Featured
-
-
Opinion |
 Disease prevention—should we target obesity or sedentary lifestyle?
Disease prevention—should we target obesity or sedentary lifestyle?
Obesity is a major health challenge that is associated with chronic disease. The authors of this Perspectives article put forward a model that places sedentary behavior and calorie overload upstream of numerous disease processes. The authors highlight the importance of physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness, which are possibly stronger predictors of risk than traditional factors, such as obesity.
- Olivier L. Charansonney
- & Jean-Pierre Després
-
Review Article |
 Transthyretin-related amyloidoses and the heart: a clinical overview
Transthyretin-related amyloidoses and the heart: a clinical overview
Diagnosis of hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis (ATTR) is challenging owing to its extremely heterogeneous phenotype. The existence of predominantly cardiac presentations should prompt cardiologists to consider ATTR in patients with otherwise unexplained left ventricular wall thickening. Orthotopic liver transplantation (or combined heart–liver transplantation) can potentially provide surgical 'gene therapy' in patients with ATTR, provided that diagnosis is timely.
- Claudio Rapezzi
- , Candida Cristina Quarta
- & Angelo Branzi
-
Review Article |
 Early detection of myocardial dysfunction and heart failure
Early detection of myocardial dysfunction and heart failure
To date, treatment strategies for heart failure have focused on the symptomatic stage of disease, often after irreversible remodeling and functional impairment have occurred. Early identification of cardiac dysfunction would allow implementation of early intervention strategies to delay the progression or to prevent the onset of heart failure altogether. This Review highlights the utility of a staged approach for patients with predisposing risk factors, which uses serological biomarkers followed by noninvasive imaging techniques.
- Geoffrey de Couto
- , Maral Ouzounian
- & Peter P. Liu
-
Review Article |
 The role of echocardiographic deformation imaging in hypertrophic myopathies
The role of echocardiographic deformation imaging in hypertrophic myopathies
Echocardiography is commonly used to assess hypertrophic myopathies. The authors of this Review outline imaging modalities that are more sensitive than standard echocardiography, which can be used to determine characteristic changes in regional deformation at an earlier stage, and provide more information about the underlying processes associated with different hypertrophic myopathies.
- Maja Cikes
- , George R. Sutherland
- & Bart H. Bijnens
-
Review Article |
 Early identification of atherosclerotic disease by noninvasive imaging
Early identification of atherosclerotic disease by noninvasive imaging
Current strategies for prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) are focused on identifying individuals at high risk by recognizing and managing established cardiovascular risk factors. Early detection of subclinical atherosclerosis is a promising opportunity for CVD prevention. In this article, the authors review the role of noninvasive imaging techniques in understanding the mechanisms of atherosclerosis and in identifying early stages of disease, and highlight their potential impact on CVD prevention.
- Valentin Fuster
- , Fátima Lois
- & Manuel Franco
-
Opinion |
 Short-term vascular risk: time to take notice?
Short-term vascular risk: time to take notice?
The current guidelines for prevention of cardiovascular disease are based on estimates of long-term risk. Smeeth and Hingorani recommend awareness of the importance of fluctuations of risk over short periods of time and suggest a new paradigm for management of cardiovascular disease that is based on targeting therapy to short periods of enhanced risk.
- Liam Smeeth
- & Aroon D. Hingorani
-
Review Article |
 Early identification of cardiovascular risk using genomics and proteomics
Early identification of cardiovascular risk using genomics and proteomics
In this Review, Drs Kullo and Cooper discuss the role of genomics and proteomics in cardiovascular risk assessment, using the specific example of atherosclerosis. The availability of good markers for risk stratification might enable the health-care system to become more proactive, moving the focus away from treatment of end-stage coronary heart disease and towards early detection of disease risk and prevention of adverse outcomes.
- Iftikhar J. Kullo
- & Leslie T. Cooper
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Widespread use of public-access AEDs improves survival after cardiac arrest
Widespread use of public-access AEDs improves survival after cardiac arrest
- Alexandra King
-
Research Highlight |
 Is long-term clopidogrel therapy necessary after DES implantation?
Is long-term clopidogrel therapy necessary after DES implantation?
- Joana Osório
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
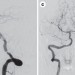 Endovascular treatment of vertebral artery stenosis
Endovascular treatment of vertebral artery stenosis
The safest and most effective treatment for symptomatic vertebral artery stenosis has not yet been proven. Here, we discuss the merits and pitfalls of endovascular treatment for this under-recognized disease entity.
- Mandy J. Binning
- & L. Nelson Hopkins
-
News & Views |
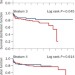 LVADs—from an imaginative leap to clinical decision making
LVADs—from an imaginative leap to clinical decision making
The development of left ventricular assist devices could be considered an 'imaginative leap'. In the current phase of critical evaluation of these devices, a study of patients who received first-generation left ventricular assist devices has indicated that they might affect late post-transplant survival. The validity and significance of these findings need to be examined further.
- Magdi H. Yacoub
-
Review Article |
 Fetal cardiac arrhythmia detection and in utero therapy
Fetal cardiac arrhythmia detection and in utero therapy
Detection of fetal conduction system abnormalities relies upon magnetocardiographic or electrocardiographic recording techniques. Appropriate fetal treatment requires awareness of arrhythmia characteristics, mechanisms, and their potential associations. This Review discusses current and future diagnostic techniques and pharmacologic treatments for fetal arrhythmia.
- Janette F. Strasburger
- & Ronald T. Wakai
-
Review Article |
 Early management of atrial fibrillation: from imaging to drugs to ablation
Early management of atrial fibrillation: from imaging to drugs to ablation
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. Early management of this disorder using imaging, antiarrhythmia drugs and catheter ablation is necessary to prevent the progression of AF. In this Review, the authors discuss the current status of important facets of the early management of AF and emphasize the need for a greater understanding of the underlying etiology, which will lead to novel treatment approaches and amelioration of AF.
- Ashok J. Shah
- , Xingpeng Liu
- & Michel Haïssaguerre
-
Review Article |
 Early identification of risk factors for sudden cardiac death
Early identification of risk factors for sudden cardiac death
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is a serious health concern worldwide. Despite the need for risk factors that can identify high-risk individuals, there are few available owing to the complex and often asymptomatic nature of SCD. In this Review, Sumeet Chugh outlines novel risk markers and predictors of SCD that will allow more effective prevention, and suggests a framework for studies in the future for the discovery and validation of these risk markers.
- Sumeet S. Chugh
-
Review Article |
 Strategic choices to reduce implantable cardioverter-defibrillator-related morbidity
Strategic choices to reduce implantable cardioverter-defibrillator-related morbidity
The number of patients undergoing implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is increasing, as the indications for device therapy have broadened. Despite the mortality benefits associated with ICDs, they can also cause substantial complications. Drs. Wazni and Wilkoff explore the issues involved in managing patients with an ICD and discuss approaches for reducing these adverse effects, from prevention of infection, and the choice of lead and implantation technique, to strategies for programming and monitoring the device.
- Oussama Wazni
- & Bruce L. Wilkoff
-
Review Article |
Intensive glycemic control and cardiovascular disease: an update
This Review discusses the effects of intensive glycemic control on cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes, and examines key factors in recent intervention trials that might have contributed to their disparate findings. The authors suggest that care of these patients should focus on achieving current treatment goals, rather than on changes to glycemic targets.
- Aparna Brown
- , L. Raymond Reynolds
- & Dennis Bruemmer
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Stress-only SPECT reduces radiation exposure but does not affect mortality
Stress-only SPECT reduces radiation exposure but does not affect mortality
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Age need not be a barrier to cardiac surgery—evidence from a nonagenarian population
Age need not be a barrier to cardiac surgery—evidence from a nonagenarian population
- Alexandra King
-
Research Highlight |
Catheter ablation improves outcome in drug-refractory, paroxysmal AF
- Alexandra King
-
-
Research Highlight |
 A new method to produce high-quality 3D images using available X-ray data
A new method to produce high-quality 3D images using available X-ray data
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
News & Views |
 Continuous-flow LVADs improve clinical outcomes
Continuous-flow LVADs improve clinical outcomes
A continuous-flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) improved survival free from disabling stroke compared with a pulsatile LVAD, when used as destination therapy over a 2-year period in patients with advanced heart failure. Both devices improved patient quality of life. Continuous-flow devices are smaller, lighter, and more simple than pulsatile LVADs and have the potential to fulfill all the requirements of a permanently implanted blood pump.
- Yukihiko Nosé
-
-
-
News & Views |
Telephone monitoring improves outcomes in patients with CHF
Klersy et al. have performed a meta-analysis of remote monitoring of patients with heart failure. Programs using structured telephone support (telephone-monitoring approach) were combined with those using transmission of physiological data (technology-assisted approach) in combination with telephone communication. Results from this study may inform policy makers regarding a potential solution to reducing hospital readmissions.
- Mary Ann McLaughlin
-
News & Views |
 Catheter ablation for prevention of ventricular tachycardia
Catheter ablation for prevention of ventricular tachycardia
Patients with structural heart disease are at risk for life-threatening ventricular tachycardias (VTs). Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) can terminate VT, but often at the cost of traumatic shocks, syncope, or even exacerbation of underlying heart disease. Catheter ablation for VT can reduce the need for ICD therapies and is an increasingly important adjunct to the treatment of these patients.
- Usha B. Tedrow
- & William G. Stevenson
-
Review Article |
 Marfan syndrome. Part 2: treatment and management of patients
Marfan syndrome. Part 2: treatment and management of patients
Over the past 30 years, we have witnessed a steady improvement in life expectancy of patients with Marfan syndrome, owing to advances in various treatments. In Part 2 of a 2-part Review on Marfan syndrome, Dr. Cañadas and colleagues discuss the present the state of the art in the management of patients with this disease.
- Victoria Cañadas
- , Isidre Vilacosta
- & Valentin Fuster
-
Review Article |
 Marfan syndrome. Part 1: pathophysiology and diagnosis
Marfan syndrome. Part 1: pathophysiology and diagnosis
The cardiovascular manifestations of Marfan syndrome are the main cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with this disease. In Part 1 of a 2-part Review on Marfan syndrome, Dr Cañadas and colleagues discuss the pathogenesis of Marfan syndrome, our idea of which has dramatically changed in the past decade, as well as the current strategy for diagnosis.
- Victoria Cañadas
- , Isidre Vilacosta
- & Valentin Fuster
-
Opinion |
 Myocardial edema—a new clinical entity?
Myocardial edema—a new clinical entity?
Controversy exists as to whether the detection of myocardial edema, to quantify myocardial damage and assess myocardial salvage, is ready for clinical use or is still only practical as a research tool. In this Perspectives article, Matthias Friedrich explains his point of view on this issue—that myocardial edema imaging using magnetic resonance technology should be seen as the essential diagnostic modality of choice for patients with suspected myocardial injury by virtue of its safety, versatility, and cost-efficiency.
- Matthias G. Friedrich
-
Review Article |
 Statin treatment for patients with heart failure
Statin treatment for patients with heart failure
Statin therapy has been associated with improved outcomes in patients with heart failure. However, two large prospective, controlled trials showed neutral effects with rosuvastatin. The authors of this Review highlight data from observational studies that have showed positive outcomes, and discuss how the design of the two large trials may have contributed to the neutral effects of statin therapy on the survival of patients with heart failure.
- W. H. Wilson Tang
- & Gary S. Francis
-
Review Article |
 Integration of coronary anatomy and myocardial perfusion imaging
Integration of coronary anatomy and myocardial perfusion imaging
Imaging techniques that assess myocardial perfusion and coronary anatomy obtain complementary information. Simultaneous dual-modality or sequential multimodal imaging techniques facilitate integration of this information, and thus have the potential to improve diagnostic and prognostic evaluations, as well as care of patients. This Review discusses the clinical utility and future directions of hybrid imaging.
- Ron Blankstein
- & Marcelo F. Di Carli
-
Review Article |
 New drug-eluting stent concepts
New drug-eluting stent concepts
The introduction of drug-eluting stents (DES) has greatly reduced in-stent restenosis. Improvements to this technology are required, however, as safety and efficacy are still a problem. This Review describes current DES and the methods that are being used to optimize the performance of these stents. The author also suggests the direction of DES in the future, including tailored therapy to improve patient outcomes.
- Rainer Wessely
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Omega-3 supplements do not prevent atrial fibrillation after CABG surgery
Omega-3 supplements do not prevent atrial fibrillation after CABG surgery
- Alexandra King
-
-
-
News & Views |
Are glucocorticoids a treatment or a risk factor?
Inflammation might be involved in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. Glucocorticoid use can attenuate inflammation and might be an effective therapy for atrial fibrillation. However, some population-based studies have reported an increased risk of atrial fibrillation associated with glucocorticoid use. Whether this link results from a direct effect of glucocorticoids or from the underlying inflammatory disease remains to be elucidated.
- Michiel Rienstra
- & Isabelle C. Van Gelder
-
-
-
News & Views |
Aldosterone antagonists are underused by clinicians
Aldosterone antagonists decrease the mortality of patients with heart failure, but an observational study by Albert and colleagues has found that a surprisingly low number of patients receive aldosterone antagonists before discharge from hospital. This article highlights potential reasons for why there is such an underuse of efficient drugs in heart failure.
- Jane-Lise Samuel
- & Claude Delcayre

 Overcoming 'resistance' to antiplatelet therapy: targeting the issue of nonadherence
Overcoming 'resistance' to antiplatelet therapy: targeting the issue of nonadherence Potential benefits of ECG screening in young athletes
Potential benefits of ECG screening in young athletes Strict heart-rate control is not necessary in patients with AF
Strict heart-rate control is not necessary in patients with AF Digital technology in cardiac care
Digital technology in cardiac care Biological ageing—a potentially modifiable risk factor for CAD?
Biological ageing—a potentially modifiable risk factor for CAD? Medication errors in dialysis patients undergoing PCI
Medication errors in dialysis patients undergoing PCI