Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlight |
 A proteomic model shows potential as a surrogate end point for CVD risk
A proteomic model shows potential as a surrogate end point for CVD risk
A model generated using proteomics and machine learning that included 27 proteins was able to predict the 4-year risk of myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke or all-cause death better than a clinical model and was sensitive to the adverse and beneficial changes in outcome.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Machine learning predicts risk in ACS
A new machine learning risk-stratification model accurately predicts the 1-year risk of ischaemic and major bleeding events in patients with an acute coronary syndrome and might be useful to guide clinical decision-making and optimize the quality of care of these patients.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
ACE2 level as a marker of CVD
Higher levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in plasma are associated with a greater risk of major cardiovascular disease events, according to a global, population-based study.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Integration of novel monitoring devices with machine learning technology for scalable cardiovascular management
Integration of novel monitoring devices with machine learning technology for scalable cardiovascular management
Advances in cardiovascular monitoring technologies have resulted in an influx of consumer-targeted wearable sensors that have the potential to detect numerous heart conditions. In this Review, Krittanawong and colleagues describe processes involved in biosignal acquisition and analysis of cardiovascular monitors, as well as their associated ethical, regulatory and legal challenges.
- Chayakrit Krittanawong
- , Albert J. Rogers
- & Sanjiv M. Narayan
-
Comment |
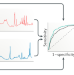 Predicting longevity using metabolomics: a novel tool for precision lifestyle medicine?
Predicting longevity using metabolomics: a novel tool for precision lifestyle medicine?
Metabolomics data can be used to identify biomarkers of all-cause mortality. In this Comment article, Després suggests that these biomarkers can also predict risk of death associated with risk factors that can be reduced through changes in lifestyle habits.
- Jean-Pierre Després
-
Research Highlight |
NIRS to identify vulnerable plaques
Near-infrared spectroscopy–intravascular ultrasonography of mildly or non-obstructive coronary arteries in patients with suspected coronary artery disease undergoing catheterization and possible percutaneous coronary intervention is safe and can detect both patients and non-culprit vulnerable plaques at high risk of secondary coronary events
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Research Highlight |
Silent myocardial infarction increases the risk of heart failure
- Gregory B. Lim
-
-
Review Article |
 Peripheral artery disease: epidemiology and global perspectives
Peripheral artery disease: epidemiology and global perspectives
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is undergoing a major epidemiological transition, with a rapid shift from high-income to low-income and middle-income countries. In this Review, Fowkes et al. describe the measurement of PAD in populations, as well as the worldwide prevalence, risk factors, and burden of the disease.
- F. Gerry R. Fowkes
- , Victor Aboyans
- & Michael H. Criqui
-
Review Article |
 Atrial fibrillation in women: epidemiology, pathophysiology, presentation, and prognosis
Atrial fibrillation in women: epidemiology, pathophysiology, presentation, and prognosis
Differences between women and men with atrial fibrillation have received far less attention in recent years than sex-specific differences in coronary heart disease and stroke. In this Review, Ko et al. discuss sex-specific differences in the incidence, prevalence, risk factors, and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation, and the clinical presentation and prognosis of patients with this prevalent arrhythmia.
- Darae Ko
- , Faisal Rahman
- & Ingrid E. Christophersen
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Use of medication for cardiovascular disease during pregnancy
Use of medication for cardiovascular disease during pregnancy
The numerous physiological changes that occur during pregnancy can affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs that a woman is receiving, often warranting an alteration in dosage. The well-being of the fetus is a major concern among pregnant women who require treatment for their heart disease. In this Review, Pieper provides an overview of the pharmacokinetic changes in drugs for cardiovascular disease during pregnancy, and how these might affect the fetus.
- Petronella G. Pieper
-
Review Article |
 Cardiovascular biomarkers and sex: the case for women
Cardiovascular biomarkers and sex: the case for women
Measurement of biomarkers is a critical component of cardiovascular care, but sex-specific differences in these markers have not been fully integrated into clinical practice. In this Review, Daniels and Maisel assess the utility of sex-specific cut-off points when measuring cardiac troponins or natriuretic peptides in the diagnosis and prognosis of acute coronary syndrome and heart failure, respectively. They also discuss sex-specific differences in novel cardiovascular biomarkers, such as galectin-3, soluble ST2, and proneurotensin.
- Lori B. Daniels
- & Alan S. Maisel
-
Review Article |
 Cardiac MRI: a central prognostic tool in myocardial fibrosis
Cardiac MRI: a central prognostic tool in myocardial fibrosis
Cardiac MRI is a noninvasive phenotyping tool that allows for accurate and easy detection and quantification of myocardial fibrosis in myocardial tissue. In this Review, Ambale-Venkatesh and Lima focus on late-gadolinium enhancement and T1 mapping strategies, and explore the different prognostic applications of this technique.
- Bharath Ambale-Venkatesh
- & João A. C. Lima
-
Review Article |
 Risk assessment methods for cardiac surgery and intervention
Risk assessment methods for cardiac surgery and intervention
Risk models to predict outcomes in cardiac surgery are increasingly being used to identify patients who might be better treated using percutaneous techniques than by surgical intervention. In this Review, Thalji and colleagues critically evaluate how the databases from which these models are derived might influence risk prediction in clinical practice, particularly for selecting patients to undergo transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
- Nassir M. Thalji
- , Rakesh M. Suri
- & Hartzell V. Schaff
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 The dynamics of the coronary collateral circulation
The dynamics of the coronary collateral circulation
The coronary collateral circulation protects the myocardium when blood flow is reduced because of an occlusion. In this Review, Zimarino and colleagues discuss the development of collateral vessels through tissue remodelling. Collaterals and their underlying adaptative mechanisms are clinically important to modern interventional cardiology.
- Marco Zimarino
- , Mariangela D'Andreamatteo
- & Raffaele De Caterina
-
Review Article |
 Managing futility in critically ill patients with cardiac disease
Managing futility in critically ill patients with cardiac disease
Cardiologists and intensivists often regard death as failure, continuing to pursue active treatment while potentially denying patients access to alternatives such as symptom control and end-of-life care. In this Review, Price and Haxby describe how decision-making should be shared between the patient, their family, and the physician, to ensure that high-quality, patient-centred care is provided to critically ill patients with cardiac disease.
- Susanna Price
- & Elizabeth Haxby
-
News & Views |
 Heart failure clinical trials: how do we define success?
Heart failure clinical trials: how do we define success?
The selection of end points for clinical trials of heart failure is challenging, with important implications for patients, the medical community, and regulatory agencies. The standards used in clinical research on patients with heart failure influence the effectiveness and value of future clinical trials, and the extent to which they can be translated into clinical practice.
- Boback Ziaeian
- & Gregg C. Fonarow
-
Opinion |
 Prognostic relevance of PCI-related myocardial infarction
Prognostic relevance of PCI-related myocardial infarction
In many clinical trials, procedure-related myocardial infarctions are assigned a similar prognostic value to spontaneous myocardial infarctions. Robbert de Winter and colleagues argue that procedure-related myocardial infarctions do not necessarily have important prognostic implications, and that the recent definition of a procedure-related myocardial infarction, including a relevant biomarker increase and supporting evidence, needs to be closely followed.
- Pier Woudstra
- , Maik J. Grundeken
- & Peter Damman
-
Review Article |
 Assessment and management of blood-pressure variability
Assessment and management of blood-pressure variability
Blood pressure is characterized by short-term and long-term fluctuations, which are the result of complex interactions between environmental and behavioural factors, on the one side, and cardiovascular regulatory mechanisms on the other. Increased blood pressure variability (BPV) leads to cardiac, vascular, and renal damage and has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Parati et al. review the mechanisms, assessment and prognostic importance of BPV. They also address the question of whether BPV should be a target for antihypertensive treatment in the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
- Gianfranco Parati
- , Juan E. Ochoa
- & Grzegorz Bilo
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 The 6-min walk test is useful for assessing prognosis in stable, ambulatory patients
The 6-min walk test is useful for assessing prognosis in stable, ambulatory patients
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
News & Views |
ACE inhibitor use in pregnancy—setting the record straight
A study by Li and coworkers demonstrates that antihypertensive-drug use and untreated hypertension in pregnancy increase the risk of congenital malformations. Supported by the results of meta-analysis, this study heralds a major shift in our understanding of the fetal risks of hypertension and the medications used to treat this condition.
- Gideon Koren
-
Review Article |
 Diagnostic and prognostic value of 3D NOGA mapping in ischemic heart disease
Diagnostic and prognostic value of 3D NOGA mapping in ischemic heart disease
Three-dimensional electromechanical mapping with the NOGA® system is a promising strategy to evaluate myocardial viability and identify motion disturbances in the ventricular wall. The authors of this Review discuss the NOGA® procedure, the validation of this novel technique, and the current and future applications of NOGA®in patients with ischemia.
- Mariann Gyöngyösi
- & Nabil Dib
-
Research Highlight |
Worse prognosis of cocaine users with ACS—a call for routine urine tests?
- Christoph A. Schmitt
-
Review Article |
 The diagnosis and management of ventricular arrhythmias
The diagnosis and management of ventricular arrhythmias
The wide spectrum of abnormal cardiac rhythms collectively known as 'ventricular arrhythmias' cause substantial morbidity and are the most common cause of sudden cardiac death. These arrhythmias have widely differing mechanisms, prognoses, and appropriate therapies, which can be determined by evaluation of the underlying disease substrate. In this Review, Dr. Roberts-Thomson and colleagues focus on the mechanisms, diagnosis, and management of monomorphic ventricular arrhythmias.
- Kurt C. Roberts-Thomson
- , Dennis H. Lau
- & Prashanthan Sanders
-
News & Views |
 Anxiety and risk of cardiac events
Anxiety and risk of cardiac events
Anxiety has been shown to have prognostic importance in the development of coronary heart disease in initially healthy adults. This finding highlights the need of future research that includes representative samples of women and minorities, and uses precise assessment tools and careful ascertainment of clinical end points.
- James A. Blumenthal
- & Patrick J. Smith
-
Research Highlight |
 A new scoring system for simple risk prediction in patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism
A new scoring system for simple risk prediction in patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
Research Highlight |
 Widespread use of public-access AEDs improves survival after cardiac arrest
Widespread use of public-access AEDs improves survival after cardiac arrest
- Alexandra King
-
-
Review Article |
 Marfan syndrome. Part 2: treatment and management of patients
Marfan syndrome. Part 2: treatment and management of patients
Over the past 30 years, we have witnessed a steady improvement in life expectancy of patients with Marfan syndrome, owing to advances in various treatments. In Part 2 of a 2-part Review on Marfan syndrome, Dr. Cañadas and colleagues discuss the present the state of the art in the management of patients with this disease.
- Victoria Cañadas
- , Isidre Vilacosta
- & Valentin Fuster

 Oxidized phospholipids in cardiovascular disease
Oxidized phospholipids in cardiovascular disease Continuous chest compressions do not improve outcomes
Continuous chest compressions do not improve outcomes Depression recognized as a risk factor in ACS
Depression recognized as a risk factor in ACS