Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Transmission of natural scene images through a multimode fibre
Transmission of natural scene images through a multimode fibre
The optical transmission of images through a multimode fibre remains an outstanding challenge. Here, the authors implement a method that statistically reconstructs the inverse transformation matrix for a fibre and demonstrate real-time imaging of natural scenes in full colour, high resolution and high frame rate.
- Piergiorgio Caramazza
- , Oisín Moran
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access Combining 3D single molecule localization strategies for reproducible bioimaging
Combining 3D single molecule localization strategies for reproducible bioimaging
3D single molecule localization microscopy suffers from several experimental biases that degrade the resolution or localization precision. Here the authors present a dual-view detection scheme combining supercritical angle fluorescence and astigmatic imaging to obtain precise and unbiased 3D super resolution images.
- Clément Cabriel
- , Nicolas Bourg
- & Sandrine Lévêque-Fort
-
Article
| Open Access A clinically translatable hyperspectral endoscopy (HySE) system for imaging the gastrointestinal tract
A clinically translatable hyperspectral endoscopy (HySE) system for imaging the gastrointestinal tract
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) enables recording both morphological and biochemical information, but image acquisition time and geometric distortions limit its clinical applicability. Here the authors overcome these challenges with an endoscope combining HSI and white light to correct for image distortion during freehand operation.
- Jonghee Yoon
- , James Joseph
- & Sarah E. Bohndiek
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded collimator for atomic beams traveling in planar silicon devices
Cascaded collimator for atomic beams traveling in planar silicon devices
Bringing atomic beam technology to the chip scale is challenging due to the long distance required to filter the velocity distribution. Here, the authors report an engineering strategy for on-chip filtering of the velocity profile of atomic beams by fabricating planar, etched microchannel arrays.
- Chao Li
- , Xiao Chai
- & C. Raman
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating temporal and spatial control of electronic transitions for bright multiphoton upconversion
Integrating temporal and spatial control of electronic transitions for bright multiphoton upconversion
Here, the authors control concentration quenching in a stoichiometric Er3+ compound using a core−shell nanostructured host and an integrated optical waveguide circuit excitation platform. The efficient telecom to ultraviolet upconversion allows for exploration of photonic applications involving upconversion nanomaterials.
- Tianying Sun
- , Yuhua Li
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
Multicolour images are difficult to acquire with large-scale microscopy approaches. Here the authors present a microtome-assisted microscope capable of trichromatic two-photon excitation and label-free nonlinear modalities based on wavelength mixing, and use it to analyze astrocyte morphology and neuronal projections in thick brain samples.
- Lamiae Abdeladim
- , Katherine S. Matho
- & Emmanuel Beaurepaire
-
Article
| Open Access Assessment of corneal substrate biomechanics and its effect on epithelial stem cell maintenance and differentiation
Assessment of corneal substrate biomechanics and its effect on epithelial stem cell maintenance and differentiation
The link between how the stiffness of the cornea affects stem cells is unclear. Here, the authors use Brillouin spectro-microscopy to show that mechanical properties of the cornea affect epithelial stem cells and after injury, treating the cornea with collagenase suppresses YAP activation, assisting in regeneration.
- Ricardo M. Gouveia
- , Guillaume Lepert
- & Che J. Connon
-
Article
| Open Access Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Imaging the mouse brain using glass cranial windows has limitations in terms of flexibility and long-term imaging. Here the authors engineer transparent polymer skulls that can fit various skull morphologies and can be implanted for over 300 days, enabling simultaneous high resolution brain imaging and electrophysiology across large cortical areas.
- Leila Ghanbari
- , Russell E. Carter
- & Suhasa B. Kodandaramaiah
-
Article
| Open Access Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Nonlinear structured illumination microscopy is a super-resolution technique that is challenging to extend to 3 dimensions. The authors obtain super-resolution image information in 3D from a 2D scan by exploiting orthogonal speckle illumination patterns and compressed sensing of the sparse fluorescence.
- M. Pascucci
- , S. Ganesan
- & M. Guillon
-
Article
| Open Access Indirect optical trapping using light driven micro-rotors for reconfigurable hydrodynamic manipulation
Indirect optical trapping using light driven micro-rotors for reconfigurable hydrodynamic manipulation
Optical tweezing with intense lasers can be harmful to biological specimens and limits the types of materials that can be trapped. Here, the authors demonstrate an indirect optical trapping approach which uses hydrodynamic forces to exert nanoscale-precision control over aqueous particles, without directly illuminating them.
- Unė G. Būtaitė
- , Graham M. Gibson
- & David B. Phillips
-
Article
| Open Access Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
Protein and RNA dynamical fingerprinting
The characterization of biomacromolecule structural vibrations has been impeded by a broad continuous vibrational density of states obscuring molecule specific vibrations. A terahertz microscopy system using polarization control produces signatures to dynamically fingerprint proteins and a RNA G-quadruplex.
- Katherine A. Niessen
- , Mengyang Xu
- & Andrea G. Markelz
-
Article
| Open Access A three-dimensional ratiometric sensing strategy on unimolecular fluorescence–thermally activated delayed fluorescence dual emission
A three-dimensional ratiometric sensing strategy on unimolecular fluorescence–thermally activated delayed fluorescence dual emission
New photoluminescent strategies are required to realize high-performance ratiometric sensors for bio-sensing applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a fluorescence-thermally activated delayed fluorescence dual emission strategy for ratiometric sensors with high precision.
- Xuping Li
- , Gleb Baryshnikov
- & Liangliang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling light in complex media beyond the acoustic diffraction-limit using the acousto-optic transmission matrix
Controlling light in complex media beyond the acoustic diffraction-limit using the acousto-optic transmission matrix
Various techniques combine light and ultrasound to study the inside of strongly scattering samples, beyond the reach of purely optical imaging. Here, Katz et al. introduce the acousto-optic transmission matrix framework that allows to control and focus light beyond the acoustic diffraction limit.
- Ori Katz
- , François Ramaz
- & Mathias Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo
Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo
Long acquisition time and high illumination intensities needed in super-resolution imaging often generate photobleaching and phototoxicity. Here the authors develop a non-deterministic scanning approach based on a real-time feedback system that enables faster acquisition with lower light doses for in vivo imaging.
- Jes Dreier
- , Marco Castello
- & Ilaria Testa
-
Article
| Open Access Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy
Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy
Two-photon microscopy is a powerful tool for studying neuronal activity but cannot easily image deeper cortical layers. Here, the authors design a custom microscope for three-photon microscopy and use it to reveal response properties of layer 5, 6, and subplate visual cortical neurons.
- Murat Yildirim
- , Hiroki Sugihara
- & Mriganka Sur
-
Article
| Open Access Precision ultrasound sensing on a chip
Precision ultrasound sensing on a chip
With the wide adoption of ultrasound methods in biomedical and technological diagnostics, sensitive probes are in demand. Here, the authors employ cavity optomechanics where optical and mechanical resonances are coupled, both enhancing the sensitivity of the device and allowing its chip-integration.
- Sahar Basiri-Esfahani
- , Ardalan Armin
- & Warwick P. Bowen
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasonic sculpting of virtual optical waveguides in tissue
Ultrasonic sculpting of virtual optical waveguides in tissue
Optical imaging of tissue is a powerful technique but delivering light deep into scattering tissue is not possible without using invasive methods. Here, the authors demonstrate that patterned ultrasound can define and control the trajectory of light in tissue using pressure-induced index contrasts.
- Maysamreza Chamanzar
- , Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti
- & Michel M. Maharbiz
-
Article
| Open Access A miniature multi-contrast microscope for functional imaging in freely behaving animals
A miniature multi-contrast microscope for functional imaging in freely behaving animals
Measuring multiple neurophysiologic variables usually requires bulky benchtop optical systems and working with anesthetized animals. Here the authors present a miniature portable microscope for neurovascular imaging in awake rodents, combining fluorescence, intrinsic optical signals and laser speckle contrast.
- Janaka Senarathna
- , Hang Yu
- & Arvind P. Pathak
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring drug nanocarriers in human blood by near-infrared fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Monitoring drug nanocarriers in human blood by near-infrared fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
While nanocarrier-based drug delivery is a promising therapeutic approach, in situ characterization of drug nanocarriers in blood remains difficult. Here, the authors demonstrate how the fluorescence correlation spectroscopy can be used to directly characterize drug nanocarriers in flowing blood.
- Inka Negwer
- , Andreas Best
- & Kaloian Koynov
-
Article
| Open Access Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement
Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement
Understanding the pH changes at cell surfaces is important for understanding the mechanisms of different physiological processes. Here, the authors report on the development of a cell membrane anchored gold nanoparticle for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy determination of pH.
- Leonardo Puppulin
- , Shigekuni Hosogi
- & Yoshinori Marunaka
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane water for probing neuronal membrane potentials and ionic fluxes at the single cell level
Membrane water for probing neuronal membrane potentials and ionic fluxes at the single cell level
Non-invasive spatiotemporal probing of electric potentials in living neurons without chemical or genetic modification provides a major advancement to neuroscience. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of membrane water as a probe for neuronal membrane potentials and ionic flux.
- M. E. P. Didier
- , O. B. Tarun
- & S. Roke
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance reconstruction of microscopic force fields from Brownian trajectories
High-performance reconstruction of microscopic force fields from Brownian trajectories
The measure of microscopic forces is currently dominated by optical methods requiring parameter-based analyses and long data acquisitions. This work describes a fast and parameter-free method that can characterize both the conservative and non-conservative force fields acting on Brownian particles.
- Laura Pérez García
- , Jaime Donlucas Pérez
- & Giovanni Volpe
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
Alignment and orientation of the molecules allows studying the photon-molecule interactions in greater detail. Here the authors demonstrate the three-dimensional orientation of SO2 molecules in using COLTRIMS and orthogonally polarized laser pulses but in the absence of DC field.
- Kang Lin
- , Ilia Tutunnikov
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Natural genetic transformation in bacteria requires DNA binding at the surface of competent cells. Here, Mirouze et al. show that wall teichoic acids are specifically produced or modified during competence in Bacillus subtilis and promote (directly or indirectly) DNA binding at the cell surface.
- Nicolas Mirouze
- , Cécile Ferret
- & Rut Carballido-López
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of bound state self-interaction in a nano-eV atom collider
Observation of bound state self-interaction in a nano-eV atom collider
Self-interaction of a bound state through its coupling to the continuum is a phenomenon that is very difficult to observe. Here, the authors optically collide atomic clouds of rubidium and potassium to observe the self-interaction energy through precise measurements of magnetically tunable Feshbach resonances.
- Ryan Thomas
- , Matthew Chilcott
- & Niels Kjærgaard
-
Article
| Open Access Crossover from positive to negative optical torque in mesoscale optical matter
Crossover from positive to negative optical torque in mesoscale optical matter
Negative optical torque has been predicted theoretically, but experimental demonstrations have been scarce. Here, the authors show that the optical torque in a mesoscopic optical matter array can be reversed depending on number, separation and configuration of nanoparticles in a circularly polarized optical trap.
- Fei Han
- , John A. Parker
- & Zijie Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-color live-cell super-resolution volume imaging with multi-angle interference microscopy
Multi-color live-cell super-resolution volume imaging with multi-angle interference microscopy
3D super-resolution imaging of dynamic processes in live cells is still challenging, especially in a large field of view. Here the authors combine SIM with multi-angle evanescent light illumination and achieve improved lateral and axial resolution, with stack acquisition time in the range of 1–2 s.
- Youhua Chen
- , Wenjie Liu
- & Xu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
The short exciton life time in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides poses limitations to efficient control of the valley pseudospin and coherence. Here, the authors manipulate the exciton coherence in a WSe2 monolayer embedded in an optical microcavity in the strong light-matter coupling regime.
- S. Dufferwiel
- , T. P. Lyons
- & A. I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrational fingerprint of localized excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal
Vibrational fingerprint of localized excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal
Long-lived excitons in a two-dimensional metal-organic crystal can be produced by visible light and detected by infrared radiation. Here, the authors show that the excitonic state of a biomimetic macrocycle can be ‘read’ by measuring the vibrations of an adsorbed ligand.
- M. Corva
- , A. Ferrari
- & E. Vesselli
-
Article
| Open Access Microsphere-based interferometric optical probe
Microsphere-based interferometric optical probe
Tagging and tracking cells with multiplexed labels can help study complex cellular behaviors in living systems. Here, Jo et al. propose and demonstrate the use of Fabry-Perot-like resonances in dielectric microspheres as such a label and call these reflectophores.
- Yongjae Jo
- , Junhwan Kwon
- & Myunghwan Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Seeded X-ray free-electron laser generating radiation with laser statistical properties
Seeded X-ray free-electron laser generating radiation with laser statistical properties
Free electron lasers are emerging as important tools for nonlinear spectroscopy in the X-ray regime. Here the authors demonstrate the second order coherence of a seeded FEL source that may be useful for measurements in quantum optics.
- Oleg Yu. Gorobtsov
- , Giuseppe Mercurio
- & Ivan A. Vartanyants
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced mRNA FISH with compact quantum dots
Enhanced mRNA FISH with compact quantum dots
FISH-based techniques to image and count mRNA in single cells can be limited by the photophysical properties of organic dyes. Here the authors develop photostable quantum dot FISH probes for multiplexed imaging.
- Yang Liu
- , Phuong Le
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Phase-controlled Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Fourier transform spectrometers are generally limited to slow scanning rates at high resolution. Here the authors demonstrate highly efficient Fourier transform spectroscopy using a dynamic phase-control technique that enables fast acquisition without compromising bandwidth or resolution.
- Kazuki Hashimoto
- & Takuro Ideguchi
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
High-performance and scalable on-chip digital Fourier transform spectroscopy
On-chip spectrometers typically have limited spectral channels and low signal to noise ratios. Here the authors introduce a digital architecture that uses switches to change the interferometer path lengths, enabling exponentially more spectral channels per circuit element and lower noise by leveraging a machine learning reconstruction algorithm.
- Derek M. Kita
- , Brando Miranda
- & Juejun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental limits and non-reciprocal approaches in non-Hermitian quantum sensing
Fundamental limits and non-reciprocal approaches in non-Hermitian quantum sensing
Non-Hermitian properties were proposed to be beneficial to sensing but it is not clear if this concept can be extended to the quantum regime. Here, Lau and Clerk self-consistently consider the impact of noise and measurement, and identify that nonreciprocity can improve sensing capabilities.
- Hoi-Kwan Lau
- & Aashish A. Clerk
-
Article
| Open Access Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Enabling concurrent, high throughput analysis of single nano particles would greatly increase the capacity to study size, composition and inter and intra particle population variance. Here, the authors present a comprehensive platform for single particle automated Raman trapping analysis without any target modification.
- Jelle Penders
- , Isaac J. Pence
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access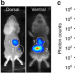 Automated quantification of bioluminescence images
Automated quantification of bioluminescence images
Analysis of bioluminescence images of bacterial distributions in living animals is mostly manual and semiquantitative. Here, the authors present an analysis platform featuring an animal mold, a probabilistic organ atlas, and a mirror gantry to perform automatic in vivo bioluminescence quantification.
- Alexander D. Klose
- & Neal Paragas
-
Article
| Open Access Remote sensing of geomagnetic fields and atomic collisions in the mesosphere
Remote sensing of geomagnetic fields and atomic collisions in the mesosphere
Remote sensing of geomagnetic fields in mesosphere is both challenging and interesting to explore the magnetic field structures and atomic collision processes. Here the authors demonstrate an atomic magnetometer that utilizes the Larmor frequency in sodium atoms and operates in kilometers range.
- Felipe Pedreros Bustos
- , Domenico Bonaccini Calia
- & Simon Rochester
-
Article
| Open Access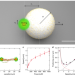 Active particles bound by information flows
Active particles bound by information flows
Synthetic active particles with inter-particle propulsion have been served as a model system to study the collective animal behaviors. Here, Khadka et al. add complexity to the model by spatially controlling particle motions through a laser feedback loop in response to the collective dynamics of particles.
- Utsab Khadka
- , Viktor Holubec
- & Frank Cichos
-
Article
| Open Access Passive sensing around the corner using spatial coherence
Passive sensing around the corner using spatial coherence
Non-line-of-sight sensing requires purposely controlling some of the properties of light during the measurement process. Here, the authors show that reflection from a diffusive surface preserves some coherence properties and the shape and the distance to an incoherently illuminated object can be measured using the spatial coherence function.
- M. Batarseh
- , S. Sukhov
- & A. Dogariu
-
Article
| Open Access Correlative microscopy approach for biology using X-ray holography, X-ray scanning diffraction and STED microscopy
Correlative microscopy approach for biology using X-ray holography, X-ray scanning diffraction and STED microscopy
X-ray techniques benefit from correlative imaging approaches, but combination with super-resolution microscopy has not been explored. Here the authors image the cardiomyocyte cytoskeleton by combining holographic X-ray imaging, X-ray scanning diffraction and STED in the same synchrotron endstation.
- M. Bernhardt
- , J.-D. Nicolas
- & T. Salditt
-
Article
| Open Access Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
The charge transfer state is the key to understand the open circuit voltage of organic solar cells and is commonly accessed by electroluminescence spectra. Here List et al. show that the reliable spectra can only be obtained by a correction of the device-specific out-coupling effect.
- Mathias List
- , Tanmoy Sarkar
- & Uli Würfel
-
Article
| Open Access Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Angle-resolved monitoring of structure parameters during crystal growth is often slow owing to mechanical movements. Here, the authors use second harmonic scattering and Fourier-plane imaging to dynamically monitor size, shape and concentration of ZIF-8 in situ during the growth process.
- Stijn Van Cleuvenbergen
- , Zachary J. Smith
- & Monique A. van der Veen
-
Article
| Open Access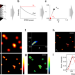 Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
A known limitation of super-resolution STED microscopy is the need of high laser power which can cause photobleaching and phototoxicity. Here the authors further optimize this method and show that modulating STED intensity during acquisition results in an enhanced resolution and reduced background.
- Maria J. Sarmento
- , Michele Oneto
- & Luca Lanzanò
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
One-dimensional materials such as carbon nanotubes have many applications, but not all of their properties can be described in the same way as for conventional media. Here, the authors devise a method to measure the complex optical susceptibility in a 1D nanomaterial and demonstrate it for carbon nanotubes.
- Fengrui Yao
- , Can Liu
- & Kaihui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-photon near-infrared emission saturation nanoscopy using upconversion nanoparticles
Multi-photon near-infrared emission saturation nanoscopy using upconversion nanoparticles
Upconversion nanoparticles offer the potential for deep tissue biological imaging. Here, Chen et al. develop super resolution optical imaging in the near-infrared for imaging with sub-50 nm resolution through almost 100 microns of tissue.
- Chaohao Chen
- , Fan Wang
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access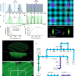 Enhanced photon collection enables four dimensional fluorescence nanoscopy of living systems
Enhanced photon collection enables four dimensional fluorescence nanoscopy of living systems
Super-resolution microscopy often suffers from low contrast and slow recording times. Here the authors present an optical implementation which makes the fluorescent proteins’ ON–OFF switching cycles more efficient, enhancing contrast and spatio-temporal resolution in 3D cell and tissue imaging.
- Luciano A. Masullo
- , Andreas Bodén
- & Ilaria Testa
-
Article
| Open Access Coherence in carotenoid-to-chlorophyll energy transfer
Coherence in carotenoid-to-chlorophyll energy transfer
Energy transfer from carotenoids to chlorophylls in light-harvesting is still not fully understood, especially in the ultrafast regime. Here, the authors investigate the coherent dynamics of this process in peridinin-chlorophyll a-protein complex via 2D electronic spectroscopy and quantum chemical calculations.
- Elena Meneghin
- , Andrea Volpato
- & Elisabetta Collini
-
Article
| Open Access Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals
Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals
Non-destructive methods to image metabolism in situ in living tissues are limited. Here the authors combine deuterium oxide probing and stimulated Raman scattering microscopy to image lipid metabolic dynamics and protein synthesis in cells and in vivo in mice, C. elegans, and zebrafish.
- Lingyan Shi
- , Chaogu Zheng
- & Wei Min

 Ultrafast multi-focus 3-D nano-fabrication based on two-photon polymerization
Ultrafast multi-focus 3-D nano-fabrication based on two-photon polymerization