Abstract
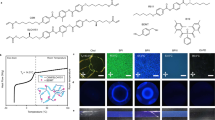
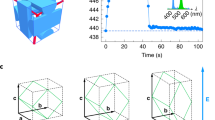
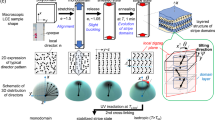
Liquid-crystalline polymers are materials of considerable scientific interest and technological value1,2,3. An important subset of these materials exhibit rubber-like elasticity, combining the optical properties of liquid crystals with the mechanical properties of rubber. Moreover, they exhibit behaviour not seen in either type of material independently2, and many of their properties depend crucially on the particular mesophase employed. Such stretchable liquid-crystalline polymers have previously been demonstrated in the nematic, chiral-nematic, and smectic mesophases2,4. Here, we report the fabrication of a stretchable gel of blue phase I, which forms a self-assembled, three-dimensional photonic crystal that remains electro-optically switchable under a moderate applied voltage, and whose optical properties can be manipulated by an applied strain. We also find that, unlike its undistorted counterpart, a mechanically deformed blue phase exhibits a Pockels electro-optic effect, which sets out new theoretical challenges and possibilities for low-voltage electro-optic devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donald, A. M., Windle, A. H. & Hanna, S. Liquid Crystalline Polymers 2nd edn (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2006).
Warner, M. & Terentjev, E. M. Liquid Crystal Elastomers (Oxford Univ. Press, 2007).
Broer, D. J., Crawford, G. P. & Žumer, S. Cross-Linked Liquid Crystalline Systems (CRC Press, 2011).
Finkelmann, H., Kock, H. J. & Rehage, G. Investigations on liquid crystalline polysiloxanes. 3: Liquid crystalline elastomers—a new type of liquid-crystalline material. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 2, 317–322 (1981).
Nakata, M. et al. End-to-end stacking and liquid crystal condensation of 6- to 20-base pair DNA duplexes. Science 318, 1276–1279 (2007).
Golubović, L. & Lubensky, T. C. Nonlinear elasticity of amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 1082–1085 (1989).
Warner, M., Bladon, P. & Terentjev, E. M. “Soft elasticity”—deformation without resistance in liquid crystal elastomers. J. Phys. II France 4, 93–102 (1994).
De Gennes, P-G. Artificial muscles based on nematic gels. Macromol. Symp. 113, 39–49 (1997).
D’allest, J. F., Gilli, J. M. & Sixou, P. Blue phase in liquid crystal polymer mixtures. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 155, 571–580 (1988).
Gilli, J. M., Kamaye, M. & Sixou, P. Phases bleues “figées” dans un polysiloxane mésomorphe. J. Phys. Fr. 50, 2911–2918 (1989).
Stegemeyer, H., Onusseit, H. & Finkelmann, H. Formation of a blue phase in a liquid-crystalline side chain polysiloxane. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 10, 571–574 (1989).
Leforestier, A. & Livolant, F. DNA liquid crystalline blue phases: Electron microscopy evidence and biological implications. Liq. Cryst. 17, 651–658 (1994).
Kitzerow, H-S. et al. Observation of blue phases in chiral networks. Liq. Cryst. 14, 911–916 (1993).
Kikuchi, H., Yokota, M., Hisakado, Y., Yang, H. & Kajiyama, T. Polymer-stabilized liquid crystal blue phases. Nature Mater. 1, 64–68 (2002).
Gerber, P. R. Electro-optical effects of a small-pitch blue-phase system. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 116, 197–206 (1985).
Hisakado, Y., Kikuchi, H., Nagamura, T. & Kajiyama, T. Large electro-optic Kerr effect in polymer-stabilized liquid-crystalline blue phases. Adv. Mater. 17, 96–98 (2005).
Chen, Y., Xu, D., Wu, S-T., Yamamoto, S-I. & Haseba, Y. A low voltage and submillisecond-response polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 141116 (2013).
Samsung Electronics, 15” Blue Phase Mode LC Display, Seminar and Exhibition Presented at the Society for Information Display (Intern. Symp., 2008).
Broer, D. J., Finkelmann, H. & Kondo, K. In-situ photopolymerization of an oriented liquid-crystalline acrylate. Makromol. Chem. 189, 185–194 (1988).
Broer, D. J., Lub, J. & Mol, G. N. Wide-band reflective polarizers from cholesteric polymer networks with a pitch gradient. Nature 378, 467–469 (1995).
Castles, F. et al. Blue-phase templated fabrication of three-dimensional nanostructures for photonic applications. Nature Mater. 11, 599–603 (2012).
McConney, M. E. et al. Electrically induced color changes in polymer-stabilized cholesteric liquid crystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 1, 417–412 (2013).
Coles, H. J. & Pivnenko, M. N. Liquid crystal ‘blue phases’ with a wide temperature range. Nature 436, 997–1000 (2005).
Finkelmann, H., Kim, S. T., Munoz, A., Palffy-Muhoray, P. & Taheri, B. Tunable mirrorless lasing in cholesteric liquid crystalline elastomers. Adv. Mater. 13, 1069–1072 (2001).
Porsch, F., Stegemeyer, H. & Hiltrop, K. Electric field-induced birefringence in liquid-crystalline blue phases. Z. Naturforsch. 39 a, 475–480 (1984).
Kitzerow, H-S. Blue phases: Prior art, potential polar effects, challenges. Ferroelectrics 395, 66–85 (2010).
Nye, J. F. Physical Properties of Crystals (Oxford Univ. Press, 1985).
Alexander, G. P. & Yeomans, J. M. Flexoelectric blue phases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 067801 (2007).
Porenta, T., Ravnik, M. & Žumer, S. Effect of flexoelectricity and order electricity on defect cores in nematic droplets. Soft Matter 7, 132–136 (2011).
Tiribocchi, A., Cates, M. E., Gonnella, G., Marenduzzo, D. & Orlandini, E. Flexoelectric switching in cholesteric blue phases. Soft Matter 9, 4831–4842 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council UK under the COSMOS project (grants EP/D04894X/1 and EP/H046658/1), and by the Defence Science & Technology Laboratory UK. We thank A. Lorenz, J. Montelongo, D. Gardiner, K. Knowles and L. Tian for useful discussions, and H. Hasebe (DIC Corp., Japan) for supplying the material UCL-011-K1. S.M.M. acknowledges The Royal Society for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.J.C. and F.C. conceived the idea. F.C., J.M.C.H., A.D.W. and S.S.C. developed the fabrication process and produced samples. F.C. carried out the experiments in the Cambridge laboratories and took the reported data. B.I.O. carried out the repeat electro-optic experiment in the Oxford laboratories. F.C. discovered the Pockels effect in distorted samples. F.C., S.J.E., B.I.O and S.M.M. interpreted the data. M.M.Q. and S.N. synthesized the bimesogenic materials. T.D.W., L.H. and C.B. supplied equipment and were collaborators on the project. S.M.M. and H.J.C. informed and directed the research. F.C. wrote the paper in collaboration with all the authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 707 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Movie 1 (WMV 12847 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Movie 2 (WMV 6623 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castles, F., Morris, S., Hung, J. et al. Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels. Nature Mater 13, 817–821 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3993
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3993
This article is cited by
-
Periodic liquid crystalline waveguiding microstructures
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Bioinspired MXene-Based Soft Actuators Exhibiting Angle-Independent Structural Color
Nano-Micro Letters (2023)
-
Nacre-inspired Zirconia/Carbon Nanocomposites with High Strength and Toughness
Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed. (2023)
-
Self-assembled liquid crystal architectures for soft matter photonics
Light: Science & Applications (2022)
-
Liquid crystal-based structural color actuators
Light: Science & Applications (2022)