Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Benzene- and pyridine-incorporated octaphyrins with different coordination modes toward two PdII centers
Benzene- and pyridine-incorporated octaphyrins with different coordination modes toward two PdII centers
The reactivity of expanded porphyrins is highly influenced by their scaffold architecture. Here, the authors construct two nonaromatic dumbbell-shaped benzene- and pyridine-incorporating octaphyrins via Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling; depending on the framework, different coordination modes are obtained upon metallation with Pd(II).
- Le Liu
- , Zhiwen Hu
- & Jianxin Song
-
Article
| Open Access High pressure synthesis of phosphine from the elements and the discovery of the missing (PH3)2H2 tile
High pressure synthesis of phosphine from the elements and the discovery of the missing (PH3)2H2 tile
Chemical elements at high pressure may behave more consistently with their periodic properties than they do at ambient conditions. The authors report the synthesis of PH3 from black phosphorous and hydrogen, and the crystallization of the van der Waals compound (PH3)2H2 which fills a gap in the chemistry of adjacent elements in the periodic table.
- Matteo Ceppatelli
- , Demetrio Scelta
- & Maurizio Peruzzini
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and X-ray characterization of 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes
Synthesis and X-ray characterization of 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes
The synthesis of closo-carboranes with more than 14 vertexes is challenging, and no examples have been reported to date. Herein, the authors present the long-sought 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes, in which the introduction of silyl groups to the two cage carbons is crucial; this finding might enable the synthesis of even larger carborane analogs in the future.
- Fangrui Zheng
- , Tsz Hin Yui
- & Zuowei Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancy layers in perovskite oxynitrides
Strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancy layers in perovskite oxynitrides
Properties of perovskite oxides can be changed by manipulating anion-vacancy order patterns, but they are difficult to control. Here the authors show strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancies in perovskite films in which the direction or periodicity of anion-vacancy planes is altered depending on the substrate employed.
- Takafumi Yamamoto
- , Akira Chikamatsu
- & Hiroshi Kageyama
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable modulation of precursor reactivity using chemical additives for systematic synthesis of high-quality quantum dots
Controllable modulation of precursor reactivity using chemical additives for systematic synthesis of high-quality quantum dots
Synthesis of high crystal quality quantum dots (QDs) requires optimization of reaction temperature and precursor reactivity. Here, the authors report precursor chemistry that enables controllable modulation of precursor reactivity using chemical additives, and systematically grow high-quality QDs from cores of various sizes and materials.
- Joonhyuck Park
- , Arun Jayaraman
- & Hee-Sun Han
-
Article
| Open Access 99TcO4− removal from legacy defense nuclear waste by an alkaline-stable 2D cationic metal organic framework
99TcO4− removal from legacy defense nuclear waste by an alkaline-stable 2D cationic metal organic framework
Separation of 99TcO4− from nuclear waste at the Savannah River Site is hampered by the extreme conditions. Here, the authors propose a solution by developing an alkaline-resistant metal organic framework material featuring unique recognition sites for selective incorporation of 99TcO4− anions.
- Nannan Shen
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the room-temperature atomic structure and growth kinetics of lithium metal
Unravelling the room-temperature atomic structure and growth kinetics of lithium metal
Atomic structure of alkali metal is difficult to be revealed at room temperature because of the chemical reactivity and irradiation sensitivity. Here the authors show that electron beam-induced in situ growth of alkali metals enables the investigation of atomic structure and growth kinetics at high spatiotemporal resolution.
- Chao Liang
- , Xun Zhang
- & Yi Yu
-
Article
| Open Access A sandwich-type cluster containing Ge@Pd3 planar fragment flanked by aromatic nonagermanide caps
A sandwich-type cluster containing Ge@Pd3 planar fragment flanked by aromatic nonagermanide caps
Sandwich-type clusters containing heterometallic interlayers have remained elusive. Here, the authors present the structure of a cluster composed of two aromatic nonagermanide caps flanking an heterometallic Ge@Pd3 planar fragment, where the Ge center is formally zerovalent.
- Hong-Lei Xu
- , Nikolay V. Tkachenko
- & Zhong-Ming Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient and air-stable Eu(II)-containing azacryptates ready for organic light-emitting diodes
Highly efficient and air-stable Eu(II)-containing azacryptates ready for organic light-emitting diodes
Though divalent-europium-based complexes are promising materials for next-generation light-emitting devices, their poor air stability limits their applicability. Here, the authors report the design of air stable divalent-europium-based complexes for efficient organic light-emitting diodes.
- Jiayi Li
- , Liding Wang
- & Zhiwei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed transition metal hydroxide nanosheet arrays on graphene for artificial CO2 reduction
Rationally designed transition metal hydroxide nanosheet arrays on graphene for artificial CO2 reduction
The development of effective, earth-abundant cocatalysts is critical for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Here, authors report the assembly of transition metal hydroxides on graphene to act as cocatalyst ensembles for efficient CO2 photoreduction.
- Kang-Qiang Lu
- , Yue-Hua Li
- & Yi-Jun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilizing a metalloid {Zn12} unit within a polymetallide environment in [K2Zn20Bi16]6−
Stabilizing a metalloid {Zn12} unit within a polymetallide environment in [K2Zn20Bi16]6−
Low-valent zinc clusters, though exceedingly rare, are appealing synthetic targets because there is evidence that they may show unconventional chemical and physical behavior. Here, the authors obtain a large heterometallic zinc-bismuth cluster anion and discover that it bears a metalloid {Zn12} core with four-center bonding and essentially zero-valent character.
- Armin R. Eulenstein
- , Yannick J. Franzke
- & Stefanie Dehnen
-
Review Article
| Open Access Solid state chemistry for developing better metal-ion batteries
Solid state chemistry for developing better metal-ion batteries
The development of high performing metal-ion batteries require guidelines to build improved electrodes and electrolytes. Here, the authors review the current state-of-the-art in the rational design of battery materials by exploiting the interplay between composition, crystal structure and electrochemical properties.
- Artem M. Abakumov
- , Stanislav S. Fedotov
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article
| Open Access Modulated structure determination and ion transport mechanism of oxide-ion conductor CeNbO4+δ
Modulated structure determination and ion transport mechanism of oxide-ion conductor CeNbO4+δ
Materials with oxygen hyperstoichiometry received great attention in solid oxide fuel cells field because of the low activation energy of interstitial ion migration. Here the authors revealed the relationship between the structure and oxide ion migration for the whole series of CeNbO4+δ compounds.
- Jian Li
- , Fengjuan Pan
- & Junliang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Regioselective functionalization of aryl azoles as powerful tool for the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant targets
Regioselective functionalization of aryl azoles as powerful tool for the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant targets
Aryl azoles are common scaffolds in pharmaceutically relevant molecules. Here, the authors report the mild and highly regioselective ortho magnesiation of aryl azoles using a tailored magnesium amide base in hydrocarbon solvents followed by an efficient Pd-catalyzed arylation.
- Ferdinand H. Lutter
- , Lucie Grokenberger
- & Paul Knochel
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature formation of CdS magic-size clusters in aqueous solutions assisted by primary amines
Room-temperature formation of CdS magic-size clusters in aqueous solutions assisted by primary amines
CdS magic-size clusters have, so far, been prepared only in organic solvents. Here, the authors report an aqueous-phase synthesis for CdS magic-size clusters at room temperature and reveal insights into the formation mechanism, including the key role of primary amines.
- Wushuang Wan
- , Meng Zhang
- & Kui Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon–silicon π single bond
Silicon–silicon π single bond
Examples of π single bonds in diradicals are rare, as they are typically unstable. Here, the authors describe a room temperature-stable closed-shell bicyclic tetrasilane that features a Si-Si π single bond between two of the non-adjacent Si centers.
- Soichiro Kyushin
- , Yoshikuni Kurosaki
- & Hideyuki Matsumoto
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-3D topotactic transformation in aluminophosphate molecular sieves and its implication in new zeolite structure generation
3D-3D topotactic transformation in aluminophosphate molecular sieves and its implication in new zeolite structure generation
Zeolites have pore structures that are attractive for shape-selective catalysis and separation, but targeted synthesis is challenging. Here, the authors propose using a 3D-3D topotactic transformation to synthesize targeted zeolites, including some that may be not feasible with conventional methods.
- Zhehao Huang
- , Seungwan Seo
- & Xiaodong Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient methane functionalization initiated by electrochemical oxidation of a vanadium (V)-oxo dimer
Ambient methane functionalization initiated by electrochemical oxidation of a vanadium (V)-oxo dimer
The undesirable geological release of methane at remote locations can be lessened through an efficient methane conversion process. Here, the authors report selective ambient functionalization of methane by a vanadium (V)-oxo electrocatalyst with a low activation energy and a high turnover frequency.
- Jiao Deng
- , Sheng-Chih Lin
- & Chong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical instability at chalcogenide surfaces impacts chalcopyrite devices well beyond the surface
Chemical instability at chalcogenide surfaces impacts chalcopyrite devices well beyond the surface
Anion vacancies are a hurdle for technologies based on chalcogenide semiconductors and topological insulators. Even at room temperature, oxidation and cyanide etching can lead to selenium vacancies in CuInSe2 photovoltaic material but suitable post deposition treatments can mitigate their effect.
- Diego Colombara
- , Hossam Elanzeery
- & Susanne Siebentritt
-
Article
| Open Access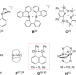 A diradical based on odd-electron σ-bonds
A diradical based on odd-electron σ-bonds
Stable diradicals are generally based on two s/p-localized or π-delocalized unpaired electrons (radicals). Here, the authors report a dication diradical that is based on two Se∴Se three-electron σ-bonds.
- Wenbang Yang
- , Li Zhang
- & Xinping Wang
-
Article
| Open Access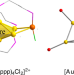 A family of lead clusters with precious metal cores
A family of lead clusters with precious metal cores
Many Zintl ions with a single endohedrally encapsulated transition metal ion are known, but relatively few where clusters of two or more metals are present. Here, the authors report the synthesis and characterization of two clusters, [Au8Pb33]6− and [Au12Pb44]12−, which contain Au8 and Au12 cores surrounded by Pb shells.
- Cong-Cong Shu
- , Harry W. T. Morgan
- & Zhong-Ming Sun
-
Article
| Open Access A flat carborane with multiple aromaticity beyond Wade–Mingos’ rules
A flat carborane with multiple aromaticity beyond Wade–Mingos’ rules
The polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory (PESPT), also known as Wade-Mingos’ rules, defines a relationship between skeletal bonding electron pairs and structure of clusters. Here the authors report the synthesis, structure and computational studies of planar C2B4R4 carboranes that do not adhere to PESPT.
- Wei Lu
- , Dinh Cao Huan Do
- & Rei Kinjo
-
Article
| Open Access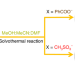 A Keplerian Ag90 nest of Platonic and Archimedean polyhedra in different symmetry groups
A Keplerian Ag90 nest of Platonic and Archimedean polyhedra in different symmetry groups
Nested polyhedra are compelling but incredibly complex synthetic targets in cluster chemistry. Here, the authors synthesize a Ag90 nanocluster comprising three concentric polyhedra with apparently incompatible octahedral (Oh) and icosahedral (Ih) symmetry, a mathematical oddity that is solved by the shells’ symmetric arrangement around rotational 2- and 3-fold axes.
- Yan-Min Su
- , Zhi Wang
- & Di Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed ruthenium complexes for 1- and 2-photon photodynamic therapy
Rationally designed ruthenium complexes for 1- and 2-photon photodynamic therapy
Photosensitizers that are stable in biological conditions with absorption in the biological spectral window are needed for photodynamic therapy. Here, the authors report on the development of a Ruthenium complex for 1 and 2-photon therapy to address these issues and demonstrate application in vivo.
- Johannes Karges
- , Shi Kuang
- & Gilles Gasser
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing oxidation resistance of Cu(I) by tailoring microenvironment in zeolites for efficient adsorptive desulfurization
Enhancing oxidation resistance of Cu(I) by tailoring microenvironment in zeolites for efficient adsorptive desulfurization
Zeolite Cu(I)Y is attractive for adsorptive removal of sulfur compounds from fuel, however practical application is limited by instability of Cu(I). Here the authors use a coating to achieve superhydrophobicity in the zeolite, leading to improved Cu(I) stability against oxidation and thiophene removal.
- Yu-Xia Li
- , Jia-Xin Shen
- & Lin-Bing Sun
-
Article
| Open Access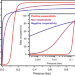 Negative cooperativity upon hydrogen bond-stabilized O2 adsorption in a redox-active metal–organic framework
Negative cooperativity upon hydrogen bond-stabilized O2 adsorption in a redox-active metal–organic framework
Oxygen capture is attractive for catalysis, sensing, and separations, but engineering stable and selective adsorbents is challenging. Here the authors combine metal-based electron transfer with secondary coordination sphere effects in a metal-organic framework, leading to strong and reversible O2 adsorption that also exhibits negative cooperativity.
- Julia Oktawiec
- , Henry Z. H. Jiang
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article
| Open Access Sn(IV)-free tin perovskite films realized by in situ Sn(0) nanoparticle treatment of the precursor solution
Sn(IV)-free tin perovskite films realized by in situ Sn(0) nanoparticle treatment of the precursor solution
Tin based perovskites are easily oxidized, which generates large density of defects and compromised the solar cell efficiency. Here Nakamura et al. add metallic tin nanoparticles in the precursor solution to suppress tin (IV) impurities and enable high efficiency tin based perovskite solar cells.
- Tomoya Nakamura
- , Shinya Yakumaru
- & Atsushi Wakamiya
-
Article
| Open Access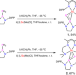 Synthesis and versatile reactivity of scandium phosphinophosphinidene complexes
Synthesis and versatile reactivity of scandium phosphinophosphinidene complexes
Rare-earth monometallic phosphinidene complexes have been elusive synthetic targets. Here, the authors describe the synthesis and tunable reactivity of two scandium phosphinophosphinidene complexes containing very unusual Sc-P multiple bonds.
- Bin Feng
- , Li Xiang
- & Yaofeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access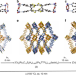 Reversible single crystal-to-single crystal double [2+2] cycloaddition induces multifunctional photo-mechano-electrochemical properties in framework materials
Reversible single crystal-to-single crystal double [2+2] cycloaddition induces multifunctional photo-mechano-electrochemical properties in framework materials
Porous coordination frameworks that undergo reversible structural transformations are promising for sensing, switching and separations. Here, the authors report an electroactive framework that exhibits a reversible single crystal-to-single crystal double [2+2] photocyclisation, leading to property changes.
- Dylan A. Sherman
- , Ryuichi Murase
- & Deanna M. D’Alessandro
-
Article
| Open Access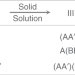 Molecule-based nonlinear optical switch with highly tunable on-off temperature using a dual solid solution approach
Molecule-based nonlinear optical switch with highly tunable on-off temperature using a dual solid solution approach
Switching of nonlinear optical signals is attractive for photoelectronics and photonics, but development is hindered by a lack of control over the switch temperature. Here the authors report a coordination polymer system that serves as an alloy-like nonlinear optical switch with a tunable switch temperature.
- Shi-Yong Zhang
- , Xia Shu
- & Xiao-Ming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spherical trihedral metallo-borospherenes
Spherical trihedral metallo-borospherenes
Borospherenes are the boron-based analogs of fullerene cages. Here, the authors report a class of Ln3B18– metallo-borospherenes with unusual spherical trihedron geometry, in which the lanthanide atoms surprisingly form a part of the cage surface.
- Teng-Teng Chen
- , Wan-Lu Li
- & Lai-Sheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Rapidly sequence-controlled electrosynthesis of organometallic polymers
Rapidly sequence-controlled electrosynthesis of organometallic polymers
The controllable synthesis of organometallic polymers that can be used in ultrahigh information storage and anti-counterfeiting security has been an unsolved challenge. Here, the authors show sequence-controlled electrosynthesis of organometallic polymers with exquisite insertion of multiple and distinct monomers.
- Jian Zhang
- , Jinxin Wang
- & Mao Li
-
Article
| Open Access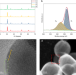 Black indium oxide a photothermal CO2 hydrogenation catalyst
Black indium oxide a photothermal CO2 hydrogenation catalyst
The utilization of white-colored, wide-bandgap CO2 hydrogenation photocatalysts has been hindered by their limited light-harvesting ability. By making stoichiometric white indium oxide non-stoichiometric and black, it is transformed from a highly inactive to a highly active photothermal catalyst.
- Lu Wang
- , Yuchan Dong
- & Geoffrey A. Ozin
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2
Room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2
Diatomic carbon (C2) is historically an elusive chemical species, considered to require high physical energy for its generation. Here, the authors describe the first room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2 and present experimental evidence for its singlet biradical (quadruple bonding) character and role as a molecular element of nanocarbons.
- Kazunori Miyamoto
- , Shodai Narita
- & Masanobu Uchiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Lattice distortion induced internal electric field in TiO2 photoelectrode for efficient charge separation and transfer
Lattice distortion induced internal electric field in TiO2 photoelectrode for efficient charge separation and transfer
The driving force for charge transfer in photoelectrochemical systems is typically derived from band bending at a surface-electrolyte interface. In this work, battery-type lithiation of TiO2 generates a built-in electric field in the bulk material, giving a 750% enhancement in photocurrent density.
- Yuxiang Hu
- , Yuanyuan Pan
- & Lianzhou Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Direct evidence of boosted oxygen evolution over perovskite by enhanced lattice oxygen participation
Direct evidence of boosted oxygen evolution over perovskite by enhanced lattice oxygen participation
While water splitting provides a renewable means to store energy, the sluggish O2 evolution half-reaction limits applications. Here, authors examine a silicon-incorporated strontium cobaltite perovskite and correlate lattice oxygen participation in O2 evolution to the oxygen ion diffusivity.
- Yangli Pan
- , Xiaomin Xu
- & Zongping Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Macroscopic Polarization Change via Electron Transfer in a Valence Tautomeric Cobalt Complex
Macroscopic Polarization Change via Electron Transfer in a Valence Tautomeric Cobalt Complex
Polarization change from directional electron transfer attracts considerable attention owing to its fast switching rate and potential light control. Here, the authors provide a proof-of-concept of electronic pyroelectricity induced by intramolecular electron transfer in the single crystal of a valence tautomeric compound.
- Shu-Qi Wu
- , Meijiao Liu
- & Osamu Sato
-
Article
| Open Access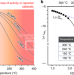 Solid solution for catalytic ammonia synthesis from nitrogen and hydrogen gases at 50 °C
Solid solution for catalytic ammonia synthesis from nitrogen and hydrogen gases at 50 °C
Ammonia synthesis via the Haber–Bosch process typically takes place at an elevated temperature in order to achieve a reasonable rate. Here the authors report on a CaFH solid solution with low activation energy for catalytic ammonia synthesis at lower temperatures.
- Masashi Hattori
- , Shinya Iijima
- & Michikazu Hara
-
Article
| Open Access Self-sustainable protonic ceramic electrochemical cells using a triple conducting electrode for hydrogen and power production
Self-sustainable protonic ceramic electrochemical cells using a triple conducting electrode for hydrogen and power production
While producing renewable fuel is crucial for a sustainable energy economy, there is still a need for active and durable materials capable of efficient fuel generation and utilization. Here, authors demonstrate a triple-conductive oxide as an oxygen electrode for H2 or electricity production.
- Hanping Ding
- , Wei Wu
- & Dong Ding
-
Article
| Open Access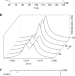 Site-selective doping of ordered charge states in magnetite
Site-selective doping of ordered charge states in magnetite
Charge ordering in magnetite is an important example of the complex behaviour that emerges in transition metal oxides. Here the authors show that doping causes selective oxidation of one site in the established trimeron pattern, introducing an additional charge-ordered structure.
- E. Pachoud
- , J. Cumby
- & J. P. Attfield
-
Article
| Open Access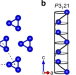 Atomic-level handedness determination of chiral crystals using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy
Atomic-level handedness determination of chiral crystals using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy
Handedness or chirality determination of crystals has always been challenging for chemists, biologists and materials scientists. Here, the authors report a method for handedness determination by atomic-resolution imaging using Cs-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy.
- Zhuoya Dong
- & Yanhang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access δ and φ back-donation in AnIV metallacycles
δ and φ back-donation in AnIV metallacycles
Metal-ligand δ and φ interactions, though considered weak, may be necessary for fully describing the electronic and geometric structures of certain compounds. Here, in actinide metallacycles, the authors discover two new types of M-L δ and φ back-bonds that contribute substantially to their unusual chemical behavior.
- Morgan P. Kelley
- , Ivan A. Popov
- & Ping Yang
-
Review Article
| Open Access A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry
A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry
The 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded to a trio of pioneers of the modern lithium-ion battery. Here, Professor Arumugam Manthiram looks back at the evolution of cathode chemistry, discussing the three major categories of oxide cathode materials with an emphasis on the fundamental solid-state chemistry that has enabled these advances.
- Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article
| Open Access Introducing the crystalline phase of dicalcium phosphate monohydrate
Introducing the crystalline phase of dicalcium phosphate monohydrate
Understanding the crystal structure of different calcium phosphates is important for a range of different subjects from geology to biomedicine. Here, the authors report on the synthesis and determination of the crystal structure of dicalcium phosphate monohydrate.
- Bing-Qiang Lu
- , Tom Willhammar
- & Denis Gebauer
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of nuclear reorganization driven by ultrafast spin transitions
Direct observation of nuclear reorganization driven by ultrafast spin transitions
Electron spin is a fundamental property of molecules, and changes in spin state affect both molecular structure and dynamics. Here, the authors resolve, by ultrafast electron diffraction, the nuclear reorganization stabilizing spin transitions in a [FeII(bpy)3](PF6)2 crystal.
- Yifeng Jiang
- , Lai Chung Liu
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Titanium-based potassium-ion battery positive electrode with extraordinarily high redox potential
Titanium-based potassium-ion battery positive electrode with extraordinarily high redox potential
The Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple is usually a good choice for anodes due to its low potential. Here, the authors show that the potential can be increased to nearly 4.0 V in KTiPO4F, which serves as a high-performance cathode for K-ion batteries.
- Stanislav S. Fedotov
- , Nikita D. Luchinin
- & Evgeny V. Antipov
-
Article
| Open Access Cation insertion to break the activity/stability relationship for highly active oxygen evolution reaction catalyst
Cation insertion to break the activity/stability relationship for highly active oxygen evolution reaction catalyst
Renewable hydrogen production from water will require understanding and improving the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) on catalyst surfaces. Here, authors report α-Li2IrO3 to transform into a hydrated birnessite phase under OER conditions that exhibits enhanced OER performances and durabilities.
- Chunzhen Yang
- , Gwenaëlle Rousse
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
Article
| Open Access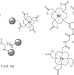 Direct solid-phase synthesis of molecular heterooligonuclear lanthanoid-complexes
Direct solid-phase synthesis of molecular heterooligonuclear lanthanoid-complexes
Lanthanoid complexes are widely used for various applications but so far it is difficult to combine multiple lanthanoids into one single molecular entity with sufficient stability. Here, the authors report a method for this purpose using peptide synthesis, and show that a trinuclear lanthanoid complex can be used to create a luminescence nanocode.
- Elisabeth Kreidt
- , Wolfgang Leis
- & Michael Seitz
-
Article
| Open Access Pt-O bond as an active site superior to Pt0 in hydrogen evolution reaction
Pt-O bond as an active site superior to Pt0 in hydrogen evolution reaction
While converting water to H2 with a catalyst offers a renewable means to produce carbon-neutral fuels, understanding the catalytic active sites has proven challenging. Here, authors show a structurally well-defined model complex with Pt-O bonding to enable efficient H2 evolution electrocatalysis.
- Fei-Yang Yu
- , Zhong-Ling Lang
- & Yang-Guang Li

 A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells
A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells