Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasound-induced reorientation for multi-angle optical coherence tomography
Ultrasound-induced reorientation for multi-angle optical coherence tomography
Accessing multi-angle views of organoids is important for biology and oncology. The authors propose ultrasound-induced reorientation for multi-angle optical coherence tomography, using a 3D-printed acoustic trap to levitate and rotate samples with a model-based algorithm for reconstruction.
- Mia Kvåle Løvmo
- , Shiyu Deng
- & Monika Ritsch-Marte
-
Article
| Open Access Light-field flow cytometry for high-resolution, volumetric and multiparametric 3D single-cell analysis
Light-field flow cytometry for high-resolution, volumetric and multiparametric 3D single-cell analysis
Current imaging flow cytometry approaches remain limited in their ability to reveal subcellular information with high-resolution and instrumental simplicity. Here, the authors present a light-field flow cytometer capable of high-content, multi-color imaging of cells with high-resolution in 3D.
- Xuanwen Hua
- , Keyi Han
- & Shu Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free identification of protein aggregates using deep learning
Label-free identification of protein aggregates using deep learning
The authors use deep learning to detect and segment unlabeled and unaltered protein aggregates in living cells from transmitted-light images. The method provides a way to quantitatively study protein aggregation dynamics in a simple, fast and accurate way.
- Khalid A. Ibrahim
- , Kristin S. Grußmayer
- & Aleksandra Radenovic
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Molecular vibrations serve as valuable signatures for the constituent elements and bonding in compounds. Here, using Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption spectroscopy, the authors study refractive index dependent vibrations of surface phonon polaritons and surface plasmon platform, targeting dynamic biomonitoring.
- Hong Zhou
- , Zhihao Ren
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Deep imaging in complex scattering media is hindered by multiple light scattering. Here, the authors proposed a method to trace multiple scattering trajectories in situ using a recorded reflection matrix and achieved enhanced imaging depth by converting these multiple scattering to signal waves.
- Sungsam Kang
- , Yongwoo Kwon
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Translating genomic tools to Raman spectroscopy analysis enables high-dimensional tissue characterization on molecular resolution
Translating genomic tools to Raman spectroscopy analysis enables high-dimensional tissue characterization on molecular resolution
Spatial transcriptomics of histological sections have revolutionized basic research, while the actual biomolecular composition of the sample has fallen behind. Here, the authors propose a novel approach to analyze untargeted spatiomolecular Raman spectroscopy data through bioinformatic tools developed for transcriptomic analyses, and integrate them with additional Omics techniques.
- Manuel Sigle
- , Anne-Katrin Rohlfing
- & Meinrad Paul Gawaz
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning-based stripe self-correction method for stitched microscopic images
A deep learning-based stripe self-correction method for stitched microscopic images
Image stitching in fluorescence microscopy can be a hindrance to image quality and to downstream quantitative analyses. Here, the authors propose a deep learning-based stripe self-correction method that corrects diverse stripes and artifacts for stitched microscopic images.
- Shu Wang
- , Xiaoxiang Liu
- & Jianxin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution multicolor fluorescence microscopy enabled by an apochromatic super-oscillatory lens with extended depth-of-focus
Super-resolution multicolor fluorescence microscopy enabled by an apochromatic super-oscillatory lens with extended depth-of-focus
Conventional super-oscillatory devices suffer from numerical-aperture related issue including depth of focus, chromatic dispersion, and focusing, Here, the authors utilised multi-objective genetic algorithm to optimise the design and experimentally demonstrated lens with an extended depth of focus, ultra-large working distance and suppressed side-lobes.
- Wenli Li
- , Pei He
- & Yiting Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme transport of light in spheroids of tumor cells
Extreme transport of light in spheroids of tumor cells
Rouge waves have been observed in a number of complex systems, but not in biological structures. Here, the authors report the observation of optical rouge waves manifesting in tumor-cell spheroids when illuminated by randomly modulated laser beams.
- Davide Pierangeli
- , Giordano Perini
- & Claudio Conti
-
Article
| Open Access The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The authors developed an open-source, low-cost, multi-channel time-tagging module for fluorescence lifetime image scanning microscopy and correlation spectroscopy that can tag in parallel multiple single-photon events with 30 ps precision.
- Alessandro Rossetta
- , Eli Slenders
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access Optical cavity-mediated exciton dynamics in photosynthetic light harvesting 2 complexes
Optical cavity-mediated exciton dynamics in photosynthetic light harvesting 2 complexes
Light-matter interaction can induce changes to the properties of the system by creating hybrid collective states of light and molecular excitations, the so called polaritons. Here the authors use femtosecond pump-probe spectroscopy to explore exciton-polariton dynamics in a photosynthetic protein, light harvesting 2 complexes, and find evidence for rapid energy transfer to dark polariton states.
- Fan Wu
- , Daniel Finkelstein-Shapiro
- & Tönu Pullerits
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography
Frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography
Optoacoustic imaging is mostly performed in the time domain. Here the authors demonstrate frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography that can operate at multiple wavelengths simultaneously and offers signal-to-noise ratio advantages over time domain methods.
- Antonios Stylogiannis
- , Ludwig Prade
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time precision opto-control of chemical processes in live cells
Real-time precision opto-control of chemical processes in live cells
There is a need to control molecular activities at high spatial precision. Here the authors report a real-time precision opto-control technology that detects a chemical-specific optical response from molecular targets, and precisely control photoswitchable microtubule polymerization inhibitors in cells.
- Matthew G. Clark
- , Gil A. Gonzalez
- & Chi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz thermal curve analysis for label-free identification of pathogens
Terahertz thermal curve analysis for label-free identification of pathogens
A label-free sensing method has been developed for identifying hazardous pathogens based on their intrinsic properties. This was possible by interrogating the temperature-dependent dielectric constant of the microbes in the far-infrared range.
- S. W. Jun
- & Y. H. Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Deep tissue localization and sensing using optical microcavity probes
Deep tissue localization and sensing using optical microcavity probes
Optical microcavities are useful as probes in cells due to their narrow emission spectra and high sensitivity to environment. Here, the authors use the unique spectral features of microcavities, which are unaffected by tissue scattering, and show 3D localisation and tracking of cells deep in tissues.
- Aljaž Kavčič
- , Maja Garvas
- & Matjaž Humar
-
Article
| Open Access 1/f-noise-free optical sensing with an integrated heterodyne interferometer
1/f-noise-free optical sensing with an integrated heterodyne interferometer
Suppressing 1/f-shaped low-frequency noise is critical but fundamentally challenging to both electrical and optical transducers. Here, the authors demonstrate a 1/f-noise-free optical sensor with integrated CMOS-compatible heterodyne interferometer and an upconversion amplifying technique, which suppresses the noise by two orders of magnitude.
- Ming Jin
- , Shui-Jing Tang
- & Yun-Feng Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Identification of neurotransmitters remains challenging for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) due to presence of noise. Here, the authors present spread spectrum SERS, which by encoding excited light and decoding SERS signals enables detection of unlabelled neurotransmitters at attomolar concentrations.
- Wonkyoung Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Kang
- & Ki-Hun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Segment-specific optogenetic stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster with linear arrays of organic light-emitting diodes
Segment-specific optogenetic stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster with linear arrays of organic light-emitting diodes
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) can offer an attractive approach for providing light stimulation in high-throughput optogenetics. Here, the authors report a microstructured OLED array that provides local photo-stimulation in Drosophila melanogaster larvae for controlled motor responses.
- Caroline Murawski
- , Stefan R. Pulver
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular resolution imaging by post-labeling expansion single-molecule localization microscopy (Ex-SMLM)
Molecular resolution imaging by post-labeling expansion single-molecule localization microscopy (Ex-SMLM)
Previous attempts to combine expansion microscopy (ExM) and single molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) have proved challenging. Here the authors show that post-labelling Ex-SMLM improves labelling efficiency, reduces linkage error, and preserves ultrastructural details.
- Fabian U. Zwettler
- , Sebastian Reinhard
- & Markus Sauer
-
Article
| Open Access Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
High throughput imaging flow cytometry suffers from trade-offs between throughput, sensitivity and spatial resolution. Here the authors introduce a method to virtually freeze cells in the image acquisition window to enable 1000 times longer signal integration time and improve signal-to-noise ratio.
- Hideharu Mikami
- , Makoto Kawaguchi
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Reverberant 3D optical coherence elastography maps the elasticity of individual corneal layers
Reverberant 3D optical coherence elastography maps the elasticity of individual corneal layers
Elastic mapping of individual layers of the cornea with elastography uses Lamb waves, which are dependent on the thickness of each layer and the direction of propagation. Here the authors present Reverberant 3D Optical Coherence Elastography to measure elasticity of single layers using waves propagating in all directions.
- Fernando Zvietcovich
- , Pornthep Pongchalee
- & Kevin J. Parker
-
Article
| Open Access Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Nonlinear structured illumination microscopy is a super-resolution technique that is challenging to extend to 3 dimensions. The authors obtain super-resolution image information in 3D from a 2D scan by exploiting orthogonal speckle illumination patterns and compressed sensing of the sparse fluorescence.
- M. Pascucci
- , S. Ganesan
- & M. Guillon
-
Article
| Open Access Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
The characterization of biomacromolecule structural vibrations has been impeded by a broad continuous vibrational density of states obscuring molecule specific vibrations. A terahertz microscopy system using polarization control produces signatures to dynamically fingerprint proteins and a RNA G-quadruplex.
- Katherine A. Niessen
- , Mengyang Xu
- & Andrea G. Markelz
-
Article
| Open Access Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
While the sharp emission lines of microlasers are advantageous for cell tagging, their relatively large size can impede cell migration and behavior. Here, Fikouras et al. develop nano-sized lasers that can readily tag and track various types of cells, including through narrow constrictions.
- Alasdair H. Fikouras
- , Marcel Schubert
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Fractal modes and multi-beam generation from hybrid microlaser resonators
Fractal modes and multi-beam generation from hybrid microlaser resonators
Although fractal optical patterns have been realized previously, the direct generation of fractal modes from a laser has proven challenging. Here, Rivera et al. modify an optical cavity with a microsphere array to produce fractal laser modes and probe live cells, which serve as a component of the resonator.
- José A. Rivera
- , Thomas C. Galvin
- & J. Gary Eden
-
Article
| Open Access Rainbow peacock spiders inspire miniature super-iridescent optics
Rainbow peacock spiders inspire miniature super-iridescent optics
Several animals and plants get their often spectacular colouration and iridescence from structural colouration. Here, Hsiung et al. show the 3-dimensional nanostructures that produce the rainbow colours on the abdomen of miniature peacock spiders.
- Bor-Kai Hsiung
- , Radwanul Hasan Siddique
- & Todd A. Blackledge
-
Article
| Open Access Super-achromatic monolithic microprobe for ultrahigh-resolution endoscopic optical coherence tomography at 800 nm
Super-achromatic monolithic microprobe for ultrahigh-resolution endoscopic optical coherence tomography at 800 nm
Optical coherence tomography is an established optical tool for in vivo clinical imaging and diagnosis applications, but endoscopic technologies remain limited. Here, Yuan et al. develop a flexible, narrow diameter, super-achromatic endoscopic probe for ultrahigh-resolution in vivo OCT imaging of small luminal organs or narrow constrictions.
- Wu Yuan
- , Robert Brown
- & Xingde Li
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional scanless holographic optogenetics with temporal focusing (3D-SHOT)
Three-dimensional scanless holographic optogenetics with temporal focusing (3D-SHOT)
Optogenetics, the optical stimulation of neurons, suffers from many technical challenges that limit the number of neurons that can be excited as well as their relative positions. Here, Pégard et al. develop a method to simultaneously stimulate an arbitrary number of neurons in 3D space with single neuron resolution.
- Nicolas C. Pégard
- , Alan R. Mardinly
- & Hillel Adesnik
-
Article
| Open Access Optical trapping of otoliths drives vestibular behaviours in larval zebrafish
Optical trapping of otoliths drives vestibular behaviours in larval zebrafish
The neural circuits of the vestibular system, which detects gravity and motion, remain incompletely characterised. Here the authors use an optical trap to manipulate otoliths (ear stones) in zebrafish larvae, and elicit corrective tail movements and eye rolling, thus establishing a method for mapping vestibular processing.
- Itia A. Favre-Bulle
- , Alexander B. Stilgoe
- & Ethan K. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Fast escape of a quantum walker from an integrated photonic maze
Fast escape of a quantum walker from an integrated photonic maze
Studying quantum transport in biological systems is difficult so developing an artificial platform that can be used to understand quantum transport is desirable. Here, Caruso, et al. demonstrate how a quantum walker can quickly reach the output of a maze by partially suppressing the presence of interference.
- Filippo Caruso
- , Andrea Crespi
- & Roberto Osellame
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
BioLEDs is an emerging group of light-emitting diodes that use duplex-strand DNA to enhance luminescence intensity. Here, Back et al.show that only the specific binding between a pair of single-strand DNA can trigger the enhancement, which potentially makes BioLEDs an easy platform for DNA recognition.
- Seung Hyuk Back
- , Jin Hyuk Park
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article |
 Spatial modulation of light transmission through a single microcavity by coupling of photosynthetic complex excitations to surface plasmons
Spatial modulation of light transmission through a single microcavity by coupling of photosynthetic complex excitations to surface plasmons
The interaction between light and molecules can lead to hybrid quantum-physical states of light and matter. Here, the authors demonstrate one such effect, spatial modulation of light, with the protein photosystem I as a first demonstration of this quantum effect with such a biological molecule.
- Itai Carmeli
- , Moshik Cohen
- & Shachar Richter
-
Article
| Open Access A highly conspicuous mineralized composite photonic architecture in the translucent shell of the blue-rayed limpet
A highly conspicuous mineralized composite photonic architecture in the translucent shell of the blue-rayed limpet
Mollusks have evolved an exquisite diversity of complex mineralized shells for protection. One such example, the blue-rayed limpet, incorporates a vivid display of blue lines, which originate from the interference of light in a nano-periodic photonic architecture buried within the animal's translucent shell.
- Ling Li
- , Stefan Kolle
- & Mathias Kolle
-
Article |
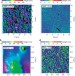 Strong coupling between chlorosomes of photosynthetic bacteria and a confined optical cavity mode
Strong coupling between chlorosomes of photosynthetic bacteria and a confined optical cavity mode
Photosynthetic bacteria growing in low light environments have evolved to use small amounts of light with high efficiency. Here, Coles et al. demonstrate strong exciton–photon coupling of about 1,000 chlorosomes to a confined cavity mode thus modifying the energy levels of the light-harvesting process.
- David M. Coles
- , Yanshen Yang
- & Jason M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access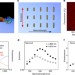 Strong antenna-enhanced fluorescence of a single light-harvesting complex shows photon antibunching
Strong antenna-enhanced fluorescence of a single light-harvesting complex shows photon antibunching
Quantum processes may have an important role in photosynthetic light-harvesting complexes, but their low fluorescence efficiency impedes studies. By coupling them to gold nanoantennas, Wientjes et al.show over 500 times enhancement of fluorescence from single molecules of light-harvesting complex 2.
- Emilie Wientjes
- , Jan Renger
- & Niek F. van Hulst
-
Article |
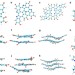 Excitonic effects from geometric order and disorder explain broadband optical absorption in eumelanin
Excitonic effects from geometric order and disorder explain broadband optical absorption in eumelanin
Eumelanin is a biological pigment capable of broadband absorption, but the origin of this ability has been unclear. Here, the authors consider various eumelanin models and conclude that a combination of ordering stacking interactions coupled with geometric disorder gives rise to the broad absorption profile.
- Chun-Teh Chen
- , Chern Chuang
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article |
 Dynamic localization of electronic excitation in photosynthetic complexes revealed with chiral two-dimensional spectroscopy
Dynamic localization of electronic excitation in photosynthetic complexes revealed with chiral two-dimensional spectroscopy
Nonlinear chiral optical activity is difficult to measure because of weak signal amidst strong achiral background. Here, the authors perform a nonlinear chiral two-dimensional spectroscopic mapping of light-harvesting complex 2 during photoexcitation and observe exciton delocalization.
- Andrew F. Fidler
- , Ved P. Singh
- & Gregory S. Engel
-
Article |
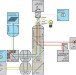 A hybrid high-speed atomic force–optical microscope for visualizing single membrane proteins on eukaryotic cells
A hybrid high-speed atomic force–optical microscope for visualizing single membrane proteins on eukaryotic cells
Scanning probe microscopy techniques are hard to apply to live cell membrane imaging at high resolution as the temporal and force sensitivity are insufficient to monitor the fast processes. Colom et al.present a solution to this problem by combining high-speed atomic force microscopy with optical microscopy.
- Adai Colom
- , Ignacio Casuso
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article
| Open Access Solar spectral conversion for improving the photosynthetic activity in algae reactors
Solar spectral conversion for improving the photosynthetic activity in algae reactors
Algae beds are a promising resource for bio-energy and gas production, but their productivity is often limited by solar energy harvesting efficiency. Wondraczek et al. promote algal growth by using photoluminescent phosphor, which shifts the light spectrum to better match the algal adsorption band.
- Lothar Wondraczek
- , Miroslaw Batentschuk
- & Christoph J. Brabec

 An optofluidic antenna for enhancing the sensitivity of single-emitter measurements
An optofluidic antenna for enhancing the sensitivity of single-emitter measurements