Featured
-
-
Article |
 A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
An approach that exploits two bioorthogonal photochemistries to achieve reversible immobilization of full-length proteins in synthetic hydrogels allows for the reversible differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts.
- Cole A. DeForest
- & David A. Tirrell
-
-
News & Views |
 Mapping curved wrinkles
Mapping curved wrinkles
A theory explains the role of curvature in controlling wrinkle patterns on elastic shells.
- Christian Santangelo
-
News & Views |
 Hydraulic cracking
Hydraulic cracking
Cracks in stretched epithelial tissue are caused by a build-up of hydraulic pressure beneath the cells when the tissue is unloaded.
- Emad Moeendarbary
- & Guillaume Charras
-
News & Views |
 Single-molecule contacts exposed
Single-molecule contacts exposed
Using a scanning tunnelling microscopy-based method it is now possible to get an atomistic-level description of the most probable binding and contact configuration for single-molecule electrical junctions.
- Richard J. Nichols
- & Simon J. Higgins
-
Article |
 Curvature-induced symmetry breaking determines elastic surface patterns
Curvature-induced symmetry breaking determines elastic surface patterns
A generalized theory is provided for the quantitative description of wrinkling morphologies and of the transitions between surface patterns in curved elastic bilayer materials.
- Norbert Stoop
- , Romain Lagrange
- & Jörn Dunkel
-
-
Letter |
 Nanometre-scale evidence for interfacial dissolution–reprecipitation control of silicate glass corrosion
Nanometre-scale evidence for interfacial dissolution–reprecipitation control of silicate glass corrosion
The usual model of glass corrosion is based on diffusion-coupled hydration and selective cation release. A novel corrosion mechanism now suggests that interfacial dissolution–reprecipitation may be a universal process that controls both silicate glass corrosion and mineral weathering.
- Roland Hellmann
- , Stéphane Cotte
- & Antoine Seyeux
-
-
Editorial |
 Assembling insight
Assembling insight
Model colloidal systems are a testbed for understanding aspects of the organization of matter.
-
News & Views |
 A switch for phase shifting
A switch for phase shifting
Temperature can switch the thermodynamic phase of colloid–polymer mixtures by tipping the balance between competing attractive interactions induced by polymer depletion or adsorption.
- Ah-Young Jee
- , Boyce Tsang
- & Steve Granick
-
News & Views |
 Reversible actuation
Reversible actuation
Janus ellipsoids self-assemble into self-limiting fibres that can be reversibly actuated by applying an electric field.
- Eric M. Furst
-
News & Views |
 Mediated by a liquid
Mediated by a liquid
The nucleation of a crystal within another can involve intermediate liquid nuclei.
- Eduardo Sanz
- & Chantal Valeriani
-
Commentary |
 Order through entropy
Order through entropy
Understanding entropic contributions to common ordering transitions is essential for the design of self-assembling systems with addressable complexity.
- Daan Frenkel
-
News & Views |
 Assembled with one component
Assembled with one component
Computer simulations of one-component three-dimensional icosahedral quasicrystals will help to understand the mechanisms that may stabilize them in experiments.
- Marc de Boissieu
-
News & Views |
 Enantioselective photoactivation
Enantioselective photoactivation
Circularly polarized light actualizes the formation of chiral twisted ribbons from achiral semiconductor nanoparticles.
- Bart Kahr
- & Alexander G. Shtukenberg
-
Commentary |
 Programmable self-assembly
Programmable self-assembly
Two conceptual strategies for encoding information into self-assembling building blocks highlight opportunities and challenges in the realization of programmable colloidal nanostructures.
- Ludovico Cademartiri
- & Kyle J. M. Bishop
-
Letter |
 Soft 3D acoustic metamaterial with negative index
Soft 3D acoustic metamaterial with negative index
Soft acoustic metamaterials that consist of a concentrated suspension of macroporous microbeads and that show a broadband negative acoustic refractive index are now demonstrated.
- Thomas Brunet
- , Aurore Merlin
- & Olivier Mondain-Monval
-
Article |
 Computational self-assembly of a one-component icosahedral quasicrystal
Computational self-assembly of a one-component icosahedral quasicrystal
A body-centred icosahedral quasicrystal has been assembled, by using molecular dynamics simulations, from a one-component fluid of particles interacting via a tunable, isotropic pair potential.
- Michael Engel
- , Pablo F. Damasceno
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Letter |
 Entropic shrinkage of an oxide glass
Entropic shrinkage of an oxide glass
Entropic elasticity, typical of rubbers and known to also occur in organic polymers with certain network structures, is now demonstrated for phosphate-glass fibres with highly anisotropic structures.
- Seiji Inaba
- , Hideo Hosono
- & Setsuro Ito
-
Letter |
 High thermal conductivity in amorphous polymer blends by engineered interchain interactions
High thermal conductivity in amorphous polymer blends by engineered interchain interactions
A high density of strong hydrogen bonds connecting two polymers that are homogeneously mixed in a thin film is shown to enhance the intrachain thermal conductance, boosting thermal transport in fully organic layers.
- Gun-Ho Kim
- , Dongwook Lee
- & Kevin P. Pipe
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Smart hybrid materials by conjugation of responsive polymers to biomacromolecules
Smart hybrid materials by conjugation of responsive polymers to biomacromolecules
The properties and applications of biomacromolecules, for example proteins, can be enhanced by the covalent attachment of synthetic polymers. This Review discusses the modification of these biomacromolecules with stimuli-responsive polymers.
- Isidro Cobo
- , Ming Li
- & Sébastien Perrier
-
Article |
 Actuation of shape-memory colloidal fibres of Janus ellipsoids
Actuation of shape-memory colloidal fibres of Janus ellipsoids
Experiments and computer simulations show that Janus ellipsoids can self-assemble into self-limiting fibres that have shape-memory properties and can be actuated by applying an external electric field.
- Aayush A. Shah
- , Benjamin Schultz
- & Michael J. Solomon
-
-
Letter |
 Re-entrant solidification in polymer–colloid mixtures as a consequence of competing entropic and enthalpic attractions
Re-entrant solidification in polymer–colloid mixtures as a consequence of competing entropic and enthalpic attractions
The competition between colloidal interactions resulting from polymer bridging and polymer exclusion in polymer–colloid dispersions leads to their solidification both on heating and on cooling.
- Lang Feng
- , Bezia Laderman
- & Paul Chaikin
-
Article |
 Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Lead sulphide colloidal nanocrystals are now used to harvest non-emissive triplet excitons generated in a tetracene layer. Depending on the length of the ligands capping the nanocrystals, exciton transfer efficiency as high as 90% can be achieved.
- Nicholas J. Thompson
- , Mark W. B. Wilson
- & Marc A. Baldo
-
News & Views |
 Stiffness does matter
Stiffness does matter
Extracellular-matrix stiffness regulates cell behaviour even when decoupled from ligand density and tethering.
- Sanjay Kumar
-
News & Views |
 Modulating optical power
Modulating optical power
Effective limiting of the intensity of low-power light transmitted through organic thin films under ambient conditions has been achieved by proper design of donor–acceptor systems.
- Anjun Qin
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article |
 Two-step nucleation mechanism in solid–solid phase transitions
Two-step nucleation mechanism in solid–solid phase transitions
Single-particle-resolution video microscopy of films of colloidal particles shows that solid–solid transitions between square and triangular lattices occur through a two-step nucleation mechanism that involves liquid nuclei.
- Yi Peng
- , Feng Wang
- & Yilong Han
-
News & Views |
 Sticky when wet
Sticky when wet
Inspired by the chemistry of adhesive proteins in mussels, hydrogels can now be made to self-heal in water without the aid of metal chelates.
- Jonathan J. Wilker
-
-
News & Views |
 Addressing challenges
Addressing challenges
Although promising, the use of organic semiconductors has not yet revolutionized consumer electronics. Synthesis of high-performance materials, enhanced control of morphology and smart exploitation of unique photophysical phenomena are the way forward to overcome the technological hurdles of this field.
- John E. Anthony
-
News & Views |
 Organic electronics meets biology
Organic electronics meets biology
The structural similarity of organic semiconductors to biological compounds suggests the use of these materials in biomedical applications, yet their implementation is not straightforward. Research in this area is growing fast, thanks to the combined efforts of the multidisciplinary bioelectronics community.
- Guglielmo Lanzani
-
-
Article |
 Extracellular matrix stiffness and composition jointly regulate the induction of malignant phenotypes in mammary epithelium
Extracellular matrix stiffness and composition jointly regulate the induction of malignant phenotypes in mammary epithelium
Malignant phenotypes in the mammary epithelium have been correlated to increases in extracellular matrix stiffness. It is now shown that the effect of matrix stiffness in normal mammary epithelial cells can be offset by an increase in basement-membrane ligands and that both the stiffness and composition of the matrix are sensed by the β4 integrin. The results suggest that the relationship between matrix stiffness and composition is a more relevant predictor of breast-cancer progression.
- Ovijit Chaudhuri
- , Sandeep T. Koshy
- & David J. Mooney
-
Letter |
 Electrostatic control of block copolymer morphology
Electrostatic control of block copolymer morphology
Block copolymers can self-assemble into nanostructures that simultaneously facilitate ion transport and provide mechanical stability. Highly asymmetric charge cohesion effects are now shown to induce the formation of nanostructures with percolated phases desired for ion transport. This strategy could lead to the design of enhanced battery electrolyte materials.
- Charles E. Sing
- , Jos W. Zwanikken
- & Monica Olvera de la Cruz
-
Letter |
 Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Liquid-crystalline elastomers combine rubber-like elasticity with the optical properties of liquid crystals, yet some of their properties depend on the particular liquid-crystal phase. Now, stretchable gels of the liquid-crystalline blue-phase I are reported. The blue-phase gels are electro-optically switchable under a moderate applied voltage, and their optical properties can be manipulated by an applied strain.
- F. Castles
- , S. M. Morris
- & H. J. Coles
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Sticky mechanical memory
Sticky mechanical memory
Physical cues from the extracellular environment influence the lineage commitment of stem cells. Now, experiments on human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on photodegradable hydrogels show that the cells' fate can also be determined by past physical environments.
- Jeroen Eyckmans
- & Christopher S. Chen
-
Article |
 New metastable form of ice and its role in the homogeneous crystallization of water
New metastable form of ice and its role in the homogeneous crystallization of water
At sufficiently low temperature, liquid water crystallizes into ices with cubic or hexagonal symmetry. A simulation study now shows that the nucleation of water into atomic stackings of cubic and hexagonal ices occurs through a metastable precursor phase with tetragonal symmetry, and that this scenario provides an explanation for the unusual pressure dependence of water’s homogeneous crystal-nucleation temperature.
- John Russo
- , Flavio Romano
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
-
Article |
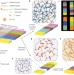 Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles
Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles
The use of encoded microparticles in industrial settings is hampered by issues of scalability, decoding robustness and encoding density. Now, easily decodable microparticles with spatially patterned rare-earth upconversion nanocrystals, exponentially scalable encoding capacities and ultralow decoding false-alarm rates that are insensitive to harsh processing environments and can be used in practical applications such as durable anti-counterfeiting labels and multiplexed bioassays are reported.
- Jiseok Lee
- , Paul W. Bisso
- & Patrick S. Doyle
-
Article |
 Synthesis and patterning of tunable multiscale materials with engineered cells
Synthesis and patterning of tunable multiscale materials with engineered cells
Biofilms are multifunctional and environmentally responsive assemblies of living and non-living components. By using synthetic gene networks in engineered cells to regulate the production of extracellular amyloid fibrils, and by interfacing the fibrils with inorganic materials such as metal nanoparticles, stimuli-responsive synthetic biofilms with switchable functions and tunable composition and structure have now been produced.
- Allen Y. Chen
- , Zhengtao Deng
- & Timothy K. Lu
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Electric fields line up graphene oxide
Electric fields line up graphene oxide
The macroscopic alignment of dilute dispersions of graphene oxide can be controlled, with extremely large optical sensitivity, through the application of weak electric fields.
- Ju Young Kim
- & Sang Ouk Kim

 Solid friction between soft filaments
Solid friction between soft filaments Soft implants for long-term use
Soft implants for long-term use Vacant holes
Vacant holes The force of shape
The force of shape Hydrogels evolve hydrogen
Hydrogels evolve hydrogen The importance of coherence
The importance of coherence Base-pair quality check
Base-pair quality check Soft-hearted robots
Soft-hearted robots Twisting thread
Twisting thread