Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cutting the costs of coastal protection by integrating vegetation in flood defences
Cutting the costs of coastal protection by integrating vegetation in flood defences
Nearly one-third of the global coastline is vegetated. Incorporating these vegetation belts in coastal protection strategies would result in more sustainable and financially-attractive designs to mitigate the impacts of extreme coastal storms.
- Vincent T. M. van Zelst
- , Jasper T. Dijkstra
- & Mindert B. de Vries
-
Article
| Open Access Delaying carbon dioxide removal in the European Union puts climate targets at risk
Delaying carbon dioxide removal in the European Union puts climate targets at risk
The implications of delaying carbon dioxide removal (CDR) are poorly understood. Here the authors highlight the potential extra costs and reduced removal potential of delayed CDR action, with a special focus on direct air capture and bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (DACCS and BECCS).
- Ángel Galán-Martín
- , Daniel Vázquez
- & Gonzalo Guillén-Gosálbez
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid oxygen exchange between hematite and water vapor
Rapid oxygen exchange between hematite and water vapor
Knowing how individual water molecules interact with surfaces is crucial for understanding surface and interface phenomena. Here, the authors show how local water-water interactions enable an unforeseen and surprisingly rapid mechanism of atom exchange between a common mineral and its surroundings.
- Zdenek Jakub
- , Matthias Meier
- & Gareth S. Parkinson
-
Article
| Open Access Mitigation potential of global ammonia emissions and related health impacts in the trade network
Mitigation potential of global ammonia emissions and related health impacts in the trade network
Ammonia emissions from agricultural sources can cause severe health impacts. Here, the authors show that about 25% of global agricultural ammonia emissions in 2012 were related to international exported goods and caused 61 thousand PM2.5 related premature deaths, which points out large ammonia mitigation potential in international trade.
- Rong Ma
- , Ke Li
- & Jing Meng
-
Article
| Open Access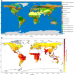 Global distribution, trends, and drivers of flash drought occurrence
Global distribution, trends, and drivers of flash drought occurrence
Flash droughts can have devastating impacts but are notoriously difficult to predict. This study identifies global hotspots of flash drought, driven by evaporative demand and precipitation deficits across varying geographic regions and crop-type, providing a framework for flash drought prediction.
- Jordan I. Christian
- , Jeffrey B. Basara
- & Robb M. Randall
-
Article
| Open Access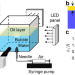 Compound jetting from bubble bursting at an air-oil-water interface
Compound jetting from bubble bursting at an air-oil-water interface
How structurally complex interfaces mediate bubble bursting might significantly impact environmental and industrial processes. Here, authors investigate the bubble-bursting jets dynamics of oil-covered aqueous surface and show how these can also disperse insoluble organic contaminants.
- Bingqiang Ji
- , Zhengyu Yang
- & Jie Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Direct copolymerization of ethylene with protic comonomers enabled by multinuclear Ni catalysts
Direct copolymerization of ethylene with protic comonomers enabled by multinuclear Ni catalysts
The applications of polyolefins are limited by the nonpolar nature of the polymer. Here the authors show a method to copolymerize ethylene with the protic vinyl acetic acid via well defined multinuclear nickel catalysts.
- Gang Ji
- , Zhou Chen
- & Yong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Increased variability in Greenland Ice Sheet runoff from satellite observations
Increased variability in Greenland Ice Sheet runoff from satellite observations
Accurate assessments of ice-sheet runoff are essential for sea-level projections. A new method using satellite altimeter observations can provide near real-time surface mass balance measurements across an entire ice sheet and reveal runoff variability not captured by global climate models.
- Thomas Slater
- , Andrew Shepherd
- & Kate Briggs
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the importance of thermogenic degassing from the Karoo Large Igneous Province (LIP) in driving Toarcian carbon cycle perturbations
Assessing the importance of thermogenic degassing from the Karoo Large Igneous Province (LIP) in driving Toarcian carbon cycle perturbations
The emplacement of the Karoo LIP occurred synchronously with the Toarcian crisis, which is characterized by negative carbon isotope excursions. Here the authors use carbon cycle modelling to show that thermogenic carbon released during LIP emplacement represents a plausible source for the negative excursions.
- Thea H. Heimdal
- , Yves Goddéris
- & Henrik H. Svensen
-
Article
| Open Access Globally consistent assessment of coastal eutrophication
Globally consistent assessment of coastal eutrophication
Satellite-derived chlorophyll data and Google Earth Engine (GEE) are used to introduce the first global map of coastal eutrophication potential as a GEE app. The prospects of the app being used as a global framework for eutrophication screening/monitoring are discussed.
- Elígio de Raús Maúre
- , Genki Terauchi
- & Michael DeWitt
-
Article
| Open Access Global greenhouse gas emissions from residential and commercial building materials and mitigation strategies to 2060
Global greenhouse gas emissions from residential and commercial building materials and mitigation strategies to 2060
Building construction causes large material-related emissions which present a serious decarbonization challenge. Here, the authors show that the building material sector could halve emissions by increasing efficiency until 2060 but even then its emissions would be twice as high as needed to meet the 1.5 °C target.
- Xiaoyang Zhong
- , Mingming Hu
- & Paul Behrens
-
Article
| Open Access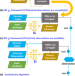 From calibration to parameter learning: Harnessing the scaling effects of big data in geoscientific modeling
From calibration to parameter learning: Harnessing the scaling effects of big data in geoscientific modeling
Much effort is invested in calibrating model parameters for accurate outputs, but established methods can be inefficient and generic. By learning from big dataset, a new differentiable framework for model parameterization outperforms state-of-the-art methods, produce more physically-coherent results, using a fraction of the training data, computational power, and time. The method promotes a deep integration of machine learning with process-based geoscientific models.
- Wen-Ping Tsai
- , Dapeng Feng
- & Chaopeng Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Global syndromes induced by changes in solutes of the world’s large rivers
Global syndromes induced by changes in solutes of the world’s large rivers
Rivers are increasingly plagued by “syndromes”, i.e. salinization, mineralization, desalinization, acidification, alkalization, hardening and softening. A global look at river biogeochemistry reveals dramatically increased flux estimates and anthropogenic drivers of syndromes.
- Jiang Wu
- , Nan Xu
- & Jinren Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Considering socio-political framings when analyzing coastal climate change effects can prevent maldevelopment on small islands
Considering socio-political framings when analyzing coastal climate change effects can prevent maldevelopment on small islands
Climate change adaptation and sea level rise pose challenges for both natural and societal dynamics. Here the authors analyse coastal processes and socio-political dimensions of erosion, leading to maldevelopment on Fuvahmulah in the Maldives.
- C. Gabriel David
- , Arne Hennig
- & Torsten Schlurmann
-
Article
| Open Access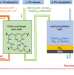 Recycling lead and transparent conductors from perovskite solar modules
Recycling lead and transparent conductors from perovskite solar modules
Perovskite photovoltaics has become more competitive against silicon counterpart in reducing cost of solar energy, yet the management of toxic lead hampers it application. Here, the authors propose a cost-effective environmental-friendly approach to recycle lead and transparent conductors.
- Bo Chen
- , Chengbin Fei
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Antarctic ozone hole modifies iodine geochemistry on the Antarctic Plateau
Antarctic ozone hole modifies iodine geochemistry on the Antarctic Plateau
The Antarctic ozone hole has had far-reaching impacts, but effects on geochemical cycles in polar regions is still unknown. Iodine records from the interior of Antarctica provide evidence for human alteration of the natural geochemical cycle of this essential element.
- Andrea Spolaor
- , François Burgay
- & Alfonso Saiz-Lopez
-
Article
| Open Access Diel cycle of sea spray aerosol concentration
Diel cycle of sea spray aerosol concentration
Sea spray aerosol (SSA) are an important way through which oceans can influence the atmosphere’s radiative properties. Here, the authors present measurements taken over a 42,000 km ship cruise in the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean and show that SSA number concentrations vary over a 24-hour cycle, possibly linked to surface water bubble-bursting dynamics.
- J. Michel Flores
- , Guillaume Bourdin
- & Ilan Koren
-
Article
| Open Access CO2, nitrogen deposition and a discontinuous climate response drive water use efficiency in global forests
CO2, nitrogen deposition and a discontinuous climate response drive water use efficiency in global forests
Water use efficiency is a key measure of plant responses to climate change. Here, the authors investigate its control by CO2, nitrogen deposition, and water availability using a global tree-ring dataset. They find an aridity threshold and quantify changes in control over the past 50 years.
- Mark A. Adams
- , Thomas N. Buckley
- & Tarryn L. Turnbull
-
Article
| Open Access Fire-derived phosphorus fertilization of African tropical forests
Fire-derived phosphorus fertilization of African tropical forests
Nowhere is biomass burning more abundant than on the African continent, but the biogeochemical impacts on forests are poorly understood. Here the authors show that biomass burning leads to high phosphorus deposition in the Congo basin, which scales with forest age as a result of increasing canopy complexity.
- Marijn Bauters
- , Travis W. Drake
- & Pascal Boeckx
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal Arctic sea ice forecasting with probabilistic deep learning
Seasonal Arctic sea ice forecasting with probabilistic deep learning
Accurate seasonal forecasts of sea ice are highly valuable, particularly in the context of sea ice loss due to global warming. A new machine learning tool for sea ice forecasting offers a substantial increase in accuracy over current physics-based dynamical model predictions.
- Tom R. Andersson
- , J. Scott Hosking
- & Emily Shuckburgh
-
Article
| Open Access Global scenarios of resource and emission savings from material efficiency in residential buildings and cars
Global scenarios of resource and emission savings from material efficiency in residential buildings and cars
Material production accounts for a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. Here, the authors show that resource efficiency and circular-economy strategies can allow for cumulative emission reductions of 20–52 Gt CO2-eq from residential buildings and 13–26 Gt CO2e-eq from cars by 2050.
- Stefan Pauliuk
- , Niko Heeren
- & Edgar G. Hertwich
-
Article
| Open Access The underappreciated role of agricultural soil nitrogen oxide emissions in ozone pollution regulation in North China
The underappreciated role of agricultural soil nitrogen oxide emissions in ozone pollution regulation in North China
Summertime ozone air pollution in North China remains severe. Here the authors find large biogenic emissions of nitrogen oxides in North China, mainly driven by fertilizer application, challenge the mitigation of ozone pollution by only reducing combustion induced ozone precursors’ emissions.
- Xiao Lu
- , Xingpei Ye
- & Yuanhang Zhang
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-state reconfiguration induced by alternating magnetic field for efficient oxygen evolution reaction
Spin-state reconfiguration induced by alternating magnetic field for efficient oxygen evolution reaction
The oxygen evolution reaction in magnetic catalysts is related with their spin configuration. Here, the authors propose a magnetic-stimulation method to rearrange spin electron occupation in thermal-differentiated superlattices.
- Gang Zhou
- , Peifang Wang
- & Lizhe Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 via molybdenum-nitrogenase in a low molybdenum Proterozoic ocean analogue
Purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 via molybdenum-nitrogenase in a low molybdenum Proterozoic ocean analogue
N2 fixation was key to the expansion of life on Earth, but which organisms fixed N2 and if Mo-nitrogenase was functional in the low Mo early ocean is unknown. Here, the authors show that purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 using Mo-nitrogenase in a Proterozoic ocean analogue, despite low Mo conditions.
- Miriam Philippi
- , Katharina Kitzinger
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
-
Article
| Open Access Closing the methane gap in US oil and natural gas production emissions inventories
Closing the methane gap in US oil and natural gas production emissions inventories
Methane emissions from oil and gas systems are underestimated in official inventories. Here the authors synthesize thousands of field measurements and develop an inventory-based model for a better understanding of why this underestimation exists and how it can be fixed.
- Jeffrey S. Rutherford
- , Evan D. Sherwin
- & Adam R. Brandt
-
Comment
| Open AccessGreen infrastructure can limit but not solve air pollution injustice
Outdoor air pollution contributes to millions of deaths worldwide yet air pollution has differential exposures across racial/ethnic groups and socioeconomic status. While green infrastructure has the potential to decrease air pollution and provide other benefits to human health, vegetation alone cannot resolve health disparities related to air pollution injustice. We discuss how unequal access to green infrastructure can limit air quality improvements for marginalized communities and provide strategies to move forward.
- Viniece Jennings
- , Colleen E. Reid
- & Christina H. Fuller
-
Article
| Open Access Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions
Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions
This paper quantifies global urban water scarcity in 2016 and 2050 and explores potential solutions. One third to nearly half of the global urban population is projected to face water scarcity problems.
- Chunyang He
- , Zhifeng Liu
- & Brett A. Bryan
-
Article
| Open Access Irrigated areas drive irrigation water withdrawals
Irrigated areas drive irrigation water withdrawals
The global water demands of irrigated agriculture are estimated through country surveys or through hydrological models, but both approaches are taxing. Here, the authors show that they can simply be estimated as a function of irrigated areas.
- Arnald Puy
- , Emanuele Borgonovo
- & Andrea Saltelli
-
Article
| Open Access Organic additive release from plastic to seawater is lower under deep-sea conditions
Organic additive release from plastic to seawater is lower under deep-sea conditions
Plastics are major marine pollutants, and while research suggests that they can release potential harmful additives into seawater, how environmental conditions influence this is unknown. Here the authors determine that byproducts released from microplastics are less under deep-sea conditions versus surface.
- Vincent Fauvelle
- , Marc Garel
- & Richard Sempéré
-
Article
| Open Access Germanium-lead perovskite light-emitting diodes
Germanium-lead perovskite light-emitting diodes
Lead toxicity poses a big hurdle for the commercialization of perovskite optoelectronics, hence reducing the environmental impact holds the answer for its future application. To tackle this challenge, the authors utilize germanium to reduce the lead content, enabling highly luminescent eco-friendly compound for LEDs.
- Dexin Yang
- , Guoling Zhang
- & Dawei Di
-
Article
| Open Access Common irrigation drivers of freshwater salinisation in river basins worldwide
Common irrigation drivers of freshwater salinisation in river basins worldwide
Freshwater salinisation is a growing water quality problem, but impacts and drivers across regional to global scales have been lacking. A new assessment of inter-regional freshwater salinisation demonstrates the importance of irrigation as a driver of salinisation.
- Josefin Thorslund
- , Marc F. P. Bierkens
- & Michelle T. H. van Vliet
-
Article
| Open Access Encapsulate α-MnO2 nanofiber within graphene layer to tune surface electronic structure for efficient ozone decomposition
Encapsulate α-MnO2 nanofiber within graphene layer to tune surface electronic structure for efficient ozone decomposition
Ozone is a major air pollutant, but its elimination is challenging. Here the authors encapsulate defective α-MnO2 nanofiber within ultrathin graphene shells to construct a hierarchical MnO2@graphene catalyst for ozone decomposition that possesses high activity and stability under humid conditions.
- Guoxiang Zhu
- , Wei Zhu
- & Yongfa Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Solar energy and regional coordination as a feasible alternative to large hydropower in Southeast Asia
Solar energy and regional coordination as a feasible alternative to large hydropower in Southeast Asia
Hydropower dams in the Lower Mekong basin have profound impact on the riverine ecosystems. Here the authors use strategic dam planning and power system modelling to show that there are economically and technically feasible alternatives to these dams with solar energy and power trading.
- Kais Siala
- , Afm Kamal Chowdhury
- & Stefano Galelli
-
Article
| Open Access Evanescent waves modulate energy efficiency of photocatalysis within TiO2 coated optical fibers illuminated using LEDs
Evanescent waves modulate energy efficiency of photocatalysis within TiO2 coated optical fibers illuminated using LEDs
Coupling photocatalyst-coated optical fibers (P-OFs) with LEDs shows potential in environmental applications. Here the authors report a strategy to maximize P-OF light usage and simultaneously establish a new platform to quantify photocatalytic performance.
- Yinghao Song
- , Li Ling
- & Chii Shang
-
Article
| Open Access Storage and export of microbial biomass across the western Greenland Ice Sheet
Storage and export of microbial biomass across the western Greenland Ice Sheet
Microbes that colonise ice sheet surfaces are important to the carbon cycle, but their biomass and transport remains unquantified. Here, the authors reveal substantial microbial carbon fluxes across Greenland’s ice surface, in quantities that may sustain subglacial heterotrophs and fuel methanogenesis.
- T. D. L. Irvine-Fynn
- , A. Edwards
- & A. Hubbard
-
Article
| Open Access Co-benefits of protecting mangroves for biodiversity conservation and carbon storage
Co-benefits of protecting mangroves for biodiversity conservation and carbon storage
Conserving mangrove biodiversity has numerous co-benefits, including climate change-mitigation. Here the authors demonstrate that blue carbon storage in mangroves can be best sustained by combining site-specific dominant species with other species with contrasting functional traits.
- Md Mizanur Rahman
- , Martin Zimmer
- & Ming Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Commercial afforestation can deliver effective climate change mitigation under multiple decarbonisation pathways
Commercial afforestation can deliver effective climate change mitigation under multiple decarbonisation pathways
Afforestation is an important greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation strategy but the efficacy of commercial (harvested) forestry is disputed. Here the authors apply dynamic life cycle assessment to show that new commercial conifer forests can achieve up to 269% more GHG mitigation than semi-natural forests, over 100 years.
- Eilidh J. Forster
- , John R. Healey
- & David Styles
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluating the climate impact of aviation emission scenarios towards the Paris agreement including COVID-19 effects
Evaluating the climate impact of aviation emission scenarios towards the Paris agreement including COVID-19 effects
Aviation contributes to climate change and ways to reduce its emissions are widely debated. Here, the authors assess the effects of technology improvements and the use of sustainable aviation fuels and find that even when these are considered aviation is unlikely to meet emissions goals in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Volker Grewe
- , Arvind Gangoli Rao
- & Katrin Dahlmann
-
Review Article
| Open Access City footprints and SDGs provide untapped potential for assessing city sustainability
City footprints and SDGs provide untapped potential for assessing city sustainability
Whether or not a city achieves absolute sustainability is difficult to assess with existing frameworks. Here the authors, in a review, show that a further integration of consumption-based accounting and benchmarking is necessary to aid the monitoring and assessment of Sustainable Development Goals in cities.
- Thomas Wiedmann
- & Cameron Allen
-
Article
| Open Access Emission impacts of China’s solid waste import ban and COVID-19 in the copper supply chain
Emission impacts of China’s solid waste import ban and COVID-19 in the copper supply chain
Advanced copper supply chain modeling shows China’s new waste trade policy may increase pollution, while limiting other low-value imports reverses this trend. Here the authors show that recycling is vulnerable to supply chain shocks, requiring investment during recoveries to promote a circular economy.
- John Ryter
- , Xinkai Fu
- & Elsa A. Olivetti
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic analysis of multiple processes controlling solar-driven H2O2 synthesis using engineered polymeric carbon nitride
Mechanistic analysis of multiple processes controlling solar-driven H2O2 synthesis using engineered polymeric carbon nitride
Solar-driven H2O2 production presents a renewable approach to chemical synthesis. Here, authors perform a mechanistic analysis on the contribution of the sodium cyanaminate moiety to the 2-electron oxygen reduction reaction performance of polymeric carbon nitride frameworks.
- Yubao Zhao
- , Peng Zhang
- & Wonyong Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Source sector and fuel contributions to ambient PM2.5 and attributable mortality across multiple spatial scales
Source sector and fuel contributions to ambient PM2.5 and attributable mortality across multiple spatial scales
Ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is one of the most important environmental health risk factors in many regions. Here, the authors present an assessment of PM2.5 emission sources and the related health impacts across global to sub-national scales and find that over 1 million deaths were avoidable in 2017 by eliminating PM2.5 mass associated with fossil fuel combustion emissions.
- Erin E. McDuffie
- , Randall V. Martin
- & Michael Brauer
-
Article
| Open Access Projected losses of ecosystem services in the US disproportionately affect non-white and lower-income populations
Projected losses of ecosystem services in the US disproportionately affect non-white and lower-income populations
Social inequalities may be reflected in how ecosystem services are distributed among groups of people. Here the authors estimate the distribution of three ecosystem services across demographic and socioeconomic groups in the US between 2020 and 2100, finding that non-white and lower-income groups disproportionately bear the loss of ecosystem service benefits.
- Jesse D. Gourevitch
- , Aura M. Alonso-Rodríguez
- & Taylor H. Ricketts
-
Article
| Open Access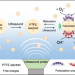 Ultrasonic activation of inert poly(tetrafluoroethylene) enables piezocatalytic generation of reactive oxygen species
Ultrasonic activation of inert poly(tetrafluoroethylene) enables piezocatalytic generation of reactive oxygen species
Controlled generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is essential in biological, chemical, and environmental fields. Here, the authors report that ultrasonication can induce polarization of inert poly(tetrafluoroethylene) to a piezoelectric electret and drive piezocatalytic generation of aqueous ROS.
- Yanfeng Wang
- , Yeming Xu
- & Guandao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access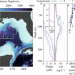 Lateral advection supports nitrogen export in the oligotrophic open-ocean Gulf of Mexico
Lateral advection supports nitrogen export in the oligotrophic open-ocean Gulf of Mexico
The middle of the Gulf of Mexico is stratified and highly oligotrophic, yet there are anomalously high fluxes of sinking particulate matter from the euphotic zone. Here the authors show that lateral advection of organic matter supports nitrogen export in the Gulf of Mexico’s open ocean.
- Thomas B. Kelly
- , Angela N. Knapp
- & Michael R. Stukel
-
Review Article
| Open Access Protein nanofibrils for next generation sustainable water purification
Protein nanofibrils for next generation sustainable water purification
Water scarcity is a rapidly spreading global challenge but water purification technologies are often not sustainable. Here, the authors review the research on water purification technologies based on protein nanofibrils as a green and affordable solution to alleviate a water crisis.
- Mohammad Peydayesh
- & Raffaele Mezzenga
-
Article
| Open Access Open fire exposure increases the risk of pregnancy loss in South Asia
Open fire exposure increases the risk of pregnancy loss in South Asia
Open fires can increase heavy exposure to hazardous particulate matters, and thus harm human health, particularly among the vulnerable individuals, such as pregnant women. Here, the authors show an association between maternal exposure to fire smoke and increased risk of pregnancy loss in South Asia.
- Tao Xue
- , Guannan Geng
- & Tong Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Biodegradation of bio-sourced and synthetic organic electronic materials towards green organic electronics
Biodegradation of bio-sourced and synthetic organic electronic materials towards green organic electronics
Waste build-up from organic electronic components is a major environmental issue; biodegradable electronic materials could be a solution to this. Here, the authors report on the biodegradation of bio-sourced and synthetic electronic materials in industrial compost at different temperatures.
- Eduardo Di Mauro
- , Denis Rho
- & Clara Santato

 Health impacts of wildfire-related air pollution in Brazil: a nationwide study of more than 2 million hospital admissions between 2008 and 2018
Health impacts of wildfire-related air pollution in Brazil: a nationwide study of more than 2 million hospital admissions between 2008 and 2018 On the problems and promises of savanna fire regime change
On the problems and promises of savanna fire regime change