Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
Pentagonal polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-based giant atoms self-assemble into Frank–Kasper phases that have not been previously observed in soft-matter systems.
- Pengyu Chen
- & Kevin D. Dorfman
-
Article |
 Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking
Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking
Lack of local phase patterning in liquid crystal elastomers has hindered their broad implementation. The authors report a laser-induced dynamic crosslinking approach with allyl sulfide groups to achieve reconfigurable high-resolution patterning of multiple liquid crystalline phases in a single film.
- Seok Hwan Choi
- , Ju Hee Kim
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Article |
 Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Conventional iontronic pressure sensors suffer from signal drift and inaccuracy owing to creep of soft materials and ion leakage. Here the authors report a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte-elastomer-based iontronic sensor that achieves a drift rate two to three orders of magnitude lower than those of conventional iontronic sensors.
- Yunfeng He
- , Yu Cheng
- & Chuan Fei Guo
-
Article |
 Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
The authors report the inverse effect of chiral-induced spin selectivity in an organic material.
- Rui Sun
- , Kyung Sun Park
- & Dali Sun
-
Article |
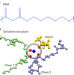 Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Solvation dynamics at picosecond timescales critically affect charge transport in aqueous systems, but conflicting values have been reported for organic electrolytes. Lifetimes on the order of 1 ns for mixtures of organic polymer and lithium salt exhibiting ultraslow dynamics of solvation shell break-up are now reported.
- Neel J. Shah
- , Chao Fang
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article |
 Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Understanding mesoscale structure and dynamics in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors is crucial. Mesoscale strain kinetics and structural hysteresis have been studied, and they uncover the coupling between charge carrier dynamics and mesoscale order in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Christopher J. Takacs
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Active and stable catalysts to accelerate the transition from fossil fuel to renewable feedstocks, reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental footprints are needed. Electrocatalysts based on copper nanocrystals encapsulated in hybrid alumina shells stable against structural reconstruction during CO2 electroreduction are reported.
- Petru P. Albertini
- , Mark A. Newton
- & Raffaella Buonsanti
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Light-induced artificial goosebumps on liquid crystal elastomer skin are used to precisely manipulate passive microstructures, achieving a localized and controllable system for programmable micromachines.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Aniket Pal
- & Metin Sitti
-
News & Views |
 Stronger together
Stronger together
Considering responsive materials as transient collective assemblies rather than individual shape-changing objects allows for emergent functionalities that cannot be derived from the properties of single objects but are driven by interactions between them.
- Arri Priimagi
-
News & Views |
 Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Early detection of electrical degradation can be identified by colour change due to the chromogenic response of blended molecules in dielectric polymers.
- Gregory A. Sotzing
- & Pritish S. Aklujkar
-
Article |
 Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals
Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals
Soft building blocks tend to be near spherical, limiting their packing structures to those found in metallic systems. Here the authors report the spontaneous generation of highly deformed mesoatoms using molecular pentagons and observe Frank–Kasper phases not found in metal alloys.
- Xian-You Liu
- , Xiao-Yun Yan
- & Stephen Z. D. Cheng
-
Article |
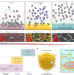 Network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres creates ultrastiff and water-rich hydrospongels
Network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres creates ultrastiff and water-rich hydrospongels
Biological tissues are extremely water rich but remain mechanically stiff, behaviour that is difficult to recapitulate in synthetic materials. Here the authors design a hydrogel/sponge hybrid material driven by a self-organized network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres that combines these properties for biofunctional materials.
- Minkyung Lee
- , Hojung Kwak
- & Dongyeop X. Oh
-
Article |
 Material assembly from collective action of shape-changing polymers
Material assembly from collective action of shape-changing polymers
Autonomous assembly, reconfiguration and disassembly are observed in living aggregates, but are difficult to replicate in synthetic soft matter. Here mechanically interlocked responsive ribbons form transient viscoelastic solids for the on-demand assembly of functional materials.
- Mustafa K. Abdelrahman
- , Robert J. Wagner
- & Taylor H. Ware
-
Feature |
 Controlling supramolecular gels
Controlling supramolecular gels
Kinetic trapping in supramolecular gels leads to varied morphologies and macroscopic properties. Emily R. Draper and Dave J. Adams discuss subtle experimental effects that can lead to reproducibility issues in these systems.
- Emily R. Draper
- & Dave J. Adams
-
News & Views |
 Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Incorporating additives that contain hydrogen-bonding nanochannels creates nanoconfined polymer gels that are highly stretchable, elastic and insensitive to notch propagation.
- Meixiang Wang
- & Michael D. Dickey
-
News & Views |
 Bridging the gap in mesoscopic length scales
Bridging the gap in mesoscopic length scales
Elastic microphase separation controls the characteristic mesoscopic length scale of bulk bicontinuous materials.
- Jörg G. Werner
-
News & Views |
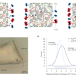 Through the MOF looking glass
Through the MOF looking glass
Processible centimetre-scale porous glasses using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF) materials are developed, while fine-tuning of the processing conditions allows control of pore size and molecular sieving properties.
- Georgia R. F. Orton
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
Article |
 Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Early detection of electrical degradation in dielectric polymers is crucial but remains challenging. A general strategy of blending the polymer with chromogenic molecules is reported, which generates a visually discernible colour change as chemically activated by oxygen radicals generated in situ, indicating the early stage of electrical degradation in polymers.
- Xiaoyan Huang
- , Shuai Zhang
- & Jinliang He
-
Article |
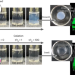 Percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation in a dilute polymer network
Percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation in a dilute polymer network
A dilute water–polymer mixture exhibits a percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation, resulting in a two gel co-continuous substrate, which is used for adipose tissue development.
- Shohei Ishikawa
- , Yasuhide Iwanaga
- & Takamasa Sakai
-
News & Views |
 Deciphering polymer networks
Deciphering polymer networks
An approach to analyse the deformation behaviour of polymer networks provides an enhanced set of structural information, improving our understanding of the elasticity of soft materials.
- Michael Lang
-
Article |
 Elastic microphase separation produces robust bicontinuous materials
Elastic microphase separation produces robust bicontinuous materials
Production of bulk bicontinuous materials is limited by the ability to make uniform microarchitectures across large volumes. Here elastic microphase separation is used to fabricate bicontinuous materials with a homogeneous microstructure, with feature sizes tuned by the matrix stiffness.
- Carla Fernández-Rico
- , Sanjay Schreiber
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article |
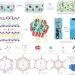 Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Simultaneously highly elastic and deformable gels that maintain their mechanical properties have remained elusive. Here, using in situ polymerization confined within nanochannels, the authors prepare hysteresis-free gels insensitive to crack propagation.
- Weizheng Li
- , Xiaoliang Wang
- & Feng Yan
-
Article |
 Accurate computational design of three-dimensional protein crystals
Accurate computational design of three-dimensional protein crystals
The process of protein crystallization is poorly understood and difficult to program through the primary sequence. Here the authors develop a computational approach to designing three-dimensional protein crystals with prespecified lattice architectures with high accuracy.
- Zhe Li
- , Shunzhi Wang
- & David Baker
-
News & Views |
 Painting on programmable reconfigurable metastructures
Painting on programmable reconfigurable metastructures
Lattices of micrometre-sized metamaterials embedded in thermoresponsive hydrogels deform upon heating to reveal encrypted images from a blank gel canvas.
- Zixiao Liu
- & Ximin He
-
Article |
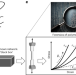 Forensics of polymer networks
Forensics of polymer networks
Extracting information about polymer network topology from mechanical properties alone remains challenging. Here the authors develop a forensic approach to quantify network structural information by analysing their nonlinear mechanics.
- Andrey V. Dobrynin
- , Yuan Tian
- & Sergei S. Sheiko
-
Article
| Open Access The laminin–keratin link shields the nucleus from mechanical deformation and signalling
The laminin–keratin link shields the nucleus from mechanical deformation and signalling
Laminin, an important component of the extracellular matrix supporting the epithelium, hinders the typical mechanoresponse of epithelial cells to an increase in substrate stiffness, by protecting the cell nucleus from mechanical deformation.
- Zanetta Kechagia
- , Pablo Sáez
- & Pere Roca-Cusachs
-
Article |
 Controlling liquid–liquid phase behaviour with an active fluid
Controlling liquid–liquid phase behaviour with an active fluid
The rational design of out-of-equilibrium demixing transitions remains challenging. Active fluids are used to control the liquid–liquid phase separation of passive DNA nanostars and establish the activity-based control of the phase diagram.
- Alexandra M. Tayar
- , Fernando Caballero
- & Zvonimir Dogic
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel muscles powering reconfigurable micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum programmability
Hydrogel muscles powering reconfigurable micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum programmability
It is difficult to program a single stimuli-responsive geometry to transform into diverse final configurations in a systematic manner. Here, linearly responsive transparent hydrogels are developed to create micro-metastructures with wide-spectrum thermal reconfigurability.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Aniket Pal
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of physically robust hydrogels
Rapid fabrication of physically robust hydrogels
Hydrogels are promising materials but are often limited by inadequate mechanical properties and time-consuming fabrication processes. Here the authors demonstrate a rapid biomimetic interfacial-bonding nanocomposite strategy for ultra-tough hydrogels with high tensile strength.
- Bingkun Bao
- , Qingmei Zeng
- & Linyong Zhu
-
Article |
 Frictionless multiphasic interface for near-ideal aero-elastic pressure sensing
Frictionless multiphasic interface for near-ideal aero-elastic pressure sensing
Solid-state pressure sensors have performance limitations in liquid environments. Here, the authors design a pressure sensor using solid–liquid–liquid–gas multiphasic interfaces where a trapped air layer modulates capacitance changes with pressure to achieve near-friction-free contact line motions for near-ideal pressure sensing.
- Wen Cheng
- , Xinyu Wang
- & Benjamin C. K. Tee
-
News & Views |
 Microcrystal actuator arrays see the light
Microcrystal actuator arrays see the light
Photochromic molecular crystal arrays aligned in the micropores of a polymer membrane show high-performance actuation when stimulated by light. These soft composites might find applications in soft robotic devices.
- Albert P. H. J. Schenning
-
Article |
 Photo-actuators via epitaxial growth of microcrystal arrays in polymer membranes
Photo-actuators via epitaxial growth of microcrystal arrays in polymer membranes
Photomechanical crystals are promising materials for converting photon energy into macroscopic work via reversible structural changes when exposed to light. Here the authors demonstrate highly ordered and compliant microcrystalline composites with a photomechanical performance exceeding that of single crystals.
- Wenwen Xu
- , David M. Sanchez
- & Ryan C. Hayward
-
Article
| Open Access Elimination of charge-carrier trapping by molecular design
Elimination of charge-carrier trapping by molecular design
Extrinsic impurities may trap electrons or holes leading to imbalanced charge transport in wide band gap organic semiconductors. Here the authors propose a bottom-up design strategy by spatially separating HOMO and LUMO orbitals to avoid charge trapping, enhancing charge transport by orders of magnitude.
- Oskar Sachnik
- , Xiao Tan
- & Paul W. M. Blom
-
News & Views |
 Better electronics from immiscibility
Better electronics from immiscibility
A bicontinuous conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrical conductivity, stretchability and fracture toughness in physiological environments achieves high-fidelity monitoring and effective stimulation of tissues and organs.
- Youdi Liu
- , Faheem Ershad
- & Cunjiang Yu
-
Article |
 Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Strong yet releasable metamaterial adhesives are fabricated using nonlinear cut architectures to achieve control of the crack propagation interface for programmable, directional and spatially selective adhesion.
- Dohgyu Hwang
- , Chanhong Lee
- & Michael D. Bartlett
-
Article |
 Electro-thermal actuation in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites
Electro-thermal actuation in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites
Piezoelectric actuators play a critical role in precision positioning devices; however, materials with high actuation strain and mechanical energy density are rare. Here a composite of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and TiO2 demonstrates superior performance in these metrics, with the ferroelectric transition driven by Joule heating.
- Yang Liu
- , Yao Zhou
- & Qing Wang
-
Article |
 Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Understanding charge-compensating interactions and ionic dynamics in organic mixed conductors can be challenging. Operando NMR spectroscopy is now used to quantify cation and water movement during doping/dedoping in mixed conductor films.
- Dongxun Lyu
- , Yanting Jin
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Soft porous crystals combine high crystallinity with structural transformability, potentially enabling applications. Here, an atropisomeric covalent organic framework is reported, which demonstrates different structural transformations upon exposure to different gases.
- Chengjun Kang
- , Zhaoqiang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article |
 High-efficiency stretchable light-emitting polymers from thermally activated delayed fluorescence
High-efficiency stretchable light-emitting polymers from thermally activated delayed fluorescence
We synthesized stretchable electroluminescent polymers capable of reaching a near-unity theoretical quantum yield through thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Their polymers show 125% stretchability with 10% external quantum efficiency and demonstrate a fully stretchable organic light-emitting diode.
- Wei Liu
- , Cheng Zhang
- & Sihong Wang
-
Article |
 The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
Redox-active non-conjugated radical polymers are promising candidates for metal-free aqueous batteries but their energy storage mechanism in an aqueous environment remains unclear. The role of the electrolyte in such polymers for designing metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes is now elucidated.
- Ting Ma
- , Cheng-Han Li
- & Jodie L. Lutkenhaus
-
Article |
 An ordered, self-assembled nanocomposite with efficient electronic and ionic transport
An ordered, self-assembled nanocomposite with efficient electronic and ionic transport
A polymer semiconductor/ionic-liquid nanocomposite exhibiting mixed conduction is reported. Using operando X-ray scattering, dynamic structural changes are observed on electrochemical charging, which enables efficient electronic transport.
- Tyler J. Quill
- , Garrett LeCroy
- & Christopher J. Takacs
-
Article
| Open Access Polarity and chirality control of an active fluid by passive nematic defects
Polarity and chirality control of an active fluid by passive nematic defects
Defects of a passive nematic liquid crystal made from actin filaments pattern the collective behaviour of active microtubules, creating macroscopic polar patterns and chiral loops.
- Alfredo Sciortino
- , Lukas J. Neumann
- & Andreas R. Bausch
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Self-regenerating living material made of printed fungi
Self-regenerating living material made of printed fungi
Three-dimensional printing of hydrogels loaded with fungal mycelium can produce living materials with unique adaptive properties in shapes that are relevant for engineering applications. The metabolic activity of the living mycelial network allows the printed structure to grow autonomously and self-regenerate when it is provided with nutrients in water.
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional printing of mycelium hydrogels into living complex materials
Three-dimensional printing of mycelium hydrogels into living complex materials
Complex living structures with self-healing and regeneration capabilities are 3D printed using bioinks composed of fungal mycelium and an agar-based hydrogel.
- Silvan Gantenbein
- , Emanuele Colucci
- & André R. Studart
-
Article |
 Optimized design of block copolymers with covarying properties for nanolithography
Optimized design of block copolymers with covarying properties for nanolithography
A discovery-oriented synthesis and characterization platform uses interchangeable polymer components to explore a large and complex parameter space to find possible combinations of components that satisfy the design rules at multiple nanolithography patterns dimensions.
- Hongbo Feng
- , Moshe Dolejsi
- & Paul F. Nealey
-
Article |
 Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Independently tailored nano- and mesoscale features are obtained in hierarchically assembled mixed graft block copolymers with precisely defined side-chain sequences.
- Ruiqi Liang
- , Yazhen Xue
- & Mingjiang Zhong
-
Article |
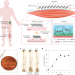 Active tissue adhesive activates mechanosensors and prevents muscle atrophy
Active tissue adhesive activates mechanosensors and prevents muscle atrophy
An implantable tissue adhesive soft actuator adheres to muscle, generating mechanical stimulation, and activates mechanosensing pathways for prevention of atrophy in disuse muscles.
- Sungmin Nam
- , Bo Ri Seo
- & David J. Mooney

 Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning
Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning