Zs. Jenei
- & W. J. Evans
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing mechanical instabilities at the nanoscale to achieve ultra-low stiffness metals
Harnessing mechanical instabilities at the nanoscale to achieve ultra-low stiffness metals
The rule of mixtures usually causes composite properties to fall between the maximum and minimum of the parent phases. Here, the authors use large-scale molecular dynamics simulations to break that rule by stabilizing a negative stiffness state in fully dense nickel-aluminum nanowires to achieve ultra-low stiffness.
- Samuel Temple Reeve
- , Alexis Belessiotis-Richards
- & Alejandro Strachan
-
Article
| Open Access Sliding of coherent twin boundaries
Sliding of coherent twin boundaries
Coherent twin boundaries (CTBs) in face-centered cubic metals are usually considered unable to slide at room temperature. Here, the authors use in situ transmission electron microscopy and molecular dynamics to show CTB sliding in copper nanopillars when leading and trailing partial dislocations have similar Schmid factors.
- Zhang-Jie Wang
- , Qing-Jie Li
- & Zhi-Wei Shan
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and ordered amide frameworks synthesised under reversible conditions which facilitate error checking
Stable and ordered amide frameworks synthesised under reversible conditions which facilitate error checking
Irreversible bond formation in covalent organic frameworks leads to amorphous materials. Here, the authors show that crystalline and ultra-stable covalent amide frameworks can be accessed by devitrification of amorphous polyamide networks.
- David Stewart
- , Dmytro Antypov
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Superelasticity and cryogenic linear shape memory effects of CaFe2As2
Superelasticity and cryogenic linear shape memory effects of CaFe2As2
Shape memory materials are capable of returning to their original form post-deformation, but those with high actuation performances remain scarce. Here the authors reveal that CaFe2As2 exhibits cryogenic linear shape memory behaviour with high recoverable strain and yield strength, owing to a reversible uni-axial phase transformation.
- John T. Sypek
- , Hang Yu
- & Seok-Woo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperconnected molecular glass network architectures with exceptional elastic properties
Hyperconnected molecular glass network architectures with exceptional elastic properties
Organic—inorganic glasses can possess unique properties and functionalities, but their poor mechanical strength and stiffness typically limit their applicability. Here the authors demonstrate that inducing hyperconnectivity into silicon-based glass networks endows them with exceptional elastic stiffness.
- Joseph A. Burg
- , Mark S. Oliver
- & Reinhold H. Dauskardt
-
Article
| Open Access Robust Bain distortion in the premartensite phase of a platinum-substituted Ni2MnGa magnetic shape memory alloy
Robust Bain distortion in the premartensite phase of a platinum-substituted Ni2MnGa magnetic shape memory alloy
In magnetic shape memory Heusler alloys, the premartensite phase is believed to be a precursor state of the martensite phase with preserved austenite phase symmetry. Here, the authors show that the premartensite is a stable phase with its own crystallographic symmetry resulting from the stepped growth of Bain distortions in the lattice.
- Sanjay Singh
- , B. Dutta
- & D. Pandey
-
Article
| Open Access Super-formable pure magnesium at room temperature
Super-formable pure magnesium at room temperature
Replacing steel or aluminium vehicle parts with magnesium would result in reduced emissions, but shaping magnesium without cracking remains challenging. Here, the authors successfully extrude and roll textured magnesium into ductile foil at low temperatures by activating intra-granular mechanisms.
- Zhuoran Zeng
- , Jian-Feng Nie
- & Nick Birbilis
-
Article
| Open Access Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami is a popular method to design building blocks for mechanical metamaterials. Here, the authors assemble a volumetric origami-based structure, predict its axial and rotational movements during folding, and demonstrate the operation of mechanical one- and two-bit memory storage.
- Hiromi Yasuda
- , Tomohiro Tachi
- & Jinkyu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Superplasticity in a lean Fe-Mn-Al steel
Superplasticity in a lean Fe-Mn-Al steel
Research in new alloy compositions and treatments may allow the increased strength of mass-produced, intricately shaped parts. Here authors introduce a superplastic medium manganese steel which has an inexpensive lean chemical composition and which is suited for conventional manufacturing processes.
- Jeongho Han
- , Seok-Hyeon Kang
- & Young-Kook Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for percolation diffusion of cations and reordering in disordered pyrochlore from accelerated molecular dynamics
Evidence for percolation diffusion of cations and reordering in disordered pyrochlore from accelerated molecular dynamics
Diffusion plays an important role in sintering, damage tolerance and transport. Here authors perform classical and accelerated molecular dynamics simulations of vacancy-mediated cation diffusion in Gd2Ti2O7 pyrochlore and report non-monotonic evolution of cation diffusivity.
- Romain Perriot
- , Blas P. Uberuaga
- & Arthur F. Voter
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-large single crystals by abnormal grain growth
Ultra-large single crystals by abnormal grain growth
Growing large single crystals cheaply and reliably for structural applications remains challenging. Here, the authors combine accelerated abnormal grain growth and cyclic heat treatments to grow a superelastic shape memory alloy single crystal to 70 cm.
- Tomoe Kusama
- , Toshihiro Omori
- & Ryosuke Kainuma
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of quenchable amorphous diamond
Synthesis of quenchable amorphous diamond
Diamond’s properties are dictated by its crystalline, fully tetrahedrally bonded structure. Here authors synthesize a bulk sp 3-bonded amorphous form of carbon under high pressure and temperature, show that it has bulk modulus comparable to crystalline diamond and that it can be recovered under ambient conditions.
- Zhidan Zeng
- , Liuxiang Yang
- & Ho-kwang Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of bulk artificial nacre with excellent mechanical properties
Mass production of bulk artificial nacre with excellent mechanical properties
Artificial materials that replicate the mechanical properties of nacre represent important structural materials, but are difficult to produce in bulk. Here, the authors exploit the bottom-up assembly of 2D nacre-mimetic films to fabricate 3D bulk artificial nacre with an optimized architecture and excellent mechanical properties.
- Huai-Ling Gao
- , Si-Ming Chen
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Oscillatory vapour shielding of liquid metal walls in nuclear fusion devices
Oscillatory vapour shielding of liquid metal walls in nuclear fusion devices
Vapour shielding is one of the interesting mechanisms for reducing the heat load to plasma facing components in fusion reactors. Here the authors report on the observation of a dynamic equilibrium between the plasma and the divertor liquid Sn surface leading to an overall stable surface temperature.
- G. G. van Eden
- , V. Kvon
- & T. W. Morgan
-
Article
| Open Access In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
To improve mechanical properties in ceramics through grain boundary engineering, precise mechanical characterization of individual boundaries is vital yet difficult to achieve. Here authors perform experiments using an in situ scanning electron microscopy based double cantilever beam test, allowing to directly view and measure stable crack growth in silicon carbide.
- Giorgio Sernicola
- , Tommaso Giovannini
- & Finn Giuliani
-
Article
| Open Access Common mechanism of thermodynamic and mechanical origin for ageing and crystallization of glasses
Common mechanism of thermodynamic and mechanical origin for ageing and crystallization of glasses
Glass is characterized by stochastic and slow structural relaxation dynamics, whose details remain elusive due to its complicated kinetic processes. Here, the authors show that avalanche-like dynamics in both ageing and devitrifying glasses are governed by thermodynamic initiation and a transient loss in mechanical stability.
- Taiki Yanagishima
- , John Russo
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C
Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C
Hypersonic and aerospace applications motivate development of materials with improved resistance against ablation and oxidation at high temperatures. Here authors demonstrate a quaternary carbide, where sealing by surface oxides, slow oxygen diffusion and a graded structure yield improved ablation resistance over established ceramics.
- Yi Zeng
- , Dini Wang
- & Ping Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic strength improvement by utilizing room-temperature deformation twinning in a partially recrystallized VCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
Cryogenic strength improvement by utilizing room-temperature deformation twinning in a partially recrystallized VCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys have high fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures due to deformation twinning but twinning is not active in this alloy at room temperature. Here authors optimize composition and thermomechanical treatments to introduce non-recrystallized grains, producing high yield strength while maintaining good ductility.
- Y. H. Jo
- , S. Jung
- & S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Hafnium—an optical hydrogen sensor spanning six orders in pressure
Hafnium—an optical hydrogen sensor spanning six orders in pressure
For monitoring hydrogen partial pressure, optical sensors have a particular safety advantage due to absence of wiring in operation area. Here authors show hysteresis-free, reproducible change in optical transmission in palladium-capped hafnium hydride films over six orders of magnitude in hydrogen partial pressure.
- C. Boelsma
- , L. J. Bannenberg
- & B. Dam
-
Article
| Open Access Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy
Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy
Whether a polymorphic transition exists in high entropy alloys or not remains unclear since discovery of these alloys more than a decade ago. Here authors report an irreversible polymorphic transition fromfcc to hcp in the prototype FeCoCrMnNi high entropy alloy and provide evidence for fccphase being more stable than hcp phase only at high temperatures.
- Fei Zhang
- , Yuan Wu
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of metallic cation-oxygen network for anomalous thermal expansion coefficients in binary phosphate glass
Formation of metallic cation-oxygen network for anomalous thermal expansion coefficients in binary phosphate glass
Physical properties of glasses are closely related to their amorphous structures, which can form complex networks depending on the chemical constituents. Here, Onoderaet al. unlock this relationship in a zinc phosphate glass at an atomistic level, which may shed light on new material designs.
- Yohei Onodera
- , Shinji Kohara
- & Takahiro Ohkubo
-
Article
| Open Access High pressure synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase of the high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi
High pressure synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase of the high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi
High-entropy alloys represent a new strategy for the design of materials with properties superior to those of conventional alloys, but are largely limited to simple phases of cubic symmetry. By applying high pressures on CrMnFeCoNi, here authors demonstrate synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase.
- Cameron L. Tracy
- , Sulgiye Park
- & Wendy L. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Energy landscape-driven non-equilibrium evolution of inherent structure in disordered material
Energy landscape-driven non-equilibrium evolution of inherent structure in disordered material
Fundamental understanding of glass dynamics is challenging owing to their complex non-equilibrium nature and thus the multi-dimensional potential energy landscape. Here, Fanet al. present a model to explore the glass energy landscape driven by thermal activation and relaxation, which are temporally decoupled.
- Yue Fan
- , Takuya Iwashita
- & Takeshi Egami
-
Article
| Open Access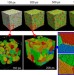 Heterogeneity in homogeneous nucleation from billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation of solidification of pure metal
Heterogeneity in homogeneous nucleation from billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation of solidification of pure metal
Nucleation is a fundamental physical process, however it is a long-standing issue whether completely homogeneous nucleation can occur. Here the authors reveal, via a billion-atom molecular dynamics simulation, that local heterogeneity exists during homogeneous nucleation in an undercooled iron melt.
- Yasushi Shibuta
- , Shinji Sakane
- & Munekazu Ohno
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
Rapid fabrication of well-controlled metallic nanostructures remains a challenge. Here, the authors directly nanoimprint several different crystalline metals by superplastic forming well below their melting temperatures, obtaining uniform nanostructures with small features and high aspect ratios in one step.
- Ze Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of acoustic Dirac-like cone and double zero refractive index
Observation of acoustic Dirac-like cone and double zero refractive index
Impedance mismatch between acoustic metamaterials and a surrounding medium hinders efficient applications, especially for zero-index materials. Here, Duboiset al. utilize the Dirac-like dispersion in a double-zero-index material to overcome this problem and to collimate sound.
- Marc Dubois
- , Chengzhi Shi
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access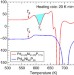 Hidden amorphous phase and reentrant supercooled liquid in Pd-Ni-P metallic glasses
Hidden amorphous phase and reentrant supercooled liquid in Pd-Ni-P metallic glasses
An anomalous exothermal calorimetric peak far below crystallization temperatures in prototypical Pd-Ni-P glasses has been recognized for four decades. Here authors use neutron and high-energy X-ray diffraction to find evidence for a polyamorphous phase transition where medium-range order undergoes large changes while short-range order changes little.
- S. Lan
- , Y. Ren
- & X. -L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Geologically-inspired strong bulk ceramics made with water at room temperature
Geologically-inspired strong bulk ceramics made with water at room temperature
Milder conditions for processing ceramics is of interest for a range of uses. Here authors report room temperature sintering of nanoparticulate powders using a solution-assisted route, yielding parts with centimetre-sized bulk parts with specific strength comparable to and possibly surpassing that of traditional structural materials like concrete.
- Florian Bouville
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Multiply fully recyclable carbon fibre reinforced heat-resistant covalent thermosetting advanced composites
Multiply fully recyclable carbon fibre reinforced heat-resistant covalent thermosetting advanced composites
The attractive strength and stability of resin matrix carbon fibre composites also make them difficult to recycle using gentle treatments which avoid degradation of structure and properties. Here authors demonstrate a composite that can be recycled for multiple cycles with little degradation.
- Yanchao Yuan
- , Yanxiao Sun
- & Lei Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical Majorana edge modes in a broad class of topological mechanical systems
Dynamical Majorana edge modes in a broad class of topological mechanical systems
Properties of topological insulators can be realized in mechanical systems, opening potential applications of topological mechanics. Here, Prodanet al. report a dynamical topological Majorana edge mode in self-assembled chains of rigid bodies with particle-hole symmetry.
- Emil Prodan
- , Kyle Dobiszewski
- & Camelia Prodan
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Materials that show twinning-induced plasticity can offer unusual combinations of strength and ductility. Here, authors study deformation twinning and dislocation behaviour in a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi and find a three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical twin network that forms from the activation of three twinning systems.
- Zijiao Zhang
- , Hongwei Sheng
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Using graphene networks to build bioinspired self-monitoring ceramics
Using graphene networks to build bioinspired self-monitoring ceramics
Micro- and nanostructures found in nature can be adopted to new uses and materials in engineered composites. Here authors demonstrate large enhancements in toughness and electrical conductivity in a ceramic upon addition of graphene at low (1 volume %) levels.
- Olivier T. Picot
- , Victoria G. Rocha
- & Eduardo Saiz
-
Article
| Open Access Complexion-mediated martensitic phase transformation in Titanium
Complexion-mediated martensitic phase transformation in Titanium
One way of tuning mechanical properties of alloys lies in utilizing athermal phase transitions. Here authors report a complexion-mediated martensitic transformation in Ti alloys yielding a nanolaminate structure of martensite bounded by planar complexions, promising new strategies for the design of high strength Ti alloys.
- J. Zhang
- , C. C. Tasan
- & D. Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access Deformation-resembling microstructure created by fluid-mediated dissolution–precipitation reactions
Deformation-resembling microstructure created by fluid-mediated dissolution–precipitation reactions
Microstructural features of deformed rocks are used to reveal deformation stresses and temperatures. Here, the authors conduct experiments showing that misleading microstructures form during fluid-mediated mineral reactions under static conditions, and propose new criteria for microstructure identification.
- Liene Spruzeniece
- , Sandra Piazolo
- & Helen E. Maynard-Casely
-
Article
| Open Access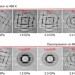 A metastable liquid melted from a crystalline solid under decompression
A metastable liquid melted from a crystalline solid under decompression
It is experimentally challenging to observe an intermediate liquid in solid–solid phase transitions due to short lifetimes of the resulting metastable states. Here, Linet al. show that a metastable bismuth liquid can be formed from a crystalline solid through decompression and maintained for hours.
- Chuanlong Lin
- , Jesse S. Smith
- & Guoyin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access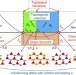 Transformable topological mechanical metamaterials
Transformable topological mechanical metamaterials
Here Rocklinet al. propose a design principle using operations that cost little energy and realize mechanical metamaterials that can be easily and reversibly transformed between states with different mechanical and acoustic properties.
- D. Zeb Rocklin
- , Shangnan Zhou
- & Xiaoming Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals
Nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals
A material with a deep melted zone (MZ) but small heat-affected zone (HAZ) is ideal for manufacturing, but improving one zone comes at the expense of the other. Here, the authors resolve this contradiction in metals by adding nanoparticles, which change the metals’ properties in such a way that both expands MZ and minimizes HAZ.
- Chao Ma
- , Lianyi Chen
- & Xiaochun Li

 Strong grain neighbour effects in polycrystals
Strong grain neighbour effects in polycrystals