Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Compaction of quasi-one-dimensional elastoplastic materials
Compaction of quasi-one-dimensional elastoplastic materials
Principles underlying crumpling of one-dimensional objects may be relevant to both biomolecular processes and to design of mechanical devices. By compacting various wires under rigid confinement and modelling observed geometric features, the authors show how friction, plasticity and torsion enhance disorder and lead to a transition from coiled to folded geometries.
- M. Reza Shaebani
- , Javad Najafi
- & Mehdi Habibi
-
Article
| Open Access Possible absence of critical thickness and size effect in ultrathin perovskite ferroelectric films
Possible absence of critical thickness and size effect in ultrathin perovskite ferroelectric films
Understanding ferroelectricity at reduced dimensions will be important for future sub-nanoscale devices based on ferroelectrics. Using high resolution electron microscopy; Gaoet al., observe the existence of a measurable polarization at a thickness of just 1.5-unit cells
- Peng Gao
- , Zhangyuan Zhang
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Organic hydrogen peroxide-driven low charge potentials for high-performance lithium-oxygen batteries with carbon cathodes
Organic hydrogen peroxide-driven low charge potentials for high-performance lithium-oxygen batteries with carbon cathodes
Reducing the charge potential is of importance to advance the performance of Li-O2 batteries. Here the authors show that hydrogen peroxide solution allows decomposition of lithium hydroxide at ∼3.5 V and the organic urea hydrogen peroxide additive enables a charge potential of only about 3.26 V and stable cycling for non-aqueous Li-O2batteries.
- Shichao Wu
- , Yu Qiao
- & Haoshen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved linear dynamics of single-molecule Brownian motion
Conserved linear dynamics of single-molecule Brownian motion
The general consensus is that random walking, such as Brownian motion, follows a linear dependence of diffusion motions with time. Here, the authors show that random motion of macromolecules in an isotropic fluid could be governed by non-random dynamics that are only detectable in their relative motions.
- Maged F. Serag
- & Satoshi Habuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective decarboxylative chlorination of β-ketocarboxylic acids
Enantioselective decarboxylative chlorination of β-ketocarboxylic acids
Due to the synthetic utility of the products, stereoselective halogenation is a powerful method for the synthesis of chiral compounds. Here the authors report an enantioselective decarboxylative chlorination, giving access to a range of α-chloroketones.
- Kazutaka Shibatomi
- , Kazumasa Kitahara
- & Seiji Iwasa
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded spintronic logic with low-dimensional carbon
Cascaded spintronic logic with low-dimensional carbon
Spintronics, graphene, and carbon nanotubes are potential components of next-generation high performance computers. Here, the authors propose and theoretically evaluate a spintronic logic family composed solely of carbon materials with the potential for a 100 × improvement in energy efficiency.
- Joseph S. Friedman
- , Anuj Girdhar
- & Alan V Sahakian
-
Article
| Open Access Quasilinear quantum magnetoresistance in pressure-induced nonsymmorphic superconductor chromium arsenide
Quasilinear quantum magnetoresistance in pressure-induced nonsymmorphic superconductor chromium arsenide
The electronic structure of the helimagnet CrAs is unusual due to its nonsymmorphic crystal symmetry. Here, the authors observe quasilinear magnetoresistance close to a pressure-driven superconducting transition, which may arise from the interaction of the band structure and magnetic fluctuations.
- Q. Niu
- , W. C. Yu
- & Swee K. Goh
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin metal-organic framework array for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting
Ultrathin metal-organic framework array for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting
Metal-organic frameworks are generally considered to be inert catalysts for many electrochemical reactions, however this is not always the case. Here the authors fabricate an ultrathin nanosheet array of metal-organic frameworks exhibiting enhanced performance toward electrocatalytic water splitting.
- Jingjing Duan
- , Sheng Chen
- & Chuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots
Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots
Growth of colloidal semiconductor quantum dots involves several stages, including an enigmatic induction period preceding nucleation. Here, the authors identify two distinct intermediates in the induction period, mapping their evolution from precursors all the way to either magic-size clusters or quantum dots.
- Mingyang Liu
- , Kun Wang
- & Kui Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Reaction-diffusion controls the spatial formation of many natural structures but is rarely applied to organic materials. Here, the authors couple reaction-diffusion to the self-assembly of a supramolecular gelator, introducing a strategy to forming soft, free-standing objects with controlled shape and functionality.
- Matija Lovrak
- , Wouter E. J. Hendriksen
- & Jan H. van Esch
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing speckle for a sub-femtometre resolved broadband wavemeter and laser stabilization
Harnessing speckle for a sub-femtometre resolved broadband wavemeter and laser stabilization
The complex speckle pattern produced by coherent multiple scattering contains information about the incident light field, which has recently been used for imaging. Metzgeret al. use speckle to construct a wavemeter with sub-femtometre resolution which is subsequently used for laser stabilization.
- Nikolaus Klaus Metzger
- , Roman Spesyvtsev
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
Article
| Open Access Hafnium—an optical hydrogen sensor spanning six orders in pressure
Hafnium—an optical hydrogen sensor spanning six orders in pressure
For monitoring hydrogen partial pressure, optical sensors have a particular safety advantage due to absence of wiring in operation area. Here authors show hysteresis-free, reproducible change in optical transmission in palladium-capped hafnium hydride films over six orders of magnitude in hydrogen partial pressure.
- C. Boelsma
- , L. J. Bannenberg
- & B. Dam
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring finite-range phase coherence in an optical lattice using Talbot interferometry
Measuring finite-range phase coherence in an optical lattice using Talbot interferometry
Quantum gas experiments are useful to study non-equilibrium many-body dynamics. Here, the authors demonstrate how the Talbot effect can be used to measure the spreading of phase coherence of ultracold atoms in an optical lattice.
- Bodhaditya Santra
- , Christian Baals
- & Herwig Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional crossbar arrays of self-rectifying Si/SiO2/Si memristors
Three-dimensional crossbar arrays of self-rectifying Si/SiO2/Si memristors
Memristors are key structural units of complex memory and computing systems, yet most currently available memristors are based on materials that are not compatible with silicon technology. Here, the authors demonstrate a CMOS-compatible, self-rectifying memristor and arrays entirely based on p-Si/SiO2/n-Si.
- Can Li
- , Lili Han
- & Qiangfei Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Organic narrowband near-infrared photodetectors based on intermolecular charge-transfer absorption
Organic narrowband near-infrared photodetectors based on intermolecular charge-transfer absorption
Interfaces of organic donor-acceptor blends provide intermolecular charge-transfer states with red-shifted but weak absorption. By introducing an optical micro-cavity; Siegmundet al., enhance their photoresponse to achieve narrowband NIR photodetection with broad spectral tunability.
- Bernhard Siegmund
- , Andreas Mischok
- & Koen Vandewal
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid visualization of grain boundaries in monolayer MoS2 by multiphoton microscopy
Rapid visualization of grain boundaries in monolayer MoS2 by multiphoton microscopy
Atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides can be grown on large scale using chemical vapour deposition which, however, determines presence of grain boundaries. Here, the authors report that third-harmonic generation imaging provides excellent sensitivity and fast speed for grain boundary visualization in MoS2.
- Lasse Karvonen
- , Antti Säynätjoki
- & Zhipei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Single-stage plasma-based correlated energy spread compensation for ultrahigh 6D brightness electron beams
Single-stage plasma-based correlated energy spread compensation for ultrahigh 6D brightness electron beams
Controlling and improving electron beam parameters are crucial for their application in free electron laser and X-ray sources. Here the authors generate quality electron beams with reduced energy spread from plasma accelerators by using a tailored escort electron bunch with the main accelerating bunch.
- G. G. Manahan
- , A. F. Habib
- & B. Hidding
-
Article
| Open Access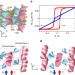 Coupled multiferroic domain switching in the canted conical spin spiral system Mn2GeO4
Coupled multiferroic domain switching in the canted conical spin spiral system Mn2GeO4
The coexistence of ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity in a multiferroic material often arises from complex magnetoelectric couplings. Here, the authors observe switching of domains in Mn2GeO4using neutron diffraction and develop a phenomenological theory to explain their results.
- T. Honda
- , J. S. White
- & T. Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access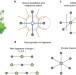 Universal fragment descriptors for predicting properties of inorganic crystals
Universal fragment descriptors for predicting properties of inorganic crystals
Machine learning methods can be useful for materials discovery; however certain properties remain difficult to predict. Here, the authors present a universal machine learning approach for modelling the properties of inorganic crystals, which is validated for eight electronic and thermomechanical properties.
- Olexandr Isayev
- , Corey Oses
- & Alexander Tropsha
-
Article
| Open Access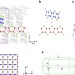 Three-dimensional Pentagon Carbon with a genesis of emergent fermions
Three-dimensional Pentagon Carbon with a genesis of emergent fermions
Whether carbon allotropes may host emergent topological fermions is unknown. Here, Zhonget al. predict a three-dimensional carbon allotrope entirely composed of pentagon rings, showing a plethora of topological fermions under strain.
- Chengyong Zhong
- , Yuanping Chen
- & Shengbai Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate prediction of X-ray pulse properties from a free-electron laser using machine learning
Accurate prediction of X-ray pulse properties from a free-electron laser using machine learning
X-ray free-electron lasers, important light sources for materials research, suffer from shot-to-shot fluctuations that necessitate complex diagnostics. Here, the authors apply machine learning to accurately predict pulse properties, using parameters that can be acquired at high-repetition rates.
- A. Sanchez-Gonzalez
- , P. Micaelli
- & J. P. Marangos
-
Article
| Open Access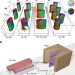 Control of morphology and formation of highly geometrically confined magnetic skyrmions
Control of morphology and formation of highly geometrically confined magnetic skyrmions
Proposals for skyrmion-based high-density memory devices require an understanding of the formation and shape of skyrmions in confined geometries. Here, the authors use electron holography to image magnetic textures in FeGe nanostripes and explore the parameters governing skyrmion morphology.
- Chiming Jin
- , Zi-An Li
- & Rafal E Dunin-Borkowski
-
Article
| Open Access Broad-spectrum kinetic resolution of alcohols enabled by Cu–H-catalysed dehydrogenative coupling with hydrosilanes
Broad-spectrum kinetic resolution of alcohols enabled by Cu–H-catalysed dehydrogenative coupling with hydrosilanes
Kinetic resolution of alcohols by silylation is an attractive method to produce enantiopure compounds, but known systems often display limited substrate scope. Here the authors report a copper catalysed enantioselective dehydrogenative silylation of alcohols that have high selectivity across a broad range of substrates.
- Xichang Dong
- , Andreas Weickgenannt
- & Martin Oestreich
-
Article
| Open Access Large spin accumulation and crystallographic dependence of spin transport in single crystal gallium nitride nanowires
Large spin accumulation and crystallographic dependence of spin transport in single crystal gallium nitride nanowires
Semiconductors are promising for high performance spintronics but the low functioning temperature hampers their applications. Here the authors achieve a strong room temperature modulation of spin-dependent resistance in GaN nanowires, which marks an important step towards practical spintronic devices.
- Tae-Eon Park
- , Youn Ho Park
- & Joonyeon Chang
-
Article
| Open Access The sands of time run faster near the end
The sands of time run faster near the end
Hourglasses measure time because the discharge rate of dry sand is constant. Here Koivistoet al. show that when such a system contains water there is a surge in discharge because the fluid drains faster than the grains, which might help us understand the transport of grains in silos.
- Juha Koivisto
- & Douglas J. Durian
-
Article
| Open Access Direct and simultaneous observation of ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium
Direct and simultaneous observation of ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium
Understanding excited carrier dynamics in semiconductors is central to the continued development of optoelectronic devices. Using extreme ultraviolet transient absorption spectroscopy, Zürchet al. directly and simultaneously observe ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium thin films.
- Michael Zürch
- , Hung-Tzu Chang
- & Stephen R. Leone
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast terahertz snapshots of excitonic Rydberg states and electronic coherence in an organometal halide perovskite
Ultrafast terahertz snapshots of excitonic Rydberg states and electronic coherence in an organometal halide perovskite
The generation of bound electron and hole pairs—excitons—is a key process in photovoltaic technologies, yet it is challenging to follow their initial dynamics. Here, Luoet al. probe the Rydberg eigenstates that characterize the excitonic transport and coherent conversion in a perovskite material.
- Liang Luo
- , Long Men
- & Jigang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental discrimination of ion stopping models near the Bragg peak in highly ionized matter
Experimental discrimination of ion stopping models near the Bragg peak in highly ionized matter
The energy loss of ions in plasma is a challenging issue in inertial confinement fusion and many theoretical models exist on ion-stopping power. Here, the authors use laser-generated plasma probed by accelerator-produced ions in experiments to discriminate various ion stopping models near the Bragg peak.
- W. Cayzac
- , A. Frank
- & M. Roth
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum test of the equivalence principle for atoms in coherent superposition of internal energy states
Quantum test of the equivalence principle for atoms in coherent superposition of internal energy states
Atom interferometers can be used in precision measurements and to test the fundamental laws of physics. Here the authors test the weak equivalence principle in the quantum regime with high sensitivity using a Bragg atom interferometer with rubidium atoms in their hyperfine states.
- G. Rosi
- , G. D’Amico
- & G. M. Tino
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Hyperpolarized molecules provide unique contrast for MRI but due to their short relaxation time need to be prepared shortly before injection. Here the authors report a method for eliminating the main source of relaxation and producing frozen polarized substances that can be stored and transported.
- Andrea Capozzi
- , Tian Cheng
- & Arnaud Comment
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of Zak phases and topological invariants in a chiral quantum walk of twisted photons
Detection of Zak phases and topological invariants in a chiral quantum walk of twisted photons
The detection of topological invariants in the bulk remains challenging even in state-of-the-art experiments. Here, Cardanoet al. propose a method to read-out the Zak phases and topological invariants in one-dimensional chiral systems and detect those in a photonic quantum walk of twisted photons.
- Filippo Cardano
- , Alessio D’Errico
- & Pietro Massignan
-
Article
| Open Access Simple and scalable growth of AgCl nanorods by plasma-assisted strain relaxation on flexible polymer substrates
Simple and scalable growth of AgCl nanorods by plasma-assisted strain relaxation on flexible polymer substrates
Rapid, scalable, low-temperature processes to fabricate nanostructures on flexible surfaces will be important for future device technologies. Parket al., develop a rigorous methodology to grow nanorods on polymer films by plasma-assisted strain relaxation.
- Jae Yong Park
- , Illhwan Lee
- & Jong-Lam Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy
Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy
Whether a polymorphic transition exists in high entropy alloys or not remains unclear since discovery of these alloys more than a decade ago. Here authors report an irreversible polymorphic transition fromfcc to hcp in the prototype FeCoCrMnNi high entropy alloy and provide evidence for fccphase being more stable than hcp phase only at high temperatures.
- Fei Zhang
- , Yuan Wu
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Article
| Open Access One-Year stable perovskite solar cells by 2D/3D interface engineering
One-Year stable perovskite solar cells by 2D/3D interface engineering
Up-scaling represents a key challenge for photovoltaics based on metal halide perovskites. Using a composite of 2D and 3D perovskites in combination with a printable carbon black/graphite counter electrode; Granciniet al., report 11.2% efficient modules stable over 10,000 hours.
- G. Grancini
- , C. Roldán-Carmona
- & Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin
-
Article
| Open Access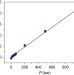 Giant barocaloric effect in the ferroic organic-inorganic hybrid [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] perovskite under easily accessible pressures
Giant barocaloric effect in the ferroic organic-inorganic hybrid [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] perovskite under easily accessible pressures
Solid-state materials that exhibit large caloric effects have the potential to replace compressed greenhouse gases in refrigeration technologies. Here the authors report near room temperature giant barocaloric effects in hybrid perovskite [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] under easily accessible pressures.
- Juan M. Bermúdez-García
- , Manuel Sánchez-Andújar
- & María A. Señarís-Rodríguez
-
Article
| Open Access Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Crystalline uraninite is believed to be the dominant form in uranium deposits. Here, the authors find that non-crystalline U(IV) generated through biologically mediated U(VI) reduction is the predominant U(IV)species in ore deposits, implying that biogenic processes are more important than previously thought.
- Amrita Bhattacharyya
- , Kate M. Campbell
- & Thomas Borch
-
Article
| Open Access Giant electron-hole transport asymmetry in ultra-short quantum transistors
Giant electron-hole transport asymmetry in ultra-short quantum transistors
By utilizing electron-hole asymmetry in ultra-short single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) transistors, McRaeet al., develop ‘two-in-one’ SWCNT quantum devices that can switch from behaving as quantum-dot transistors for holes to quantum buses for electrons by changing the transistor’s gate voltage
- A. C. McRae
- , V. Tayari
- & A. R. Champagne
-
Article
| Open Access Anapole nanolasers for mode-locking and ultrafast pulse generation
Anapole nanolasers for mode-locking and ultrafast pulse generation
Here, the authors introduce the concept of nanocscale lasers based on a tightly confined anapole mode. Using first-principle calculations they show that the superposition of internal modes can generate radiation-less states that are scattering free, potentially overcoming the limitations of conventional nanolasers.
- Juan S. Totero Gongora
- , Andrey E. Miroshnichenko
- & Andrea Fratalocchi
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven liquid metal nanotransformers for biomedical theranostics
Light-driven liquid metal nanotransformers for biomedical theranostics
Liquid metals are excellent candidate materials for biomedicine, owing to their intriguing optical properties and chemical stability. Here, the authors design multifunctional theranostic liquid metal nanocapsules that, upon irradiation, generate heat and reactive oxygen species and change shape to release drugs.
- Svetlana A. Chechetka
- , Yue Yu
- & Eijiro Miyako
-
Article
| Open Access Pairwise frictional profile between particles determines discontinuous shear thickening transition in non-colloidal suspensions
Pairwise frictional profile between particles determines discontinuous shear thickening transition in non-colloidal suspensions
Shear thickening characterizes liquid suspensions of particles that reversibly solidify subject to stress. Here, Comtetet al. show that shear thickening occurs at the transition from lubricated contacts to frictional contacts at a single-particle level, which can be linked to the change in macroscopic rheology.
- Jean Comtet
- , Guillaume Chatté
- & Annie Colin
-
Article
| Open Access Turbulence hierarchy in a random fibre laser
Turbulence hierarchy in a random fibre laser
Random fibre lasers constitute a class of lasers where the optical feedback is provided by multiple scattering in a disordered system. Here, Gonzálezet al. theoretically and experimentally study the statistical turbulence behaviour in relation to the lasing transition in such lasers.
- Iván R. Roa González
- , Bismarck C. Lima
- & Raman Kashyap
-
Article
| Open Access Hot excited state management for long-lived blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes
Hot excited state management for long-lived blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes
Large-scale commercialization of organic light-emitting diodes is impeded by the short operational lifetime of blue emitting materials. Leeet al. show a strategy to manage the energy dissipation on molecular dissociation using dopants with high triplet exciton energy that improves device stability.
- Jaesang Lee
- , Changyeong Jeong
- & Stephen R. Forrest
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time monitoring of hydrophobic aggregation reveals a critical role of cooperativity in hydrophobic effect
Real-time monitoring of hydrophobic aggregation reveals a critical role of cooperativity in hydrophobic effect
Hydrophobic interactions occur between nonpolar molecules in water and their experimental quantification can help the understanding of biological self-assembly. Here Jianget al. examine the kinetics and thermodynamics of hydrophobic aggregation in a bulk environment and characterize its cooperativity.
- Liguo Jiang
- , Siqin Cao
- & Xuhui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy is a sensitive gas detection method whereby radiation-induced sound waves from gas absorption are detected. Here, Wuet al. use the beat frequency between a modulated laser and a tuning fork resonance to increase sensitivity and avoid frequent calibrations.
- Hongpeng Wu
- , Lei Dong
- & Frank K. Tittel
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of metallic cation-oxygen network for anomalous thermal expansion coefficients in binary phosphate glass
Formation of metallic cation-oxygen network for anomalous thermal expansion coefficients in binary phosphate glass
Physical properties of glasses are closely related to their amorphous structures, which can form complex networks depending on the chemical constituents. Here, Onoderaet al. unlock this relationship in a zinc phosphate glass at an atomistic level, which may shed light on new material designs.
- Yohei Onodera
- , Shinji Kohara
- & Takahiro Ohkubo
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time visualization of clustering and intracellular transport of gold nanoparticles by correlative imaging
Real-time visualization of clustering and intracellular transport of gold nanoparticles by correlative imaging
The interaction of nanoparticles intracellularly has been investigated widely but the mechanisms of such interactions are not fully understood. Here, the authors utilize a semi-quantitative technique to assess the intracellular transportation and clustering potential of nanoparticles in real-time.
- Mengmeng Liu
- , Qian Li
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Oligolysine-based coating protects DNA nanostructures from low-salt denaturation and nuclease degradation
Oligolysine-based coating protects DNA nanostructures from low-salt denaturation and nuclease degradation
The instability of DNA nanostructures in physiological environments has hampered their use as therapeutics and diagnostic agents inin vivoapplications. Here, the authors show that coating DNA origami with oligolysine-PEG moieties improves their pharmacokinetic properties in mouse models.
- Nandhini Ponnuswamy
- , Maartje M. C. Bastings
- & William M. Shih
-
Article
| Open Access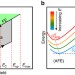 Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Antiferroelectric capacitors hold great promise for high-power energy storage. Here, through a first-principles-based computational approach, authors find high theoretical energy densities in rare earth substituted bismuth ferrite, and propose a simple model to assess the storage properties of a general antiferroelectric material.
- Bin Xu
- , Jorge Íñiguez
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent control of the silicon-vacancy spin in diamond
Coherent control of the silicon-vacancy spin in diamond
Silicon vacancy centres in diamond have favourable optical properties for use in quantum information processing. Here, the authors demonstrate coherent control of silicon vacancy spins, a prerequisite for the implementation of quantum computing operations.
- Benjamin Pingault
- , David-Dominik Jarausch
- & Mete Atatüre

 Tailoring protein nanomechanics with chemical reactivity
Tailoring protein nanomechanics with chemical reactivity