Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin
Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) arises from clonal (premalignant) haematopoietic precursors in the bone marrow, and BPDCN skin tumours first develop at sun-exposed anatomical sites and are distinguished by clonally expanded mutations induced by ultraviolet radiation.
- Gabriel K. Griffin
- , Christopher A. G. Booth
- & Andrew A. Lane
-
Article
| Open Access The menin inhibitor revumenib in KMT2A-rearranged or NPM1-mutant leukaemia
The menin inhibitor revumenib in KMT2A-rearranged or NPM1-mutant leukaemia
Revumenib, a potent and selective oral inhibitor of the menin–KMT2A interaction, is associated with a low frequency of treatment-related adverse events and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukaemia.
- Ghayas C. Issa
- , Ibrahim Aldoss
- & Eytan M. Stein
-
Article |
 Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukaemia
Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukaemia
Extensive genomic analyses of the chromatin architecture in acute myeloid leukaemia reveals several characteristics, including subtype-specific distal enhancers and silencers, that may represent new anticancer therapeutic targets.
- Jie Xu
- , Fan Song
- & Feng Yue
-
Article
| Open Access The longitudinal dynamics and natural history of clonal haematopoiesis
The longitudinal dynamics and natural history of clonal haematopoiesis
A long-term study of 385 human donors reports that driver gene mutations and age determine the lifelong dynamics of clonal haematopoiesis
- Margarete A. Fabre
- , José Guilherme de Almeida
- & George S. Vassiliou
-
Article |
 Non-genetic determinants of malignant clonal fitness at single-cell resolution
Non-genetic determinants of malignant clonal fitness at single-cell resolution
Non-genetic malignant clonal dominance is a cell-intrinsic and heritable property that underpins clonal output and response to therapy in cancer.
- Katie A. Fennell
- , Dane Vassiliadis
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
Article |
 Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development
Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development
The NUP98–HOXA9 oncogenic fusion protein found in leukaemia undergoes phase separation in the nucleus, which helps to promote activation of leukaemic genes and to establish aberrant chromatin looping.
- Jeong Hyun Ahn
- , Eric S. Davis
- & Gang Greg Wang
-
Article |
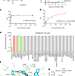 Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia
Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia
Treatment with a specific inhibitor of the N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 leads to reduced growth of cancer cells, indicating the potential of approaches targeting RNA-modifying enzymes for anticancer therapy.
- Eliza Yankova
- , Wesley Blackaby
- & Tony Kouzarides
-
Article |
 Single-cell mutation analysis of clonal evolution in myeloid malignancies
Single-cell mutation analysis of clonal evolution in myeloid malignancies
The evolution of myeloid malignancies is investigated using combined single-cell sequencing and immunophenotypic analysis.
- Linde A. Miles
- , Robert L. Bowman
- & Ross L. Levine
-
Article |
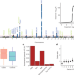 Inherited myeloproliferative neoplasm risk affects haematopoietic stem cells
Inherited myeloproliferative neoplasm risk affects haematopoietic stem cells
A genome-wide association study identifies 17 genetic loci that are associated with the risk of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), and shows that the modulation of haematopoietic stem cell function drives MPN risk.
- Erik L. Bao
- , Satish K. Nandakumar
- & Vijay G. Sankaran
-
Article |
 Signalling input from divergent pathways subverts B cell transformation
Signalling input from divergent pathways subverts B cell transformation
Analysis of B-cell leukaemia samples reveals that oncogenic mutations do not cause malignant transformation unless they converge on the same signalling pathway, and that it may be possible clinically to combine inhibition of the principal oncogenic driver with reactivation of divergent pathways.
- Lai N. Chan
- , Mark A. Murakami
- & Markus Müschen
-
Article |
 HBO1 is required for the maintenance of leukaemia stem cells
HBO1 is required for the maintenance of leukaemia stem cells
The MYST acetyltransferase HBO1 is a critical regulator in maintaining leukaemia stem cells, and a small-molecule inhibitor of HBO1 is developed that shows efficacy against a range of acute myeloid leukaemia cells.
- Laura MacPherson
- , Juliana Anokye
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
Article |
 The U1 spliceosomal RNA is recurrently mutated in multiple cancers
The U1 spliceosomal RNA is recurrently mutated in multiple cancers
A highly recurrent A>C somatic mutation in U1 small nuclear RNA, which alters the splicing pattern of genes that include known drivers of cancer, is identified in several types of tumour.
- Shimin Shuai
- , Hiromichi Suzuki
- & Lincoln D. Stein
-
Letter |
 Coordinated alterations in RNA splicing and epigenetic regulation drive leukaemogenesis
Coordinated alterations in RNA splicing and epigenetic regulation drive leukaemogenesis
Analyses of transcriptomes from patients with acute myeloid leukaemia identified frequently co-occurring mutations of IDH2 and SRSF2, which functional analyses showed to have distinct and coordinated leukaemogenic effects on the epigenome and RNA splicing.
- Akihide Yoshimi
- , Kuan-Ting Lin
- & Omar Abdel-Wahab
-
Letter |
 Absence of NKG2D ligands defines leukaemia stem cells and mediates their immune evasion
Absence of NKG2D ligands defines leukaemia stem cells and mediates their immune evasion
Leukaemic stem cells in acute myeloid leukaemia are defined by a lack of expression of NKG2D ligands, which mediates their ability to evade surveillance by NK cells.
- Anna M. Paczulla
- , Kathrin Rothfelder
- & Claudia Lengerke
-
Article |
 Growth dynamics in naturally progressing chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Growth dynamics in naturally progressing chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Analysis of growth dynamics in a dataset from 107 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) reveals both exponential and logistic patterns of growth, which are associated with differences in genetic attributes and clinical outcomes.
- Michaela Gruber
- , Ivana Bozic
- & Catherine J. Wu
-
Letter |
 Epigenetic evolution and lineage histories of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Epigenetic evolution and lineage histories of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
A single-cell approach is used to follow the heritable stochastic changes to DNA methylation that occur in primary chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and healthy B cells, allowing the tracing of cell lineage histories and evolution during treatment with ibrutinib.
- Federico Gaiti
- , Ronan Chaligne
- & Dan A. Landau
-
Article |
 Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia
Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia
Analyses of samples from patients with acute myeloid leukaemia reveal that drug response is associated with mutational status and gene expression; the generated dataset provides a basis for future clinical and functional studies of this disease.
- Jeffrey W. Tyner
- , Cristina E. Tognon
- & Brian J. Druker
-
Article |
 The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia
The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia
A large-scale genomics study shows that the cell of origin and founding mutations determine disease subtype and lead to the expression of multiple haematopoietic lineage-defining antigens in mixed phenotype acute leukaemia.
- Thomas B. Alexander
- , Zhaohui Gu
- & Charles G. Mullighan
-
Letter |
 Widespread intronic polyadenylation inactivates tumour suppressor genes in leukaemia
Widespread intronic polyadenylation inactivates tumour suppressor genes in leukaemia
The inactivation of tumour suppressor genes at the level of mRNA occurs by the generation of truncated proteins in leukaemia.
- Shih-Han Lee
- , Irtisha Singh
- & Christine Mayr
-
Article |
 Leukaemia hijacks a neural mechanism to invade the central nervous system
Leukaemia hijacks a neural mechanism to invade the central nervous system
Expression of α6 integrin enables acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells to use neural migratory pathways to invade the central nervous system and metastasize to the brain.
- Hisayuki Yao
- , Trevor T. Price
- & Dorothy A. Sipkins
-
Letter |
 Histidine catabolism is a major determinant of methotrexate sensitivity
Histidine catabolism is a major determinant of methotrexate sensitivity
Histidine metabolism influences the sensitivity of cancer cells to methotrexate, with mice bearing leukaemia xenografts showing increased response to the drug upon histidine supplementation.
- Naama Kanarek
- , Heather R. Keys
- & David M. Sabatini
-
Letter |
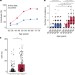 Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals
Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals
Individuals who are at high risk of developing acute myeloid leukaemia can be identified years before diagnosis using genetic information from blood samples.
- Sagi Abelson
- , Grace Collord
- & Liran I. Shlush
-
Letter |
 Acquired resistance to IDH inhibition through trans or cis dimer-interface mutations
Acquired resistance to IDH inhibition through trans or cis dimer-interface mutations
A new mechanism of acquired clinical resistance in two patients with acute myeloid leukaemia driven by mutant IDH2 is described, in which a second-site mutation on the wild-type allele induces therapeutic resistance to IDH2 inhibitors.
- Andrew M. Intlekofer
- , Alan H. Shih
- & Eytan M. Stein
-
Letter |
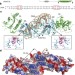 Structural basis for DNMT3A-mediated de novo DNA methylation
Structural basis for DNMT3A-mediated de novo DNA methylation
A crystal structure of DNMT3A and its regulatory partner DNMT3L bound to DNA reveals the mechanistic basis for DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation and establishes its aetiological link to human disease.
- Zhi-Min Zhang
- , Rui Lu
- & Jikui Song
-
Letter |
 Clonal evolution mechanisms in NT5C2 mutant-relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Clonal evolution mechanisms in NT5C2 mutant-relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Mutations in the nucleotidase-encoding gene NT5C2 drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed acute lymphoid leukaemia but the mutations also lead to a loss-of-fitness phenotype and to collateral drug sensitivity, which could be exploited for therapy.
- Gannie Tzoneva
- , Chelsea L. Dieck
- & Adolfo A. Ferrando
-
Letter |
 BCAT1 restricts αKG levels in AML stem cells leading to IDHmut-like DNA hypermethylation
BCAT1 restricts αKG levels in AML stem cells leading to IDHmut-like DNA hypermethylation
The mechanistic basis for the role of the metabolic enzyme BCAA transaminase 1 (BCAT1) in acute myeloid leukaemias.
- Simon Raffel
- , Mattia Falcone
- & Andreas Trumpp
-
Article |
 Ascorbate regulates haematopoietic stem cell function and leukaemogenesis
Ascorbate regulates haematopoietic stem cell function and leukaemogenesis
Ascorbate depletion in mice increased haematopoietic stem-cell frequency and promoted leukaemogenesis, partly by reducing the function of the Tet2 tumour suppressor enzyme.
- Michalis Agathocleous
- , Corbin E. Meacham
- & Sean J. Morrison
-
Letter |
 Tracing the origins of relapse in acute myeloid leukaemia to stem cells
Tracing the origins of relapse in acute myeloid leukaemia to stem cells
Identification of the cell types from which relapse arises in acute myeloid leukaemia, by following leukaemia propagation from patient-derived leukaemia samples.
- Liran I. Shlush
- , Amanda Mitchell
- & John E. Dick
-
Article |
 Myeloid progenitor cluster formation drives emergency and leukaemic myelopoiesis
Myeloid progenitor cluster formation drives emergency and leukaemic myelopoiesis
During emergency myelopoiesis in mice, clusters of self-renewing granulocyte/macrophage progenitors (GMP) are transiently formed in the bone marrow cavity to produce a burst of myeloid cells; in leukaemia, GMP clusters persist and constantly generate myeloid leukaemia cells.
- Aurélie Hérault
- , Mikhail Binnewies
- & Emmanuelle Passegué
-
Letter |
 The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR–ABL1
The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR–ABL1
The selective allosteric ABL1 inhibitor ABL001 (asciminib) represents a new inhibitory mechanism for BCR–ABL1-driven malignancies, and its efficacy and evolving mechanisms of resistance do not overlap with those of other BCR–ABL1 kinase inhibitors.
- Andrew A. Wylie
- , Joseph Schoepfer
- & William R. Sellers
-
Letter |
 Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia
Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia
ENL, identified in a genome-scale loss-of-function screen as a crucial requirement for proliferation of acute leukaemia, is required for leukaemic gene expression, and its YEATS chromatin-reader domain is essential for leukaemic growth.
- Michael A. Erb
- , Thomas G. Scott
- & James E. Bradner
-
Letter |
 ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute myeloid leukaemia
ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute myeloid leukaemia
The chromatin-reader protein ENL regulates oncogenic programs in acute myeloid leukaemia by binding via its YEATS domain to acetylated histones on the promoters of actively transcribed genes and recruiting the transcriptional machinery.
- Liling Wan
- , Hong Wen
- & Xiaobing Shi
-
Letter |
 A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia
A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia
A rapid gene signature test (LSC17) that captures stem cell expression programs in acute myeloid leukaemia patients at diagnosis is associated with therapy response and survival, facilitating initial treatment stratification.
- Stanley W. K. Ng
- , Amanda Mitchell
- & Jean C. Y. Wang
-
Letter |
 T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
Here, leukaemia cells are followed by intravital microscopy as they infiltrate mouse bone marrow and respond to chemotherapy, revealing that at all stages analysed they are highly motile and do not display any associations with particular bone marrow sub-compartments.
- Edwin D. Hawkins
- , Delfim Duarte
- & Cristina Lo Celso
-
Article |
 Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells
Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells
Leukaemic stem cells (LSCs) are responsible for BCR–ABL-driven chronic myeloid leukaemia relapse; here, p53 and MYC signalling networks are shown to regulate LSCs concurrently, and targeting both these pathways has a synergistic effect in managing the disease.
- Sheela A. Abraham
- , Lisa E. M. Hopcroft
- & Tessa L. Holyoake
-
Letter |
 Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
A small-molecule inhibitor of the Mediator-associated kinases CDK8 and CDK19 inhibits growth of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells and induces upregulation of super-enhancer-associated genes with tumour suppressor and lineage-controlling functions; Mediator kinase inhibition therefore represents a promising therapeutic approach for AML.
- Henry E. Pelish
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Matthew D. Shair
-
Letter |
 BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitors that target bromodomain chromatin readers such as BRD4 are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, in a MLL–AF9 mouse leukaemia model, resistance to BET inhibitors is shown to emerge from leukaemia stem cells, and be partly due to increased Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
- Chun Yew Fong
- , Omer Gilan
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
BET bromodomain inhibitors are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, AML cells are shown to evade sensitivity to BET inhibition through rewiring the transcriptional regulation of BRD4 target genes such as MYC in a process that is facilitated by suppression of PRC2 and WNT signalling activation.
- Philipp Rathert
- , Mareike Roth
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Letter |
 Erosion of the chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cell pool by PPARγ agonists
Erosion of the chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cell pool by PPARγ agonists
Although imatinib gives good clinical results in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), residual disease attributed to quiescent CML stem cells remains in many patients; here glitazones are shown to reduce the pool of CML stem cells and achieve lasting disease eradication in CML patients in combination with imatinib.
- Stéphane Prost
- , Francis Relouzat
- & Philippe Leboulch
-
Inside View |
 Inside View: Fondation ARC
Inside View: Fondation ARC
-
Letter |
 Signalling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Signalling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
This study shows that, despite malignant transformation, autoimmune checkpoints are still functional in B-cell leukaemia, with targeted activation of these checkpoints effectively killing patient-derived B-cell leukaemia in a transplant model; the results represent a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance in leukaemia patients.
- Zhengshan Chen
- , Seyedmehdi Shojaee
- & Markus Müschen
-
Letter |
 Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Somatic TP53 mutations are highly prevalent in therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome, which arise as complications of cytotoxic chemotherapy or radiotherapy; although it was believed that these TP53 mutations are directly induced by cytotoxic therapy, new data indicate that they predate cytotoxic therapy and that haematopoietic progenitors harbouring these pre-existing mutations may selectively expand after exposure to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Terrence N. Wong
- , Giridharan Ramsingh
- & Richard K. Wilson
-
Letter |
 Contrasting roles of histone 3 lysine 27 demethylases in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Contrasting roles of histone 3 lysine 27 demethylases in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) is a haematological malignancy with a poor prognosis and no available targeted therapies; now two histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases, JMJD3 and UTX, are shown to have contrasting roles in human T-ALL cells and a mouse model of the disease, and a small molecule demethylase inhibitor is found to inhibit the growth of T-ALL cell lines, introducing a potential therapeutic avenue for acute leukaemia.
- Panagiotis Ntziachristos
- , Aristotelis Tsirigos
- & Iannis Aifantis
-
Letter |
 DNA-damage-induced differentiation of leukaemic cells as an anti-cancer barrier
DNA-damage-induced differentiation of leukaemic cells as an anti-cancer barrier
Histone methyl-transferase MLL4 is required for stem-cell activity and an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukaemia harbouring the MLL–AF9 oncogene.
- Margarida A. Santos
- , Robert B. Faryabi
- & André Nussenzweig
-
Article |
 RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer
RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer
The translation of many messenger RNAs that encode important oncogenes and transcription factors depends on the eIF4A RNA helicase to resolve G-quadruplex structures, implying eIF4A inhibition as an effective cancer therapy.
- Andrew L. Wolfe
- , Kamini Singh
- & Hans-Guido Wendel
-
Letter |
 Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Here, a covalent inhibitor targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) demonstrates in vitro and in vivo efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by downregulating oncogenic transcriptional programs.
- Nicholas Kwiatkowski
- , Tinghu Zhang
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
Outlook |
 Therapy: This time it's personal
Therapy: This time it's personal
Tailoring cancer treatment to individual and evolving tumours is the way of the future, but scientists are still hashing out the details.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Letter |
 Constitutional and somatic rearrangement of chromosome 21 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Constitutional and somatic rearrangement of chromosome 21 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
A rare constitutional translocation between chromosomes 15 and 21 predisposes to catastrophic chromosomal damage followed by amplification of megabase regions, causing a specific subtype of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
- Yilong Li
- , Claire Schwab
- & Christine J. Harrison
-
Letter |
 A stable transcription factor complex nucleated by oligomeric AML1–ETO controls leukaemogenesis
A stable transcription factor complex nucleated by oligomeric AML1–ETO controls leukaemogenesis
A multiprotein complex containing AML1–ETO, the most common fusion protein found in acute myeloid leukaemia, is revealed and analysed in leukaemic cells, and a novel, functionally important protein-binding interface is identified.
- Xiao-Jian Sun
- , Zhanxin Wang
- & Robert G. Roeder

 Epitope editing enables targeted immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukaemia
Epitope editing enables targeted immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukaemia