Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous symmetry breaking of dissipative optical solitons in a two-component Kerr resonator
Spontaneous symmetry breaking of dissipative optical solitons in a two-component Kerr resonator
Dissipative solitons and their symmetry breaking is important for photonic applications. Here the authors show that dissipative solitons can undergo spontaneous symmetry breaking in a two-component nonlinear optical ring resonator, resulting in the coexistence of distinct vectorial solitons with asymmetric, mirror-like states of polarization.
- Gang Xu
- , Alexander U. Nielsen
- & Miro Erkintalo
-
Article
| Open Access Full recovery of ultrafast waveforms lost under noise
Full recovery of ultrafast waveforms lost under noise
Extracting weak, ultrafast single-shot waveforms from a noisy background has critical uses in many applications. Here, the authors present a method to enhance signals and recover arbitrary waveforms from very noisy backgrounds by manipulating the physical waveform spectra in real time.
- Benjamin Crockett
- , Luis Romero Cortés
- & José Azaña
-
Article
| Open Access Long-range optofluidic control with plasmon heating
Long-range optofluidic control with plasmon heating
Here, the authors combine digital holographic microscopy with thermoplasmonics in order to identify different contributions of thermally driven fluid dynamic phenomena. They find that local thermal perturbation leads to long-range changes in the dynamics of the system, and demonstrate an all-optical control strategy for microfluidic devices.
- B. Ciraulo
- , J. Garcia-Guirado
- & R. Quidant
-
Article
| Open Access 1/f-noise-free optical sensing with an integrated heterodyne interferometer
1/f-noise-free optical sensing with an integrated heterodyne interferometer
Suppressing 1/f-shaped low-frequency noise is critical but fundamentally challenging to both electrical and optical transducers. Here, the authors demonstrate a 1/f-noise-free optical sensor with integrated CMOS-compatible heterodyne interferometer and an upconversion amplifying technique, which suppresses the noise by two orders of magnitude.
- Ming Jin
- , Shui-Jing Tang
- & Yun-Feng Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Gain-switched semiconductor laser driven soliton microcombs
Gain-switched semiconductor laser driven soliton microcombs
Here, the authors generate dissipative Kerr solitons with stable repetition rates and low optical power threshold. They achieve this by actively switching the bias current of injection-locked III-V semiconductor lasers and pulse-pumping crystalline and integrated microresonators with picosecond laser pulses.
- Wenle Weng
- , Aleksandra Kaszubowska-Anandarajah
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Point-to-point stabilized optical frequency transfer with active optics
Point-to-point stabilized optical frequency transfer with active optics
Atomic clocks and their networks are useful tools for optical communications and frequency metrology. Here the authors use phase stabilization and active tip-tilt to suppress atmospheric effects and enable optical frequency transfer through free-space.
- Benjamin P. Dix-Matthews
- , Sascha W. Schediwy
- & Peter Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Identification of neurotransmitters remains challenging for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) due to presence of noise. Here, the authors present spread spectrum SERS, which by encoding excited light and decoding SERS signals enables detection of unlabelled neurotransmitters at attomolar concentrations.
- Wonkyoung Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Kang
- & Ki-Hun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoelectromechanical modulation of a strongly-coupled plasmonic dimer
Nanoelectromechanical modulation of a strongly-coupled plasmonic dimer
Squeezing light into a nanometer gap offers strong light–matter interaction. Here, the authors develop a nanoelectromechanical system to dynamically control the gap of a plasmonic dimer at nanometer scale, enabling the realization of a light-intensity modulator that operates at high speed and with a low power consumption.
- Jung-Hwan Song
- , Søren Raza
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid guided space-time optical modes in unpatterned films
Hybrid guided space-time optical modes in unpatterned films
Waveguides typically function by using boundary conditions to contain light. Here, the authors show that by using space-time wavepackets, light can be guided in an unpatterned planar waveguide as the field remains localized along the unbounded dimension.
- Abbas Shiri
- , Murat Yessenov
- & Ayman F. Abouraddy
-
Article
| Open Access Segment-specific optogenetic stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster with linear arrays of organic light-emitting diodes
Segment-specific optogenetic stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster with linear arrays of organic light-emitting diodes
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) can offer an attractive approach for providing light stimulation in high-throughput optogenetics. Here, the authors report a microstructured OLED array that provides local photo-stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster larvae for controlled motor responses.
- Caroline Murawski
- , Stefan R. Pulver
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Free-space optical delay line using space-time wave packets
Free-space optical delay line using space-time wave packets
Delay lines are a critical part of future optical communications. Here, the authors create a delay line in free space by tuning the group velocities of multiple inline space-time wavepackets to introduce different delays.
- Murat Yessenov
- , Basanta Bhaduri
- & Ayman F. Abouraddy
-
Article
| Open Access High resolution spectral metrology leveraging topologically enhanced optical activity in fibers
High resolution spectral metrology leveraging topologically enhanced optical activity in fibers
Optical rotation in a medium, which is typically small, can be enhanced by harnessing spin-orbit interaction in fiber modes. Here the authors use this effect to develop a fiber-based wavelength-measurement technique with high resolution.
- Aaron P. Greenberg
- , Gautam Prabhakar
- & Siddharth Ramachandran
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable radiofrequency filters based on versatile soliton microcombs
Reconfigurable radiofrequency filters based on versatile soliton microcombs
For microcomb-based radiofrequency filters pulse shapers are required, which increase the system cost, footprint, and complexity. Here, the authors bypass this need by exploiting versatile soliton states inherent in microresonator and achieve reconfigurable radiofrequency filters.
- Jianqi Hu
- , Jijun He
- & Camille-Sophie Brès
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of Al2O3/2D perovskite heterostructure dielectric for high performance MoS2 phototransistors
Rational design of Al2O3/2D perovskite heterostructure dielectric for high performance MoS2 phototransistors
Designing high-performance photodetectors based on hybrid perovskites remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate that Al2O3/2D perovskite heterostructure can be utilized as photoactive dielectric for high-performance MoS2 phototransistors with broadband photoresponse, high photogain and reliability operation.
- Jiayang Jiang
- , Xuming Zou
- & Lei Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-acoustic dual-frequency comb spectroscopy
Photo-acoustic dual-frequency comb spectroscopy
Here, the authors show that the resolution and speed limitations in broadband photo-acoustic spectroscopy can be overcome by combining dual-comb spectroscopy with photo-acoustic detection. This enables broadband detection and allows for rapid and sensitive multi-species molecular analysis across all wavelengths of light.
- Thibault Wildi
- , Thibault Voumard
- & Tobias Herr
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic spatiotemporal beams that combine two independent and controllable orbital-angular-momenta using multiple optical-frequency-comb lines
Dynamic spatiotemporal beams that combine two independent and controllable orbital-angular-momenta using multiple optical-frequency-comb lines
Orbital angular momentum takes several forms in structured light beams. Here, the authors demonstrate control of dynamic spatiotemporal beams combining two forms of orbital angular momenta, by coherently adding frequency comb lines.
- Zhe Zhao
- , Hao Song
- & Alan E. Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Vernier frequency division with dual-microresonator solitons
Vernier frequency division with dual-microresonator solitons
For advanced microcomb applications, the exact detection of the high repetition rate becomes difficult due to the limited bandwidth of the photodiodes. Here, the authors present a Vernier dual-comb method to sample the main soliton comb and divide the repetition rate by a generating low frequency beat notes.
- Beichen Wang
- , Zijiao Yang
- & Xu Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond electronic timing with rising edges of photocurrent pulses
Attosecond electronic timing with rising edges of photocurrent pulses
For edge-sensitive timing applications, the edge jitter of electrical pulses is important. Here, the authors report on very low rising edge jitter extracted from an optical frequency comb and explore the best condition for low jitter by minimizing the amplitude-to-timing conversion in photodiodes.
- Minji Hyun
- , Changmin Ahn
- & Jungwon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle shortwave infrared pulses
Optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle shortwave infrared pulses
Short-wavelength infrared pulses are important for applications in strong field physics and nonlinear optics. Here the authors show multi-stage optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle SWIR pulses with carrier-envelope phase stability.
- Yu-Chieh Lin
- , Yasuo Nabekawa
- & Katsumi Midorikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular resolution imaging by post-labeling expansion single-molecule localization microscopy (Ex-SMLM)
Molecular resolution imaging by post-labeling expansion single-molecule localization microscopy (Ex-SMLM)
Previous attempts to combine expansion microscopy (ExM) and single molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) have proved challenging. Here the authors show that post-labelling Ex-SMLM improves labelling efficiency, reduces linkage error, and preserves ultrastructural details.
- Fabian U. Zwettler
- , Sebastian Reinhard
- & Markus Sauer
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid integrated photonics using bulk acoustic resonators
Hybrid integrated photonics using bulk acoustic resonators
Here, the authors demonstrate acousto-optic modulation of silicon nitride microring resonators using high-overtone bulk acoustic wave resonances, allowing modulation in the GHz range via acoustic waves. As an application, an optical isolator is demonstrated with 17 dB non-reciprocity.
- Hao Tian
- , Junqiu Liu
- & Sunil A. Bhave
-
Article
| Open Access Pushing the boundaries of optoacoustic microscopy by total impulse response characterization
Pushing the boundaries of optoacoustic microscopy by total impulse response characterization
Characterizing the total impulse response (TIR) of photoacoustic microscopes has been challenging due to difficulties distributing appropriate point sources. Here, the authors present a method for 3D generation of spatially-distributed optoacoustic point sources and show that subsequent TIR correction results in improved image quality.
- Markus Seeger
- , Dominik Soliman
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source
Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source
Microcombs provide many opportunities for integration in optical communications systems. Here, the authors implement a soliton crystal microcomb as a tool to demonstrate more than 44 Tb/s communications with high spectral efficiency.
- Bill Corcoran
- , Mengxi Tan
- & David J. Moss
-
Article
| Open Access Heteronuclear soliton molecules in optical microresonators
Heteronuclear soliton molecules in optical microresonators
Molecules of solitons provide insight into fundamental interactions between them and the underlying nonlinear system. The reported heteronuclear molecules, comprised of dissipative solitons with distinct frequencies, temporal widths, and energies enter the multistability regime and yield in interlocked frequency combs.
- Wenle Weng
- , Romain Bouchand
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Chaos-assisted two-octave-spanning microcombs
Chaos-assisted two-octave-spanning microcombs
Here, the authors demonstrate the use of chaos to obtain 2-octave comb generation. The deformation lifts the circular symmetry and creates chaotic tunneling channels that enable broadband collection of intracavity emission with a single waveguide, introducing a new degree of freedom to microcomb studies.
- Hao-Jing Chen
- , Qing-Xin Ji
- & Yun-Feng Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access A self-operating broadband spectrometer on a droplet
A self-operating broadband spectrometer on a droplet
Compact spectrometers can be useful in many applications and many sophisticated architectures have been proposed. In this work, the authors show that with an evaporating droplet on a fiber tip, spectrometry can be robustly and accurately performed with a simple and passive microfluidic system.
- P. Malara
- , A. Giorgini
- & G. Gagliardi
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot link discovery for terahertz wireless networks
Single-shot link discovery for terahertz wireless networks
At terahertz frequencies, link discovery by scanning is impractically slow. Here, the authors propose an alternative, single-shot link-finding method based on a leaky-wave device.
- Yasaman Ghasempour
- , Rabi Shrestha
- & Daniel M. Mittleman
-
Article
| Open Access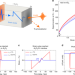 Large non-thermal contribution to picosecond strain pulse generation using the photo-induced phase transition in VO2
Large non-thermal contribution to picosecond strain pulse generation using the photo-induced phase transition in VO2
Ultrafast driving of vanadium dioxide can induce a large structural phase transition, which can be used to generate picosecond strain pulses. Here the authors show that the photo-induced phase transition can contribute 0.45% strain without causing undesirable heating.
- Iaroslav A. Mogunov
- , Sergiy Lysenko
- & Alexandra M. Kalashnikova
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-efficient frequency comb generation in AlGaAs-on-insulator microresonators
Ultra-efficient frequency comb generation in AlGaAs-on-insulator microresonators
Despite larger nonlinear coefficients, waveguide losses have prevented using semiconductors instead of dielectric materials for on-chip frequency-comb sources. By significantly reducing waveguide loss, ultra-low-threshold Kerr comb generation is demonstrated in a high-Q AlGaAs-on-insulator microresonator system.
- Lin Chang
- , Weiqiang Xie
- & John E. Bowers
-
Article
| Open Access Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
High throughput imaging flow cytometry suffers from trade-offs between throughput, sensitivity and spatial resolution. Here the authors introduce a method to virtually freeze cells in the image acquisition window to enable 1000 times longer signal integration time and improve signal-to-noise ratio.
- Hideharu Mikami
- , Makoto Kawaguchi
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-tolerant single photon sensitive three-dimensional imager
Noise-tolerant single photon sensitive three-dimensional imager
Imagers capable of reconstructing three-dimensional scenes in the presence of strong background noise are desirable for many remote sensing and imaging applications. Here, the authors report an imager operating in photon-starved and noise-polluted environments through quantum parametric mode sorting.
- Patrick Rehain
- , Yong Meng Sua
- & Yu-Ping Huang
-
Article
| Open Access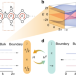 A square-root topological insulator with non-quantized indices realized with photonic Aharonov-Bohm cages
A square-root topological insulator with non-quantized indices realized with photonic Aharonov-Bohm cages
Topological insulators are characterized by quantized topological invariants. Here, the authors report an insulator state showing spectral bands without quantized indices, yet robust boundary states in a photonic setup.
- Mark Kremer
- , Ioannis Petrides
- & Alexander Szameit
-
Article
| Open Access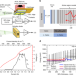 High-speed modulation of a terahertz quantum cascade laser by coherent acoustic phonon pulses
High-speed modulation of a terahertz quantum cascade laser by coherent acoustic phonon pulses
The typical electronic modulation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers is fundamentally limited at fast timescales by device properties. Here the authors propose and study an alternative, acoustic mechanism for modulating such THz QCLs at high speed.
- Aniela Dunn
- , Caroline Poyser
- & Anthony Kent
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow-noise photonic microwave synthesis using a soliton microcomb-based transfer oscillator
Ultralow-noise photonic microwave synthesis using a soliton microcomb-based transfer oscillator
In order to satisfy a wide range of modern microwave applications, improved methods are needed to produce low-noise microwave signals. Here the authors demonstrate ultra-low noise microwave synthesis via optical frequency division using a transfer oscillator method applied to a microresonator-based comb on the path to future self-referenced integrated sources.
- Erwan Lucas
- , Pierre Brochard
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access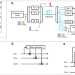 Phase-coherent lightwave communications with frequency combs
Phase-coherent lightwave communications with frequency combs
Frequency combs have the potential to be used as multi-wavelength sources in future optical communications through fiber. Here the authors demonstrate joint phase processing of multi-wavelength comb transmission, and show two schemes to improve performance and reduce complexity.
- Lars Lundberg
- , Mikael Mazur
- & Peter A. Andrekson
-
Article
| Open Access Optical vector analysis with attometer resolution, 90-dB dynamic range and THz bandwidth
Optical vector analysis with attometer resolution, 90-dB dynamic range and THz bandwidth
Typical methods for optical vector analysis have tradeoffs among resolution, dynamic range, and bandwidth. The authors use an asymmetric optical probe signal generator and receiver to perform attometer resolution measurement over a THz of bandwidth while maintaining high dynamic range, aiming to characterize emerging optical devices.
- Ting Qing
- , Shupeng Li
- & Shilong Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Topological control of extreme waves
Topological control of extreme waves
Theories state that transitions between extreme waves are allowed but experimental confirmations are lacking because of lack of control strategies. Here, the authors propose and experimentally report, for the first time, the use of topological indices to control the generation of extreme waves.
- Giulia Marcucci
- , Davide Pierangeli
- & Claudio Conti
-
Article
| Open Access Reverberant 3D optical coherence elastography maps the elasticity of individual corneal layers
Reverberant 3D optical coherence elastography maps the elasticity of individual corneal layers
Elastic mapping of individual layers of the cornea with elastography uses Lamb waves, which are dependent on the thickness of each layer and the direction of propagation. Here the authors present Reverberant 3D Optical Coherence Elastography to measure elasticity of single layers using waves propagating in all directions.
- Fernando Zvietcovich
- , Pornthep Pongchalee
- & Kevin J. Parker
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh resolution and color gamut with scattering-reducing transmissive pixels
Ultrahigh resolution and color gamut with scattering-reducing transmissive pixels
Tradeoffs between size and performance have limited plasmonic structural color vibrancy at high resolution. Here the authors present a nanophotonic resonant metal-coated nanowire capable of being used as a size invariant, vibrant multicolor pixel.
- June Sang Lee
- , Ji Yeon Park
- & Jerome K. Hyun
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable broadband optical field spectral shaping with megahertz resolution using a simple frequency shifting loop
Programmable broadband optical field spectral shaping with megahertz resolution using a simple frequency shifting loop
Full spectral and temporal control of light has a multitude of applications but is often limited in frequency resolution. The authors implement a scheme using a frequency shifting optical loop for optical field spectral shaping with a high degree of control and megahertz resolution
- Côme Schnébelin
- , José Azaña
- & Hugues Guillet de Chatellus
-
Article
| Open Access Gain-through-filtering enables tuneable frequency comb generation in passive optical resonators
Gain-through-filtering enables tuneable frequency comb generation in passive optical resonators
In normal dispersion, modulation instability, which is a precursor of Kerr combs, is forbidden due to phase mismatch. Here, the authors show the compensation of such phase mismatch by introducing frequency-dependent loss using a notch filter, hence leading to effective parametric gain and comb formation.
- Florent Bessin
- , Auro M. Perego
- & Arnaud Mussot
-
Article
| Open Access Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link
Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link
Phase-coherent transfer of optical frequencies over long open-air paths is necessary in photonic applications. Here the authors demonstrate the parallel transmission of multiple optical carriers in air up to 18 km using a stable near-infrared frequency comb.
- Hyun Jay Kang
- , Jaewon Yang
- & Seung-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access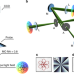 Polarization nano-tomography of tightly focused light landscapes by self-assembled monolayers
Polarization nano-tomography of tightly focused light landscapes by self-assembled monolayers
The realisation of 4D light fields, where longitudinal polarisation represents the fourth dimension, has been limited by the lack of appropriate analysis techniques. Here, the authors use interaction with self-assembled monolayers of fluorescent molecules, which allow for identification of non-paraxial light fields based on a single image frame.
- Eileen Otte
- , Kemal Tekce
- & Cornelia Denz
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-dynamic therapy following photosensitiser activation by accelerated protons demonstrated through fluorescence and singlet oxygen production
Proton-dynamic therapy following photosensitiser activation by accelerated protons demonstrated through fluorescence and singlet oxygen production
The authors use accelerated protons on photosensitizers (PS, conventionally excited by light), to generate fluorescence and singlet oxygen which can enhance the efficacy of proton therapy. A pilot study on glioblastoma cells confirms differential cell death upon irradiation in the presence of PS.
- M. Grigalavicius
- , M. Mastrangelopoulou
- & T. A. Theodossiou
-
Article
| Open Access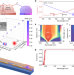 Beyond 100 THz-spanning ultraviolet frequency combs in a non-centrosymmetric crystalline waveguide
Beyond 100 THz-spanning ultraviolet frequency combs in a non-centrosymmetric crystalline waveguide
Frequency combs are useful for precision measurements and to explore atomic and molecular transitions. Here Liu et al. demonstrate photonic chip-based ultraviolet frequency combs of high coherence and broad spectral bandwidth by implementing cubic and quadratic nonlinearities in a non-centrosymmetric material.
- Xianwen Liu
- , Alexander W. Bruch
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access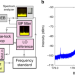 Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Here, the authors demonstrate full stabilization and control of the two key parameters of a four-wavemixing-based quantum cascade laser comb with metrological precision. These fully-controlled, frequency scalable comb emitters will allow an increasing number of mid- and far-IR applications.
- Luigi Consolino
- , Malik Nafa
- & Saverio Bartalini
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter
Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter
Optical clock networks have many applications from precision time keeping, sensing to fundamental physics. Here the authors demonstrate robust and free-space femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks via a moving quadcopter.
- Hugo Bergeron
- , Laura C. Sinclair
- & Nathan R. Newbury
-
Article
| Open Access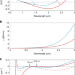 Mid infrared gas spectroscopy using efficient fiber laser driven photonic chip-based supercontinuum
Mid infrared gas spectroscopy using efficient fiber laser driven photonic chip-based supercontinuum
The mid-infrared spectral region is important for gas sensing applications. Here, Grassani et al. demonstrate efficient supercontinuum generation from fibre-lasers injected into silicon nitride waveguides to provide a turn-key mid-IR source with milliwatt-level output.
- Davide Grassani
- , Eirini Tagkoudi
- & Camille-Sophie Brès
-
Article
| Open Access Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Nonlinear structured illumination microscopy is a super-resolution technique that is challenging to extend to 3 dimensions. The authors obtain super-resolution image information in 3D from a 2D scan by exploiting orthogonal speckle illumination patterns and compressed sensing of the sparse fluorescence.
- M. Pascucci
- , S. Ganesan
- & M. Guillon

 High spatiotemporal resolution optoacoustic sensing with photothermally induced acoustic vibrations in optical fibres
High spatiotemporal resolution optoacoustic sensing with photothermally induced acoustic vibrations in optical fibres