Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access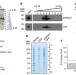 Plasma membrane-derived extracellular microvesicles mediate non-canonical intercellular NOTCH signaling
Plasma membrane-derived extracellular microvesicles mediate non-canonical intercellular NOTCH signaling
ARMMs are extracellular vesicles that bud directly at the plasma membrane; their function is poorly understood. Here the authors purify and carryout a proteomics analysis of the protein components of ARMMs, and show that NOTCH receptors are recruited into ARMMs and can be transferred to recipient cells to mediate NOTCH signaling.
- Qiyu Wang
- & Quan Lu
-
Article
| Open Access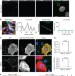 RSV glycoprotein and genomic RNA dynamics reveal filament assembly prior to the plasma membrane
RSV glycoprotein and genomic RNA dynamics reveal filament assembly prior to the plasma membrane
Assembly of filamentous RSV particles is incompletely understood due to a lack of techniques suitable for live-cell imaging. Here Vanover et al. use labeled soybean agglutinin to selectively label RSV G protein and show how filamentous RSV assembly, initiated in the cytoplasm, uses G protein recycled from the plasma membrane.
- Daryll Vanover
- , Daisy V. Smith
- & Philip J. Santangelo
-
Article
| Open Access Novel ecto-tagged integrins reveal their trafficking in live cells
Novel ecto-tagged integrins reveal their trafficking in live cells
Integrins are cell-surface adhesion receptors that are modulated by endo-exocytic trafficking, but existing tools to study this process can interfere with function. Here the authors develop β1 integrins carrying traceable tags in the extracellular domain; a pH-sensitive pHlourin tag or a HaloTag to facilitate dye attachment.
- Clotilde Huet-Calderwood
- , Felix Rivera-Molina
- & David A. Calderwood
-
Article
| Open Access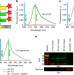 SRpHi ratiometric pH biosensors for super-resolution microscopy
SRpHi ratiometric pH biosensors for super-resolution microscopy
Ratiometric fluorescent pH probes are useful tools to monitor acidification of vesicles during endocytosis, but the size of vesicles is below the diffraction limit. Here the authors develop a family of ratiometric pH sensors for use in STED super-resolution microscopy, and optimize their delivery to endosomes.
- Douglas S. Richardson
- , Carola Gregor
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article
| Open Access A systematic exploration of the interactions between bacterial effector proteins and host cell membranes
A systematic exploration of the interactions between bacterial effector proteins and host cell membranes
Microbial pathogens secrete effector proteins into host cells to affect cellular functions. Here, the authors use a yeast-based screen to study around 200 effectors from six bacterial species, showing that over 30% of them interact with the eukaryotic plasma membrane or intracellular organelles.
- Bethany A. Weigele
- , Robert C. Orchard
- & Neal M. Alto
-
Article
| Open Access Planar polarized Rab35 functions as an oscillatory ratchet during cell intercalation in the Drosophila epithelium
Planar polarized Rab35 functions as an oscillatory ratchet during cell intercalation in the Drosophila epithelium
Various stages of tissue morphogenesis involve the contraction of epithelial surfaces. Here, the authors identify the Rab GTPase Rab35 as an essential component of this contractile process, which functions as a membrane ratchet to ensure unidirectional movement of intercalating cells.
- Cayla E. Jewett
- , Timothy E. Vanderleest
- & J. Todd Blankenship
-
Article
| Open Access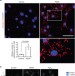 Assay to visualize specific protein oxidation reveals spatio-temporal regulation of SHP2
Assay to visualize specific protein oxidation reveals spatio-temporal regulation of SHP2
Protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are thought to be major targets of receptor-activated reactive oxygen species (ROS). Here the authors describe a method that allows the localized visualization of oxidized intermediates of PTPs inside cells during signaling, and provide support for the “redoxosome” model.
- Ryouhei Tsutsumi
- , Jana Harizanova
- & Benjamin G. Neel
-
Article
| Open Access Land-locked mammalian Golgi reveals cargo transport between stable cisternae
Land-locked mammalian Golgi reveals cargo transport between stable cisternae
The different composition of Golgi cisternae gave rise to two different models for intra-Golgi traffic: one where stable cisternae communicate via vesicles and another one where cisternae biochemically mature to ensure anterograde transport. Here, the authors provide evidence in support of the stable compartments model.
- Myun Hwa Dunlop
- , Andreas M. Ernst
- & James E. Rothman
-
Article
| Open Access Atg4 proteolytic activity can be inhibited by Atg1 phosphorylation
Atg4 proteolytic activity can be inhibited by Atg1 phosphorylation
The protease Atg4 mediates Atg8 lipidation, required for autophagosome biogenesis, but also triggers Atg8 release from the membranes, however is unclear how these steps are coordinated. Here the authors show that phosphorylation by Atg1 inhibits Atg4 at autophagosome formation sites.
- Jana Sánchez-Wandelmer
- , Franziska Kriegenburg
- & Fulvio Reggiori
-
Article
| Open Access Identification and characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin
Identification and characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin
There are seven well-established types of Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs). Here the authors report the identification and characterization of a new type of BoNT—BoNT/X—which cleaves a different site on canonical BoNTs substrates and targets SNARE family members not cleaved by known BoNTs.
- Sicai Zhang
- , Geoffrey Masuyer
- & Pål Stenmark
-
Article
| Open Access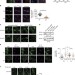 Spatial cycles mediated by UNC119 solubilisation maintain Src family kinases plasma membrane localisation
Spatial cycles mediated by UNC119 solubilisation maintain Src family kinases plasma membrane localisation
The peripheral membrane proto-oncogene Src family protein tyrosine kinases (SFKs) transmit growth factor signals to the cytoplasm. Here the authors show that the solubilising factor UNC119 sequesters myristoylated SFKs to maintain its enrichment at the plasma membrane to enable signal transduction.
- Antonios D. Konitsiotis
- , Lisaweta Roßmannek
- & Philippe I. H. Bastiaens
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of the ATP-bound Vps4E233Q hexamer and its complex with Vta1 at near-atomic resolution
Cryo-EM structures of the ATP-bound Vps4E233Q hexamer and its complex with Vta1 at near-atomic resolution
The ESCRT-III and Vps4 complexes mediate a variety of membrane remodelling events. Here the authors describe the structure of the Vps4 hexamer complexed to its cofactor Vta1, and show that Vta1 bridges adjacent Vps4 subunits to promote formation of the active hexamer during ESCRT-III filament disassembly.
- Shan Sun
- , Lin Li
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Article
| Open Access AGC family kinase 1 participates in trogocytosis but not in phagocytosis in Entamoeba histolytica
AGC family kinase 1 participates in trogocytosis but not in phagocytosis in Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica can kill host cells by trogocytosis, while it ingests dead cells by phagocytosis. Here, Somlata et al. show that EhAGCK1, an AGC family kinase, is specifically involved in trogocytosis, shedding light on the molecular differences between trogocytosis and phagocytosis.
- Somlata
- , Kumiko Nakada-Tsukui
- & Tomoyoshi Nozaki
-
Article
| Open Access Flat clathrin lattices are dynamic actin-controlled hubs for clathrin-mediated endocytosis and signalling of specific receptors
Flat clathrin lattices are dynamic actin-controlled hubs for clathrin-mediated endocytosis and signalling of specific receptors
Clathrin lattices coat flat membrane regions, called plaques, whose regulation and function are poorly understood. Here the authors find that plaques are regulated by actin dynamics and contain both the endocytic and the cell adhesion machineries, and are involved in endocytosis of specific cargos, and cell migration.
- Daniela Leyton-Puig
- , Tadamoto Isogai
- & Metello Innocenti
-
Article
| Open Access An exported protein-interacting complex involved in the trafficking of virulence determinants in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes
An exported protein-interacting complex involved in the trafficking of virulence determinants in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes
Plasmodium-infected red blood cells export virulence factors, such asPfEMP1, to the cell surface. Here, the authors identify a protein complex termed EPIC that interacts with PfEMP1 during export, and they show that knockdown of an EPIC component affects parasite virulence.
- Steven Batinovic
- , Emma McHugh
- & Leann Tilley
-
Article
| Open Access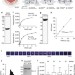 Lipid-mediated PX-BAR domain recruitment couples local membrane constriction to endocytic vesicle fission
Lipid-mediated PX-BAR domain recruitment couples local membrane constriction to endocytic vesicle fission
The spatiotemporal regulation of membrane scaffolds recruitment and coupling between membrane deformation and fission in endocytosis are unclear. Here the authors show that lipid conversion at endocytic pits recruits SNX9, which couples local membrane constriction to fission in endocytosis.
- Johannes Schöneberg
- , Martin Lehmann
- & Frank Noé
-
Article
| Open Access Routing of the RAB6 secretory pathway towards the lysosome related organelle of melanocytes
Routing of the RAB6 secretory pathway towards the lysosome related organelle of melanocytes
The anterograde movement of Golgi-derived vesicles requires the small GTPase RAB6, while its effector ELKS targets these vesicles to particular areas of the plasma membrane. Here the authors show that RAB6 and ELKS function in the biogenesis of melanosome, demonstrating that the secretory pathway can be directed towards intracellular organelles of endosomal origin.
- Anand Patwardhan
- , Sabine Bardin
- & Cédric Delevoye
-
Article
| Open Access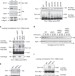 An ubiquitin-dependent balance between mitofusin turnover and fatty acids desaturation regulates mitochondrial fusion
An ubiquitin-dependent balance between mitofusin turnover and fatty acids desaturation regulates mitochondrial fusion
Mitochondrial fusion is crucial for cellular homeostasis but its regulation is still not fully understood. Here the authors report that a cross-talk between ubiquitin protease Ubp2 and ligases Mdm30 and Rsp5 modulates mitofusin Fzo1 levels and fatty acids saturation and thus mitochondrial fusion.
- Laetitia Cavellini
- , Julie Meurisse
- & Mickael M. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Constriction of the mitochondrial inner compartment is a priming event for mitochondrial division
Constriction of the mitochondrial inner compartment is a priming event for mitochondrial division
The role of morphological alterations in the mitochondrial inner-membrane in regulating mitochondrial division are unknown. Here, the authors describe spontaneous and repetitive constriction of the mitochondrial inner compartment, and suggest this acts as a priming event for efficient mitochondrial division.
- Bongki Cho
- , Hyo Min Cho
- & Woong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Sara phosphorylation state controls the dispatch of endosomes from the central spindle during asymmetric division
Sara phosphorylation state controls the dispatch of endosomes from the central spindle during asymmetric division
Asymmetric segregation of cell fate determinants during cell division governs daughter cell fate. Here the authors show that Sara endosomes, known to regulate Notch signalling, are targeted to the mitotic spindle and once phosphorylated are asymmetrically dispatched into a daughter cell to determine cell fate.
- Sylvain Loubéry
- , Alicia Daeden
- & Marcos Gonzalez-Gaitan
-
Article
| Open Access Myosin Va molecular motors manoeuvre liposome cargo through suspended actin filament intersections in vitro
Myosin Va molecular motors manoeuvre liposome cargo through suspended actin filament intersections in vitro
Cellular cargo transported along actin filaments is faced with a directional choice at an intersection. Here the authors show that myosin Va-bound cargo prefers to go straight through the intersection, and propose a model to explain this by a tug-of-war between motors on the lipid cargo that engage the actin tracks.
- Andrew T. Lombardo
- , Shane R. Nelson
- & David M. Warshaw
-
Article
| Open Access Regulated membrane remodeling by Mic60 controls formation of mitochondrial crista junctions
Regulated membrane remodeling by Mic60 controls formation of mitochondrial crista junctions
The MICOS complex has an essential role in crista junction formation and mitochondrial inner membrane morphology. Here, the authors show that one of its components, Mic60, known to form contact sites between inner and outer membranes, also displays membrane-shaping activity.
- Manuel Hessenberger
- , Ralf M. Zerbes
- & Oliver Daumke
-
Article
| Open Access Impaired prosaposin lysosomal trafficking in frontotemporal lobar degeneration due to progranulin mutations
Impaired prosaposin lysosomal trafficking in frontotemporal lobar degeneration due to progranulin mutations
Mutations in the granulin gene are associated with frontotemporal lobe dementia (FTLD) and a lysosomal storage disease. The authors show that reduced progranulin levels leads to impaired neuronal uptake and lysosomal delivery of prosaposin, and that decreased prosaposin expression in mice leads to FTLD-like behaviour.
- Xiaolai Zhou
- , Lirong Sun
- & Fenghua Hu
-
Article
| Open Access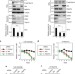 Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells
Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells
The role of exosomes in intercellular communication is well established, however less in known about the biological roles of exosome secretion in exosome-secreting cells. Here the authors show that exosome secretion controls cellular homeostasis in exosome-secreting cells by removing harmful cytoplasmic DNA from cells.
- Akiko Takahashi
- , Ryo Okada
- & Eiji Hara
-
Article
| Open Access A new inhibitor of the β-arrestin/AP2 endocytic complex reveals interplay between GPCR internalization and signalling
A new inhibitor of the β-arrestin/AP2 endocytic complex reveals interplay between GPCR internalization and signalling
Beta-arrestins play central roles in the mechanisms regulating GPCR signalling and trafficking. Here the authors identify a selective inhibitor of the interaction between β-arrestin and the β2-adaptin subunit of the clathrin adaptor protein AP-2, which they use to dissect the role of the β-arrestin/β2-adaptin interaction in GPCR signalling.
- Alexandre Beautrait
- , Justine S. Paradis
- & Michel Bouvier
-
Article
| Open Access Exosome-delivered EGFR regulates liver microenvironment to promote gastric cancer liver metastasis
Exosome-delivered EGFR regulates liver microenvironment to promote gastric cancer liver metastasis
EGFR signalling has been linked to cancer development but whether it has any role in pre-metastatic niche formation is not known. Here the authors show that gastric cancer cells send EGFR through exosomes to the liver where it causes the establishment of a favourable microenvironment thus promoting metastasis.
- Haiyang Zhang
- , Ting Deng
- & Yi Ba
-
Article
| Open Access Retrograde transport of TrkB-containing autophagosomes via the adaptor AP-2 mediates neuronal complexity and prevents neurodegeneration
Retrograde transport of TrkB-containing autophagosomes via the adaptor AP-2 mediates neuronal complexity and prevents neurodegeneration
The endocytic adaptor protein complex AP-2 is mostly known for its role in endocytosis and in synaptic vesicle reformation. Here the authors show that AP-2 also mediates retrograde transport of TrkB-containing autophagosomes in neurons; this process promotes neuronal complexity and prevents the degeneration of cortical and thalamic neurons.
- Natalia L. Kononenko
- , Gala A. Claßen
- & Volker Haucke
-
Article
| Open Access The Par3 polarity protein is an exocyst receptor essential for mammary cell survival
The Par3 polarity protein is an exocyst receptor essential for mammary cell survival
The exocyst delivers basolateral proteins from the secretory pathway to the plasma membrane of epithelial cells close to tight junctions. Here the authors show that Par3 acts as a docking site for the exocyst to regulate polarized delivery of basolateral proteins and this is essential to prevent apoptosis and promote mammary cell survival.
- Syed Mukhtar Ahmed
- & Ian G. Macara
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation of Rab-coupling protein by LMTK3 controls Rab14-dependent EphA2 trafficking to promote cell:cell repulsion
Phosphorylation of Rab-coupling protein by LMTK3 controls Rab14-dependent EphA2 trafficking to promote cell:cell repulsion
Ephrin receptors mediate contact inhibition, but their intracellular trafficking during this process is unknown. Here the authors show that EphA2 receptor trafficking is regulated by the Rab GTPase effector Rab-coupling protein, which associates with Rab14-endosomes upon LMTK3-mediated phosphorylation.
- Christine Gundry
- , Sergi Marco
- & Jim C. Norman
-
Article
| Open Access Zyxin regulates endothelial von Willebrand factor secretion by reorganizing actin filaments around exocytic granules
Zyxin regulates endothelial von Willebrand factor secretion by reorganizing actin filaments around exocytic granules
The adaptor protein zyxin is known for its mechanosensing function in the maintenance of actin network. Here the authors show that zyxin is key to blood homeostasis and thrombosis by controlling the endothelial release of von Willebrand factor and the formation of actin scaffolds on exocytic granules.
- Xiaofan Han
- , Pin Li
- & Jincai Luo
-
Article
| Open Access A Rab5 endosomal pathway mediates Parkin-dependent mitochondrial clearance
A Rab5 endosomal pathway mediates Parkin-dependent mitochondrial clearance
Damaged mitochondria are normally cleared through canonical and alternative autophagy pathways. Here, the authors report that mitochondria can be cleared through an autophagy-independent endosomal-lysosomal pathway that depends on Parkin-dependent sequestration of mitochondria in Rab5-positive early endosomes.
- Babette C. Hammerling
- , Rita H. Najor
- & Åsa B. Gustafsson
-
Article
| Open Access Sec3 promotes the initial binary t-SNARE complex assembly and membrane fusion
Sec3 promotes the initial binary t-SNARE complex assembly and membrane fusion
Membrane fusion during exocytosis is mediated by interaction between SNARE proteins on vesicles and the cell membrane, but how SNARE complex assembly is initiated remains unknown. Here, the authors show that interaction of Sec3 with Sso2 on the plasma membrane promotes formation of an Sso2–Sec9 complex, an early step in SNARE assembly, likely by inhibiting Sso2 auto-inhibition.
- Peng Yue
- , Yubo Zhang
- & Wei Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Pyruvate kinase type M2 promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating synaptosome-associated protein 23
Pyruvate kinase type M2 promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating synaptosome-associated protein 23
Exosomes, vesicles secreted by cancer cells, have a role in cancer progression but the mechanisms regulating their biogenesis are mostly unknown. Here the authors show that PKM2, a rate-limiting glycolytic enzyme overexpressed in cancer cells, mediates exosomes exocytosis by phosphorylating SNAP-23.
- Yao Wei
- , Dong Wang
- & Ke Zen
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture and mechanism of the late endosomal Rab7-like Ypt7 guanine nucleotide exchange factor complex Mon1–Ccz1
Architecture and mechanism of the late endosomal Rab7-like Ypt7 guanine nucleotide exchange factor complex Mon1–Ccz1
The Mon1-Ccz1 (MC1) complex is a Rab guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RabGEF) for Ypt7/Rab7 important for endosomal maturation. Here the authors present the biochemical and structural characterization of MC1, elucidating its catalytic mechanism and showing that MC1 represents novel class of RabGEFs.
- Stephan Kiontke
- , Lars Langemeyer
- & Daniel Kümmel
-
Article
| Open Access HS1BP3 negatively regulates autophagy by modulation of phosphatidic acid levels
HS1BP3 negatively regulates autophagy by modulation of phosphatidic acid levels
Autophagy must be tightly controlled at each step of the process. Here the authors show that HS1BP3 binds phosphatidic acid (PA) at autophagosome precursors and negatively regulates autophagosome formation by modulating the activity and localization of the PA-producing enzyme phospholipase D1.
- Petter Holland
- , Helene Knævelsrud
- & Anne Simonsen
-
Article
| Open Access Two pathways regulate cortical granule translocation to prevent polyspermy in mouse oocytes
Two pathways regulate cortical granule translocation to prevent polyspermy in mouse oocytes
Mammalian eggs release cortical granules to avoid being fertilized by more than a single sperm as polyspermy results in nonviable embryos. Here, the authors describe the mechanism driving translocation of the granules to the cortex in the mouse egg and show this process is essential to prevent polyspermy.
- Liam P. Cheeseman
- , Jérôme Boulanger
- & Melina Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal control of interferon-induced JAK/STAT signalling and gene transcription by the retromer complex
Spatiotemporal control of interferon-induced JAK/STAT signalling and gene transcription by the retromer complex
Endocytosis of the type I interferon receptor (IFNAR) is required for JAK/STAT signalling. Here the authors show that the internalized IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 subunits are differentially sorted by the retromer complex at the early endosome and this controls JAK/STAT signalling and gene transcription.
- Daniela Chmiest
- , Nanaocha Sharma
- & Christophe Lamaze
-
Article
| Open Access A mutation in VPS15 (PIK3R4) causes a ciliopathy and affects IFT20 release from the cis-Golgi
A mutation in VPS15 (PIK3R4) causes a ciliopathy and affects IFT20 release from the cis-Golgi
VPS15 is known as a VPS34-associated protein that functions in intracellular trafficking and autophagy. Here the authors identify a role for VPS15 in ciliopathy and ciliary phenotypes, and show that it interacts with GM130 and functions in IFT20-dependent cis-Golgi to cilium trafficking.
- Corinne Stoetzel
- , Séverine Bär
- & Hélène Dollfus
-
Article
| Open Access ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
Multivesicular bodies (MVB) are endosomal compartments that can either fuse with the plasma membrane for the secretion of exosomes, or fuse with the lysosome and be degraded along with their contents. Here, the authors show that ISGylation of the MVB protein TSG101 impairs exosome secretion and acts as a regulator of MVB fate.
- Carolina Villarroya-Beltri
- , Francesc Baixauli
- & Francisco Sánchez-Madrid
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic insights into regulation of the retromer coat by TBC1d5
Structural and mechanistic insights into regulation of the retromer coat by TBC1d5
Retromer is recruited to endosomes by the small GTPase Rab7 and sorting nexin 3. Here, the authors report the interaction between a GTPase-activating protein TBC1d5 and Rab7, examine the biochemical details of the interaction with retromer, and discuss the implications for receptor trafficking.
- Da Jia
- , Jin-San Zhang
- & Michael K. Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access Self-propelling vesicles define glycolysis as the minimal energy machinery for neuronal transport
Self-propelling vesicles define glycolysis as the minimal energy machinery for neuronal transport
How neurons produce energy to fuel fast axonal transport is only partially understood. Authors here report that most glycolytic enzymes are enriched in motile vesicles, and such glycolytic machinery can produce ATP autonomously to propel vesicle movement along microtubules in a cell-free assay.
- María-Victoria Hinckelmann
- , Amandine Virlogeux
- & Frédéric Saudou
-
Article
| Open Access Enrichment of hydroxylated C24- and C26-acyl-chain sphingolipids mediates PIN2 apical sorting at trans-Golgi network subdomains
Enrichment of hydroxylated C24- and C26-acyl-chain sphingolipids mediates PIN2 apical sorting at trans-Golgi network subdomains
Sphingolipids in the trans-Golgi network have been implicated in polar trafficking. Here Wattelet-Boyer et al. show that hydroxylated C24- and C26-acyl-chain sphingolipids are enriched in trans-Golgi network subdomains that are critical for polar sorting of the PIN2 auxin carrier in plant cells.
- Valérie Wattelet-Boyer
- , Lysiane Brocard
- & Yohann Boutté
-
Article
| Open Access Dysferlin-mediated phosphatidylserine sorting engages macrophages in sarcolemma repair
Dysferlin-mediated phosphatidylserine sorting engages macrophages in sarcolemma repair
Sarcolemma lesions are sealed by a repair patch of lipids and proteins that prevents cell death and myopathy. Here the authors show that the "eat-me" signal phosphatidylserine is sorted from adjacent sarcolemma to the repair patch in a Dysferlin dependent process in zebrafish and human cells.
- Volker Middel
- , Lu Zhou
- & Uwe Strähle
-
Article
| Open Access Anks1a regulates COPII-mediated anterograde transport of receptor tyrosine kinases critical for tumorigenesis
Anks1a regulates COPII-mediated anterograde transport of receptor tyrosine kinases critical for tumorigenesis
EphA2/ErbB2 complex is important in promoting breast cancer but the mechanism by which these receptor tyrosine kinases are exported from the endoplasmic reticulum is unknown. Here the authors show that Anks1a acts as a cargo adaptor in sorting EphA2 into COPII vesicles, thus modulating the surface level of EphA2.
- Haeryung Lee
- , Hyuna Noh
- & Soochul Park
-
Article
| Open Access High cell-surface density of HER2 deforms cell membranes
High cell-surface density of HER2 deforms cell membranes
HER2 is frequently overexpressed in breast cancer in association with increased metastatic potential. Here, the authors show that HER2 overexpression causes deformation of cell membranes in a signalling-independent manner that contributes to the disease phenotype by disrupting epithelial features.
- Inhee Chung
- , Mike Reichelt
- & Mark X. Sliwkowski
-
Article
| Open Access Fscn1 is required for the trafficking of TGF-β family type I receptors during endoderm formation
Fscn1 is required for the trafficking of TGF-β family type I receptors during endoderm formation
It is unclear how the cytoskeleton acts to assist in TGF-β signalling downstream of the receptor. Here, in zebrafish, the authors show that the actin-bundling protein FSCN1 interacts with TGF-β type I receptors ALK 4 and 5, enabling actin filament mediated vesicle trafficking and endoderm formation.
- Zhaoting Liu
- , Guozhu Ning
- & Qiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sec16 alternative splicing dynamically controls COPII transport efficiency
Sec16 alternative splicing dynamically controls COPII transport efficiency
The transport of secretory proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi depends on COPII-coated vesicles. Here, the authors show that activation-induced alternative splicing of Sec16 controls adaptation of COPII transport to increased secretory cargo upon T cell activation.
- Ilka Wilhelmi
- , Regina Kanski
- & Florian Heyd
-
Article
| Open Access Cingulin and actin mediate midbody-dependent apical lumen formation during polarization of epithelial cells
Cingulin and actin mediate midbody-dependent apical lumen formation during polarization of epithelial cells
Polarisation of epithelial cells causes lumen formation, which is mediated by apical membrane initiation site (AMIS) and FIP5, but how this is regulated is unclear. Here, the authors identify cingulin as a FIP-5 interacting protein, recruiting the Rac1-WAVE/Scar complex to the AMIS and branched actin formation.
- Anthony J. Mangan
- , Daniel V. Sietsema
- & Rytis Prekeris
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Lysine hydroxylation of procollagen precursors by LH3 is required for collagen fibril crosslinking and stabilization. Here the authors show that the trafficking protein VIPAR is required for correct sorting of LH3 into post-Golgi collagen carriers and for correct collagen modification and structure.
- Blerida Banushi
- , Federico Forneris
- & Paul Gissen

 ORP5 and ORP8 bind phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-biphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P
2) and regulate its level at the plasma membrane
ORP5 and ORP8 bind phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-biphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P
2) and regulate its level at the plasma membrane