Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Thousands of tons of water are processed every year for hydrogen isotope separation, using extremely costly technology. Here the authors demonstrate a fully-scalable graphene electrochemical pump, which promises to dramatically reduce the energy and capital costs.
- M. Lozada-Hidalgo
- , S. Zhang
- & A. K. Geim
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional double-bended saturation of carrier occupation in optically excited graphene due to many-particle interactions
Unconventional double-bended saturation of carrier occupation in optically excited graphene due to many-particle interactions
Saturable absorption, a technologically relevant property of graphene, is usually explained with Pauli blocking of optically driven carriers in the strong-excitation regime. Here, Winzeret al. reveal a new saturation regime at low excitations, resulting in a double-bended saturation behaviour.
- Torben Winzer
- , Martin Mittendorff
- & Andreas Knorr
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: Precise determination of graphene functionalization by in situ Raman spectroscopy
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Precise determination of graphene functionalization by in situ Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a versatile tool to gain insight into the functionalization of graphene-based materials, yet unequivocal assignment of the vibrational modes associated with covalent binding has so far remained elusive. Here, the authors succeed in an experimental and theoretical identification of this molecular fingerprint.
- Philipp Vecera
- , Julio C. Chacón-Torres
- & Andreas Hirsch
-
Article
| Open Access Highly selective covalent organic functionalization of epitaxial graphene
Highly selective covalent organic functionalization of epitaxial graphene
Organic functionalization is key to the development of graphene-based functional composites, yet selective covalent functionalization is hindered by graphene chemical inertness. Here, the authors demonstrate a versatile route to graphene covalent bonding with amino-terminated organic molecules.
- Rebeca A. Bueno
- , José I. Martínez
- & José A. Martín-Gago
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetotransport on the nano scale
Magnetotransport on the nano scale
Macroscopic magneto-transport measurements enable investigation of the transport properties of materials in the presence of magnetic fields, yet they do not allow access to atomic scale details. Here, the authors combine scanning tunneling potentiometry with magnetic fields to demonstrate nanoscale magneto-transport.
- Philip Willke
- , Thomas Kotzott
- & Martin Wenderoth
-
Article
| Open Access Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media
Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media
Ruthenium is the cheapest platinum-group metal, yet active hydrogen evolution catalysts with low amounts of ruthenium have yet to be designed. Here, the authors report the preparation of a ruthenium–cobalt nanoalloy and demonstrate its potential as an effective hydrogen evolution catalyst in basic media.
- Jianwei Su
- , Yang Yang
- & Qianwang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable transmission of quantum Hall edge channels with full degeneracy lifting in split-gated graphene devices
Tunable transmission of quantum Hall edge channels with full degeneracy lifting in split-gated graphene devices
Quantum point contacts are gate-tunable constrictions allowing for control of charge carrier transmission in 2D electron gases. Here, the authors fabricate a hBN/graphene/hBN van der Waals heterojunction to enable quantum point contact devices in the integer and fractional quantum Hall regimes.
- Katrin Zimmermann
- , Anna Jordan
- & Benjamin Sacépé
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanics of individual aerographite tetrapods
Nanomechanics of individual aerographite tetrapods
Aerographite is a highly porous and lightweight carbon material obtained from hollow tubular tetrapod building units. Here, the authors present a comprehensive investigation of tetrapod deformation mechanisms which are at the core of aerographite nanomechanical properties.
- Raimonds Meija
- , Stefano Signetti
- & Nicola M. Pugno
-
Article
| Open Access A microprocessor based on a two-dimensional semiconductor
A microprocessor based on a two-dimensional semiconductor
Two-dimensional materials are receiving increasing interest as they could pave the way to a paradigm shift in nano-electronics. Here, the authors demonstrate a 1-bit implementation of a microprocessor consisting of 115 transistors, using atomically thin MoS2.
- Stefan Wachter
- , Dmitry K. Polyushkin
- & Thomas Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene nanoribbons consist of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Despite non-hexagonal rings generally being more unstable, the authors demonstrate the successful synthesis of graphene-like nanoribbons with periodically embedded four- and eight-membered carbon rings, with tailored electronic properties.
- Meizhuang Liu
- , Mengxi Liu
- & Dingyong Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Electronic skins and health monitoring devices rely on integrated tactile sensors, which often require tailored degrees of sensitivity in specific pressure ranges. Here, the authors fabricate a versatile matrix array of pressure-sensitive graphene transistors operating in the wide 250 Pa to 3 MPa pressure range.
- Sung-Ho Shin
- , Sangyoon Ji
- & Jang-Ung Park
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz and mid-infrared plasmons in three-dimensional nanoporous graphene
Terahertz and mid-infrared plasmons in three-dimensional nanoporous graphene
Recently, fabrication processes have realised three-dimensional nanoporous graphene. Here, the authors reveal two-dimensional Dirac plasmons in three-dimensional nanoporous graphene disclosing strong plasmonic absorptions tunable from terahertz to mid-infrared via controllable doping level and porosity.
- Fausto D’Apuzzo
- , Alba R. Piacenti
- & Stefano Lupi
-
Article
| Open Access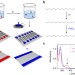 Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Two-dimensional material heterostructures enable unique electronic features by introducing periodic potentials. Here, Gobbiet al. use a monolayer supramolecular lattice with a tunable one-dimensional periodic potential to modify the electronic structure of graphene.
- Marco Gobbi
- , Sara Bonacchi
- & Emanuele Orgiu
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time reliable determination of binding kinetics of DNA hybridization using a multi-channel graphene biosensor
Real-time reliable determination of binding kinetics of DNA hybridization using a multi-channel graphene biosensor
Monitoring DNA binding and single-base mismatches accurately in real time is difficult, especially for miniaturized devices. Here the authors report a graphene field-effect transistor array capable of reliably measuring DNA hybridization kinetics and affinity at the picomolar level.
- Shicai Xu
- , Jian Zhan
- & Yaoqi Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Casimir force phase transitions in the graphene family
Casimir force phase transitions in the graphene family
The Casimir force is a ubiquitous interaction arising from electromagnetic quantum fluctuations. Here, the authors uncover the underlying physics governing Casimir force phase transitions in staggered 2D materials in the graphene family.
- Pablo Rodriguez-Lopez
- , Wilton J. M. Kort-Kamp
- & Lilia M. Woods
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable conversion of quasi-freestanding polymer chains to graphene nanoribbons
Controllable conversion of quasi-freestanding polymer chains to graphene nanoribbons
A key step in the on-surface synthesis of graphene nanoribbons is thermal annealing of polymer precursors on a metal substrate. Here, Maet al. decouple the cyclodehydrogenation reaction from the catalytic metal substrate and grow graphene nanoribbons by injecting charges at molecular sites.
- Chuanxu Ma
- , Zhongcan Xiao
- & An-Ping Li
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Graphene nanoribbons are promising candidates for 2D material electrical interconnects; however, the top-down fabrication of nanoribbons has remained a challenge. Here, Chenet al. have used a hexagonal boron nitride template to grow narrow, integrated graphene nanoribbons with small bandgaps.
- Lingxiu Chen
- , Li He
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically controlled terahertz magneto-optical phenomena in continuous and patterned graphene
Electrically controlled terahertz magneto-optical phenomena in continuous and patterned graphene
Time reversal symmetry breaking gives rise to magnetic circular dichroism and Faraday rotation in graphene. The authors use terahertz magneto-electro-optical spectroscopy to demonstrate that electrostatic doping at a fixed magnetic field allows inversion of magnetic circular dichroism and Faraday rotation.
- Jean-Marie Poumirol
- , Peter Q. Liu
- & Alexey B. Kuzmenko
-
Article
| Open Access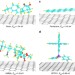 Rosin-enabled ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene for large-area flexible organic light-emitting diodes
Rosin-enabled ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene for large-area flexible organic light-emitting diodes
Ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene over large areas is crucial for the future development of flexible electronics and optoelectronics. Using a rosin-assisted method, the authors transfer graphene with an ultraclean surface and uniform small sheet resistance—a 4-inch monolithic organic light-emitting diode is demonstrated.
- Zhikun Zhang
- , Jinhong Du
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene
An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene
The functional integration of sound generation and detection on a single device is required to assist mute people. Here, the authors demonstrate a graphene-based artificial throat capable of detecting and converting diverse throat vibrations into meaningful sound within a single device.
- Lu-Qi Tao
- , He Tian
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast radiative heat transfer
Ultrafast radiative heat transfer
Electron relaxation, which is the dominant release channel of electronic heat in nanostructures, occurs with characteristic times of several picoseconds. Here, the authors predict that an ultrafast (femtosecond) radiative cooling regime takes place in plasmonically active neighboring graphene nanodisks prior to electron relaxation.
- Renwen Yu
- , Alejandro Manjavacas
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon-assisted high-harmonic generation in graphene
Plasmon-assisted high-harmonic generation in graphene
High-harmonic generation is a nonlinear optical phenomenon that may be harnessed towards realisation of ultrafast light sources. Here, the authors theoretically show that localized plasmons in graphene nanodisks result in broadband and electrically tunable high-harmonic generation.
- Joel D. Cox
- , Andrea Marini
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Few-layered graphene offers a powerful platform to investigate electronic interactions beyond the non-interacting electron picture approximation. Here, the authors report the signature of strong electronic interactions and quantum Hall ferromagnetism in trilayer graphene with ABA stacking.
- Biswajit Datta
- , Santanu Dey
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
Article
| Open Access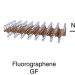 Room temperature organic magnets derived from sp3 functionalized graphene
Room temperature organic magnets derived from sp3 functionalized graphene
Developing room-temperature magnets from materials containing onlysporbitals has remained an elusive but important goal. Here, Zbořil and co-workers report hydroxofluorographenes that exhibit room-temperature antiferromagnetic ordering and low-temperature ferromagnetic behaviour with high magnetic moments.
- Jiří Tuček
- , Kateřina Holá
- & Radek Zbořil
-
Article
| Open Access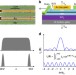 Edge currents shunt the insulating bulk in gapped graphene
Edge currents shunt the insulating bulk in gapped graphene
The absence of a bandgap in the electronic spectrum of graphene can be overcome by breaking its lattice symmetry. The authors show that the insulating state of gapped graphene is electrically shorted by narrow edge channels exhibiting high conductivity.
- M. J. Zhu
- , A. V. Kretinin
- & M. Ben Shalom
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring the thermal and electrical transport properties of graphene films by grain size engineering
Tailoring the thermal and electrical transport properties of graphene films by grain size engineering
Understanding the effect of grain boundaries on the electrical and thermal transport properties of graphene is of both fundamental and technological importance. Here, the authors fabricate graphene films with controlled grain size, and determine the scaling laws of thermal and electrical conductivities.
- Teng Ma
- , Zhibo Liu
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access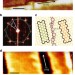 Large positive in-plane magnetoresistance induced by localized states at nanodomain boundaries in graphene
Large positive in-plane magnetoresistance induced by localized states at nanodomain boundaries in graphene
Owing to long spin lifetime and diffusion length, graphene holds promise for spintronics, yet it does not possess intrinsic magnetic properties. Here, the authors observe experimentally a large, positive magnetoresistance at graphene nanodomain boundaries.
- Han-Chun Wu
- , Alexander N. Chaika
- & Ching-Ray Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Graphene, and other 2D materials, do not exist as strictly planar sheets but instead have topographic ripples on the sub-nanometre scale. Here, Latychevskaiaet al. present a method to non-invasively image ripples in 2D materials with a single-shot, wide-area, electron diffraction measurement.
- Tatiana Latychevskaia
- , Wei-Hao Hsu
- & Ing-Shouh Hwang
-
Article
| Open Access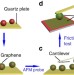 Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Superlubricity can be unstable in graphene systems, especially under high applied loads. Here the authors use microspheres uniformly coated by graphene to measure friction between 2D materials and show that superlow friction is preserved for long periods of time under high loads and various atmospheres.
- Shu-Wei Liu
- , Hua-Ping Wang
- & Jianbin Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Slow-light-enhanced energy efficiency for graphene microheaters on silicon photonic crystal waveguides
Slow-light-enhanced energy efficiency for graphene microheaters on silicon photonic crystal waveguides
Slow light can be used to sustain strong light–matter interaction in silicon photonics. Here, the authors combine graphene with a silicon slow-light photonic crystal waveguide, demonstrating a fast and energy-efficient graphene microheater.
- Siqi Yan
- , Xiaolong Zhu
- & Yunhong Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Using graphene networks to build bioinspired self-monitoring ceramics
Using graphene networks to build bioinspired self-monitoring ceramics
Micro- and nanostructures found in nature can be adopted to new uses and materials in engineered composites. Here authors demonstrate large enhancements in toughness and electrical conductivity in a ceramic upon addition of graphene at low (1 volume %) levels.
- Olivier T. Picot
- , Victoria G. Rocha
- & Eduardo Saiz
-
Article
| Open Access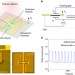 Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
There is emerging interest in photodetectors in the mid-infrared driven by increasing need to monitor the environment for security and healthcare purposes. Sassiet al. show a thermal photodetector, based on the coupling between graphene and a pyroelectric crystal, which shows high temperature sensitivity.
- U. Sassi
- , R. Parret
- & A. Colli
-
Article
| Open Access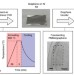 Single-step ambient-air synthesis of graphene from renewable precursors as electrochemical genosensor
Single-step ambient-air synthesis of graphene from renewable precursors as electrochemical genosensor
Graphene films are commonly produced by thermal chemical vapour deposition, which is capable of producing high-quality films but still limited by factors such as high cost. Here, the authors report the growth of single-to-few-layer continuous graphene films under ambient-air conditions.
- Dong Han Seo
- , Shafique Pineda
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov
-
Article
| Open Access p-wave triggered superconductivity in single-layer graphene on an electron-doped oxide superconductor
p-wave triggered superconductivity in single-layer graphene on an electron-doped oxide superconductor
Unconventional superconductivity may be triggered when graphene is deposited on a high temperature superconductor. Here, Di Bernardoet al. observe spectroscopic evidence for p-wave superconductivity in single layer graphene on an electron-doped cuprate superconductor.
- A. Di Bernardo
- , O. Millo
- & J. W. A. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Slow cooling and efficient extraction of C-exciton hot carriers in MoS2 monolayer
Slow cooling and efficient extraction of C-exciton hot carriers in MoS2 monolayer
Light-matter interaction in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides is dominated by excitonic effects and hot-carrier relaxation/extraction mechanisms. Here, the authors report that the C exciton in two-dimensional MoS2exhibits a slower hot-carrier cooling than band-edge excitons.
- Lei Wang
- , Zhuo Wang
- & Hong-Bo Sun
-
Article
| Open Access 3D nitrogen-doped graphene foam with encapsulated germanium/nitrogen-doped graphene yolk-shell nanoarchitecture for high-performance flexible Li-ion battery
3D nitrogen-doped graphene foam with encapsulated germanium/nitrogen-doped graphene yolk-shell nanoarchitecture for high-performance flexible Li-ion battery
The development of materials for energy storage hinges on the design of electrodes with large capacity, flexibility, fast charge–discharge rate and long cycling lifetime. Here, the authors develop electrodes based on nitrogen doped graphene with encapsulated Ge quantum dots with yolk-shell architecture.
- Runwei Mo
- , David Rooney
- & Hui Ying Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Robust fractional quantum Hall effect in the N=2 Landau level in bilayer graphene
Robust fractional quantum Hall effect in the N=2 Landau level in bilayer graphene
Electron-electron interactions in many-body systems may manifest themselves through the fractional quantum Hall effect. Here, the authors perform transport measurements in bilayer graphene, and observe particle-hole symmetric fractional quantum Hall states in theN=2 Landau level.
- Georgi Diankov
- , Chi-Te Liang
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast electronic response of graphene to a strong and localized electric field
Ultrafast electronic response of graphene to a strong and localized electric field
Graphene has so far demonstrated remarkable properties, making it increasingly interesting for ultrafast electronic applications. Here, the authors show that, when probed by a highly charged ion, freestanding graphene is able to provide dozens of electrons for ion neutralization within a few femtoseconds.
- Elisabeth Gruber
- , Richard A. Wilhelm
- & Friedrich Aumayr
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Detection of electric fields, central to chemical and biological processes, has been limited to measurements of current (e.g., electrodes) and secondary reporters (e.g., fluorescent dyes). Here, the authors demonstrate an optical platform capable of imaging electric field dynamics with high spatio-temporal resolution.
- Jason Horng
- , Halleh B. Balch
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Current crowding mediated large contact noise in graphene field-effect transistors
Current crowding mediated large contact noise in graphene field-effect transistors
The performance of graphene field effect transistors is adversely affected by fluctuations in the electrical resistance at the graphene/metal interface. Here, the authors unveil the microscopic origin of such contact noise, highlighting the role of current crowding.
- Paritosh Karnatak
- , T. Phanindra Sai
- & Arindam Ghosh
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional non-woven fabrics of interfused graphene fibres
Multifunctional non-woven fabrics of interfused graphene fibres
Carbon-based fibres are at the core of electrically conductive multifunctional fabrics, yet improving the weak interaction between fibres remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate an assembly method where graphene fibres are fused at junctions with record specific electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Zheng Li
- , Zhen Xu
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanical electro-optical modulator based on atomic heterostructures
Nanomechanical electro-optical modulator based on atomic heterostructures
Van der Waals heterostructures can be combined with metallic nanostructures to enable enhanced light–matter interaction. Here, the authors fabricate a broadband mechanical electro-optical modulator using a graphene/hexagonal boron nitride vertical heterojunction, suspended over a gold nanostripe array.
- P. A. Thomas
- , O. P. Marshall
- & A. N. Grigorenko
-
Article
| Open Access Modulated phases of graphene quantum Hall polariton fluids
Modulated phases of graphene quantum Hall polariton fluids
High-mobility graphene can play host to exciton polaritons—hybrid matter–light particles, which can form into a state known as a quantum Hall polariton fluid. Here, the authors show that electron–electron interactions can act to destabilize this state and lead to the formation of a modulated phase.
- Francesco M. D. Pellegrino
- , Vittorio Giovannetti
- & Marco Polini
-
Article
| Open Access A two-dimensional spin field-effect switch
A two-dimensional spin field-effect switch
By forming heterostructures of different layered two-dimensional materials, functional spintronic devices may be built by exploiting the materials’ different spin-orbit coupling and spin transport properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a spin switch in a gated structure of graphene and MoS2.
- Wenjing Yan
- , Oihana Txoperena
- & Fèlix Casanova
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogenated monolayer graphene with reversible and tunable wide band gap and its field-effect transistor
Hydrogenated monolayer graphene with reversible and tunable wide band gap and its field-effect transistor
The absence of a band gap in graphene hinders its use in electronics. Here, the authors open a band gap as large as 3.9 electronvolts in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition by treating it in hydrogen plasma, and then use this material to create a room temperature field- effect transistor.
- Jangyup Son
- , Soogil Lee
- & Jongill Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Growing three-dimensional biomorphic graphene powders using naturally abundant diatomite templates towards high solution processability
Growing three-dimensional biomorphic graphene powders using naturally abundant diatomite templates towards high solution processability
High-volume, low-cost production of graphene is pivotal for the industrial advance of this 2D material. Here, the authors make use of naturally occurring diatomite as a 3D substrate for graphene growth, obtaining non-planar porous graphene structures after removal of the silica templates.
- Ke Chen
- , Cong Li
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
The wettability properties of graphene hold promise for the realisation of flow control devices. Here, the authors demonstrate that the degree of water penetration through a nickel mesh coated with graphene can be controlled electrically, enabling dynamic locomotion of water droplets.
- Rassoul Tabassian
- , Jung-Hwan Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced commensurate stacking of graphene on boron nitride
Pressure-induced commensurate stacking of graphene on boron nitride
Van der Waals heterostructures enable fabrication of materials with engineered functionalities. Here, the authors demonstrate precise control over the interaction between layers by application of pressure with a scanning tunnelling microscopy tip.
- Matthew Yankowitz
- , K. Watanabe
- & Brian J. LeRoy
-
Article
| Open Access Robust ultra-low-friction state of graphene via moiré superlattice confinement
Robust ultra-low-friction state of graphene via moiré superlattice confinement
Two-dimensional materials show remarkable lubrication properties, yet chemical modifications may hinder such capabilities. Here, the authors show that when graphene is aligned on a Ge(111) substrate, ultra-low friction can be preserved even after graphene fluorination or oxidation.
- Xiaohu Zheng
- , Lei Gao
- & Xi Wang

 Absorptive pinhole collimators for ballistic Dirac fermions in graphene
Absorptive pinhole collimators for ballistic Dirac fermions in graphene