Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Clinical trial links oncolytic immunoactivation to survival in glioblastoma
Clinical trial links oncolytic immunoactivation to survival in glioblastoma
Treatment with the oncolytic herpes virus CAN-3110 is associated with improved survival responses in patients with recurrent glioblastoma, particularly in individuals who are seropositive for HSV1.
- Alexander L. Ling
- , Isaac H. Solomon
- & E. Antonio Chiocca
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Sturgeon is a pretrained neural network that uses incremental results from nanopore sequencing to rapidly classify central nervous system tumours and can be used to aid critical decision-making during surgery.
- C. Vermeulen
- , M. Pagès-Gallego
- & J. de Ridder
-
Article |
 Remote neuronal activity drives glioma progression through SEMA4F
Remote neuronal activity drives glioma progression through SEMA4F
Callosal projection neurons located in the hemisphere contralateral to primary glioblastoma promote progression and widespread infiltration, and screening of axon guidance genes identified SEMA4F as a key regulator of tumourigenesis and activity-dependent progression.
- Emmet Huang-Hobbs
- , Yi-Ting Cheng
- & Benjamin Deneen
-
Article |
 Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation
Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation
Glioblastoma stem cells co-opt lysine uptake and degradation to shunt the production of crotonyl-CoA, remodelling the chromatin landscape to evade interferon-induced intrinsic effects on glioblastoma stem cell maintenance and extrinsic effects on immune response.
- Huairui Yuan
- , Xujia Wu
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Article
| Open Access Glioblastoma remodelling of human neural circuits decreases survival
Glioblastoma remodelling of human neural circuits decreases survival
High-grade gliomas functionally remodel neural circuits in the human brain, promoting tumour progression and impairing cognition.
- Saritha Krishna
- , Abrar Choudhury
- & Shawn L. Hervey-Jumper
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell spatial immune landscapes of primary and metastatic brain tumours
Single-cell spatial immune landscapes of primary and metastatic brain tumours
Imaging mass cytometry of human brain tumours provides spatial information that, combined with existing transcriptomic data, reveals the existence of a cellular neighbourhood containing a rare macrophage population associated with prolonged survival.
- Elham Karimi
- , Miranda W. Yu
- & Logan A. Walsh
-
Article |
 Autonomous rhythmic activity in glioma networks drives brain tumour growth
Autonomous rhythmic activity in glioma networks drives brain tumour growth
A population of highly interconnected cells in glioblastoma makes these tumours resistant to general damage but vulnerable to targeted disruption of this small fraction of cells and their rhythmic Ca2+ oscillations.
- David Hausmann
- , Dirk C. Hoffmann
- & Frank Winkler
-
Article |
 Human fetal cerebellar cell atlas informs medulloblastoma origin and oncogenesis
Human fetal cerebellar cell atlas informs medulloblastoma origin and oncogenesis
Integrated single-cell atlases of human fetal cerebella and MBs show potential cell populations predisposed to transformation and regulatory circuitries underlying tumour cell states and oncogenesis, highlighting hitherto unrecognized transitional progenitor intermediates predictive of disease prognosis.
- Zaili Luo
- , Mingyang Xia
- & Q. Richard Lu
-
Article |
 Unified rhombic lip origins of group 3 and group 4 medulloblastoma
Unified rhombic lip origins of group 3 and group 4 medulloblastoma
Multi-omic mapping shows that group 3 and group 4 medulloblastomas have a common, human-specific developmental origin in the cerebellar rhombic lip, providing a basis for their ambiguous molecular features and overlapping anatomical location, and for the difficulty of modelling these tumours in mice.
- Kyle S. Smith
- , Laure Bihannic
- & Paul A. Northcott
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-restricted mTOR inhibition with binary pharmacology
Brain-restricted mTOR inhibition with binary pharmacology
The combination of the brain-permeable mTOR inhibitor RapaLink-1 and the brain-impermeable FKBP12 ligand RapaBlock enable brain-specific inhibition of mTOR.
- Ziyang Zhang
- , Qiwen Fan
- & Kevan M. Shokat
-
Article |
 Olfactory sensory experience regulates gliomagenesis via neuronal IGF1
Olfactory sensory experience regulates gliomagenesis via neuronal IGF1
A mouse model of gliomagenesis reveals that olfaction can directly regulate the genesis of gliomas, showing that sensory experience and gliomagenesis are linked and providing insight into the neural circuitry involved.
- Pengxiang Chen
- , Wei Wang
- & Chong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access GD2-CAR T cell therapy for H3K27M-mutated diffuse midline gliomas
GD2-CAR T cell therapy for H3K27M-mutated diffuse midline gliomas
A phase I dose-escalation trial of GD2-CAR T cells in children and young adults with diffuse midline gliomas to assess the feasibility of manufacturing, safety and tolerability, and to preliminarily assess efficacy.
- Robbie G. Majzner
- , Sneha Ramakrishna
- & Michelle Monje
-
Article |
 Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Analysis of crystal structures of anaplastic lymphoma kinase elucidate the mechanism by which ligand binding and the glycine-rich domain regulate its activity.
- Tongqing Li
- , Steven E. Stayrook
- & Daryl E. Klein
-
Article |
 A clinically applicable integrative molecular classification of meningiomas
A clinically applicable integrative molecular classification of meningiomas
Multi-omics datasets are integrated to generate a unified and clinically informed molecular classification of meningiomas.
- Farshad Nassiri
- , Jeff Liu
- & Gelareh Zadeh
-
Article |
 NF1 mutation drives neuronal activity-dependent initiation of optic glioma
NF1 mutation drives neuronal activity-dependent initiation of optic glioma
Mouse models of NF1-associated optic pathway glioma show that tumour initiation and growth are driven by aberrantly high levels of NLGN3 shedding in the optic nerve in response to retinal neuron activity.
- Yuan Pan
- , Jared D. Hysinger
- & David H. Gutmann
-
Article
| Open Access A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 in newly diagnosed glioma
A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 in newly diagnosed glioma
A phase 1 clinical trial provides evidence that a vaccine against mutant IDH1 is safe and produces a T helper immune response in patients with glioma.
- Michael Platten
- , Lukas Bunse
- & Wolfgang Wick
-
Article |
 Oncometabolites suppress DNA repair by disrupting local chromatin signalling
Oncometabolites suppress DNA repair by disrupting local chromatin signalling
Metabolites that are elevated in tumours inhibit the lysine demethylase KDM4B, resulting in aberrant hypermethylation of histone 3 lysine 9 and decreased homology-dependent DNA repair.
- Parker L. Sulkowski
- , Sebastian Oeck
- & Peter M. Glazer
-
Article |
 Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas
Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas
Temozolomide therapy seems to lead to mismatch repair deficiency and hypermutation in gliomas, but not to an increase in response to immunotherapy.
- Mehdi Touat
- , Yvonne Y. Li
- & Keith L. Ligon
-
Article |
 PIK3CA variants selectively initiate brain hyperactivity during gliomagenesis
PIK3CA variants selectively initiate brain hyperactivity during gliomagenesis
Glioblastoma tumours expressing oncogenic PIK3CA variants secrete the glycan GPC3, which promotes the formation of neural synapses, brain synaptic hyperexcitability and gliomagenesis.
- Kwanha Yu
- , Chia-Ching John Lin
- & Benjamin Deneen
-
Article |
 The molecular landscape of ETMR at diagnosis and relapse
The molecular landscape of ETMR at diagnosis and relapse
Analyses of primary and relapse samples of embryonal tumours with multilayered rosettes provide insights into the molecular mechanisms that underlie the development and opportunities for the treatment of this deadly disease.
- Sander Lambo
- , Susanne N. Gröbner
- & Marcel Kool
-
Article |
 Longitudinal molecular trajectories of diffuse glioma in adults
Longitudinal molecular trajectories of diffuse glioma in adults
The GLASS Consortium studies the evolutionary trajectories of 222 patients with a diffuse glioma to aid in our understanding of tumour progression and treatment failure
- Floris P. Barthel
- , Kevin C. Johnson
- & Roel G. W. Verhaak
-
Article |
 Recurrent noncoding U1 snRNA mutations drive cryptic splicing in SHH medulloblastoma
Recurrent noncoding U1 snRNA mutations drive cryptic splicing in SHH medulloblastoma
Highly recurrent hotspot r.3A>G mutations are identified in U1 splicesomal small nuclear RNAs in about 50% of Sonic hedgehog medulloblastomas, which result in disrupted RNA splicing and the activation of oncogenes.
- Hiromichi Suzuki
- , Sachin A. Kumar
- & Michael D. Taylor
-
Article |
 Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression
Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression
Neurons form glutamatergic synapses with glioma cells in mice and humans, and inhibition of AMPA receptors reduces glioma cell invasion and growth.
- Varun Venkataramani
- , Dimitar Ivanov Tanev
- & Thomas Kuner
-
Article |
 Resolving medulloblastoma cellular architecture by single-cell genomics
Resolving medulloblastoma cellular architecture by single-cell genomics
Characterization of medulloblastoma tissues using single-cell transcriptomics shows that the different molecular subtypes consist of distinct developmental phenotypes.
- Volker Hovestadt
- , Kyle S. Smith
- & Paul A. Northcott
-
Article |
 Childhood cerebellar tumours mirror conserved fetal transcriptional programs
Childhood cerebellar tumours mirror conserved fetal transcriptional programs
Sequencing data from the developing cerebellum are compared with bulk sequencing data from paediatric tumours, providing insights into their potential origins and suggesting that many cerebellar tumours have their origins early in utero.
- Maria C. Vladoiu
- , Ibrahim El-Hamamy
- & Michael D. Taylor
-
Article |
 Gboxin is an oxidative phosphorylation inhibitor that targets glioblastoma
Gboxin is an oxidative phosphorylation inhibitor that targets glioblastoma
Gboxin and its chemical derivatives inhibit the growth of primary human and mouse glioblastoma cells, but not of mouse embryonic fibroblasts or neonatal astrocytes, by targeting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation complexes.
- Yufeng Shi
- , S. Kyun Lim
- & Luis F. Parada
-
Letter |
 Tracking tumour evolution in glioma through liquid biopsies of cerebrospinal fluid
Tracking tumour evolution in glioma through liquid biopsies of cerebrospinal fluid
Identification and sequencing of circulating tumour DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with glioma.
- Alexandra M. Miller
- , Ronak H. Shah
- & Ingo K. Mellinghoff
-
Letter |
 Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
In a phase I trial, highly individualized peptide vaccines against unmutated tumour antigens and neoepitopes elicited sustained responses in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, respectively, in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma.
- Norbert Hilf
- , Sabrina Kuttruff-Coqui
- & Wolfgang Wick
-
Letter |
 Neoantigen vaccine generates intratumoral T cell responses in phase Ib glioblastoma trial
Neoantigen vaccine generates intratumoral T cell responses in phase Ib glioblastoma trial
Neoantigen-targeting vaccines are a feasible therapy for tumours with a low mutation burden and immunologically ‘cold’ tumour microenvironment, as neoantigen-specific T cells from the peripheral blood migrate into intracranial glioblastoma, thereby altering the immune milieu of the glioblastoma.
- Derin B. Keskin
- , Annabelle J. Anandappa
- & David A. Reardon
-
Article |
 A homing system targets therapeutic T cells to brain cancer
A homing system targets therapeutic T cells to brain cancer
Therapeutic T cells bearing ligands engineered to optimize adhesion and transmigration through the blood–brain barrier can be targeted to brain tumours.
- Heba Samaha
- , Antonella Pignata
- & Nabil Ahmed
-
Letter |
 Human glioblastoma arises from subventricular zone cells with low-level driver mutations
Human glioblastoma arises from subventricular zone cells with low-level driver mutations
Human neural stem cells from the subventricular zone are identified as the cells of origin that contain the driver mutations for glioblastomas.
- Joo Ho Lee
- , Jeong Eun Lee
- & Jeong Ho Lee
-
Article |
 DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours
DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours
An online approach for the DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours across all entities and age groups has been developed to help to improve current diagnostic standards.
- David Capper
- , David T. W. Jones
- & Stefan M. Pfister
-
Letter |
 Therapeutic targeting of ependymoma as informed by oncogenic enhancer profiling
Therapeutic targeting of ependymoma as informed by oncogenic enhancer profiling
Super enhancers regulate oncogenes and other molecular targets in ependymomas, and identification of these genes provides potential therapeutic targets.
- Stephen C. Mack
- , Kristian W. Pajtler
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Letter |
 Targeting neuronal activity-regulated neuroligin-3 dependency in high-grade glioma
Targeting neuronal activity-regulated neuroligin-3 dependency in high-grade glioma
The growth of adult and paediatric brain tumours depends on a microenvironmental signalling pathway involving the activity-regulated secretion of neuroligin-3 (NLGN3) from normal neurons and oligodendrocyte precursor cells, highlighting the potential of NLGN3 as a therapeutic target.
- Humsa S. Venkatesh
- , Lydia T. Tam
- & Michelle Monje
-
Article |
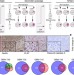 Fate mapping of human glioblastoma reveals an invariant stem cell hierarchy
Fate mapping of human glioblastoma reveals an invariant stem cell hierarchy
Using unique barcodes for tumour cells, the authors explore the dynamics of human glioblastoma subpopulations, and suggest that clonal heterogeneity emerges through stochastic fate decisions of a neutral proliferative hierarchy.
- Xiaoyang Lan
- , David J. Jörg
- & Peter B. Dirks
-
Article
| Open Access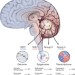 The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes
The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes
Genomic analysis of 491 medulloblastoma samples, including methylation profiling of 1,256 cases, effectively assigns candidate drivers to most tumours across all molecular subgroups.
- Paul A. Northcott
- , Ivo Buchhalter
- & Peter Lichter
-
Letter |
 Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
An in vivo RNA interference screening strategy in glioblastoma enabled the identification of a host of epigenetic targets required for glioblastoma cell survival that were not identified by parallel standard screening in cell culture, including the transcription pause–release factor JMJD6, and could be a powerful tool to uncover new therapeutic targets in cancer.
- Tyler E. Miller
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Letter |
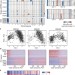 Single-cell RNA-seq supports a developmental hierarchy in human oligodendroglioma
Single-cell RNA-seq supports a developmental hierarchy in human oligodendroglioma
A single sentence summarizing your paper (websum), which will appear online on the table of contents and in e-alerts, has been provided below. Please check this sentence for accuracy and appropriate emphasis.
- Itay Tirosh
- , Andrew S. Venteicher
- & Mario L. Suvà
-
Article |
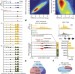 Active medulloblastoma enhancers reveal subgroup-specific cellular origins
Active medulloblastoma enhancers reveal subgroup-specific cellular origins
Genomic studies of the paediatric brain tumour medulloblastoma have revealed four clinically distinct molecular subgroups; here active gene regulatory elements in 28 primary medulloblastoma tissues are mapped to reveal differentially regulated enhancers across the different subgroups, allowing insights into the transcription factors that characterize subgroup divergence and the cellular origin of the poorly characterized Group 3 and 4 subgroups.
- Charles Y. Lin
- , Serap Erkek
- & Paul A. Northcott
-
Article |
 Divergent clonal selection dominates medulloblastoma at recurrence
Divergent clonal selection dominates medulloblastoma at recurrence
To address the question of whether a recurrent tumour is genetically similar to the tumour at diagnosis, the evolution of medulloblastoma has been studied in both an in vivo mouse model of clinical tumour therapy as well as in humans with recurrent disease; targeted tumour therapies are usually based on targets present in the tumour at diagnosis but the results from this study indicate that post-treatment recurring tumours (compared with the tumour at diagnosis) have undergone substantial clonal divergence of the initial dominant tumour clone.
- A. Sorana Morrissy
- , Livia Garzia
- & Michael D. Taylor
-
Article |
 An ID2-dependent mechanism for VHL inactivation in cancer
An ID2-dependent mechanism for VHL inactivation in cancer
HIFα transcription factors are highly expressed in cancer stem cells from glioma; DYRK1 kinases inhibit the protein ID2 to modulate the level of HIF2α and the tumorigenic properties of glioblastoma-associated cancer stem cells.
- Sang Bae Lee
- , Veronique Frattini
- & Anna Lasorella
-
Letter |
 Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas
Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas
An epigenetic mechanism in which gain-of-function IDH mutations promote gliomagenesis by disrupting chromosomal topology is presented, with IDH mutations causing the binding sites of the methylation-sensitive insulator CTCF to become hypermethylated; disruption of a CTCF boundary near the glioma oncogene PDGFRA allows a constitutive enhancer to contact and activate the oncogene aberrantly.
- William A. Flavahan
- , Yotam Drier
- & Bradley E. Bernstein
-
Article |
 Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network
Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network
Brain tumours are difficult to treat because of their propensity to infiltrate brain tissue; here long processes, or tumour microtubes, extended by astrocytomas are shown to promote brain infiltration and to create an interconnected network that enables multicellular communication and that protects the tumours from radiotherapy-induced cell death, suggesting that disruption of the network could be a new therapeutic approach.
- Matthias Osswald
- , Erik Jung
- & Frank Winkler
-
Letter |
 SHMT2 drives glioma cell survival in ischaemia but imposes a dependence on glycine clearance
SHMT2 drives glioma cell survival in ischaemia but imposes a dependence on glycine clearance
Tumours are a low-oxygen environment, in this study glioblastoma cells are found to overexpress the serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT2; SHMT acts to reduce oxygen consumption, which confers the tumour cells with a survival advantage.
- Dohoon Kim
- , Brian P. Fiske
- & David M. Sabatini
-
Letter |
 Tetanus toxoid and CCL3 improve dendritic cell vaccines in mice and glioblastoma patients
Tetanus toxoid and CCL3 improve dendritic cell vaccines in mice and glioblastoma patients
A clinical trial in patients with glioblastoma shows increased immune and anti-tumour responses to dendritic cell vaccination after pre-conditioning the site of vaccination with tetanus toxoid (Td); similar results are also seen in mice in part due to the actions of the chemokine CCL3, and the findings may represent new ways to improve the efficacy of anti-cancer vaccines.
- Duane A. Mitchell
- , Kristen A. Batich
- & John H. Sampson
-
Letter |
 A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity
A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity
The mutant IDH1 protein, which is expressed in a large fraction of human gliomas, is shown to be immunogenic; mutant-specific immune responses can be detected in patients with IDH1 mutated gliomas and generated in mice and are shown to treat established IDH1 mutant tumours in a syngeneic MHC humanized mouse model in a CD4 T-cell-dependent manner.
- Theresa Schumacher
- , Lukas Bunse
- & Michael Platten
-
Letter |
 Novel somatic and germline mutations in intracranial germ cell tumours
Novel somatic and germline mutations in intracranial germ cell tumours
Intracranial germ cell tumours are rare tumours affecting mainly male adolescents, mainly in Asia; here the authors identify frequent mutations in the KIT/RAS and AKT/mTOR signalling pathways as well as rare germline variants in JMJD1C, suggesting potential therapeutic strategies focusing on the inhibition of KIT/RAS activation and the AKT1/mTOR pathway.
- Linghua Wang
- , Shigeru Yamaguchi
- & Ching C. Lau
-
Letter |
 Decoding the regulatory landscape of medulloblastoma using DNA methylation sequencing
Decoding the regulatory landscape of medulloblastoma using DNA methylation sequencing
Medulloblastoma is a malignant childhood brain tumour presenting major clinical challenges; here, a comprehensive genome-wide DNA methylation data set from human and mouse tumours, coupled with analysis of histone modifications, RNA transcripts and genome sequencing, uncovers a wealth of alterations that provide insights into the epigenetic regulation of transcription and genome organization in medulloblastoma pathogenesis.
- Volker Hovestadt
- , David T. W. Jones
- & Peter Lichter
-
Article |
 C11orf95–RELA fusions drive oncogenic NF-κB signalling in ependymoma
C11orf95–RELA fusions drive oncogenic NF-κB signalling in ependymoma
At least two-thirds of supratentorial ependymomas contain oncogenic fusions between RELA, the principal effector of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling, and uncharacterized gene C11orf95; C11orf95–RELA fusion proteins translocate spontaneously to the nucleus to activate NF-κB target genes, and rapidly transform neural stem cells to form tumours in mice
- Matthew Parker
- , Kumarasamypet M. Mohankumar
- & Richard J. Gilbertson

 Glioma synapses recruit mechanisms of adaptive plasticity
Glioma synapses recruit mechanisms of adaptive plasticity