Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical nonequilibrium pathway to stabilising magnetic Weyl semimetals in pyrochlore iridates
All-optical nonequilibrium pathway to stabilising magnetic Weyl semimetals in pyrochlore iridates
Topological states may emerge in nonequilibrium but the mechanisms are much less understood. Here Topp et al. propose a nonequilibrium route to obtain the magnetic Weyl semimetallic phase in pyrochlore iridates by ultrafast modification of the effective electron-electron interactions with short laser pulses.
- Gabriel E. Topp
- , Nicolas Tancogne-Dejean
- & Michael A. Sentef
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional molecular modulators for perovskite solar cells with over 20% efficiency and high operational stability
Multifunctional molecular modulators for perovskite solar cells with over 20% efficiency and high operational stability
Engineering hybrid perovskites at the molecular level to solve the stability problem remains a challenge. Here Grätzel et al. design a multifunctional molecular modulator that interacts with the perovskite via modes elucidated by solid state NMR spectroscopy and show high efficiency and operational stability.
- Dongqin Bi
- , Xiong Li
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy-density dual-ion battery for stationary storage of electricity using concentrated potassium fluorosulfonylimide
High-energy-density dual-ion battery for stationary storage of electricity using concentrated potassium fluorosulfonylimide
Lithium-free graphite dual-ion battery offers a new means of energy storage. Here the authors show such device utilizing a highly concentrated electrolyte solution of KFSI in alkyl carbonates that exhibits a high energy density and high energy efficiency as well as an average discharge voltage of 4.7 V.
- Kostiantyn V. Kravchyk
- , Preeti Bhauriyal
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and stable high-energy lithium-sulfur full batteries with only 100% oversized lithium
Flexible and stable high-energy lithium-sulfur full batteries with only 100% oversized lithium
Lightweight and flexible energy storage devices are needed to persistently power wearable devices. Here the authors employ metallized carbon fabrics as hosts for sulfur and lithium to achieve flexibility, electrochemical stability and high energy density in a lithium-sulfur battery.
- Jian Chang
- , Jian Shang
- & Zijian Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced mRNA FISH with compact quantum dots
Enhanced mRNA FISH with compact quantum dots
FISH-based techniques to image and count mRNA in single cells can be limited by the photophysical properties of organic dyes. Here the authors develop photostable quantum dot FISH probes for multiplexed imaging.
- Yang Liu
- , Phuong Le
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling nanoscale flexoelectricity at extreme temperature by tuning cation diffusion
Enabling nanoscale flexoelectricity at extreme temperature by tuning cation diffusion
The limited number of materials with a switchable electrical polarization available for applications can be increased by exploiting the flexoelectric effect. Here, switchable polarization in nanoparticles induced by an elemental distribution dependent strain gradient up to 800 °C is demonstrated.
- Leopoldo Molina-Luna
- , Shuai Wang
- & Matias Acosta
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Fourier transform spectrometers are generally limited to slow scanning rates at high resolution. Here the authors demonstrate highly efficient Fourier transform spectroscopy using a dynamic phase-control technique that enables fast acquisition without compromising bandwidth or resolution.
- Kazuki Hashimoto
- & Takuro Ideguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Sandwich structures such as corrugated cardboard offer low weight and high bending stiffness, but they are difficult to produce at the nanoscale. Here, the authors combine webbing and perforation to produce alumina ‘nanocardboard’ with ultralow areal density that recovers without damage from extreme deformation.
- Chen Lin
- , Samuel M. Nicaise
- & Igor Bargatin
-
Article
| Open Access Rewriting the phase diagram of a diamagnetic liquid crystal by a magnetic field
Rewriting the phase diagram of a diamagnetic liquid crystal by a magnetic field
Magnetically induced phase behaviour in a soft matter system is of potential interest for magneto-responsive compounds. Here the authors fabricate a discotic ionic liquid crystalline hybrid material which can be switched from orthorhombic to cubic phase in the absence or presence of a strong magnetic field.
- Fatin Hajjaj
- , Takashi Kajitani
- & Takanori Fukushima
-
Article
| Open Access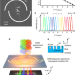 Angular-momentum nanometrology in an ultrathin plasmonic topological insulator film
Angular-momentum nanometrology in an ultrathin plasmonic topological insulator film
Multiplexed vortex light beams are promising for optical communications, but efficient mode sorting is so far limited to bulk optics. Here the authors develop a scalable vortex beam sorter that uses a plasmonic topological insulator structure to spatially separate the modes to resolve them on a standard CMOS detector.
- Zengji Yue
- , Haoran Ren
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access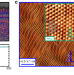 Ballistic tracks in graphene nanoribbons
Ballistic tracks in graphene nanoribbons
Electronic highways were realized by means of epitaxially grown graphene nanoribbons on SiC substrates. Here, the authors use spatially-resolved two-point probe and conductive AFM measurements, supplemented by tight-binding calculations, to image the one-dimensional ballistic transport channels.
- Johannes Aprojanz
- , Stephen R. Power
- & Christoph Tegenkamp
-
Article
| Open Access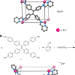 Design and self-assembly of hexahedral coordination cages for cascade reactions
Design and self-assembly of hexahedral coordination cages for cascade reactions
Supramolecular containers are promising enzyme mimics, but they currently accommodate only a limited range of chemical transformations. Here, the authors describe coordination cages that catalyze two-component cascade reactions without relying on an external or encapsulated catalytic species.
- Jingjing Jiao
- , Zijian Li
- & Yong Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Shear-band affected zone revealed by magnetic domains in a ferromagnetic metallic glass
Shear-band affected zone revealed by magnetic domains in a ferromagnetic metallic glass
Metallic glasses deform along nanoscale shear bands, and while it is known that they affect the neighboring glass regions, exactly how is unclear. Here, the authors use magnetic force microscopy to atomically resolve the shear-band affected zone and show its effects extends much further than previously thought.
- L. Q. Shen
- , P. Luo
- & W. H. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring macromolecular size distributions and interactions at high concentrations by sedimentation velocity
Measuring macromolecular size distributions and interactions at high concentrations by sedimentation velocity
Many aspects of concentrated macromolecular solutions, such as encountered in cytosol or in pharmaceutical formulations, are dependent on particle size distributions and weak intermolecular interactions. Here, the authors exploit hydrodynamic separation in the centrifugal field to measure both.
- Sumit K. Chaturvedi
- , Jia Ma
- & P. Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-hierarchical profiling the structure-activity relationships of engineered nanomaterials at nano-bio interfaces
Multi-hierarchical profiling the structure-activity relationships of engineered nanomaterials at nano-bio interfaces
Understanding nano-bio interactions is key to optimizing the biocompatible design of nanomaterials. Here, the authors combine proteomic and metabolomics studies to evaluate the effect of varying physicochemical properties of iron oxide nanoparticles in macrophage-like cells and mouse lungs.
- Xiaoming Cai
- , Jun Dong
- & Ruibin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Inherent potential of steelmaking to contribute to decarbonisation targets via industrial carbon capture and storage
Inherent potential of steelmaking to contribute to decarbonisation targets via industrial carbon capture and storage
Carbon budget is diminishing to comply with the target under 2 °C scenario. Facing the limited capacity to improve energy efficiency, the authors show that steelmaking with inherent decarbonisation process can potentially help achieve 2050 emission reduction targets under 2 °C scenario before 2030.
- Sicong Tian
- , Jianguo Jiang
- & Vasilije Manovic
-
Article
| Open Access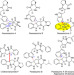 Efficient biosynthesis of heterodimeric C3-aryl pyrroloindoline alkaloids
Efficient biosynthesis of heterodimeric C3-aryl pyrroloindoline alkaloids
The hexahydropyrrolo[2, 3-b]indole (HPI) framework is found in many natural products. Here, the authors discover a P450 enzyme and develop a whole-cell biocatalysis system that produces the HPI naseseazine C (NAS-C) and 30 NAS-C analogs, several of which show neuroprotective properties.
- Wenya Tian
- , Chenghai Sun
- & Xudong Qu
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
On-chip spectrometers typically have limited spectral channels and low signal to noise ratios. Here the authors introduce a digital architecture that uses switches to change the interferometer path lengths, enabling exponentially more spectral channels per circuit element and lower noise by leveraging a machine learning reconstruction algorithm.
- Derek M. Kita
- , Brando Miranda
- & Juejun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering synergetic core-shell transformation from [Mo6O22@Ag44] to [Mo8O28@Ag50]
Deciphering synergetic core-shell transformation from [Mo6O22@Ag44] to [Mo8O28@Ag50]
Understanding how one metal nanocluster transforms into another is of synthetic and fundamental importance. Here, the authors use mass spectrometry to reveal an acid-induced structural transformation between two Ag clusters that proceeds via a breakage-growth-reassembly mechanism.
- Zhi Wang
- , Hai-Feng Su
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion-limited reactions in dynamic heterogeneous media
Diffusion-limited reactions in dynamic heterogeneous media
“Diffusing diffusivity” concept has been recently put forward to account for rapid structural rearrangements in soft matter and biological systems. Here the authors propose a general mathematical framework to compute the distribution of first-passage times in a dynamically heterogeneous medium.
- Yann Lanoiselée
- , Nicolas Moutal
- & Denis S. Grebenkov
-
Article
| Open Access Raising the redox potential in carboxyphenolate-based positive organic materials via cation substitution
Raising the redox potential in carboxyphenolate-based positive organic materials via cation substitution
Organic electrode materials could enable novelty chemistry required by the new generation of batteries. Here the authors show the synthesis and electrochemical performance of Mg(Li2)-p-DHT as a lithiated cathode material that cycles at 3.4 V due to the presence of a spectator cation in the host structure.
- Alia Jouhara
- , Nicolas Dupré
- & Philippe Poizot
-
Article
| Open Access Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Though the Preisach model successfully describes hysteretic switching in ferroelectrics, the physical reality of the model remains elusive. Here, the authors explained the origin of the experimental Preisach distribution and its effect on switching kinetics and materials’ potential applications
- Indrė Urbanavičiūtė
- , Tim D. Cornelissen
- & Martijn Kemerink
-
Article
| Open Access Design of Peptoid-peptide Macrocycles to Inhibit the β-catenin TCF Interaction in Prostate Cancer
Design of Peptoid-peptide Macrocycles to Inhibit the β-catenin TCF Interaction in Prostate Cancer
Small molecules and peptide inhibitors have their benefits and faults when it comes to inhibiting protein-protein interactions. Here, the authors designed a peptoid-peptide hybrid that inhibited β-catenin/TCF interactions, leading to inhibition of Wnt signalling in models of prostate cancer.
- Jeffrey A. Schneider
- , Timothy W. Craven
- & Susan K. Logan
-
Article
| Open Access A microfabricated nerve-on-a-chip platform for rapid assessment of neural conduction in explanted peripheral nerve fibers
A microfabricated nerve-on-a-chip platform for rapid assessment of neural conduction in explanted peripheral nerve fibers
Peripheral nerves have a complex physiology and it is therefore difficult to measure axonal activity in vitro. Here the authors make a nerve-on-a-chip platform to align peripheral nerves and permit measurement of conduction amplitude and velocity along several axons in a single experiment.
- Sandra Gribi
- , Sophie du Bois de Dunilac
- & Stéphanie P. Lacour
-
Article
| Open Access Defluorosilylation of fluoroarenes and fluoroalkanes
Defluorosilylation of fluoroarenes and fluoroalkanes
Transformation of strong C-F bonds into C-Si bonds is an extremely useful strategy for further derivatization of organic molecules. Here, the authors report a nickel-catalyzed strategy to convert aryl fluorides into sylylated arenes while defluorosilylation of alkyl fluorides is achieved under metal-free conditions.
- Benqiang Cui
- , Shichong Jia
- & Norio Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Scaling and data collapse from local moments in frustrated disordered quantum spin systems
Scaling and data collapse from local moments in frustrated disordered quantum spin systems
There are many proposals for new forms of quantum matter in frustrated magnets but in practice disorder prevents the realisation of theoretically-tractable idealised models. Kimchi et al. show that recently observed scaling behavior common to several disordered quantum magnets can be understood as the emergence of a universal random-singlet regime.
- Itamar Kimchi
- , John P. Sheckelton
- & Patrick A. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Spin transfer torque driven higher-order propagating spin waves in nano-contact magnetic tunnel junctions
Spin transfer torque driven higher-order propagating spin waves in nano-contact magnetic tunnel junctions
Nano-contact-based spin wave generation may enable high-frequency magnonic devices but has been limited to long wavelengths and weak signal strengths. Here the authors demonstrate high-order short-wavelength propagating spin waves with increased transmission rates and propagation lengths in magnetic tunnel junction stacks.
- A. Houshang
- , R. Khymyn
- & J. Åkerman
-
Article
| Open Access Universality of defect-skyrmion interaction profiles
Universality of defect-skyrmion interaction profiles
Clear understanding of the influence from material inhomogeneities and defects is one of the keys to achieve reliable Skyrmion based devices. Here the authors report their first principles studies on the interaction of single skyrmions with single-atom impurities and reveal its universal shape originated from the defect’s electron filling.
- Imara Lima Fernandes
- , Juba Bouaziz
- & Samir Lounis
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying an efficient, thermally robust inorganic phosphor host via machine learning
Identifying an efficient, thermally robust inorganic phosphor host via machine learning
Identifying phosphors with good thermal stability and quantum efficiency is a prerequisite to improve the performance of white LED light sources. Here, a combined machine learning and density functional theory method is introduced to identify next generation inorganic phosphors.
- Ya Zhuo
- , Aria Mansouri Tehrani
- & Jakoah Brgoch
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable infrared hyperbolic metasurfaces using phase change materials
Reconfigurable infrared hyperbolic metasurfaces using phase change materials
Here, the authors demonstrate that the dispersion of hyperbolic phonon polaritons can be controlled using the permittivity changes inherent in the different phases of phase change materials. This enables direct launching, reflection, transmission and refraction at the phase change material domain boundaries.
- T. G. Folland
- , A. Fali
- & J. D. Caldwell
-
Article
| Open Access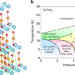 Spherical neutron polarimetry under high pressure for a multiferroic delafossite ferrite
Spherical neutron polarimetry under high pressure for a multiferroic delafossite ferrite
Spherical neutron polarimetry (SNP) experiment in conjunction with high pressure condition faces many experimental difficulties. Here the authors report development of SNP with nonmagnetic hybrid anvil high pressure cell and application to the magnetoelectric multiferroic delafossite CuFeO2 system.
- Noriki Terada
- , Navid Qureshi
- & Toyotaka Osakabe
-
Article
| Open Access Master clinical medical knowledge at certificated-doctor-level with deep learning model
Master clinical medical knowledge at certificated-doctor-level with deep learning model
AI is used increasingly in medical diagnostics. Here, the authors present a deep learning model that masters medical knowledge, demonstrated by it having passed the written test of the 2017 National Medical Licensing Examination in China, and can provide help with clinical diagnosis based on electronic health care records.
- Ji Wu
- , Xien Liu
- & Ping Lv
-
Article
| Open Access Composite fermion liquid to Wigner solid transition in the lowest Landau level of zinc oxide
Composite fermion liquid to Wigner solid transition in the lowest Landau level of zinc oxide
In two-dimensional electron systems, strong Coulomb interactions lead to the formation of new phases. Here the authors observe a transition between two of these correlated phases, a composite fermion liquid and Wigner solid, in a zinc oxide heterostructure.
- D. Maryenko
- , A. McCollam
- & M. Kawasaki
-
Article
| Open Access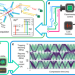 Multiparameter optimisation of a magneto-optical trap using deep learning
Multiparameter optimisation of a magneto-optical trap using deep learning
Dynamics in cold atomic ensembles involve complex many-body interactions that are hard to treat analytically. Here, the authors use machine learning to optimise the cooling and trapping of neutral atoms, showing an improvement in the resulting resonant optical depth compared to more traditional solutions.
- A. D. Tranter
- , H. J. Slatyer
- & G. T. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Self-powered H2 production with bifunctional hydrazine as sole consumable
Self-powered H2 production with bifunctional hydrazine as sole consumable
While water electrolysis provides an attractive means to produce high-energy hydrogen (H2), the process imposes significant material overpotential barriers. Here, authors employ the more-facile hydrazine splitting reaction, coupled to a hydrazine fuel cell, to perform self-powered H2 evolution.
- Xijun Liu
- , Jia He
- & Yi Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures
Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures
Manipulating the assembly of π-conjugated organic molecules into alloys to control composition and shape remains a largely unsolved problem. Here the authors show the co-assembly of two structurally similar organic semiconductors into two-component helices by control of their growth kinetics as well as the molar ratio of the building blocks.
- Yilong Lei
- , Yanqiu Sun
- & Hongbing Fu
-
Article
| Open Access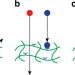 Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Gels filtering particles by interactions are a goal of nanotechnology; this is difficult when particles are larger than the mesh of the gel. Here, the authors present an equilibrium mechanism where binding dynamics of crosslinks are affected by interacting particles so that particles experience enhanced diffusion.
- Carl P. Goodrich
- , Michael P. Brenner
- & Katharina Ribbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) based therapy in solid cancers is limited. Here they repurpose nanodiamonds (NDs) as a safe and potent autophagic inhibitor to improve the efficacy of ATO-based treatment in solid tumors and show the combination therapy to work better in orthotopic liver cancer model.
- Zhifen Cui
- , Yu Zhang
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access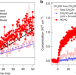 The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals has recently been suggested as the source of missing methanol in the remote troposphere. Here, the authors present direct experimental measurements demonstrating the reaction leads to further underprediction of modelled methanol.
- Rebecca L. Caravan
- , M. Anwar H. Khan
- & Craig A. Taatjes
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
The emergence of superconductivity from the normal state in the cuprates above the transition temperature (Tc) has been controversial. Here, Pelc et al. report nonlinear conductivity, resulting from superconducting precursors only, vanishing exponentially above Tc both with temperature and with magnetic field.
- Damjan Pelc
- , Marija Vučković
- & Neven Barišić
-
Review Article
| Open Access Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
Polyelectrolytes are a class of macromolecules containing charged groups. Here the authors review properties and functions of metallo-polyelectrolytes to shed light on how to harness fundamental physiochemical properties for applications in biomedical sciences and advanced materials.
- Tianyu Zhu
- , Ye Sha
- & Chuanbing Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Narrow bounds for the quantum capacity of thermal attenuators
Narrow bounds for the quantum capacity of thermal attenuators
Bounding the capacity of thermal attenuators would give a powerful instrument to describe decoherence occurring in optical fibres and free space links. Here, the authors improve on the existing upper bounds in the region of small thermal noise, which is of interest for quantum communication.
- Matteo Rosati
- , Andrea Mari
- & Vittorio Giovannetti
-
Article
| Open Access Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Interactions between metal nanoparticles (NPs) and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) in their composite forms have proven to exhibit beneficial properties. Here the authors present a unique approach to immobilise Pd NPs and, more importantly, to generate tunable basic sites within an anionic defective MOF.
- Ying Chuan Tan
- & Hua Chun Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces
Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces
Current digital coding metasurfaces are only space-encoded. Here, the authors propose space-time modulated digital coding metasurfaces to obtain simultaneous manipulations of electromagnetic waves and present harmonic beam steering, beam shaping, and scattering-signature control as application examples.
- Lei Zhang
- , Xiao Qing Chen
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
Interfering RNA have a range of therapeutic and research based applications, issues with delivery have made systems that make siRNA in situ of interest. Here, the author report on the creation of a DNA hydrogel with improved stability and transcription efficiency over plasmid DNA.
- Jaejung Song
- , Minhyuk Lee
- & Nokyoung Park
-
Article
| Open Access A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy
A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy
It is challenging to design photosensitizers (PS) with high quantum yields generating singlet oxygen due to severe aggregation between the hydrophobic PSs. Here they develop organoplatinum(II) metallatocage-based PS to overcome these challenges and show excellent antitumor effect.
- Guocan Yu
- , Shan Yu
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Exciton diffusion length and directionality are important parameters in artificial photosynthetic devices. Here, the authors present a way to make crystalline chromophore assemblies with bespoke architecture, fabricating one exhibiting anisotropic exciton transport properties.
- Ritesh Haldar
- , Marius Jakoby
- & Christof Wöll
-
Article
| Open Access Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Hematite has been proposed as a suitable photocatalyst for water splitting based on its stability and appealing optical band gap, but its performance has not reached theoretical expectations. Here the authors show that this is due to intra-gap polaronic states that reduce the effective electronic band gap.
- Christian Lohaus
- , Andreas Klein
- & Wolfram Jaegermann
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Ultrafast light pulses can manipulate and probe materials faster than relaxation timescales, leading to new electronic states and insights into equilibrium properties. Okazaki et al. use the properties of photo-induced metallic states to investigate unconventional correlated behaviour in Ta2NiSe5 and Ta2NiS5.
- Kozo Okazaki
- , Yu Ogawa
- & Shik Shin

 Engineering bacterial vortex lattice via direct laser lithography
Engineering bacterial vortex lattice via direct laser lithography