Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access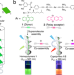 A bioinspired sequential energy transfer system constructed via supramolecular copolymerization
A bioinspired sequential energy transfer system constructed via supramolecular copolymerization
Sequential energy transfer is ubiquitous in natural light harvesting systems, but most artificial mimics have unsatisfactory energy transfer efficiency. Here, authors synthesize a sequential energy transfer system with overall efficiency of 87.4% via supramolecular copolymerization mimicking the aggregation mode of bacteriochlorophyll pigments in green photosynthetic bacteria.
- Yifei Han
- , Xiaolong Zhang
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Stability of high-temperature salty ice suggests electrolyte permeability in water-rich exoplanet icy mantles
Stability of high-temperature salty ice suggests electrolyte permeability in water-rich exoplanet icy mantles
Hot cubic ice is shown to retain dissolved salt in its lattice, suggesting the mantle of water-rich exoplanets is more permeable to electrolytes than assumed, which has implications on its properties and on the element cycles inside such planets.
- Jean-Alexis Hernandez
- , Razvan Caracas
- & Stéphane Labrosse
-
Article
| Open Access Bicyclic-ring base doping induces n-type conduction in carbon nanotubes with outstanding thermal stability in air
Bicyclic-ring base doping induces n-type conduction in carbon nanotubes with outstanding thermal stability in air
The preparation of stable n-type carbon nanotubes is desirable for their potential applications in molecular electronics. Here, the authors report that doping with bicyclic-ring organic superbases enables the synthesis of n-type carbon nanotubes with excellent thermal stability in air.
- Shohei Horike
- , Qingshuo Wei
- & Kenji Ishida
-
Article
| Open Access Secondary through-space interactions facilitated single-molecule white-light emission from clusteroluminogens
Secondary through-space interactions facilitated single-molecule white-light emission from clusteroluminogens
Although mature and systematic theories of molecular photophysics have been developed, it is still challenging to endow clusteroluminogens (CLgens) with designed photophysical properties by manipulating through-space interactions. Here, the authors design three CLgens that show multiple emissions and white-light emission in the crystalline state, and emphasize the important role of secondary through-space interactions between the acceptor and non-conjugated donor units.
- Jianyu Zhang
- , Parvej Alam
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Generation and direct observation of a triplet arylnitrenium ion
Generation and direct observation of a triplet arylnitrenium ion
Nitrenium ions are highly electrophilic reactive intermediates of formula R−N−R+, nitrogen analogue of carbenes. Here the authors report the detection of a triplet nitrenium ion using time-resolved spectroscopic methods and ab initio computations, allowing a glimpse at the properties and behavior of this important class of intermediates.
- Lili Du
- , Juanjuan Wang
- & Arthur H. Winter
-
Article
| Open Access Excited state non-adiabatic dynamics of large photoswitchable molecules using a chemically transferable machine learning potential
Excited state non-adiabatic dynamics of large photoswitchable molecules using a chemically transferable machine learning potential
The authors introduce a diabatic neural network to accelerate excitedstate, non-adiabatic simulations of azobenzene derivatives. The model predicts quantum yields for unseen species that are correlated with experiment.
- Simon Axelrod
- , Eugene Shakhnovich
- & Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli
-
Article
| Open Access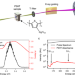 Direct observation of ultrafast exciton localization in an organic semiconductor with soft X-ray transient absorption spectroscopy
Direct observation of ultrafast exciton localization in an organic semiconductor with soft X-ray transient absorption spectroscopy
A detailed understanding of ultrafast exciton dynamics is crucial for improving the efficiency of organic light-harvesting-devices. Here, the authors track exciton localization on a sub-50 fs timescale in an organic semiconductor using time resolved soft x-ray absorption spectroscopy.
- D. Garratt
- , L. Misiekis
- & J. P. Marangos
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy reveals the homogeneous line profile of chromophores solvated in nanoclusters
High-resolution two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy reveals the homogeneous line profile of chromophores solvated in nanoclusters
Understanding the interaction of single chromophores with nanoparticles remains a challenging task in nanoscience. Here the authors provide insight into the interaction between isolated base-free phthalocyanine molecules and He and Ne nanoclusters in the gas phase using high-resolution two-dimensional spectroscopy.
- Ulrich Bangert
- , Frank Stienkemeier
- & Lukas Bruder
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Inconsistent kinetic isotope effect in ammonia charge exchange reaction measured in a Coulomb crystal and in a selected-ion flow tube
Inconsistent kinetic isotope effect in ammonia charge exchange reaction measured in a Coulomb crystal and in a selected-ion flow tube
- Shaun G. Ard
- , Albert A. Viggiano
- & Nicholas S. Shuman
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: Inconsistent kinetic isotope effect in ammonia charge exchange reaction measured in a Coulomb crystal and in a selected-ion flow tube
- L. S. Petralia
- , A. Tsikritea
- & B. R. Heazlewood
-
Article
| Open Access Lanthanum nitrate as aqueous electrolyte additive for favourable zinc metal electrodeposition
Lanthanum nitrate as aqueous electrolyte additive for favourable zinc metal electrodeposition
Zinc metal is a promising anode material for aqueous secondary batteries. However, the unfavourable morphologies formed on the electrode surface during cycling limit its application. Here, the authors report the tailoring of the surface morphology using a lanthanum nitrate aqueous electrolyte additive.
- Ruirui Zhao
- , Haifeng Wang
- & Yunhui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access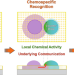 Droplets in underlying chemical communication recreate cell interaction behaviors
Droplets in underlying chemical communication recreate cell interaction behaviors
While a hallmark of living systems, developing sensory-motor interactions in inanimate systems remains challenging. Here, authors show that nanoporous surfaces can be used to create stimuli-responsive droplet interplay with shape transformation and complex behaviours reminiscent of living cell actions.
- Agustin D. Pizarro
- , Claudio L. A. Berli
- & Martín G. Bellino
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the facet surface strain state of supported multi-faceted Pt nanoparticles during reaction
Imaging the facet surface strain state of supported multi-faceted Pt nanoparticles during reaction
Understanding strain dynamics and their relationship with crystallographic facets have been largely unexplored. Here the authors demonstrate how the 3D lattice displacement and strain evolution depend on the crystallographic facets of Pt nanoparticles during CO oxidation reaction, providing new insights in the relationship between facet-related surface strain and chemistry.
- Maxime Dupraz
- , Ni Li
- & Marie-Ingrid Richard
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Is configurational entropy the main stabilizing term in rock-salt Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O high entropy oxide?
Is configurational entropy the main stabilizing term in rock-salt Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O high entropy oxide?
- Martina Fracchia
- , Mauro Coduri
- & Umberto Anselmi Tamburini
-
Article
| Open Access Fluent molecular mixing of Tau isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary tangles
Fluent molecular mixing of Tau isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary tangles
The tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease contains two isoforms. Using solid-state NMR and seeded growth of isotopically labeled tau, here the authors determined that the two isoforms mix fluently on the molecular level to propagate the AD tau structure.
- Aurelio J. Dregni
- , Pu Duan
- & Mei Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic hetero-metallic bondings visualized by sequential atom imaging
Dynamic hetero-metallic bondings visualized by sequential atom imaging
The dynamic assembly and disassembly of atoms and molecules is challenging to characterize in real time, with atomic resolution and elemental identification. Here, the authors report direct observation of more than twenty homo and hetero-metallic compounds, including labile Ag-Cu dimers and Au-Ag-Cu trimers.
- Minori Inazu
- , Yuji Akada
- & Kimihisa Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Free charge photogeneration in a single component high photovoltaic efficiency organic semiconductor
Free charge photogeneration in a single component high photovoltaic efficiency organic semiconductor
When light hits organic semiconductors, bound charge pairs, called excitons, are usually produced. Here, the authors show that in the best performing organic solar material to date, free charges, rather than excitons, are directly created by light.
- Michael B. Price
- , Paul A. Hume
- & Justin M. Hodgkiss
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the electronegativity-dominated intermediate adsorption on high-entropy alloy electrocatalysts
Unraveling the electronegativity-dominated intermediate adsorption on high-entropy alloy electrocatalysts
High-entropy alloy catalysts are an emerging class of materials and identification of catalytically active sites is critical. Here, we provide evidence that metal site electronegativity differences stabilize bound *OH and *H intermediates.
- Jiace Hao
- , Zechao Zhuang
- & Han Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Triplet-driven chemical reactivity of β-carotene and its biological implications
Triplet-driven chemical reactivity of β-carotene and its biological implications
The endoperoxides of β-carotene play a key role in signaling of photooxidative stress in plant cells and are regarded as the products of chemical deactivation of singlet oxygen. The authors show that these compounds are instead formed in a reaction between oxygen and β-carotene in their triplet states, revealing the importance of the triplet states in the photoprotection of photosynthetic apparatus.
- Mateusz Zbyradowski
- , Mariusz Duda
- & Leszek Fiedor
-
Article
| Open Access Printable logic circuits comprising self-assembled protein complexes
Printable logic circuits comprising self-assembled protein complexes
Proteins are promising molecular materials for next-generation electronic devices. Here, the authors fabricated printable digital logic circuits comprising resistors and diodes from self-assembled photosystem I complexes that enable pulse modulation.
- Xinkai Qiu
- & Ryan C. Chiechi
-
Article
| Open Access Stopping molecular rotation using coherent ultra-low-energy magnetic manipulations
Stopping molecular rotation using coherent ultra-low-energy magnetic manipulations
Manipulating the rotational motions of molecules may provide a tool for controlling chemical processes. Here the authors demonstrate that the rotation of a D2 molecule can be stopped, upon collision with a metal surface, by a magnetic field that affects the rotational levels to a much smaller extent than the energy difference upon de-excitation.
- Helen Chadwick
- , Mark F. Somers
- & Gil Alexandrowicz
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence of tetrahedral symmetry breaking in SiO2 glass under pressure
Experimental evidence of tetrahedral symmetry breaking in SiO2 glass under pressure
Understanding the structural origin of the anomalous properties of SiO2 liquid and glass at high pressures is fundamental in wide range of scientific fields. Here, the authors find experimental evidence of a bimodal behavior in the translational order of silicon’s second shell and breaking of local tetrahedral symmetry in SiO2 glass under pressure.
- Yoshio Kono
- , Koji Ohara
- & Makina Yabashi
-
Article
| Open Access The initial charge separation step in oxygenic photosynthesis
The initial charge separation step in oxygenic photosynthesis
The photosystem II reaction center (PSII-RC) is a model system to understand the initial steps of photosynthesis, but its excited state dynamics is difficult to disentangle with most spectroscopic methods. Here the authors perform a two-dimensional electronic-vibrational spectroscopic study of PSII-RC, providing detailed insight into such dynamics and into the mechanism of charge separation.
- Yusuke Yoneda
- , Eric A. Arsenault
- & Graham R. Fleming
-
Article
| Open Access High-mobility semiconducting polymers with different spin ground states
High-mobility semiconducting polymers with different spin ground states
Semiconducting polymers with high-spin at their neutral ground state are rarely reported. Here the authors synthesize three semiconducting polymers with different spin ground states and high hole/electron mobility, by appropriate choice of the building blocks’ singlet-triplet energy gap, spin distributions and solid-state interchain interactions.
- Xiao-Xiang Chen
- , Jia-Tong Li
- & Ting Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Red edge effect and chromoselective photocatalysis with amorphous covalent triazine-based frameworks
Red edge effect and chromoselective photocatalysis with amorphous covalent triazine-based frameworks
Chromoselective catalysis offers an intriguing opportunity to enable a specific reaction pathway in photocatalysis. Here, the authors look into the ability of covalent triazine frameworks to enable the synthesis of different organic compounds by using safer red light instead of harsh UV light.
- Yajun Zou
- , Sara Abednatanzi
- & Aleksandr Savateev
-
Article
| Open Access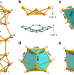 Symmetry collapse due to the presence of multiple local aromaticity in Ge244−
Symmetry collapse due to the presence of multiple local aromaticity in Ge244−
Gaining insight on the structural transformations from atomic clusters to bulk materials is challenging. Here the authors synthesize a continuous cluster of germanium Ge244−, which can be viewed as two terminal Ge9 units bridged via a Ge6 central fragment, and characterize it by several techniques including X-ray diffraction; theoretical analysis indicates the presence of three aligned independent aromatic fragments.
- Hong-Lei Xu
- , Nikolay V. Tkachenko
- & Zhong-Ming Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral photochemistry of achiral molecules
Chiral photochemistry of achiral molecules
The authors report non-adiabatic first principles molecular dynamics to show how an achiral molecule can be converted to a chiral one upon photoexcitation. These results demonstrate the possibility of asymmetric photochemistry starting from achiral reactants.
- Umberto Raucci
- , Hayley Weir
- & Todd J. Martínez
-
Article
| Open Access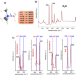 The stability of covalent dative bond significantly increases with increasing solvent polarity
The stability of covalent dative bond significantly increases with increasing solvent polarity
Non covalent complexes are often considerably destabilized in the solvent. Here the authors combine vibrational Raman and NMR spectroscopy with a coupled-cluster computational investigation to show that the solvent polarity enhance the complex stability of a Me3NBH3 complex.
- Rabindranath Lo
- , Debashree Manna
- & Pavel Hobza
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the activity of single-atom Fe-N-C catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
Insights into the activity of single-atom Fe-N-C catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
It is of high importance to understand the origin of single-atom Fe-N4 activity in oxygen reduction reaction. Here, the authors provide a model to understand the catalytic activity of Fe-N4 site from the spatial structure and energy level of the frontier orbitals by density functional theory calculations.
- Kang Liu
- , Junwei Fu
- & Min Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Using automated synthesis to understand the role of side chains on molecular charge transport
Using automated synthesis to understand the role of side chains on molecular charge transport
Development of organic electronic materials relies on understanding structure-function relationships in conjugated polymers but the synthetic workload to make large numbers of new compounds presents a practical barrier to properly survey conjugated organic derivatives. Here, the authors use automated synthesis to prepare a library of conjugated oligomers with systematically varied side chain composition followed by single-molecule characterization of charge transport.
- Songsong Li
- , Edward R. Jira
- & Charles M. Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access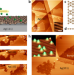 Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Here, the authors report the use of ultrahigh vacuum tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to characterize the oxidation processes of monolayer borophene with atomic-scale resolution and single-bond sensitivity, demonstrating the potential of the technique for probing the local chemistry of surface adsorbates on low-dimensional materials.
- Linfei Li
- , Jeremy F. Schultz
- & Nan Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Doubly linked chiral phenanthrene oligomers for homogeneously π-extended helicenes with large effective conjugation length
Doubly linked chiral phenanthrene oligomers for homogeneously π-extended helicenes with large effective conjugation length
Helically twisted conductive nanocarbon materials are applicable to optoelectronic and electromagnetic molecular devices but the design of nanocarbons with an absorption edge in the low energy region is challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of a helically fused oligophenanthrenes and demonstrate an increased effective conjugation length leading to an absorption edge in the NIR region.
- Yusuke Nakakuki
- , Takashi Hirose
- & Kenji Matsuda
-
Article
| Open Access Driving chemical reactions with polariton condensates
Driving chemical reactions with polariton condensates
Molecules that collectively exhibit laser-like phenomena at room temperature offer exciting prospects for the future of chemical synthesis. Here, the authors study hybrid light-molecule systems that show such a laser-like state known as a vibrational polariton condensate, and theoretically observe a large effect of this state on chemical reactivity at room temperature.
- Sindhana Pannir-Sivajothi
- , Jorge A. Campos-Gonzalez-Angulo
- & Joel Yuen-Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Direct investigation of the reorientational dynamics of A-site cations in 2D organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite by solid-state NMR
Direct investigation of the reorientational dynamics of A-site cations in 2D organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite by solid-state NMR
The reorientational dynamics of A-site cations in two-dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites play an important role in determining their physical properties. Here the authors use solid state NMR and isotope labelling to reveal multiple modes of reorientational motions of methylammonium cations and the role of structural rigidity of the organic spacers on their dynamics.
- Cheng-Chieh Lin
- , Shing-Jong Huang
- & Tsyr-Yan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid age-grading and species identification of natural mosquitoes for malaria surveillance
Rapid age-grading and species identification of natural mosquitoes for malaria surveillance
Knowing the age of malaria-transmitting mosquitoes is important to understand transmission risk as only old mosquitoes can transmit the disease. Here, the authors develop a method based on mid-infrared spectra of mosquito cuticle that can rapidly identify the species and age class of main malaria vectors.
- Doreen J. Siria
- , Roger Sanou
- & Francesco Baldini
-
Article
| Open Access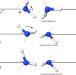 Ammonia dimer: extremely fluxional but still hydrogen bonded
Ammonia dimer: extremely fluxional but still hydrogen bonded
The long-standing question whether ammonia dimer is hydrogen bonded is solved by first-principles quantum mechanical calculations. The authors show that the dimer is extremely fluxional, but the probability of hydrogen-bonded configurations prevails.
- Jing Aling
- , Krzysztof Szalewicz
- & Ad van der Avoird
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-gated single-molecule field-effect transistors beyond Moore’s law
Dual-gated single-molecule field-effect transistors beyond Moore’s law
Conventional silicon-based transistors, which sit at the heart of every computer, are fast approaching the limit of miniaturisation. Here, Meng et al demonstrate a field-effect transistor composed of a single rutheniumdiarylethene molecule with large on/off ratio.
- Linan Meng
- , Na Xin
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Picosecond pulse-shaping for strong three-dimensional field-free alignment of generic asymmetric-top molecules
Picosecond pulse-shaping for strong three-dimensional field-free alignment of generic asymmetric-top molecules
Field-free 3D alignment of complex molecules is an important step toward the imaging of molecular dynamics. Here, the authors demonstrate pulse-shaping of long picosecond pulses for the 3D field-free alignment of the prototypical non-rotation-symmetric molecule indole.
- Terry Mullins
- , Evangelos T. Karamatskos
- & Jochen Küpper
-
Article
| Open Access Excellently balanced water-intercalation-type heat-storage oxide
Excellently balanced water-intercalation-type heat-storage oxide
There are few well-balanced heat storage materials up to date. Here, the authors report that δ-type K0.33MnO2 ∙ nH2O can be an excellently balanced heat storage material exhibiting a “water-intercalation mechanism”.
- Takuya Hatakeyama
- , Norihiko L. Okamoto
- & Tetsu Ichitsubo
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced liquid-liquid transition in a family of ionic materials
Pressure-induced liquid-liquid transition in a family of ionic materials
Liquid−liquid transitions (LLTs) have been reported for some molecular systems but are difficult to observe under high pressure conditions. Here the authors report and characterize a first-order LLT in a series of ionic liquids containing the trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium cation and anions of different sizes and shapes, using calorimetric and dielectric measurements.
- Zaneta Wojnarowska
- , Shinian Cheng
- & Marian Paluch
-
Article
| Open Access Al13− and B@Al12− superatoms on a molecularly decorated substrate
Al13− and B@Al12− superatoms on a molecularly decorated substrate
Anionic aluminium clusters are promising candidates for the fabrication of superatom-assembled nanomaterials. Here, the authors report enhanced stability for Al13− and boron-doped B@Al12− on a molecularly decorated p-type organic substrate.
- Masahiro Shibuta
- , Tomoya Inoue
- & Atsushi Nakajima
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced bond oscillations in ironpentacarbonyl give delayed synchronous bursts of carbonmonoxide release
Photoinduced bond oscillations in ironpentacarbonyl give delayed synchronous bursts of carbonmonoxide release
The photodissociation of transition metal carbonyls is involved in catalysis and synthetic processes. Here the authors, using semi-classical excited state molecular dynamics, observe details of the early stage dynamics in the photodissociation of Fe(CO)5, including synchronous bursts of CO at periodic intervals of 90 femtoseconds.
- Ambar Banerjee
- , Michael R. Coates
- & Michael Odelius
-
Article
| Open Access Uptake of N2O5 by aqueous aerosol unveiled using chemically accurate many-body potentials
Uptake of N2O5 by aqueous aerosol unveiled using chemically accurate many-body potentials
The reactive uptake of N2O5 to aqueous aerosol is a major loss channel for nitrogen oxides in the troposphere. Here authors report a theoretical investigation on the N2O5 uptake into aqueous aerosol and determine the hydrolysis rates by numerically solving a molecularly detailed reaction–diffusion equation.
- Vinícius Wilian D. Cruzeiro
- , Mirza Galib
- & Andreas W. Götz
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic fluid with phototunable dielectric permittivity
Anisotropic fluid with phototunable dielectric permittivity
Light stimuli are widely used to control material properties, yet it remains challenging to reversibly photocontrol the dielectric permittivity. Nishikawa et al. achieve this goal in an anisotropic fluid via its liquid crystal phase transition induced by isomerization of an azobenzene-tethered phototrigger.
- Hiroya Nishikawa
- , Koki Sano
- & Fumito Araoka
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
The targeted discovery of molecules with specific structural and chemical properties is an open challenge in computational chemistry. Here, the authors propose a conditional generative neural network for the inverse design of 3d molecular structures.
- Niklas W. A. Gebauer
- , Michael Gastegger
- & Kristof T. Schütt
-
Article
| Open Access Photochemistry of the pyruvate anion produces CO2, CO, CH3–, CH3, and a low energy electron
Photochemistry of the pyruvate anion produces CO2, CO, CH3–, CH3, and a low energy electron
Pyruvic acid and its conjugate base, the pyruvate anion, are largely present in the atmosphere. Here the authors, using photoelectron imaging and quantum chemistry calculations, investigate the photochemistry of isolated pyruvate anions initiated by UVA radiation and report the formation of CO2, CO, and CH3− further decomposing into CH3 and a free electron.
- Connor J. Clarke
- , Jemma A. Gibbard
- & Basile F. E. Curchod
-
Article
| Open Access Superresolution concentration measurement realized by sub-shot-noise absorption spectroscopy
Superresolution concentration measurement realized by sub-shot-noise absorption spectroscopy
Here, the authors use entangled photon pairs as the light source for absorption spectroscopy and demonstrate sub-shot-noise spectra in the entire visible wavelength region. They quantify chemical species in highly diluted solutions with precision beyond the limit of conventional spectroscopy.
- Korenobu Matsuzaki
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article
| Open Access Facet-dependent electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide over Ag3PO4 crystals
Facet-dependent electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide over Ag3PO4 crystals
The electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide is important in many industrial sectors. Here, the authors demonstrate efficient and facet-selective formation of propylene oxide using Ag3PO4 cubes and investigate the reaction mechanism.
- Jingwen Ke
- , Jiankang Zhao
- & Zhigang Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of vibronic coupling in a 4f molecular magnet with FIRMS
Analysis of vibronic coupling in a 4f molecular magnet with FIRMS
For molecular magnets and qubits, coupling between vibrations and electronic spins has a strong influence on spin state lifetime. Here, Kragskow et al present direct measurements of the vibronic transitions in a molecular magnet, showing the critical role of an “envelope effect” in the spectra.
- Jon G. C. Kragskow
- , Jonathan Marbey
- & Nicholas F. Chilton

 Single molecule demonstration of Debye–Stokes–Einstein breakdown in polystyrene near the glass transition temperature
Single molecule demonstration of Debye–Stokes–Einstein breakdown in polystyrene near the glass transition temperature