Featured
-
-
Letter |
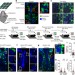 T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
Here, leukaemia cells are followed by intravital microscopy as they infiltrate mouse bone marrow and respond to chemotherapy, revealing that at all stages analysed they are highly motile and do not display any associations with particular bone marrow sub-compartments.
- Edwin D. Hawkins
- , Delfim Duarte
- & Cristina Lo Celso
-
Article |
 Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells
Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells
Leukaemic stem cells (LSCs) are responsible for BCR–ABL-driven chronic myeloid leukaemia relapse; here, p53 and MYC signalling networks are shown to regulate LSCs concurrently, and targeting both these pathways has a synergistic effect in managing the disease.
- Sheela A. Abraham
- , Lisa E. M. Hopcroft
- & Tessa L. Holyoake
-
Article |
 Deletions linked to TP53 loss drive cancer through p53-independent mechanisms
Deletions linked to TP53 loss drive cancer through p53-independent mechanisms
The loss of the TP53 gene is often involved in the development of human cancer; here, the deletion of other genes in the vicinity is shown also to contribute to cancer progression in a mouse model.
- Yu Liu
- , Chong Chen
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
Letter |
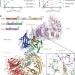 Structural basis of lenalidomide-induced CK1α degradation by the CRL4CRBN ubiquitin ligase
Structural basis of lenalidomide-induced CK1α degradation by the CRL4CRBN ubiquitin ligase
Thalidomide and its derivative lenalidomide bind the CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase and target protein substrates for degradation; structural and functional data determined here show that casein kinase 1α and the lymphoid transcription factor Ikaros, the efficacy targets of lenalidomide in two different blood cancers, interact with the CRBN–lenalidomide interface through a β-hairpin destruction motif.
- Georg Petzold
- , Eric S. Fischer
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Letter |
 Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
A small-molecule inhibitor of the Mediator-associated kinases CDK8 and CDK19 inhibits growth of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells and induces upregulation of super-enhancer-associated genes with tumour suppressor and lineage-controlling functions; Mediator kinase inhibition therefore represents a promising therapeutic approach for AML.
- Henry E. Pelish
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Matthew D. Shair
-
Letter |
 BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitors that target bromodomain chromatin readers such as BRD4 are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, in a MLL–AF9 mouse leukaemia model, resistance to BET inhibitors is shown to emerge from leukaemia stem cells, and be partly due to increased Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
- Chun Yew Fong
- , Omer Gilan
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
BET bromodomain inhibitors are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, AML cells are shown to evade sensitivity to BET inhibition through rewiring the transcriptional regulation of BRD4 target genes such as MYC in a process that is facilitated by suppression of PRC2 and WNT signalling activation.
- Philipp Rathert
- , Mareike Roth
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Letter |
 Erosion of the chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cell pool by PPARγ agonists
Erosion of the chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cell pool by PPARγ agonists
Although imatinib gives good clinical results in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), residual disease attributed to quiescent CML stem cells remains in many patients; here glitazones are shown to reduce the pool of CML stem cells and achieve lasting disease eradication in CML patients in combination with imatinib.
- Stéphane Prost
- , Francis Relouzat
- & Philippe Leboulch
-
Article |
 Lenalidomide induces ubiquitination and degradation of CK1α in del(5q) MDS
Lenalidomide induces ubiquitination and degradation of CK1α in del(5q) MDS
Lenalidomide, a derivative of thalidomide, is an effective drug for myelodysplastic syndrome; lenalidomide binds the CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes degradation of casein kinase 1a, on which the malignant cells rely for survival.
- Jan Krönke
- , Emma C. Fink
- & Benjamin L. Ebert
-
Letter |
 MYC regulates the core pre-mRNA splicing machinery as an essential step in lymphomagenesis
MYC regulates the core pre-mRNA splicing machinery as an essential step in lymphomagenesis
The critical effectors of MYC overexpression during lymphomagenesis in transgenic mice are defined.
- Cheryl M. Koh
- , Marco Bezzi
- & Ernesto Guccione
-
Inside View |
 Inside View: Fondation ARC
Inside View: Fondation ARC
-
Letter |
 Signalling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Signalling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
This study shows that, despite malignant transformation, autoimmune checkpoints are still functional in B-cell leukaemia, with targeted activation of these checkpoints effectively killing patient-derived B-cell leukaemia in a transplant model; the results represent a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance in leukaemia patients.
- Zhengshan Chen
- , Seyedmehdi Shojaee
- & Markus Müschen
-
Letter |
 Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Somatic TP53 mutations are highly prevalent in therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome, which arise as complications of cytotoxic chemotherapy or radiotherapy; although it was believed that these TP53 mutations are directly induced by cytotoxic therapy, new data indicate that they predate cytotoxic therapy and that haematopoietic progenitors harbouring these pre-existing mutations may selectively expand after exposure to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Terrence N. Wong
- , Giridharan Ramsingh
- & Richard K. Wilson
-
Letter |
 Loss of signalling via Gα13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma
Loss of signalling via Gα13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma
Inactivation of the S1PR2–Gα13–ARHGEF1 signalling pathway in mice allows Akt activation and promotes dissemination of germinal centre B cells, consistent with a role of function-disrupting mutations in the systemic dissemination of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Jagan R. Muppidi
- , Roland Schmitz
- & Jason G. Cyster
-
Letter |
 Contrasting roles of histone 3 lysine 27 demethylases in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Contrasting roles of histone 3 lysine 27 demethylases in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) is a haematological malignancy with a poor prognosis and no available targeted therapies; now two histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases, JMJD3 and UTX, are shown to have contrasting roles in human T-ALL cells and a mouse model of the disease, and a small molecule demethylase inhibitor is found to inhibit the growth of T-ALL cell lines, introducing a potential therapeutic avenue for acute leukaemia.
- Panagiotis Ntziachristos
- , Aristotelis Tsirigos
- & Iannis Aifantis
-
Letter |
 DNA-damage-induced differentiation of leukaemic cells as an anti-cancer barrier
DNA-damage-induced differentiation of leukaemic cells as an anti-cancer barrier
Histone methyl-transferase MLL4 is required for stem-cell activity and an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukaemia harbouring the MLL–AF9 oncogene.
- Margarida A. Santos
- , Robert B. Faryabi
- & André Nussenzweig
-
Article |
 RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer
RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer
The translation of many messenger RNAs that encode important oncogenes and transcription factors depends on the eIF4A RNA helicase to resolve G-quadruplex structures, implying eIF4A inhibition as an effective cancer therapy.
- Andrew L. Wolfe
- , Kamini Singh
- & Hans-Guido Wendel
-
Article |
 Structure of the DDB1–CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide
Structure of the DDB1–CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide
The crystal structures of thalidomide and its derivatives bound to the E3 ligase subcomplex DDB1–CRBN are shown; these drugs are found to have dual functions, interfering with the binding of certain cellular substrates to the E3 ligase but promoting the binding of others, thereby modulating the degradation of cellular proteins.
- Eric S. Fischer
- , Kerstin Böhm
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Letter |
 Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis
Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis
Global transcriptional and epigenomic analyses in diverse cell types reveal that the primary action of Myc is to up- and downregulate transcription of distinct groups of genes, rather than to amplify transcription of all active genes; general RNA amplification, when observed, is better explained as an indirect consequence of Myc’s action on cellular physiology.
- Arianna Sabò
- , Theresia R. Kress
- & Bruno Amati
-
Letter |
 Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Here, a covalent inhibitor targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) demonstrates in vitro and in vivo efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by downregulating oncogenic transcriptional programs.
- Nicholas Kwiatkowski
- , Tinghu Zhang
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
Outlook |
 Therapy: This time it's personal
Therapy: This time it's personal
Tailoring cancer treatment to individual and evolving tumours is the way of the future, but scientists are still hashing out the details.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Article |
 Cell competition is a tumour suppressor mechanism in the thymus
Cell competition is a tumour suppressor mechanism in the thymus
T cells develop from thymic precursor cells that are constantly replaced with newly arriving bone marrow progenitor cells, and the ‘old’ and ‘new’ cells are shown here to compete; in the absence of cell competition, when the influx of new bone marrow progenitor cells is blocked, the old cells acquire the ability to self-renew and eventually become transformed, leading to the development of a form of leukaemia.
- Vera C. Martins
- , Katrin Busch
- & Hans-Reimer Rodewald
-
Letter |
 Constitutional and somatic rearrangement of chromosome 21 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Constitutional and somatic rearrangement of chromosome 21 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
A rare constitutional translocation between chromosomes 15 and 21 predisposes to catastrophic chromosomal damage followed by amplification of megabase regions, causing a specific subtype of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
- Yilong Li
- , Claire Schwab
- & Christine J. Harrison
-
Letter |
 Synthetic lethal metabolic targeting of cellular senescence in cancer therapy
Synthetic lethal metabolic targeting of cellular senescence in cancer therapy
In mice with Eµ-myc transgenic lymphomas in which therapy-induced senescence (TIS) depends on the H3K9 histone methyltransferase Suv39h1, TIS-competent lymphomas but not TIS-incompetent Suv39h1– lymphomas show increased glucose utilization and ATP production after senescence-inducing chemotherapy to cope with proteotoxic stress elicited by factors of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP); senescent cancers are selectively vulnerable to drugs that block glucose utilization or autophagy.
- Jan R. Dörr
- , Yong Yu
- & Clemens A. Schmitt
-
Letter |
 A stable transcription factor complex nucleated by oligomeric AML1–ETO controls leukaemogenesis
A stable transcription factor complex nucleated by oligomeric AML1–ETO controls leukaemogenesis
A multiprotein complex containing AML1–ETO, the most common fusion protein found in acute myeloid leukaemia, is revealed and analysed in leukaemic cells, and a novel, functionally important protein-binding interface is identified.
- Xiao-Jian Sun
- , Zhanxin Wang
- & Robert G. Roeder
-
Outlook |
 Living with leukaemia
Living with leukaemia
Leukaemias are cancers of the blood or bone marrow. But how do they form, and can they be treated?
- Emily Elert
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Assembly line immunotherapy
Perspective: Assembly line immunotherapy
Bruce L. Levine and Carl H. June explore how to make engineered immune cells that can eradicate cancer widely available.
- Bruce L. Levine
- & Carl H. June
-
Outlook |
 Epigenetics: Reversible tags
Epigenetics: Reversible tags
Enzymes that modify gene expression without changing the DNA sequence are now viewed as central to the development of leukaemia — and may lead to new drugs.
- Jessica Wright
-
Outlook |
 Stem cells: Bad seeds
Stem cells: Bad seeds
Leukaemia treatments must eliminate the versatile cells that can bring the cancer back to life years later.
- Cassandra Willyard
-
Outlook |
 Drug safety: Double jeopardy
Drug safety: Double jeopardy
Leukaemia in children is highly curable, but many survivors suffer severe, even life-threatening, long-term effects. Scientists are seeking ways to deliver a safer cure.
- Mary Carmichael
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Combined forces
Perspective: Combined forces
Beginning treatment with a combination of drugs should help to stop drug resistance developing, says Charles L. Sawyers.
- Charles L. Sawyers
-
Outlook |
 Cell banks: Life blood
Cell banks: Life blood
Stem cells from the umbilical cord are among the latest weapons in the fight against leukaemia.
- Melinda Wenner Moyer
-
Outlook |
 Drug development: Target practice
Drug development: Target practice
Better designs for clinical trials and the use of combination therapies may improve leukaemia treatment.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
Outlook |
 Genetics: Written in blood
Genetics: Written in blood
Technologies that rapidly sequence DNA reveal deep genetic diversity both within and among individuals with leukaemia.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
-
Letter |
 EZH2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations
EZH2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations
EZH2 is a methyltransferase that is mutated in lymphoma; here a potent small molecule inhibitor of EZH2 is described, which inhibits the proliferation of EZH2 mutant cell lines and growth of EZH2 mutant xenografts in mice, thus providing a potential treatment for EZH2 mutant lymphoma.
- Michael T. McCabe
- , Heidi M. Ott
- & Caretha L. Creasy
-
Letter |
 Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling
B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is found not to be dependent on exogenous antigens; instead, signalling may involve the binding of the BCR heavy-chain complementarity-determining region to self epitopes on the same receptor, a finding that may have important implications for understanding the pathogenesis of CLL and potential therapeutic approaches.
- Marcus Dühren-von Minden
- , Rudolf Übelhart
- & Hassan Jumaa
-
Letter |
 Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics
Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics
RNA sequencing of Burkitt lymphoma tumours allows identification of mutations affecting the transcription factor TCF3, its negative regulator ID3 and the cell cycle regulator CCND3; these pathways reveal new targets for potential therapeutic intervention.
- Roland Schmitz
- , Ryan M. Young
- & Louis M. Staudt
-
Letter |
 Heterodimeric JAK–STAT activation as a mechanism of persistence to JAK2 inhibitor therapy
Heterodimeric JAK–STAT activation as a mechanism of persistence to JAK2 inhibitor therapy
Chronic exposure to JAK2 inhibitors leads to reactivation of downstream signalling through the formation of heterodimers between JAK2 and other JAK kinases in myeloproliferative neoplasms, which can be overcome with Hsp90 inhibitors.
- Priya Koppikar
- , Neha Bhagwat
- & Ross L. Levine
-
Letter |
 IDH1(R132H) mutation increases murine haematopoietic progenitors and alters epigenetics
IDH1(R132H) mutation increases murine haematopoietic progenitors and alters epigenetics
Mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenases IDH1 and IDH2 are common in human gliomas and acute myeloid leukaemias; here, mice that carry the IDH1(R132H) mutation are described, in a new model that should help in investigating the links between mutant IDH1 and leukaemia.
- Masato Sasaki
- , Christiane B. Knobbe
- & Tak W. Mak
-
Letter |
 A tumour suppressor network relying on the polyamine–hypusine axis
A tumour suppressor network relying on the polyamine–hypusine axis
AMD1 and eIF5A are identified as two genes involved in the polyamine–hypusine pathway, a new tumour suppressor network regulating apoptosis.
- Claudio Scuoppo
- , Cornelius Miething
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
Letter |
 Inhibitory receptors bind ANGPTLs and support blood stem cells and leukaemia development
Inhibitory receptors bind ANGPTLs and support blood stem cells and leukaemia development
The binding of angiopoietin-like proteins to immune-inhibitory receptors maintains ‘stemness’ of haematopoietic stem cells and supports leukaemia development.
- Junke Zheng
- , Masato Umikawa
- & Cheng Cheng Zhang
-
Letter |
 Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia
Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia
Internal tandem duplication mutations in FLT3, known to be associated with a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukaemia, are now shown to be a valid therapeutic target for the disease.
- Catherine C. Smith
- , Qi Wang
- & Neil P. Shah
-
Letter
| Open Access Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing
Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing
The sequencing of AML genomes of eight patients before and after relapse reveals two major patterns of clonal evolution, with chemotherapy appearing to have a role in both patterns.
- Li Ding
- , Timothy J. Ley
- & John F. DiPersio
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
The genetic basis of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
This work shows that treatments used for acute myeloid leukaemia and targeted therapies could be used for early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
- Jinghui Zhang
- , Li Ding
- & Charles G. Mullighan
-
Letter |
 FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
FBXO11 is identified as the F-box protein that normally targets BCL6 for degradation, and FBXO11 deletions or mutations that prevent this function and thus stabilize BCL6 are found in B-cell lymphomas.
- Shanshan Duan
- , Lukas Cermak
- & Michele Pagano
-
Research Highlights |
Sisterhood of lymphoma
-
-
Outlook |
 Genetics: Profiling a shape-shifter
Genetics: Profiling a shape-shifter
Unlocking the genetic secrets of multiple myeloma could reveal new ways to attack this killer disease.
- Courtney Humphries
-
Outlook |
 Diagnostics: The early bird
Diagnostics: The early bird
Identifying the patients most likely to progress from a precancerous condition to multiple myeloma could help doctors catch the disease early and stop it taking hold.
- Lauren Gravitz

 A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia
A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia